1 Forms of the disease and causes of
Ascites of the abdominal cavity are classified according to various criteria:
- By the amount of fluid: small, moderate or significant.
- By the presence of microorganisms in the liquid: sterile or infected.
- By responsiveness to drug therapy: amenable to conservative treatment or resistant to it( refractory).If there is a repeated accumulation of fluid, this is a sign that ascites has acquired a stable form requiring more radical treatments.
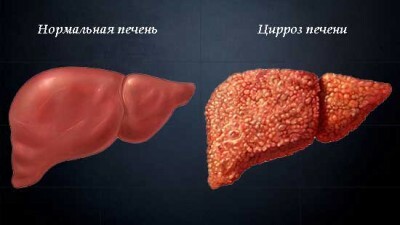
Most often( in 80% of cases) ascites occurs against a cirrhosis of the liver, which has reached the final stage of decompensation. This stage is characterized by depletion of liver resources, serious violations of the hepatic and abdominal circulation, that is, the appearance of favorable conditions for the accumulation of fluid.
Recommended to read
- Symptoms of peritonitis
- How to take Espumizane before the ultrasound of the abdominal cavity
- What to do if the total protein in the blood is lowered
- Effective agent for gastritis and gastric ulcer
About 10% of the causes of ascites are oncological diseases of the peritoneum with metastases in the stomach, ovarian cancer in women. This terrible disease leads to difficulty in lymph circulation and blockage of lymphatic drainage pathways, as a result of which free fluid in the abdominal cavity, without having an outlet, begins to accumulate. Ascites, caused by oncology, are quite aggressive. Usually its occurrence directly indicates the approach of the patient's death.
About 5% of the causes of ascites are cardiac diseases, accompanied by decompensation of blood circulation and general stagnation of blood in the body."Cardiac" ascites often occurs against the background of puffiness of the legs, and in especially severe cases the body swells almost completely, up to the armpits, the fluid accumulates not only in the abdominal but also in the pleural cavity, that is, in the lungs.
-
 IMPORTANT TO KNOW! Gastritis? Ulcer? To have a stomach ulcer not turned into cancer, drink a glass. ..Read the article & gt; & gt;
IMPORTANT TO KNOW! Gastritis? Ulcer? To have a stomach ulcer not turned into cancer, drink a glass. ..Read the article & gt; & gt;
In rare cases, ascites develops against a background of kidney disease, pancreas, alcoholic hepatitis, tuberculosis of the peritoneum and stomach problems, for example, with its acute enlargement.
The fastest liquid in the abdomen is formed with cancer, the slowest - with heart disease.
2 Symptoms of the pathology
Symptoms of ascites appear suddenly or accumulate gradually, for several months, until their totality causes the patient to undergo examination:
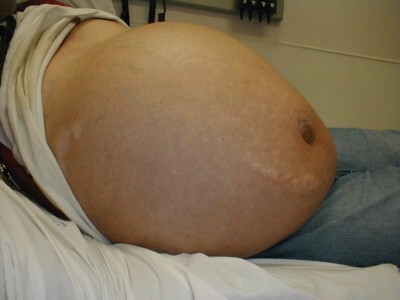
- The main symptom is an increase in the abdomen volume. In the standing position the abdomen noticeably slackens, in the prone position it looks flattened, with the edges protruding along the sides. The navel is greatly expanded, with a very strong protrusion it can even develop an umbilical hernia.
- Ascites, due to portal hypertension, are easily recognized by the characteristic pattern of venous vessels located on the skin of the abdomen near the navel: they scatter in the form of rays. This figure is called "jellyfish head" by physicians.
- Patients are seriously breathing, they have a noticeable shortness of breath. The reason for this is that the accumulated fluid in the abdominal cavity "lifts" the diaphragm from below, reducing the volume of the chest cavity and compressing the lungs, preventing them from completely breaking down when inhaling.
- Difficult movements, inability to bend.
-
 Gastroenterologist VAZHENOV: "I beg you, if you began to worry about abdominal pain, heartburn, nausea, do not in any way do gases. .."Read more & gt; & gt;
Gastroenterologist VAZHENOV: "I beg you, if you began to worry about abdominal pain, heartburn, nausea, do not in any way do gases. .."Read more & gt; & gt;
The disease that led to the development of ascites can also be reflected in the general symptoms of fever, intoxication, weight loss with an enlarged abdomen, cyanotic extremities, widening of the subcutaneous veins on the abdomen, and so on.
