Staphylococcus aureus (Staphylococcus aureus) is a spherical, fixed and aerobic (capable exist in the air) bacteria, Gram stained positively, which causes a variety of diseases in children and less often in adults.
The name of the "golden" Staphylococcus aureus obtained from the glow, which produces plated on nutrient medium. In Greek slaphyle - «bunch» and coccus - «spherical», Staphylococcus under a microscope resembles a bunch of grapes. Staphylococcus aureus is widely distributed in the environment, it is possible to sow with household items, from toys to medical instruments, from breast milk, and skin and mucous membranes of the patient and healthy person.
How dangerous Staphylococcus aureus
Normally, aureus lives on the skin and mucous virtually all people. But healthy people with good immune systems do not suffer from a staph infection as normal microflora inhibits staph growth and does not show its pathogenic nature. But with the weakening of the body's defenses microbe "raises its head" and causes a variety of diseases, even blood infection or sepsis.
Highly pathogenic Staphylococcus aureus is associated with three factors.
- Firstly, the microbe is highly resistant to antiseptics and environmental factors (withstands boiling for 10 minutes, drying, freezing, ethyl alcohol, hydrogen peroxide, with the exception of "Green stuff").
- Secondly, Staphylococcus aureus penicillinase produces enzymes and ligase, making it protected from almost all antibiotics penicillin and helps melt the skin, including sweat glands, and penetrate deep into the body.
- And thirdly, the microbe produces endotoxin, which leads both to food poisoning and syndrome of intoxication of an organism, until the development of infectious and toxic shock.
And, of course, it should be noted that immunity to Staphylococcus aureus absent, and people who recover from a staph infection, can become infected with it again.
Special danger Staphylococcus aureus is for infants who are in the hospital. That hospital is a high concentration of microbes in the environment, so that no small importance attaches to violation of the rules of asepsis and sterilization of instruments and carriers of staphylococcus among honey. personnel.
Causes
There is no doubt that the cause of staph infection is usually Staphylococcus aureus. Infection occurs when a decrease in immunity, which contributes to a number of factors:
- antibiotics and hormonal preparations;
- stress;
- improper diet;
- hypo- and beriberi;
- infection;
- intestinal dysbiosis;
- failure to comply with rules of personal hygiene;
- prematurity;
- immaturity of the baby at birth;
- artificial feeding;
- later breastfeeding.
Forms of Staph Infection
Distinguish generalized and local forms of staph infection.
By the generalized forms include sepsis (Pyosepticemia and septikotsemiya).
For local forms include diseases of the skin, mucous membranes, internal organs, bones, joints, breast and umbilical cord. Also, a separate column is to provide food poisoning Staphylococcus endotoxin.
Furthermore, staphylococcal infection may be primary and secondary (if the primary focus). Recovered downstream acute and chronic forms of prolonged and severity staphylococcal infection mild, moderate and severe.
Symptoms according to the affected organ
Symptoms of staph infection depend on where the localization of staph in the body of the child and the degree of reduction of the body's defenses. The key elements of a staph infection include
- increased body temperature
- pronounced intoxication syndrome (lethargy, weakness, anorexia, nausea).
omphalitis
Defeat microbe umbilical wound, which is accompanied by swelling of the umbilical ring, purulent discharge from the wound. With involvement of the umbilical vein and probed densified thickened Vienna. Also, there is congestion, which extends up to the side of the sternum.
