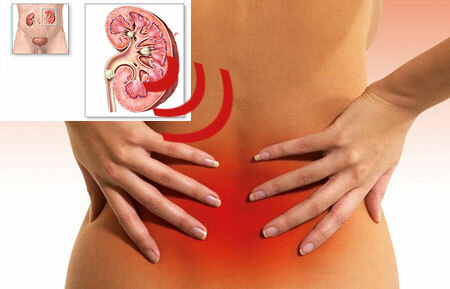
What is it? Urethritis is an inflammation of the urethra, which can be triggered by the multiplication of pathogens. The disease occurs in both women and men, can occur in both acute and chronic forms.
If treatment of the inflammatory process does not start on time, then it will affect the overlying parts of the genitourinary system. Therefore, it is important not to engage in self-medication and not to ignore the symptoms of urethritis, but as soon as possible to consult a doctor.
Before starting treatment, the doctor needs to find out what triggered the onset of the disease. Sometimes the patient's physiological characteristics or her way of life lead to inflammation. If you do not eliminate the primary cause of urethritis in women, then it will appear regularly.
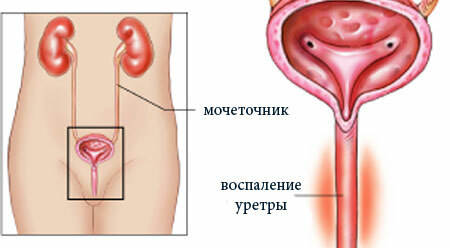
The factors contributing to the development of the disease are:
- Microtrauma, obtained by passing the kidney stones through the urethra. Sexually transmitted diseases( STIs).
- Non-observance of the rules of genital hygiene. As a result, a large number of bacteria that cause inflammation accumulate in the urethra.
- Mechanical damage to the urethra as a result of medical manipulation. Excessive consumption of salt, sour or pickled food.
- Dehydration of the body.
- Inflammatory processes in the vagina or on the labia.
- General immunodeficiency caused by severe disease.
- Subcooling of the pelvic organs.
- Anatomical narrowing of the urethral lumen.
Content
- 1 symptoms of urethritis in women
- 1.1 Types urethritis
- 2 urethral inflammation Treatment
- 2.1 Treatment of acute urethritis
- 2.2 Treatment of chronic urethritis
- 2.3 Complications inflammation of the urethra
- 2.4 disease prevention
symptoms of urethritis in

women symptoms of urethritis in womenare felt at an early stage of the disease. As a rule, they are clearly pronounced and cause great discomfort. Among the signs of the disease can be noted the following:
- Rezi at the beginning of urination, or throughout the period of urination. It is important not to confuse cystitis and urethritis, which women often appear almost simultaneously. However, with cystitis, pain appears only at the end of urination.
- Aching in the lower abdomen. Purulent discharge from the urethra.
- Bloody discharge from the urethra.
- Swelling and redness of the mucous membranes of the urethra.
- Constant itching in the vagina or in the labia.
Inflammation of the urethra has a fairly pronounced symptomatology, so when diagnosing a doctor the general picture of the disease is based on the results of a patient's interview.
However, the diagnosis of urethritis also includes bacteriological examination of the excreta from the urethra for sowing. This procedure will help not only to identify the causative agent of the infection, but also determine its susceptibility to this or that kind of antibiotic.
In addition to bacteriological culture, a woman needs a urine test. If there are no discharges from the urethra, and the urine test does not help to accurately diagnose the disease, the doctor prescribes the PCR analysis.
Types of urethritis
Diagnosis helps to determine not only the causative agent of infection, but also in what form the disease occurs: in acute or chronic.
Acute urethritis is characterized by the rapid development of the disease. Symptoms have a pronounced character and rapidly increase within 12 to 20 hours.
Chronic urethritis of in women has three stages of development. At the first stage, the disease is exacerbated only periodically, but most of the time it is secretive. At the second stage, the number of exacerbations increases, and getting rid of the pain and discomfort becomes more difficult.
In the third stage, the inflammatory processes in the urethra become permanent, without remissions.
Treatment of inflammation of the urethra

Treatment of urethritis involves the use of both medications and physiotherapy. When appointing drugs and procedures, the doctor will build on what form of the disease is found in the patient.
Acute urethritis is much faster and easier to cure than chronic, which is often found in the advanced stage. The chronic form of the disease can not arise by itself.
As a rule, it is a consequence of an untreated acute form of urethral inflammation, when the patient managed to overcome only the symptoms of urethritis, but not the cause.
Treatment of acute urethritis
- Antibiotics: Monural, Amoxiclav, Ciprofloxacin, Azithromycin.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs: Ibuklin, Indomethacin( candles with urethritis).
- Physiotherapy: mud and paraffin applications, washing the urethra with uroseptic solutions, electrophoresis, sessile baths with medicinal herbs( chamomile, sage, yarrow, oak bark).
All these measures are taken together to ensure that the treatment is as effective as possible.
Treatment of chronic urethritis
Physiotherapy is the same as in the acute course of the disease. But, antibiotics for chronic urethritis will have stronger women, for example, Levomycetin or Gentamycin.
They are necessary because weak antibiotics can only eliminate the symptoms of the disease in the chronic form of the disease.
- In case of neglected cases, when the inflammation of the urethra is almost not included in the stage of remission, the doctor can prescribe urethra stamping, which involves cauterizing the mucous membrane affected by the inflammatory process.
Complications of urethral inflammation
The triggered cases of the disease not only cause unpleasant and painful sensations, but can lead to more serious diseases that affect the kidneys, and in some cases, the fallopian tubes( if the infection gets into the vagina and cervix).
Complications of urethritis can result in long and expensive treatment. If the infection affects the appendages, then there will be a threat of adhesion in the fallopian tubes, which is then very difficult to get rid of.
- Therefore, when the first symptoms appear, it is better not to postpone the visit to the doctor.
Prevention of the disease
To avoid inflammation of the genitourinary system, it is necessary to refrain from promiscuous sexual intercourse, to avoid hypothermia, and to conduct hygienic procedures of the perineal region in a timely manner.
Do not forget that the prevention of urethritis includes scheduled visits to the gynecologist and a fence from the vagina for the study of microflora.
Usually urethritis has such a symptomatology that it will not allow to remain inactive, because it will be unbearable to live with pain. However, it is important not to start self-medication and take antibiotics, completely without knowing which pathogen triggered the onset of the disease.
This can only aggravate the situation and promote the transformation of the acute form of urethritis into a chronic one, which is much more difficult to cope with.