 Pain is a signal that there are problems in the body. Using various methods, a person can help himself to cope with acute pain on his own.
Pain is a signal that there are problems in the body. Using various methods, a person can help himself to cope with acute pain on his own.
Medication will help relieve pain, but will not solve the problem. Anesthetics will disconnect pain receptors, and the acute form of the disease will go to the chronic stage.
Postisometric relaxation is the best way to solve an existing problem.
Contents of the article
- General concepts
- Therapeutic effect of the
- procedure Indications for
- therapy There are contraindications to
- It's worth knowing!
- Cervical manipulations
- Exercises for the thoracic spine
- Methods for the lumbosacral spine
- Therapy for the humeroscapular periarthritis
General concepts
The joints are surrounded by muscles. Relaxation of some and reduction of others guarantees smooth movements. Pathologies of joint displacements irritate the receptors of muscle fibers and tendons.
The small periarticular muscles that fix the position of the joint, as well as the muscular-fascial large groups, contract, which leads to changes in the biomechanics of the body.
To restore the normal volume of motor function and joint position. But self-correction is difficult because of the tension in the periarticular muscles.
Effective healing of the body is possible only after carrying out procedures aimed at relaxing the muscles.
The technique was developed in the 70s of the last century by American orthopedists.
Therapeutic effect of the
method The method has a number of therapeutic effects:
- relieves pain syndrome;
- eliminates muscular-fascial rigidity;
- eliminates functional blockade of joints;
- relieves reflex muscle spasm;
- causes a receptor response in the joint capsule;
- activates afferent innervation.
Indications for
therapy Postisometric relaxation is used in such cases: 
- musculoskeletal pain of any origin;
- training of muscles for manipulation;
- muscle contraction with regional postural imbalance;
- local hypertonicity;
- neurologic manifestations of degenerative-dystrophic pathologies of the spine.
There are also contraindications to
For this method of treatment, there are a number of contraindications:
- purulent skin diseases;
- high temperature;
- Eczema;
- transient ischemic attack;
- skin lesions in the area of exposure;
- severe pain during the procedure;
- pain enhancement during the procedure;
- atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels;
- arrhythmia;
- thrombosis, thrombophlebitis, thromboembolism;
- patient failure;
- decompensation of diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- pulmonary insufficiency over 2-3 degrees.
It's worth knowing!
Basic Rules for Manipulation:
- An introductory conversation with a patient, in which isometric contractions and PIRMs are shown and explained.
- Before starting to perform exercises, the joint is brought to the side of restraint, achieving maximum stress and tension of the contracted muscle. The limit of movement restriction is the level of pain intensification.
- The position of the patient should not create restrictions for movement in a given direction, while the fixed part of the body must be fixed.
- The doctor takes the starting position, given the hygiene of poses, movement and ergonomics.
- Movement, stimulating muscle contraction, is carried out as painlessly as possible and corresponds to the direction of the previous muscle contraction.
- The strength of muscle contraction should not exceed 30% of the maximum. Do not increase the pain.
- Muscle contraction resistance should suffice to prevent the body or limb from moving in space. The muscle must be tense, but the movement is not carried out, being kept at the expense of resistance.
- Additional muscle tension lasts from 5 to 7 seconds.
- After the voltage, it is necessary to take a short pause to relax the muscle.
- With each new movement, the amplitude increases, given the increased amount of passive movements.
- Several approaches are being implemented, gradually increasing the freedom of movement of the joint and muscle relaxation.
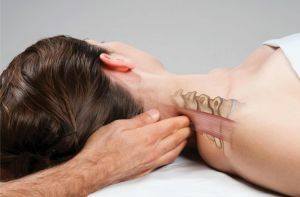
Cervical manipulations
Methods of postisometric muscle relaxation for the cervical spine:
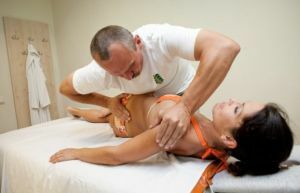
- When the exercise is performed, the patient sits .Place the elbows on the shoulders of the patient. The palms are arranged depending on which segments need to be stimulated( the upper segments are below the auricles, the middle ones and the lower ones on the transverse processes of the second vertebra of the neck).
- Move the elbows, pulling the patient's head up .Hold the upper point for a while, then press the
 force and gently dilute the elbows.
force and gently dilute the elbows. - Stand close to the seated patient. With your right hand, grab his head, the patient's chin is located on the elbow. From the back of the head, fix with your left hand. Gently pull the patient's head up, hold it for a while, then slowly return it to its original position.
