As is known, at present the patient voluntarily can agree to vaccination against a particular disease or refuse it. Unfortunately, many opponents do not understand the importance of this procedure. After being vaccinated, a person protects himself from many serious infections and complications developing on their background. Great attention was paid to rubella vaccination. There are many disputes and myths about the need to vaccinate against this disease. Still, most specialists, despite the fact that the virus itself is not dangerous to the life of its "owner", are of the opinion about the need for specific prevention.
Contents
- 1 The need for prevention of rubella
- 1.1 Elena Malysheva talks about rubella and graft from her - video
- 2 Vaccination in children and adults
- 4 Contraindications
- 4 Possible side effects from vaccination
- 5 Precautions
- 6 Doctor Myasnikov speaks about vaccination against measles and rubella - video
The need for the prevention of rubella
About rubella, probably all of us have heard since childhood. This is a widespread acute disease of an infectious nature, with airborne transmission from person to person, penetrating into the body by inserting into the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract. It is believed that they are mainly affected by children. But statistics say that it affects both children and adults to the same extent.

Children with rubella are lighter than adults
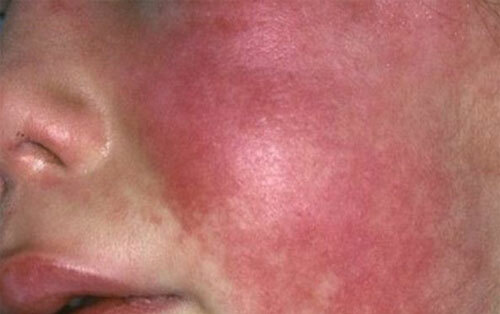
A pathology of small red papular rash, moderately high body temperature, which rarely exceeds the 39 degree mark, and generalized lymphadenopathy, that is, an increase in lymph nodes at different points of the body. As a rule, the infection occurs in outbreaks, occurs in large collectives( kindergartens, schools, barracks, and so on).After the transfer of the disease, a fairly stable immunity is formed, which protects against repeated infection. Although there are cases of infection a second time, but this is more likely an exception.

Rubella spreads quickly in close groups( kindergartens, schools, etc.)
Rubella is especially dangerous for women bearing babies, especially in the first trimester. If infection occurred during this period, then the question of abortion, that is, abortion, is raised. This is due to the fact that the virus contributes to the formation of severe developmental anomalies in the fetus, and at later periods, its death is possible. If the baby is born, it is high probability( up to eighty five percent) that he will have a so-called congenital rubella, manifested in the triad of developmental anomalies, namely blindness( cataract), deafness and heart disease. Therefore, when planning a pregnancy, a woman must take care of protecting her and her future child from rubella and its consequences in advance, for which she needs to be vaccinated, if this has not already been done. In this regard, the question is raised about the mandatory and timely vaccination of girls.

