There are two types of knee cruciate ligament:
- posterior;
- front.
Rupture of cruciate ligament
Scheme of ligament of knee joint
Consider the causes and symptoms of ruptures for each species. The anterior ligament is damaged tens of times more often, so this injury will be given more attention.
material Content
- 1 anterior cruciate ligament
- 1.1 Because if anything breaks PKS
- 1.2 Symptoms injury
- 1.3 Diagnostics
- 2 posterior cruciate ligament
- 3 How is it treated
- 3.1 Conservative
- 3.2 Surgery
- 3.3 Video - Holdingarthroscopy
- 4 Rehabilitation
- 4.1 Video - Treatment for damage PKC
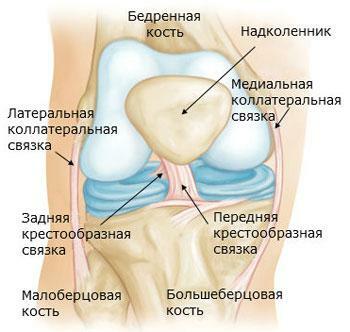
Front cruciate ligament
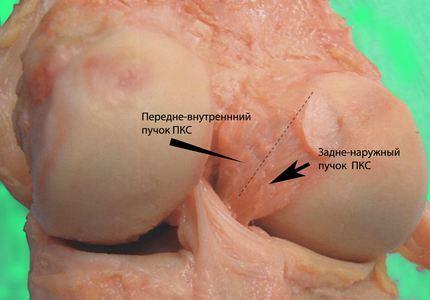
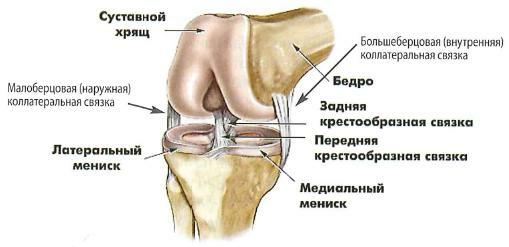
Knee ligaments
In medical circles this ligament is indicatedaetsya abbreviation PKS is the most injuries to the knee. Usually ligament tears are associated with sports and often occur due to the curvature of the shin. Diagnosis can be performed by several methods, but the most effective of them is MRI.
Determine the rupture of the knee ligament
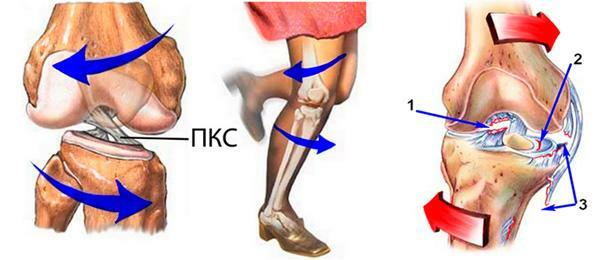
The main function of the PKC is to keep the tibia from shifting inwards and forwards. From this, the mechanism of injury is also clear, in which a break occurs - often this is a rotation movement on one limb, when the foot does not move, and the thigh with the body scrolls outward. Although it is worth noting that in reality both mechanisms and causes of breaks are much more complicated.
Mechanism of sprain and rupture of ligaments
Because of what breaks occur
PKD Ligament damage - Scheme
The ligament can be damaged due to direct injury( when contacting the joint) and indirect( for non-contact effects - for example, with a rotation on the leg followed by a sharpinhibition).
The most common mechanism is the external deviation of the shin and the scrolling of the hip inwards. Quite often it happens in football, hockey and other sports where it is required to turn around quickly or to land after a jump with the subsequent turn of the body. By the way, under these circumstances, the meniscus breaks.

Dangerous traumatic jumps
Please note! Understanding of the mechanisms is necessary to identify and prevent PKC ruptures. The correct diagnosis is made only on condition that the victim in detail will describe the moment of injury. For this reason, knowledge is needed for both doctors and people involved in sports.