- The patient lies on the back, knees are bent, and the shins hang from the surface on which the patient is lying .One hand is located on the back of the head, and the other hand, take the patient by the chin. Slightly bend your knees, and put the feet in parallel. Slowly bend backwards, until the knees and elbows are completely unbent. As soon as the muscles of the patient completely relax, stay for a while, then gradually relax the effort, and smoothly return to its original position.
- The patient lies on the back, the shoulders are located on the edge of the massage table, and the legs are fixed with the straps. Arms connect on the back of the patient's head, gently grasp and squeeze the head with the inner surface of the forearms, trying to connect them. Slowly bend backwards, while increasing the force on inhalation, and loosen it on exhalation.
All exercises should be repeated 6 to 8 times.
How post-isometric relaxation is performed by specialists you can learn from the video:
Exercises for the thoracic spine
Methods of PIR on the thoracic spine:
- The patient assumes the position on the side of the , the leg, which is slightly bent at the bottom, and the upper leg is located in the popliteal fossa of the lower limb, the knee and most of the thigh hanging from the massage table. Stand so that the patient's face is in front of you. One hand lay on the shoulder joint. The second hand is on the rib, and the index and middle fingers are pressed against the rib, grasping its angle. The joint of the shoulder should be turned away from you, while the pelvis, on the contrary, turn to your side.
- Ask the patient to breathe deeply into the , while exerting pressure against the resistance of the arm located on the rib. At this time, the patient should look towards the direction of pressure. After 10 seconds, the patient exhales slowly, relaxes and looks at himself.
- The patient sits, arms cross on the chest , and brushes his shoulder joints. Stand behind the patient and grasp his elbow joints. Lean back until the arms are straightened, place the pelvis so that the area above the crest of the ileum is under the thoracic spine of the patient. This is necessary for additional support.
- Position of the patient, as in the second reception of .Stand behind the back of the patient, and grab from the bottom of his elbow joints. Distort the patient's torso until his back begins to rest on the lower chest. Then fully straighten your arms in the elbows, and gently bend back together with the patient. Do not allow the patient to rise from the surface of the massage table.
Exercises do from 6 to 7 times.
Methods for the lumbosacral spine
Methods for the lumbar puncture:
- The patient lies on the back of the , with his hands clasping the head of the massage table. Stand in the legs of the patient, legs should be on the width of the shoulders. Embrace the legs in the ankle joint area and lift the patient over the couch by about 30 cm. Lean back, while pulling the patient's legs toward him. Exercise 3-5 times.
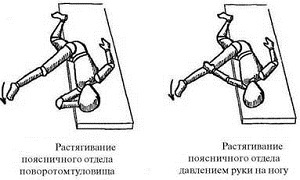
- The patient lies on the back, hands are located along the body of the , the ankles protrude beyond the edge of the massage table. Expand your pelvis to the bottom edge of the table, place your feet on the width of your shoulders. The anterior upper axis of the ileum extends forward, so that the patient rests against it with a foot. Lean back, clutching the other leg with both hands. At the same time, return the pelvis to its original position, pushing the leg, which the patient rests, forward. Force increase and loosen gradually. Exercise is repeated 7 times.
- The patient lies on the back, with knees and hip joints bent , arms crossed on the chest. Stand at the feet of the patient. Socks of his feet rest against your hips. Embrace the legs of the patient with both hands, while the forearms should be at the level of the popliteal pits. Lean back, while pulling the upper part of the lower legs with forearms. In this case, the pelvis of the patient is detached from the couch, which makes it possible to bend forward in the lumbar spine. Run 6-7 repetitions.
Therapy of the humeroparous periarthritis
 Postisometric relaxation in the treatment of humeroscapular periarthritis is an important part of restoring the activity of the joint.
Postisometric relaxation in the treatment of humeroscapular periarthritis is an important part of restoring the activity of the joint.
It consists in a short( 10 second) isometric performance of the muscles, with the effort should be minimal, and then passive stretching during the same time.
The complex of exercises should be repeated no more than 5 times. This will allow the muscles to relax and reduce the sensation of pain. Exercises are selected individually for each patient, taking into account the degree of joint damage and concomitant pathology.
Only he will be able to pick up a set of exercises that will be most effective for you.