The defeat of the skin
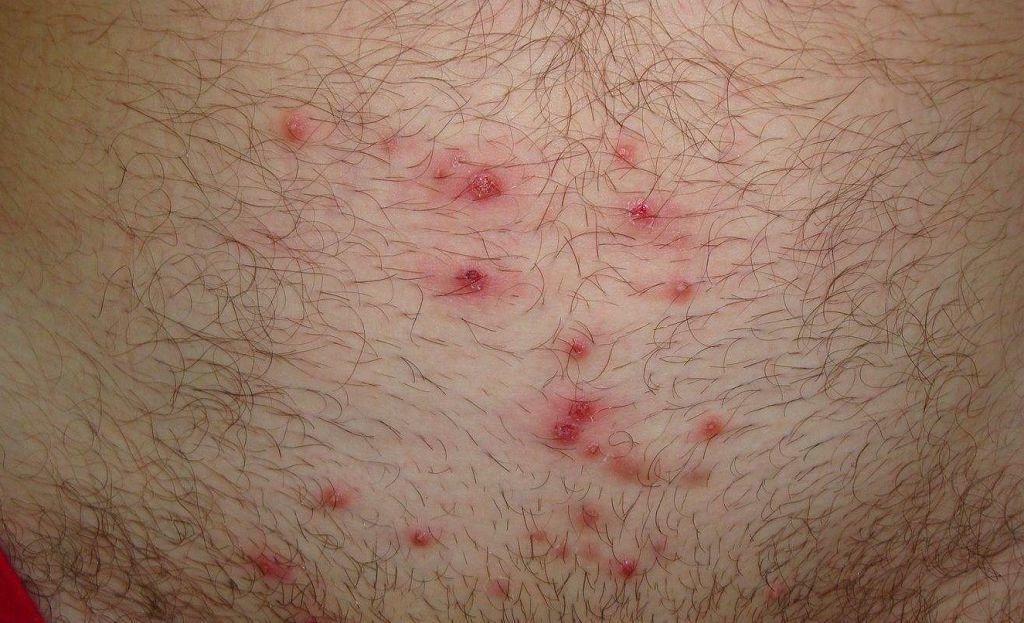
- When psevdofurunkuleze (loss of sweat and sebaceous glands is not) appear dense, red nodules in the skin folds (the accumulation of sweat glands), which are then suppurate.
- Vezikulopustulez characterized by the formation of bubbles with the liquid contents, which spontaneously opened and in their place is formed crust.
- Exfoliative dermatitis (Ritter disease), or "scalded skin syndrome" characterized by the formation of large bubbles in appearance resembling burns, skin exfoliated and then formed unprotected wounds.
- Abscess - loss of deep layers of the skin with redness and visible seal. Shaped cavity containing pus.
- Felon - defeat at phalanx.
- Cellulitis - in addition to the process of the skin is involved subcutaneous tissue, which abscesses.
eye disease
If it affects the mucous membrane of the eye develops conjunctivitis (Photophobia, lacrimation, eyelid edema, purulent discharge from the eyes).
The defeat of the respiratory tract
Rhinitis - redness of the mucosa with copious purulent discharge from the nose. With the penetration of infection develops below anginaCharacterized by sore throat, pharyngitis, Tracheitis dry and painful cough.
Infection of the bronchi and the lungs leads to bronchitis and pneumonia. As a rule, bronchitis and pneumonia occur combines with pharyngitis, rhinitis, tracheitis.
It showed a significant increase in temperature (up to 39-40 ° C), dry cough, shortness of breath.
Perhaps the development of airway stenosis.
Central lesion
The penetration of Staphylococcus aureus in the brain leads to the development meningitis and brain abscess. Disease in children is more severe, with fever and symptoms of intoxication.
Characterized by "brain" vomiting, headaches, positive meningeal symptoms episyndrome and skin rash. When spinal tap fluid flows under pressure, it has a greenish tint doped with pus.
urinary tract defeat
develop urethritis, cystitis, pyelonephritis. Characteristic symptoms: frequent and painful urination, pain in the lumbar region, fever. protein defined in the analysis of urine, a large number of leukocytes, Sown Staphylococcus aureus.
The defeat of the bones and joints
When infected bones and joints develop arthritis, osteomyelitis.
food poisoning
Developed with the use of contaminated or spoiled food, and proceeds from an acute enterocolitis phenomena. Characterized by fever, nausea, vomiting, up to 10 or more times per day, loose stools with a dash of green.
Sepsis
Blood poisoning, or sepsis, occurs in patients with severe immunodeficiency. During severe illness, with a very high fever, severe symptoms of intoxication, disturbance of consciousness (from excitation to flaccidity).
falls sharply blood pressure, the patient loses consciousness and may fall into a coma during the development of infectious-toxic shock.
