What is it?
Coxsackie virus is a group of 30 active enteroviruses that multiply in the child's gastrointestinal tract. For the first time the disease was diagnosed in the small US city of Coxsackie, and due to the high level of infectiousness, the entire globe quickly flew around.
The second name of the disease is the "hand-foot-mouth" cider. Often this pathology occurs in children under 5 years of age, and very rarely in adults. After the transfer of the disease caused by the Coxsackie virus, a person develops a permanent immunity to infection and is not re-infected.
A large group of virus particle data is divided into two classes: A-type and B-type, which contain up to 20 viruses each. The difference is what complications arise after the transfer of infections initiated by one of the two types of the Coxsackie virus.
- After A-type, meningitis and throat diseases can develop.
- B-type is more dangerous and threatens with serious changes in the brain( mental and degenerative disorders), cardiac and skeletal muscles.
The cause of Coxsackie's disease is oral( infection in the mouth) and airborne transmission of the virus upon contact with the infected child. The most dangerous age for the disease is the interval from birth to 2 years. At this time, the hygiene of the baby is especially important.
All contact with sick children should be ruled out and the child should not take dirty items in the mouth that were on the street. If this happens, wash the child and disinfect his hands - so the chance of infection will go down.
Contents
- 1 Coxsackie virus - incubation period and infectiousness
- 2 Symptoms of the Coxsackie virus in children, photo
- 2.1 How does the infection occur?
- 2.2 General symptomatology of Coxsackie virus complications
- 3 Coxsackie virus in adults - features of
- 4 Treatment of Coxsackie virus in children
- 4.1 Forecast of
Coxsackie virus - incubation period and infectiousness of
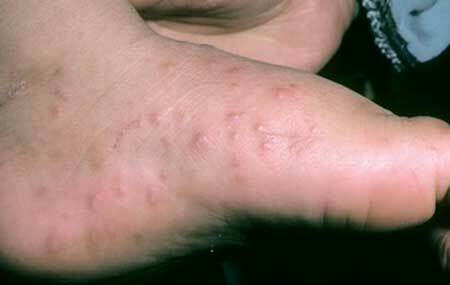
of Coxsackie virus, photo of rashes in child
Coxsackie virus is infectious at 98%if it is a question of close contact with the patient or his things. An exception can only be the transfer of such an infection a few years ago. After the subsidence of the clinical manifestations, the dangerous particles still stand out for a while with saliva and faeces, therefore it is necessary to behave extremely cautiously the next 2 months after the recovery of the sick child.
Infection can occur both outdoors and indoors. According to statistics, most often a child picks up an infection in a kindergarten. However, there is no need to panic, because at the first diagnosed cases, quarantine is declared in the institution.
The incubation period of the Coxsackie virus is from 4 to 6 days - it is dangerous in autumn and summer, when air is enriched with moisture. High humidity is a necessary condition for the viability of a given microorganism.
It is necessary to know several facts about the virus in order to better represent its nature:
- At normal temperature, the infectious agent on the objects does not die within a week;
- The virus survives when treated with 70% alcohol;
- Coxsackie is not terrible acidic stomach and a local solution of chloride acid;
- Destroying the infectious agent can be 0.3% formalin fluid, as well as exposure to ultraviolet light, very high temperatures and irradiation;
- The virus multiplies in the human intestine, but manifestations of infection in the form of nausea and vomiting are practically not found( can be observed in patients with the initially ill intestine);
- Antibodies of mother's milk neutralize the virus in the child's body, so infecting children who are naturally breastfed is rare, and if observed, it is mild;
- The first signs of Coxsackie infection can be confused with ARVI, influenza, chickenpox and allergies, so you need to know in advance the symptoms of Coxsackie infection.
Symptoms of the Coxsackie virus in children, photo
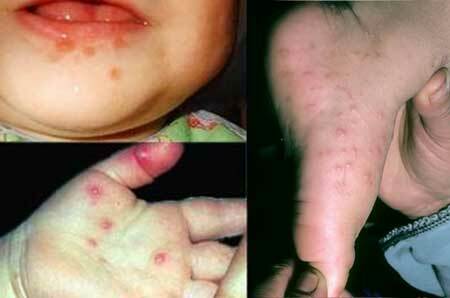
It is often difficult to determine that the clinical manifestations observed in humans are caused by the Coxsackie virus. Symptoms in a child are similar to less dangerous acute infections. It starts with the usual weakness and malaise. The infected child looks indifferent, refuses food, quickly becomes tired. There may be rumbling in the abdomen and spasms.