A frequent consequence of ascites is an increase in intra-abdominal pressure, which in turn contributes to the onset of umbilical hernia, hemorrhoids, varicocele, or prolapse of the rectum.
3 Is it possible to recognize the disease at an early stage?
In the initial stages of ascites, the signs of the disease are usually not pronounced. The person is not bothered by pain, he only occasionally can complain of a feeling of overflow after eating in the stomach, heaviness and discomfort in the abdomen. But these symptoms are typical for very many diseases.

A more or less accurate sign indicating the accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity is thirst, but it should completely eliminate diabetes, because thirst is one of its most characteristic symptoms.
TIP FROM THE MAIN GASTROENTEROLOGIST
Korotov SV: "I can recommend only one remedy for the rapid treatment of Ulcer and Gastritis, which is now recommended by the Ministry of Health. .." Read the reviews & gt; & gt;
The abdomen does not increase immediately, but when at least 1 liter of fluid is already in the abdominal cavity. An experienced doctor may notice that in the prone position the stomach of the patient acquires a vague shape, and when pushing from one side the movement responds in another, a small wave passes through the belly. However, it is almost impossible to understand this independently.
If there is a suspicion of ascites, the exact answer about the presence or absence of fluid in the stomach in the early stages will be given only by ultrasound.
4 Composition of intraperitoneal fluid
The composition of the intra-abdominal fluid is quite complex and depends on many factors, in particular, from the underlying disease that triggered the development of ascites. Even patients with the same disease have a different composition of fluid. For example, with ascites of the abdominal cavity, which has developed as a result of cirrhosis of the liver, the liquid in the first stages is saturated with protein and is of some value to the body. Therefore, it is inadvisable to withdraw it, sometimes it is better to "return" to the body after "treatment".
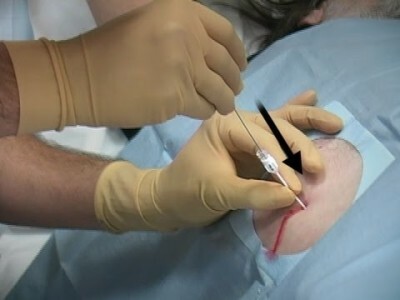
For this reason, in the initial diagnosis of ascites, fluid from the abdominal cavity must be taken for research. The analysis will determine its composition, as well as the presence and extent of infection, which is a great danger and is often observed in patients with advanced cirrhosis of the liver. Infected fluid is a sign of developing ascites-peritonitis, which, if not immediately taken due measures, inevitably leads to a fatal outcome.
Where does the infection in the abdominal cavity come from? Of course, it does not penetrate from the outside, its source is the human body itself. When the intestine is in the liquid for a long time, its walls loosen, and their permeability increases. The pathogens contained in the feces can enter the liquid and begin to multiply in it. Symptoms of infection are increased temperature and pain. The work of the kidneys is broken, after which there is a coma and death of a man in just a few days. Therefore, the state of infection of intra-abdominal fluid is very dangerous, but fortunately, from the time of infection, it can sometimes take several weeks, which is enough to provide the patient with the necessary care.
Analysis of fluid, in addition to determining its composition and infection, helps to make an accurate diagnosis, that is, to identify the cause of ascites. The fact is that preliminary examination methods, for example, ultrasound, are not 100% reliable.
5 Conservative, symptomatic and surgical treatment of
Because ascites is only a consequence of the underlying disease, to eliminate it, it is necessary to eliminate the causes of the pathology that has arisen. For treatment, one of three methods is chosen: conservative, symptomatic or surgical.
In uncomplicated ascites, treatment consists in normalizing liver function. This is achieved by drug therapy aimed at suppressing inflammatory processes in the hepatic parenchyma. The patient is prescribed diuretics to increase excretion in the urine sodium. It is prescribed compliance with bed( sometimes semi-post) regimen for improving lymph flow and reducing the number of liver metabolites. In ascites caused by portal vein hypertension, the administration of albumin, hepatoprotectors and the introduction of plasma are prescribed.