Pyosepticemia - Staphylococcus aureus circulating in the blood to the formation of purulent foci, as baby's skin and in internal organs.
When septicemia characterized by the development of infectious toxicosis. Septicemia may complicate accession of pneumonia development DIC etc.
Diagnostics
Differential diagnosis of staphylococcal infection should be carried out with streptococcal infection. In the diagnosis of staphylococcal etiology use the following serological methods different speed and high precision:
- Standard in vitro coagulase test, which lasts 4 hours, but when a negative result is extended to day.
- Latex agglutination, at which commercial kits are used latex particles bound with antibodies to Staphylococcus (A-protein, clumping factor and number of surface antigens), which makes it useful also for the identification of strains and species exciter
Also use:
- General blood and urine tests (blood is determined by leukocytosis, neutrophilia, increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate, but protein in the urine, Leukocytes, staphylococci).
- Sowing of biological material on nutrient media.
Seeding is carried out on nutrient medium to identify the causative agent of the disease and to determine its sensitivity and resistance to antibiotics.
Sowing feces must be made not later than 3 hours after defecation, with strokes of the mouth and throat should be taken on an empty stomach, to the dentifrice and to the medication.
Smear with staphylococcal conjunctivitis lower eyelid is taken with a sterile swab dipped in distilled water and to washing.
Skin diseases swabs taken after pre-treatment of the skin around the wound antiseptic solution and removing necrotic (scabs) from the wound.
- Agglutination Vidal
It allows you to determine the dynamics of the disease and the effectiveness of treatment. It carried out 2 or more times at intervals of 7-10 days. Increase in blood antibody titer higher than 1: 100 shows the progression of the infection.
- Phage typing of staphylococci isolated
Allows to determine the sensitivity of microorganism to phages, viruses for appropriate treatment.
Treatment
In milder forms of staph infection antibiotics are not required.
At moderate and severe forms are appointed semisynthetic penicillins (amoxiclav), which are effective in microorganism resistance to penicillins and cephalosporins (kefzol, ceftriaxone).
Treatment time depends on the severity of disease and infection of the skin or internal organs (from 7 days to several months).
In chronic inflammatory skin diseases (furunculosis, carbuncle, impetigo) assigned local treatment - mupirocin or pleuromutilin derivatives. In their absence, it can be made wound treatment antiseptic solutions: brilliant green, hydrogen peroxide, potassium permanganate and antibacterial ointments (sintomitsinovaja, oleandomitsinovaya ointment Bactroban).
at conjunctivitis daily eyes washed with a weak solution of potassium permanganate, and buried Albucidum 30% solution 4-5 times a day.
Purulent skin lesions (abscesses, Cellulitis) produced surgical opening of abscesses to drain pus.
Also shown assignment antistaphylococcal bacteriophage antistaphylococcal plasma and immunoglobulin (in sepsis and severe disease).
When staphylococcal food poisoning antibiotics are not assigned, used antistaphylococcal toxoid. Conduct gastric lavage and replenishing of the circulating blood volume intravenous infusions of saline solutions (nat. solution, glucose solution, and other rehydron).
For prevention of intestinal dysbiosis recommended the use of antifungal agents (Diflucan, nystatin) in parallel with antibiotics.
At the same time appointed immunotherapy (vitamins B, C, levamisole, Taktivin and others).
Treatment of staphylococcal infections in children engaged in children's infectious disease physician.
Methods of treatment are selected according to the defeat of various organs. The child is hospitalized in a private room-box, where a daily change of bed clothes and daily sick souls.
Complications and prognosis
Especially dangerous Staphylococcus aureus for infants. Possible complications:
- sepsis;
- toxic shock;
- coma;
- fatal outcome.
Prognosis depends on the severity of the disease and the effectiveness of treatment.
When lung lesions of the skin and mucous membranes forecast favorable. Massive infection by Staphylococcus aureus, particularly in the development of sepsis in 50% lethal ends.