The name "hands-feet-mouth" was not given to the disease in vain, since the lesions of these areas are the first anxious bell. On the hands, palms, between the fingers, on the phalanges, feet, on the mucous membrane and around the mouth appear reddish blisters. Their size does not exceed 0.3 cm, but they intensively itch. The appearance of such bright points is possible throughout the body: on the abdomen, back, buttocks of the child.
Itching is so unpleasant that it provokes dizziness and lack of sleep in children.
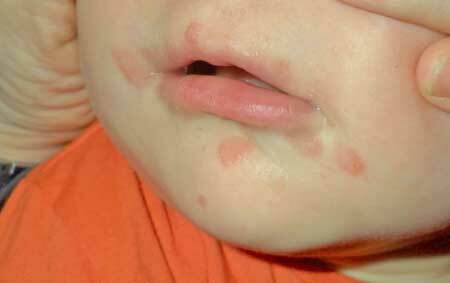
Without a symptomatic drug that will stop the itching, it's by no means impossible. Due to irritation of the mucous in the mouth, saliva is constantly released. For this reason, it is necessary to turn the child's head on its side to prevent aspiration( ingestion) of saliva into the respiratory tract.
It is almost impossible to take food in the state of destruction of mucous ulcers and blisters. But for a speedy recovery in the body should be water, better if it will be cool.
To feed the baby, it is necessary to pre-lubricate the mouth with an anesthetic gel: Holisal, Holitsest, Kamistad.
- Possible nausea, vomiting, and constant rumbling in the intestine.
- If the baby is breastfeeding, offer him a breast permanently - as mentioned above, immunoglobulins that suppress the development of the Coxsackie virus are found in breast milk.
How does the infection occur?
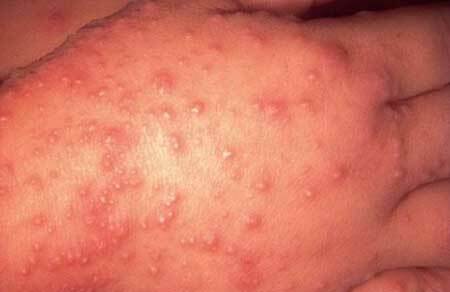
Symptoms of the Coxsackie virus photo
There are four forms of infection in which the Coxsackie virus occurs in children. It is necessary to know the symptoms of each of them in order to start treatment in time.
1. Flu-like syndrome( flu-like)
This is the easiest of all possible forms of infection. The duration of the disease does not exceed 3 days, during which the child's body temperature is maintained at 38-39.5 °.
Among the symptoms can be identified only general weakness, muscle pain and aches in the bones. On the fourth day, the signs of infection disappear, and the number of complications after flu-like syndrome is minimal.
2. Intestinal localization of
Can be caused by both A-type and B-type. A greater likelihood of catching the intestinal form in children under 2 years of age, with cases in the children's team may be single. Body temperature can rise to 39 °, which causes lethargy and body aches.
This manifestation of Coxsackie infection can be mistaken for a typical intestinal poisoning, since all symptoms of intoxication are on the face. In the first days, the child has vomiting and frequent urge to go to the toilet. The chair becomes more frequent 6-7 times a day, which increases the risk of dehydration.
The younger the patient, the greater the likelihood of additional symptoms like ARVI, such as sore throat, runny nose, dry cough. The organism of the schoolboy is able to cope with the infection in 2-3 days, while the baby has to fight with the disease for about a week.
Intestinal localization Coxsackie infections can affect the functioning of enterocytes( intestinal cells), which produce the enzyme lactase. Therefore, the next month after recovery, the baby may suffer from intolerance to dairy products, including breast milk, and therefore refuse to breast-feed or add a medical lactase to the baby's diet.
3. Boston disease
Symptoms are very similar to rubella - the entire body of the baby is covered with red blisters. As a rule, children under 5 years old are susceptible to the disease. Boston disease lasts 3-5 days and is characterized by a high temperature of up to 40 °.
Complications after this form are almost impossible.
4. Bronholm disease( pleurodynia)
The temperature of 39.5 - 40 ° is kept for 3 days. Along with the fever, the child experiences severe pain in the muscles. Especially severe can be spasms in the chest, back and around the navel.