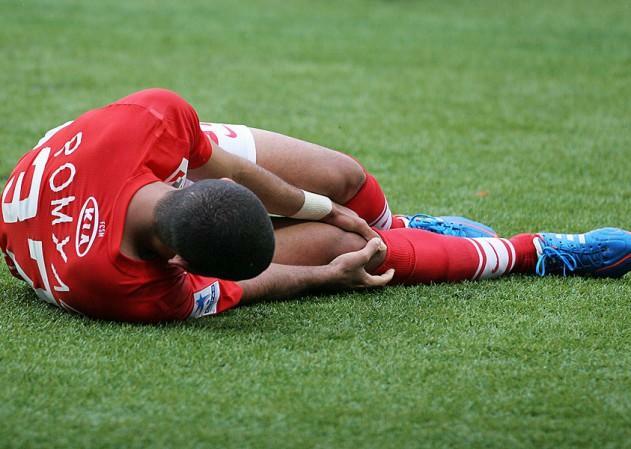

Knee injury in the athlete
If the athlete understands the mechanisms of injury, he can avoid situations that lead to the rupture of the PKC.It is also worth noting that indirect influence predominates among other mechanisms and implies that the knee joint has not been subjected to external loads. If such loads were, then it is a contact mechanism( often a blow to the hip or directly to the knee).
Symptomatology of injury
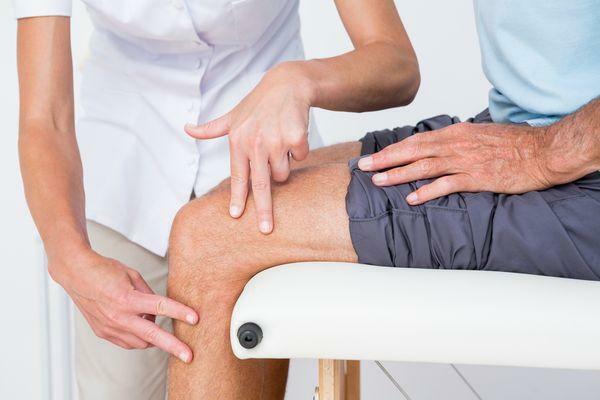
Knee joint examination by a doctor
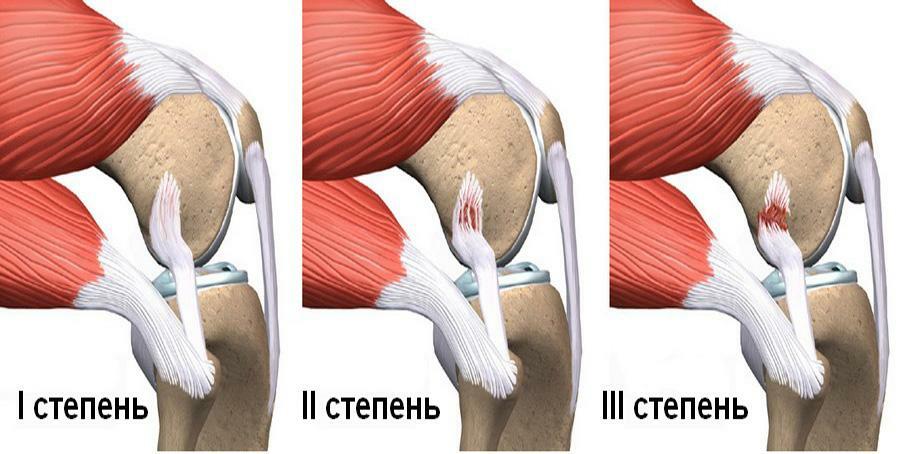
The main sign of rupture of the PKC is the apparent instability of the joint. And if you ignore it for a long time, it can cause early arthritis. In the case of pronounced instability, a ligation reconstruction operation is required( performed in one of several ways).Then in half a year the person will restore the former physical activity.
