Some diseases are caused by a hereditary predisposition, however, to activate the pathological process, some predisposing factors are required. One of these diseases is rheumatoid arthritis.
Contents of
- 1 Rheumatoid arthritis - what is it?
- 2 Causes of the disease
- 3 The first signs of rheumatoid arthritis
- 3 Symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis
- 5 Diagnosis of arthritis
- 6 Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
- 7 Complications of rheumatoid arthritis
- 8 Prevention of rheumatoid arthritis
- 9 Rheumatoid arthritis Mk 10
Rheumatoid arthritis - what is it?
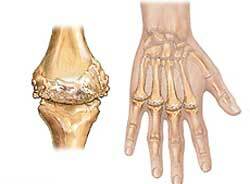 Rheumatoid arthritis is a connective tissue disorder that develops in people with a genetic predisposition after exposure to some provoking factors. The disease is most often found in women older than 40 years and is characterized by the development of irreversible degenerative and inflammatory processes in small joints, as a result of which their normal functioning is disrupted.
Rheumatoid arthritis is a connective tissue disorder that develops in people with a genetic predisposition after exposure to some provoking factors. The disease is most often found in women older than 40 years and is characterized by the development of irreversible degenerative and inflammatory processes in small joints, as a result of which their normal functioning is disrupted.
Rheumatoid arthritis is seropositive( occurs in most cases) and seronegative. In the first case, the rheumatoid factor is present in the patient's blood, the development of the disease is gradual.
When seronegative RA is detected, the rheumatoid factor is absent, the clinical picture of the disease develops rapidly, begins with inflammation of the wrist or knee joints.
In the ICD 10, rheumatoid arthritis is M05( seropositive), M06( seronegative), and M08( juvenile) - a detailed code table at the end of the article.
Often, rheumatoid arthritis is confused with arthrosis or ordinary arthritis. These are completely different diseases, although in both cases joint damage is observed, than rheumatoid arthritis differs from arthritis can be seen in the table:
| Rheumatoid arthritis and arthritis: differences | ||
| Comparison | Rheumatoid arthritis | Arthritis |
| How the pathological process of the | proceeds The pathological process develops as a result of exposure to the body of any factors against which the immune system begins to produce antibodies that destroy the joint tissue | Degenerative processes in the jointoccur as a result of a prolonged disruption of its blood supply |
| Age in which the disease most often occurs | Occurs at any age | In most cases, it occurs in the elderly, especially those who have undergone intensive joint stress. |
| Are pathologies related to each other? | May develop against arthritis as a complication of | Develops on its own |
| Causes of | Autoimmune diseases; Allergic reactions; Postponed infectious diseases. | Injured; Genetic predisposition; Increased load on the joint; Subcooling of extremities against which the inflammatory process develops; Disturbance of blood circulation in the joints. |
| Symptoms | Pain syndrome, aggravated with joint loads; Local hyperthermia, swelling above the joint. | Pain in the joint with loads that subsides at rest and increases with changing weather conditions. When you move the joint, you hear a crunch and click. |
| Laboratory Diagnostic Parameters | Rheumatological tests detect the presence of inflammation in the joints of | No deviations from the norm |
| Treatment of | Anti-inflammatory drugs do not cure the disease completely, but somewhat reduce the clinical manifestations of | . Anti-inflammatory drugs relieve pain syndrome. With unbiased cartilage integrity, chondroprotectors are prescribed in the joint. |
Causes of the disease
 Numerous factors can be the cause of the development of the disease of rheumatoid arthritis, the most common of them are:
Numerous factors can be the cause of the development of the disease of rheumatoid arthritis, the most common of them are:
- Heredity - in the patients whose genomes were cases of this disease, genes are present in the body, on them the immune system starts producing antibodies;
- Infectious diseases - rubella, herpes simplex, Epstein-Barr virus, hepatitis and others. These diseases most often provoke the further development of rheumatoid arthritis.
The first signs of rheumatoid arthritis
Most often rheumatoid arthritis develops during the cold season, the provoking factor may be hypothermia, transferred viral or infectious diseases, surgery, food allergy.
At the initial stage of development, the disease may not manifest itself in a pronounced clinic, patients with rheumatoid arthritis are troubled by common symptoms:
- Increased sweating;
- Weakness in the muscles, even at rest;
- Minor body temperature jumps not caused by viral infection;
- Rapid fatigue;
- Weight Loss.
As the pathological process progresses, pain in the joint area is added, which is aching, periodic, permanent.
After the slightest physical exertion or against the background of treatment with anti-inflammatory drugs, pain syndrome increases, symmetrical lesion of small joints appears.