Especially dangerous rubella virus for pregnant women
Experts need to disagree about the need for vaccination with boys. Some consider this an additional and absolutely unnecessary burden on the body, while others say that it is extremely necessary. On the one hand, rubella itself is a disease that is easily transmitted in childhood with the development of persistent immunity after recovery, on the other - there is a danger of contamination of others. As stated above, the disease is dangerous for pregnant women, or rather, for a future child. For example, the situation is extremely undesirable when there is a non-vaccinated child in the family( not necessarily a male) who becomes ill with rubella and a pregnant child( mother, aunt, sister, etc.) or her husband( dad, uncle, brother, etc.)a woman who is in a position becomes infected with an infection.
To avoid rubella in a boy and further infection of all family members, it is advisable to administer it according to the schedule of
vaccinations. The adult organism is much more difficult to cope with the disease: the disease contributes to the development of many complications( arthritis, encephalitis, thrombocytopenia and others).
In addition, it should be noted that the person who has recovered from rubella releases a small amount of the virus into the environment during the fifty to sixty days after recovery, in connection with which it remains potentially dangerous for others. Therefore, in order to avoid mass infection, the question is raised about the importance of early vaccination against infection.
Even if a person gets rubella after vaccination, the infection is much easier( some even do not notice that they are ill) and without complications.
Elena Malysheva talks about rubella and vaccination from her - video
Vaccination for children and adults
Rubella vaccination is included in the National Schedule of preventive vaccinations, which is approved by the order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation. The procedure is free of charge for all categories of citizens in accordance with the mandatory health insurance program.
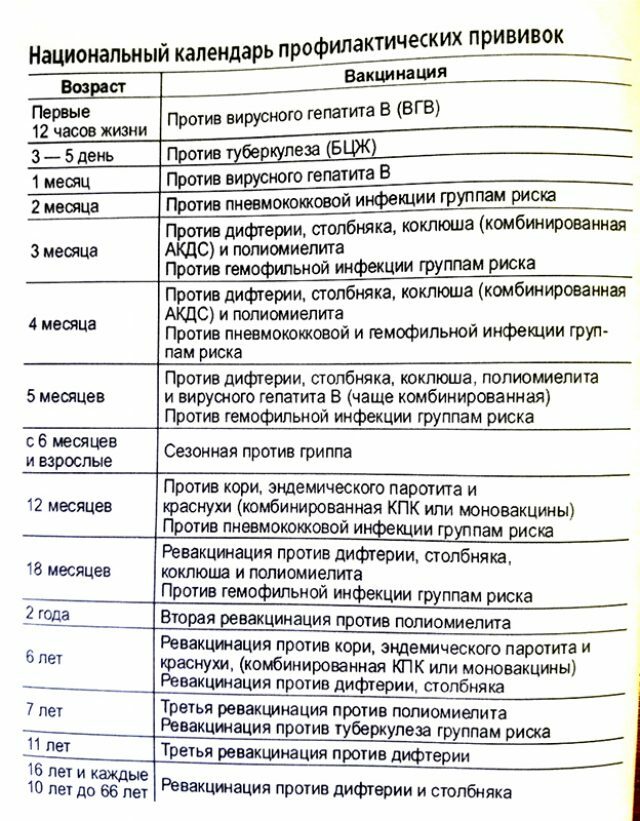
Vaccination against rubella is included in the National Schedule of Prophylactic Inoculations
According to the calendar, the vaccine is first given to children at the age of twelve months in conjunction with the vaccine against mumps and measles( MMC).Due to the fact that after all, not all children are immunized, they are re-vaccinated( or rather revaccination) at the age of six before moving from kindergarten to school. The second revaccination occurs at the age of fourteen and affects only the girls. If, for some reason, the vaccine has not been delivered, it is necessary not to delay this and make it at the first convenient opportunity.
Special attention is paid to girls and women of reproductive age( from eighteen to forty years old) planning a pregnancy. During the period of bearing the baby, immunization is possible only until the sixth week of gestation. It is up to this time that it is considered that the vaccination will not have a negative effect on the embryo, with the opposite only in half the percentage of cases. In the remaining periods of pregnancy, vaccination is strictly contraindicated, since a weakened virus with a blood stream can penetrate the placental barrier and affect the fetus.