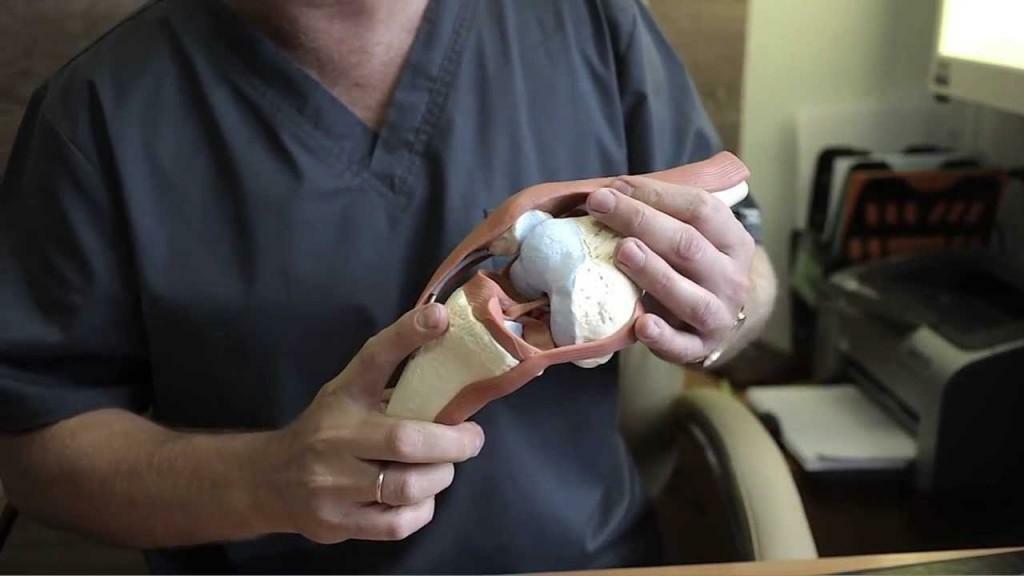
Treatment of injuries of the cruciate ligament of the knee joint by surgical procedure
As noted above, the rupture is due to trauma, after which acute pain and swelling occur in the knee. Cracks are often heard, although this symptom can also occur when other ligaments are ruptured. Another person can feel "dislocating" the shin to the side and forward. If you have any of the symptoms, you should immediately seek medical help.

Symptoms of rupture of ligaments
When the PKC ruptures inside the joint, blood can enter - this phenomenon is called hemarthrosis. During the first few days, the severity of the pain and hemarthrosis can be so strong that the doctor simply can not examine the knee with his hands( which makes it possible to make an accurate diagnosis).
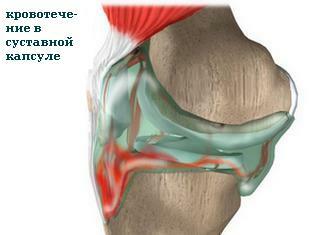
Knee Arthritis
Diagnosis
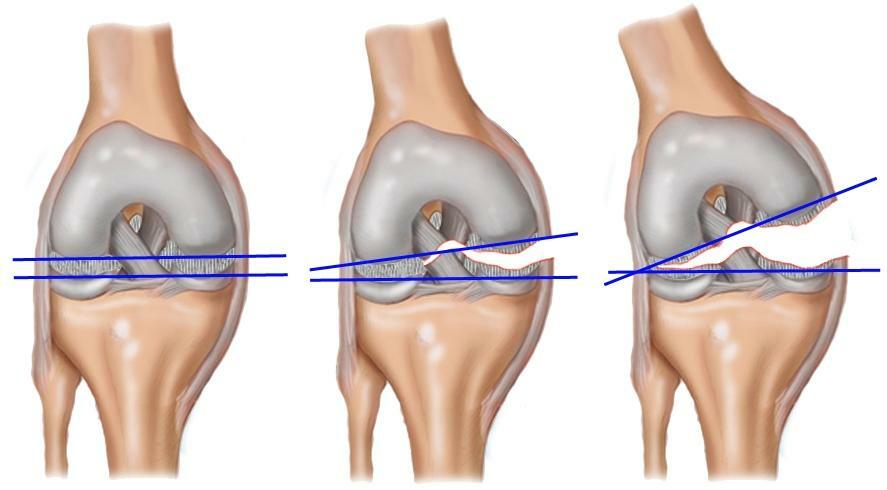
First the doctor should determine the mechanism of the injury, then proceed to the examination of the joints. The first to be examined is an intact knee( so the patient will be able to get acquainted with the examination procedure, moreover, in what follows will compare with the results).If testing is conducted carefully, then no additional research methods for diagnosing rupture of PKS will be required. But in view of the need to exclude other injuries( for example, rupture of other ligaments or meniscus), MRI, ultrasound, X-ray examination can be used.