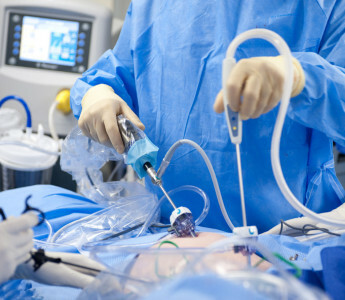
Symptomatic treatment is resorted to if conservative methods are ineffective, and there is no reduction in the amount of fluid. Then a laparocentesis is performed - a puncture of the abdominal wall followed by pumping out the excess fluid. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia.
No more than 5 liters can be pumped out in a single laparoscopy session. The following procedures are prescribed with an interval of 3-4 days. Each subsequent procedure is more dangerous than the previous one, since it increases the possibility of intestinal damage. In addition, with the fluid being removed, the protein is washed out from the body, which provokes the further development of ascites. Therefore, symptomatic treatment of ascites of the abdominal cavity is not shown to every patient.
With the rapid accumulation of fluid, the treatment method is the installation of special drainage catheters, which allow for the permanent removal of liquid.
With frequent and persistent recurrences of ascites, an operation is performed, during which the portal and inferior vena cava are connected and a collateral circulation is created. If the removal of ascitic fluid has been repeatedly performed prior to surgery, plasma transfusion and a protein diet are additionally prescribed. In more severe cases, liver transplantation is necessary.
6 Diet
The diet with abdominal ascites is the most important factor in the successful fight against the disease at an early stage. The diet is aimed at creating a negative sodium balance and saturation of the body with proteins. The consumption of salt and liquid is reduced to a minimum( up to 1 g of salt and up to 1 liter of liquid per day).

You can not use the following products:
- fresh baked pastry;
- meat and poultry fatty varieties;
- sausages of all kinds, smoked and canned products;
- strong broths, made from red meat, fish, mushrooms;
- whole milk;
- spicy and salty sauces;
- all types of legumes;
- millet;
- sharp and burning vegetables: garlic, turnips, sorrel, radish, onions;
- sweets, except jelly and marshmallow;
- coffee;
- alcohol;
- cold drinks.
The patient must eat:
- parsley;
- cucumbers;
- lemons;
- eggplant;
- cabbage;
- lean meat: rabbit, chicken, turkey;
- chicken broth without skin;
- boiled fish of low-fat varieties;
- eggs in the form of an omelet;
- sour cream( very small portions);
- porridge on diluted milk;
- nuts;
- dried fruits;
- cottage cheese;The juice of pomegranate is diluted with water.
Food should be steamed and without salt. Avoid fried, and eat vegetables stewed, boiled or baked.
7 Forecast
In many ways, it depends on the underlying underlying disease( diabetes mellitus, liver cancer, spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, and others) and the effectiveness of its treatment. However, for 50% of patients with ascites, the disease ends in a lethal outcome within 2 years. If diuretics become completely ineffective, half of the patients live no more than six months.
Ascites are pathologies that require urgent medical attention. If you let the disease into its own right, without taking any measures, it will progress steadily. At the slightest suspicion of the presence of fluid in the abdominal cavity, an examination should immediately be performed to confirm or exclude ascites. In time, the treatment will help to significantly alleviate the patient's condition and increase the chances of a favorable prognosis of the disease.
- 1 Forms of the disease and causes of
- 2 Symptoms of pathology
- 3 Can disease be recognized at an early stage?
- 4 Intraperitoneal fluid composition
- 5 Conservative, symptomatic and surgical treatment
- 6 Diet
- 7 Forecast
Abdominal cramp or abdominal ascites is a disease in which the abdominal cavity is filled with a liquid, the amount of which sometimes can reach 20-25 liters. Because of this, the patient's stomach takes enormous dimensions, causing him a lot of suffering.
Ascites of the abdominal cavity, the treatment of which depends on its complexity, is not a self-developing disease, it can be a symptom or a complicated consequence of other ailments, for example, cancer diseases with metastases in the stomach and the like. Its appearance indicates the untimely or incorrectly conducted treatment of the underlying disease. The impetus for the development of ascites is a violation of blood and lymph circulation in the abdominal cavity( thus accumulating a transudate or non-inflammatory fluid) or inflammatory processes leading to the appearance of exudate or effusion. If a high content of protein and leukocytes is found in the liquid, this is a terrible symptom, indicating the infection and reproduction of microorganisms, which is fraught with the development of ascitic peritonitis( inflammation of the peritoneum).
Do you have gastritis?
GALINA SAVINA: "How easy is it to cure gastritis at home for 1 month. A proven method - write down a recipe. ..!"Read more & gt; & gt;