Inflammatory process with rheumatoid arthritis of joints is accompanied by fever, patient fatigue, general weakness, muscle pain.
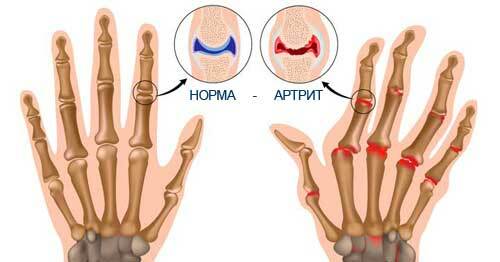
A characteristic sign of rheumatoid arthritis of the hands is the appearance of stiffness in the morning, mainly after sleep. The patient can not perform the usual actions with his fingers, they do not seem to obey.
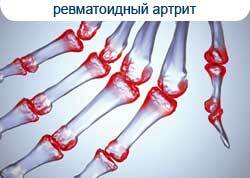 Attempts to move with your fingers are accompanied by increased pain, after about 40 minutes it passes. Morning stiffness is due to the fact that during the night in the area affected by the degenerative and inflammatory process joints accumulate pathological fluid, which prevents full-fledged movements.
Attempts to move with your fingers are accompanied by increased pain, after about 40 minutes it passes. Morning stiffness is due to the fact that during the night in the area affected by the degenerative and inflammatory process joints accumulate pathological fluid, which prevents full-fledged movements.
As the pathological process progresses, the patient experiences visible deformities of the limbs - "walrus fins", fingers in the form of a spindle and the neck of a swan. The first signs of rheumatoid arthritis include other joint lesions:
- Violation and a sharp restriction of mobility of the ulnar and radiolucent joints;
- Shoulder joint damage - increase of local body temperature, skin hyperemia over the inflamed joint, pain syndrome, limitation of mobility, gradual muscle atrophy;
- Defeat of the joints of the foot, namely, deformation of the fingers, severe pain during exercise( walking, running), inability to pick up shoes, disrupt gait and stability;
- Inflammation and gradual deformation of the ankle;
- Knee joint damage, limited mobility;
- Deformation of the joints of the spinal column( usually in the last stages of the disease);
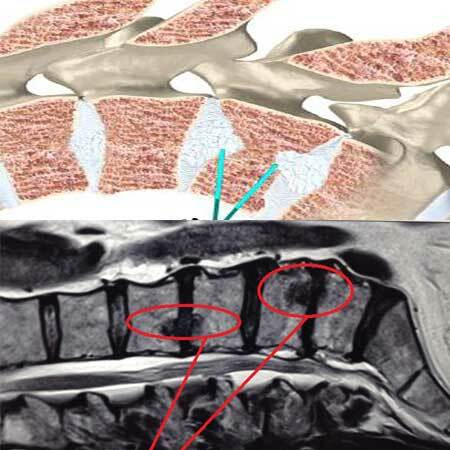
- The defeat of the joint of the first cervical vertebra of the atlas, as a result of which the mobility of the neck is severely disrupted, there are severe pains in the back of the head, a crunch when trying to turn the head sideways.
In addition to articular lesions, signs of rheumatoid arthritis are other manifestations:
- Appearance under the skin, the so-called rheumatoid nodules;Excessive dryness and flaky skin;
- Hemorrhages under small skin( ecchymosis and petechiae);
- Increased brittleness of nails;
- Lethalization of the tissues of the okolonogte bed;
- Dysfunction of the muscles that are attached to the joints affected by the inflammatory and degenerative process, a decrease in their tone, gradual atrophy;
- Minor impairments in the functioning of the digestive tract - bloating, flatulence, deterioration of appetite;
- Development of diseases of the respiratory system - dry pleurisy, lung tissue damage;
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system - endocarditis, pericarditis, myocarditis;
- Severe lesions of the glomerulus of the kidneys, development of glomerulonephritis.
Symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis

The first symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis of the fingers, photos
In most cases, rheumatoid arthritis develops gradually, the first symptoms of the disease are:
- Signs of general intoxication of the body( fever, weakness, lethargy, pale skin, drowsiness,increased body temperature);
- Symptoms of joint damage;
- Symptoms of extraarticular lesions.
After a while, signs of joint damage are added to the common signs of body intoxication:
- Swelling and redness of the skin over the joint lesion;
- Pain during movement, increased load, temperature changes;
- Reduced mobility in the joint;
- Morning stiffness;
- Sharp restriction of movements and gradual deformation of the joint.