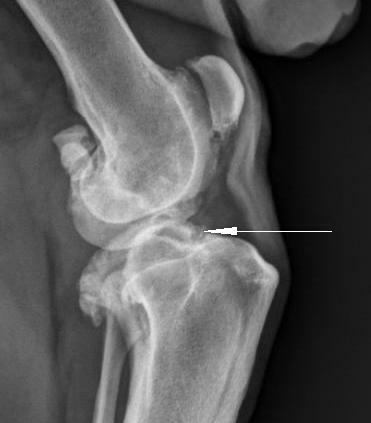
The location of the cruciate ligament from the surface of the tibia
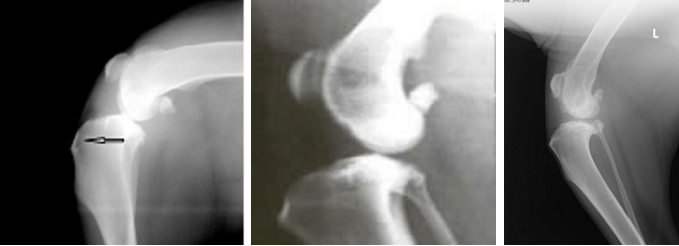
is shown. X-ray signs of PCD rupture are caused by the displacement of the tibial condyles forward relative to the femur
The posterior cruciate ligament
The knee structure is normal, the front view is
It is located directly behind the front,requires a powerful impact. Often, the fracture of the ZKS is a consequence of a shock on the shin( it can happen during sports or an accident).For example, if a low car hit the bumper under the knee joint. This can happen with drivers as well - when an accident occurs, a person moves forward and knocks against the dashboard.
Please note! To avoid this type of injury, modern models of cars are equipped with additional airbags located under the dashboard.
The only effective way to avoid a gap is to limit activity. You can still strengthen the muscles of the joint, but this does not always help.
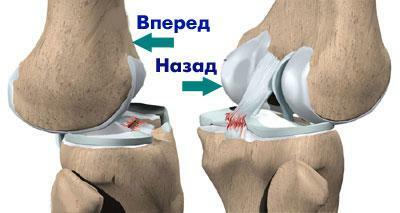
Diagnosis is carried out in the same way as when the PKC ruptures, but the doctor must take into account that such a trauma happens only with very strong impacts. Therefore, an X-ray is always carried out - fractures are looked for on it. A clear sign that the ZKS is damaged is a weak subluxation of the knees back - this is clearly seen in the picture in the lateral projection.
How it is treated
A rupture of the cruciate ligament of the knee can be treated with conservative methods and with surgical intervention. We will become acquainted with the peculiarities of each variant.
Conservative methods
Treatment of the knee
Immediately after the injury, swelling and pain are removed, after which the former joint mobility is restored. Conservative methods include cold compresses, anti-inflammatory drugs and, of course, rest. In addition, the patient can be assigned special exercises and physiotherapy.
Knee compresses
As for exercises, they are aimed at restoring mobility and preventing muscle atrophy. It is also recommended to wear special knee pads, which can be of several types.