If a woman does not have time to get pregnant before the pregnancy, it is advisable to do so before the sixth week of gestation.
. If there are no problems with the health of a child or an adult, then special preparation is not required before vaccination. Nevertheless, there are a number of recommendations that help reduce the risk of adverse reactions of the body in response to the introduction of the vaccine. Unfortunately, in many medical and preventive institutions this is not told to patients. So, what you need to know:
- If you tend to allergic reactions of various types, you should start taking antihistamines two to three days before the vaccination. In the next two to three days, their use is also advisable.
- Suspend for 2-5 days taking medications containing vitamin D. Restoration of treatment should not be made until the fifth day after vaccination.
- Ten days prior to immunization, people who are often ill, are recommended to take fortifying agents that help boost the body's immune forces.
- Dense food intake is not recommended before grafting.
Before the vaccination it is necessary to take tests. A common blood test is needed to exclude any diseases, as well as a blood test for the rubella antibody titer, if these are not found or are in the least amount, the vaccination is carried out in full.
The duration of the protection is individual for each person. Someone after the introduction of one vaccine becomes protected for a long time, someone has to be vaccinated according to the schedule. To find out if there is rubella immunity, it is enough to pass the test for antibodies to the infection. If they are present, the vaccine has not yet completed its action, and if there are no - it's time to get vaccinated again. The World Health Organization( WHO) recommends revaccination every ten years for complete protection against the disease.
Twelve-month-old children are inoculated into the pedicle. At an older age, the injection is performed in the shoulder region. There are two types of rubella vaccines:
- One-component. Contains in its composition only the rubella virus, which was weakened by exposure to certain chemicals. In most cases, such a vaccine is administered in case of repeated revaccination to adults.
- Three-component. This polyvalent vaccine contains three weakened viruses: mumps, measles and rubella. This vaccination is carried much easier, almost unnoticeable, rather than one-component. It is put only for the first time at the age of twelve months and at six years with revaccination.
There are two types of rubella vaccine: one-component and three-component
It should be noted that the vaccine, although weakened, but alive. Therefore, the vaccinated person has rubella in an easy degree. It is not entirely correct to say that it is contagious to others, since experts have not yet reached a final conclusion whether this is so or not. Nevertheless, doctors advise to limit contact with him for five days, especially unvaccinated and not previously sick women in the position.
Contraindications
Like any manipulation, the formulation of the vaccination against rubella has a number of relative and absolute contraindications.
Absolute contraindications suggest that under no circumstances should a child or adult be vaccinated against rubella. These include:
- malignant diseases;
- immunodeficiency syndrome;
- serious complications after the previous vaccination;
- severe allergic manifestations.
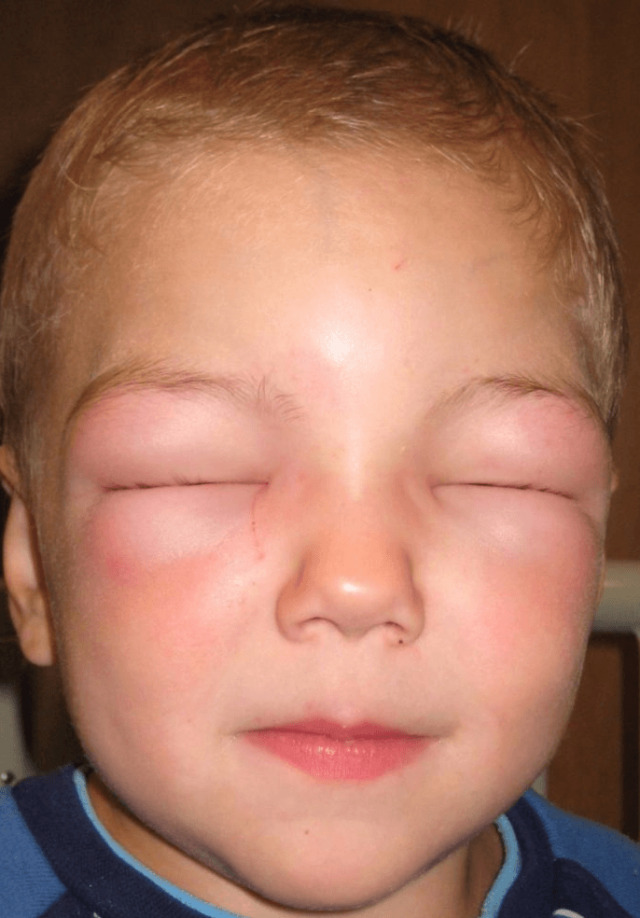
In case of severe allergic reactions to the first inoculation against rubella, for example, in the form of Quincke edema, the revaccination of
should be discarded. Relative contraindications are temporary. This means that under favorable circumstances vaccination is carried out, albeit with a deviation from the schedule. The vaccination can be delayed:
- during pregnancy;
- with exacerbation of chronic processes in the body;
- for inflammatory diseases, infections( both viral and bacterial);
- during teething in children, accompanied by a rise in body temperature;
- during treatment with agents from the pharmacological group of immunosuppressors.

During the period of temporary weakening of immunity( cold, exacerbation of chronic diseases, etc.) should be delayed with vaccination
The vaccine is administered two weeks after recovery. In the case of chronic diseases - the procedure is carried out exclusively during the remission period, when acute manifestations of the illness subsided.
Possible side effects from vaccination
As a rule, the response reactions of the body in response to a rubella vaccination occur in childhood. In most cases, the child does not react to the vaccine in any way. Adults usually do not notice any changes in their state of health. Nevertheless, everyone should know what consequences may occur after the vaccination. Most often noted:
- redness and induration of the injection area;
- increase in body temperature( sometimes it can reach forty degrees);
- dizziness;
- headaches;
- single manifestations of vomiting or diarrhea;
- runny nose;
- sore throat and cough;
- thrombocytopenia( reduced platelet count in the blood);
- appearance of a red rash in some parts of the body;
- enlargement of lymph nodes( mainly cervical and parotid), as well as their soreness;
- excessive sweating;
- general weakness.
With a normal immune response of the body, all these manifestations disappear on their own within three to four days. This is considered a normal reaction, indicating the correct production of antibodies to the disease.

Raise body temperature - a normal reaction to the inoculation of
Precautions
After vaccination, you should follow certain precautions to avoid complications:
- on the day of vaccination, you can not take a shower and bathe your baby;
- in the first few days( from two to five) it is undesirable to be in places of a large congestion of people( in children's polyclinics advise not to drive a child outside for two days);
- if the child goes to the garden, try to sit with him at home whenever possible for four to five days;
- does not introduce new products into the diet( concerns both adults and children), especially those that can lead to the development of an allergic reaction;
- to increase the intake of liquid( preferably water);
- adults should stop taking alcoholic beverages within six to seven days.
Doctor Myasnikov speaks about vaccination against measles and rubella - video
Everyone on a voluntary basis decides whether to put him inoculated against this or that infection or not. Despite many controversies about vaccination against rubella, it must be said that it is important and necessary. It was after the introduction of mass immunization that humanity, if not completely rid of many dangerous diseases, so significantly reduced their appearance.