The attack lasts from 1 to 20 minutes and repeats on average once an hour, during the movements increases. It is associated with the lesion of the peritoneum and the pleura, which, when rubbing, provoke a pain syndrome.
The positive thing is that catching the form of pleurodynia is very difficult, because its causative agent does not like flat terrain and moderate climate.
General symptomatology of complications of the Coxsackie virus
In addition to the typical clinical picture that is characteristic of different variants of the Coxsackie infection, during and after the disease, the following health problems can occur in small patients. They are associated with the defeat of one or another system of the child's body:
- Muscles: myositis. Pain in the muscles increases in direct proportion to the increase in body temperature.
- Eyes: conjunctivitis, fear of bright light, lacrimation, hemorrhage in the eyeball.
- Heart: myocarditis, endocarditis, pericarditis. All these diseases mean localized damage to the muscular tissue of the heart.
- Intestine: diarrhea, discoloration of the stool, mucous and blood substances in the stool.
- Nervous system: convulsions, headache, paralysis, loss of consciousness.
- Liver: an organ increase, acute hepatitis, pain and heaviness in the right upper quadrant.
- Skin: Vesicular rash on extremities and exanthema( solid reddening) on the trunk and back.
- Testicles in boys: orchitis, if not to stop which a teenager may develop aspermia( she is the cause of male infertility).
If the first suspicion of a viral infection occurs, Coxsackie immediately call a pediatrician to avoid the aforementioned complications.
Coxsackie virus in adults - features of
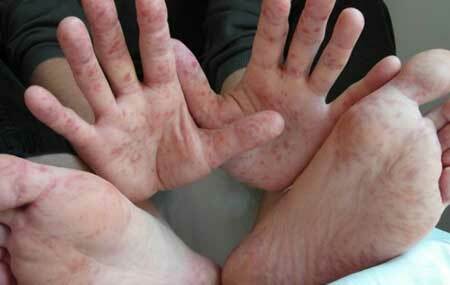
Coxsackie virus in adults is a rare medical case. The older the person, the less likely he or she will become infected with such an infection. The ways of getting the virus are the same for patients of any age.
Parents can get sick only if they have close contact with an infected or newly infected infant with a low level of immune response.
Even if this happened, the recovery will come no later than in three days. For adults, this infection is not dangerous.
If a pregnant woman is pregnant with the Coxsackie virus in the third trimester of the fetus, the infection can be transmitted to the child. However, this is not very dangerous for the life and health of the baby, since treatment even in newborns is successfully carried out.
Still, if the pregnant woman had contact with a child infected with the virus, urgent disinfection of the hands and the person with a prophylactic purpose is necessary.
Treatment of the Coxsackie virus in children
Therapy is primarily aimed at alleviating symptoms - treatment of the Coxsackie virus in children requires the following recommendations and medications:
- Means to reduce itching on the skin: for children - gel Finistil or Vital baby;for adults - an antihistamine drug Suprastin.
- Means to reduce pain in the oral cavity - antacids Relzer, Maalox, Gestid.
- Immunomodulating agents based on interferon - Roferon, Viferon, Neofir or Cycloferon.
- To reduce body temperature - Nurofen, Cefexon, Paracetamol. Analgin should not be taken categorically.
- Means for the normalization of metabolic processes: nootropic drugs, vitamins B1 and B2.
- Adults are advised to drink chamomile tea, to eliminate itching in the mouth, children under 3 can only be given cool water.
The pediatrician will narrow down the list of prescriptions for a particular case and determine the permissible periods of return to the collective. For the time of illness of one of the family members, it is recommended to give him personal cutlery and disinfect personal hygiene products.
If one of the relatives weakened immunity, he will be assigned vitamins or immunomodulating medications.
Forecast
Adult patients can return to the usual rhythm of life after 3 days, in severe cases - no later than 10 days after the appearance of the first symptoms. The child after 3 days passes only the temperature, and the remaining symptoms can remain for 1-2 weeks.
Complete healing of red blisters is observed after 6-7 days, and the rash after 10-12.The appearance of complications depends on the quality of treatment and the timeliness of contacting a doctor.
With the quality treatment of the Coxsackie virus in a child, the risks of problems with the heart, liver and testicles in boys are minimal.