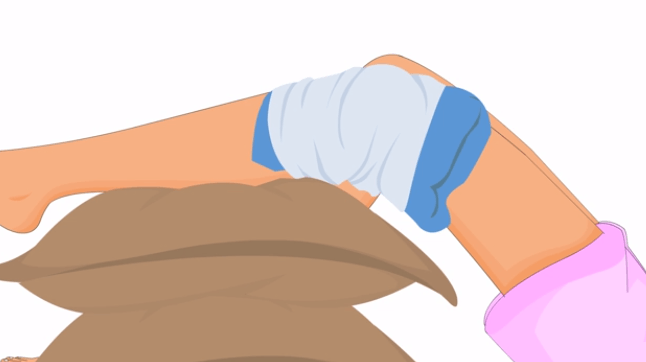
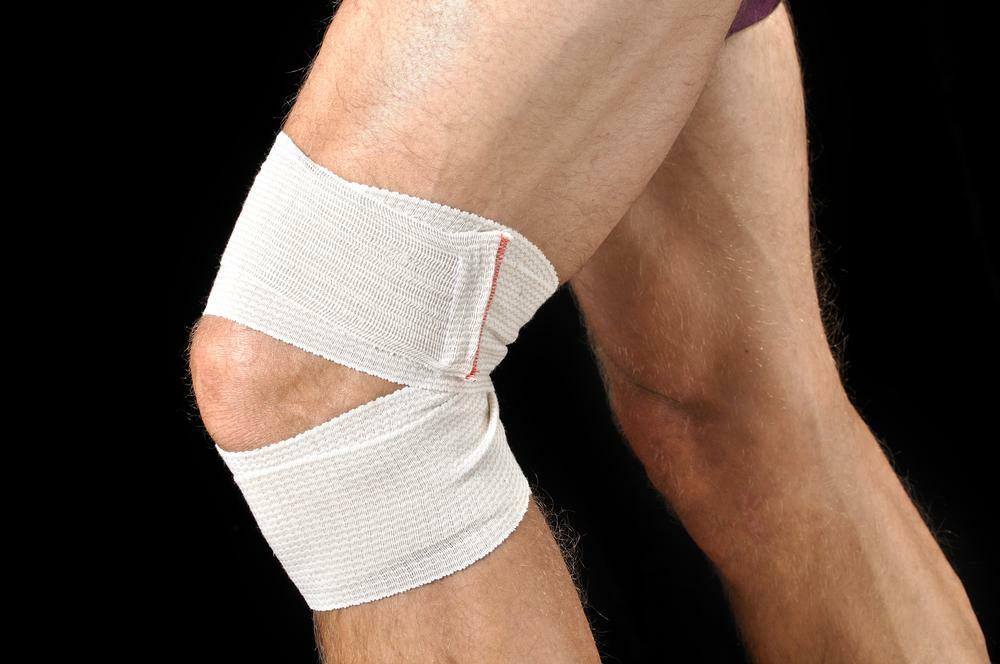
- Bandage is a knitted fabric that fits tightly around the knee and maintains its stability. In order to improve fixing, modern bandages are equipped with special inserts made of silicone, made in the form of rings.
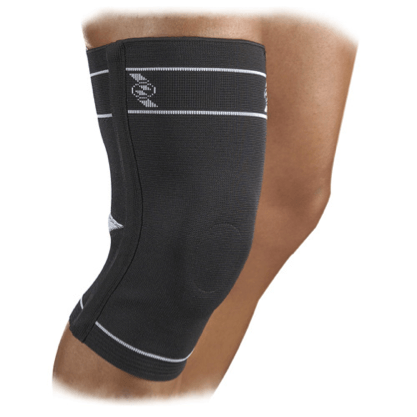

Bandage
- Orthosis is another orthopedic product that compensates for impaired knee functions. In the majority it is rather complicated devices made of plastic, iron and fabric.