The first symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis of the fingers are similar to common features, but may be more pronounced:
- pain when driving;
- redness of the skin over the joints of the fingers and swelling;
- temperature increase;
- limited ability to move;
- morning stiffness of fingers;
- possible lymphadenopathy and the appearance of rheumatoid nodules
It is important not to ignore the first symptoms of finger arthritis, and immediately go to a rheumatologist for diagnosis and prescribing. Launched cases of the disease are much more difficult to treat and restore all the functions of the joint.
Extra-articular lesions of the body develop against the backdrop of rapid progression of rheumatoid arthritis, as a result of which blood circulation and nutrition of tissues adjacent to the affected joint are disrupted.
Diagnosis of arthritis
 If the above described clinical manifestations of rheumatoid arthritis appear, the patient should contact the district therapist as soon as possible, who will appoint a detailed examination to confirm the diagnosis.
If the above described clinical manifestations of rheumatoid arthritis appear, the patient should contact the district therapist as soon as possible, who will appoint a detailed examination to confirm the diagnosis.
Diagnostics of RA includes:
- Collection of anamnesis of a patient's life - hereditary predisposition, suffered joint trauma, surgery, recent infectious and viral infections;
- Biochemical blood test - special attention is paid to ESR, the level of C-reactive protein, creatinine;
- General blood test - examine the level of hemoglobin;
- Urine analysis - characterized by protein content, increased urea levels;
- X-ray examination - the areas of deformation and inflammatory process in the joints are clearly visible in the picture;
- Detection of rheumatoid factor;
- Intraarticular fluid examination.
Timely diagnosis and treatment of rheumatoid arthritis can prevent numerous complications and significantly improve the patient's quality of life.
Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
As there are no exact reasons for the development of rheumatoid arthritis, treatment of the disease is reduced to symptomatic therapy and prevention of further progression of joint deformities.
Preparations for rheumatoid arthritis are selected by the attending physician, depending on the clinical picture of the disease:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - Nimesil, Nurofen, Ibuprofen, Meloxicam and others - allow to quickly eliminate pain, relieve swelling, reduce signs of inflammation and restore joint mobility;
- Glucocorticosteroids - prescribed in the form of ointments or injections inside the affected joint - can quickly remove pain, swelling, inflammation, acute process, restore mobility;
- Calcium preparations and vitamin D - strengthen the bone, prevent the destruction of tissues;
- Chondroprotectors - drugs that contribute to the restoration of cartilage tissue of the affected and deformed joint;
Vitamin Complexes.
Outside the period of exacerbations of the disease, the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis consists of exercise therapy, physiotherapy procedures, surgical intervention to correct joint deformities and restore its mobility.
Complications of rheumatoid arthritis
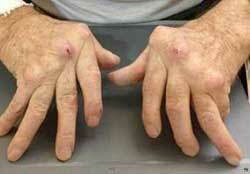 In the absence of timely diagnosis and treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, the patient gradually develops complications:
In the absence of timely diagnosis and treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, the patient gradually develops complications:
- Severe depression results from a significant deterioration in the quality of life, inability to self-service and visible degenerative changes in the limbs;
- Heart Disease;
- Diseases of the respiratory system;
- Weak muscles, decreased tone, gradual atrophy;
- Decreased general immunity, a tendency to develop infections;
- Violation of the external condition and functioning of the skin and nails - deformation of the nail bed, hemorrhages under the skin, scratching.
Prevention of rheumatoid arthritis
Patients at risk for the prevention of rheumatoid arthritis should follow simple medical advice:
- Daily gymnastic exercises;
- Timely treatment of viral and infectious diseases;
- To lead a healthy lifestyle - tempered, properly balanced to eat;
- Do not overcool;
- Drugs should be taken only as directed by a physician.
Rheumatoid arthritis μB 10
In the ICD 10 rheumatoid arthritis is under the headings: M05 - seropositive, M06 - seronegative and M08 - juvenile.
Rubric M05 - seropositive rheumatoid arthritis
- M05.0 - Felty syndrome( with splenomegaly and leukopenia);
- M05.1 - Rheumatoid lung disease;
- M05.2 - Rheumatoid vasculitis;
- M05.3 - RA with damage to other organs or systems;
- M05.8 - other rheumatoid arthritis seropositive;
- M05.9 - unspecified seropositive RA.
Rubric M06 - rheumatoid arthritis seronegative
- M06.1 - Still's disease in adults;
- M06.2 - rheumatoid bursitis;
- M06.3 - rheumatoid nodule;
- M06.4 - polyarthropathy;
- M06.8 - other specified rheumatoid arthritis;
- M06.9 - unspecified rheumatoid arthritis.
Rubric M08 - juvenile arthritis
- M08.1 - adolescent ankylosing spondylitis;
- M08.2 - juvenile arthritis with systemic onset;
- M08.3 - seronegative youthful polyarthritis.