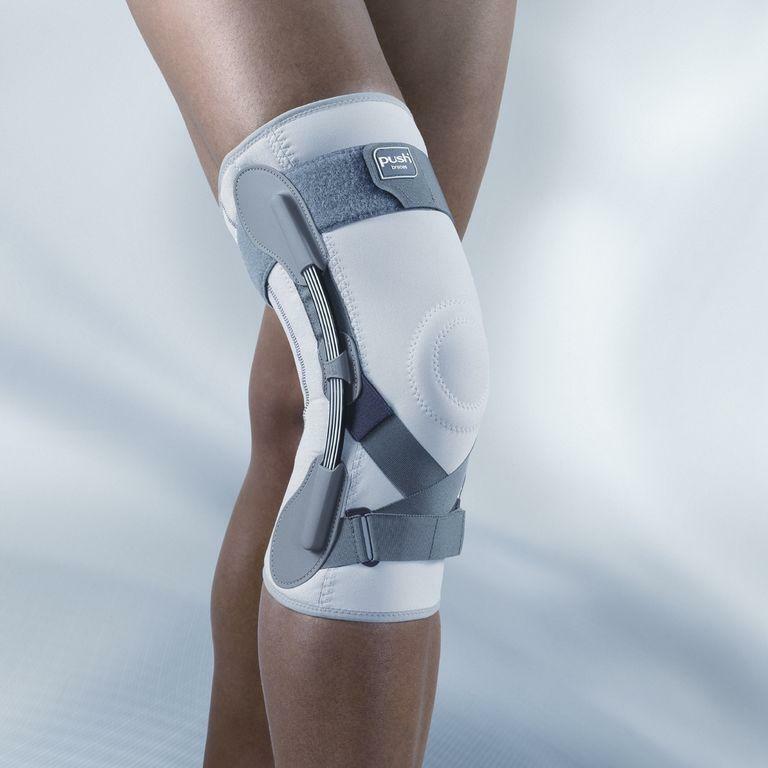
Orthosis
- Support is also used in conservative therapy. If a person does not engage in active sports, then when carrying a support, the operation may not be required.
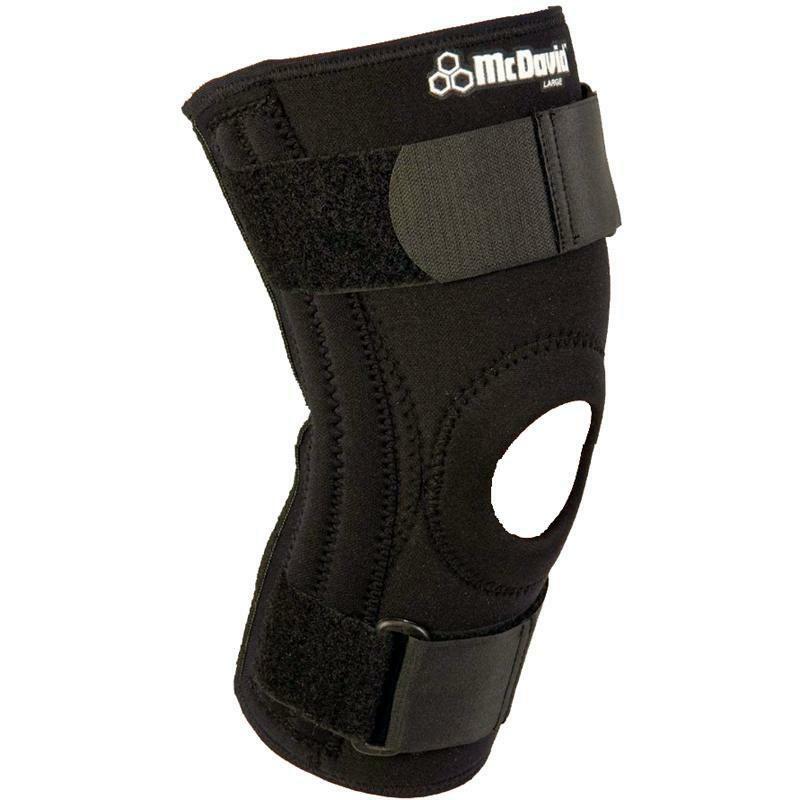
Support
Please note! Not always calipers are able to fully protect the knee joint, moreover, when practicing sports they can give a false sense of reliability.
For this reason, sports people are recommended to conduct operations, and calipers are appointed at least six months later.
Surgical treatment
In case of ineffectiveness of conservative methods, surgical treatment is performed. Even if it is immediately clear that there is no way to do without surgery, the patients are still prescribed physiotherapy and gymnastics at the beginning to relieve swelling and restore mobility.
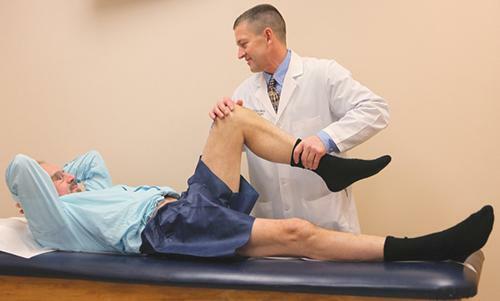
Treatment of rupture of knee joints of the knee joint
As a rule, with rupture of PKC and ZKS, arthroscopy is performed - one of the least traumatic operations. The torn ligament can not be sewn - for its restoration, grafts or piece prostheses are used. The most effective arthroscopy shows after a course of exercises and physiotherapy, and this once again proves how important conservative therapy is. Usually the operation is done six months after the injury, but sometimes it happens in a few years.
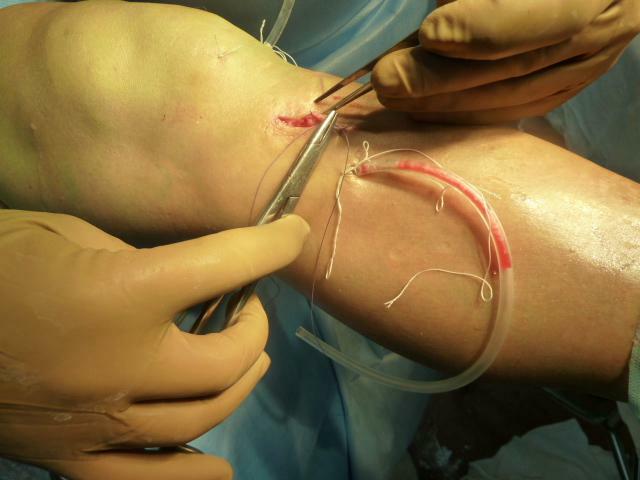
Arthroscopy of the knee joint
Arthroscopic operation
We also add that the transplants can be of two types:
- autografts( other patient tendons);
- allografts( tendons from the donor).
The advantage of the second option is that the operation takes half the time, because the surgeon does not need to first cut the transplant.
Video - Carrying out arthroscopy
Rehabilitation
The characteristics of the rehabilitation course depend on what treatment was performed. Methods of conservative treatment have been described above( the use of specific ones is possible only according to the doctor's prescription), so let's talk about postoperative rehabilitation.
Rehabilitation course
Rehabilitation course consists of five stages and is calculated for at least six months. For the convenience of visitors, the information is presented in the form of a table.
Table. Stages of postoperative rehabilitation
| Stage | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| First stage | Weeks 1-4 | Reduces pain, restores joint function, achieves mobility without crutches. About ten days after the stitches are removed, the plaster is removed as well, and a circular gypsum dressing is put on instead. The working capacity of the femoral muscles is restored by means of electrostimulation. The patient is regularly engaged in therapeutic gymnastics, massages are done to him. |
| The second stage of | Weeks 5-10 | When the goals of the first stage are reached, we can proceed to the second. In turn, the goal of the second stage is complete elimination of puffiness, restoration of the full range of movements, improvement of muscle strength and control during walking. The exercises that are performed at this stage are aimed at gradually increasing the mobility of the knee, as well as strengthening the extensor. Gymnastics can be supplemented with underwater massage and exercises in the pool. |
| The third stage of | Weeks 11-16 | Muscular endurance is improved, the person slowly but surely returns to the functional activity, learning to run again. Active movements( attacks, squats) and exercises of imitative character( application of the training apparatus "Alpinist", exercise bike, running track, etc.) are carried out. |
| Fourth stage | Weeks 17-24 | Restoration of the previous range of movements, elimination of "remnants" of pain and swelling, restoration of muscular endurance with long-term loads. At first simple exercises are performed, in which the injured limb is acted vertically, but in time they are complicated by attacks, goose walking, walking on toe-toes, running with acceleration and cycling. |
| The fifth stage( it is also called training) | Weeks 25-28 | Restoration of the motor functions of the joint with regard to sports specialization( if the patient is an athlete).The training program is made individually. |
After the rehabilitation, the knee joint is tested, X-ray images are re-made. If everything is fine with him, the course stops, and the patient can return to his old life.