There are a few diseases in the world that belong to a person only because he is a person. For example, the defeat of blood vessels and the deposition of cholesterol on their walls is also found in the animal world. Increase in blood pressure is characteristic of all warm-blooded animals.
Improper diet can lead to the depletion and deficiency of protein and vitamins in both chicken, elephant, mollusk, and freestyle wrestler.
But osteochondrosis refers to diseases that only humans can be proud of: even with its closest relatives - primates, this disease is almost absent. We shall understand in displays of signs and methods of treatment of an osteochondrosis of a cervical department of a backbone.
Contents
- 1 Cervical osteochondrosis, what is it?
- 2 Symptoms of cervical spine osteochondrosis
- 3 Diagnosis of cervical osteochondrosis
- 4 Treatment of cervical osteochondrosis, preparations
- 4.1 Gymnastics for cervical osteochondrosis
- 5 Prevention of cervical osteochondrosis
Cervical osteochondrosis, what is it?
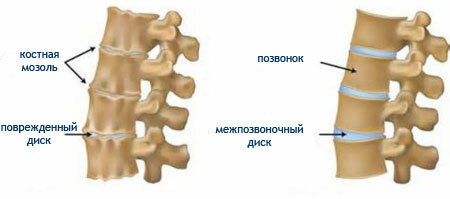
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is a disease of bone and cartilaginous tissue, which are degenerative and dystrophic. The basis is the dystrophy( disruption of cartilage nutrition), and then - its destruction or degeneration.
In fact, with , the initially suffers from cartilaginous intervertebral discs, and then the "snowball" is supplemented by bone reaction( osteophytes), the appearance of protrusions and hernias, radicular symptoms, the appearance of instability in the cervical region, and severe headaches and chronicmuscular spasm of deep neck muscles with regional blood circulation disorder.
The cause of osteochondrosis discs in the cervical or cervical thoracic region is only one: it is a historically established vertical position of a person.
Neither cats, nor cows or hippopotami have such a constant axial load on the vertically located back, the spine is in a relaxed, "sagging" state, and the intervertebral disks feel comfortable.
In humans, the following factors predispose to the development of cervical osteochondrosis:
- Frequent presence in the vertical position;
- Injuries and sudden movements, head shots, for example, about low ceilings;
- Wearing loads on the shoulders, in some countries - on the head;
- Lack of active movement. It leads to the weakness of the muscular corset, which is of the utmost importance in the cervical spine.
Also, additional factors of include wearing winter heavy collars and fur hats in order to "serve fashion", reduced fluid intake, resulting in primary dehydration of the cartilage tissue. This increases the fragility of the discs and causes "their subsidence"( narrowing of the thickness), reducing the elastic buffer properties.
In adolescence, osteochondrosis can result in a violation of posture when performing written assignments and working at a computer. Congenital changes of the spine, for example, scoliotic deformity in the thoracic region.
It should be remembered - the higher the spine section is located, the stronger the impulse, which can have a damaging effect, by analogy with the "whiplash" trauma. Therefore, failure or violation of compensatory mechanisms that protect our skull from excessive shaking also leads to osteochondrosis of the cervical spine. These are the reasons:
- Flat-footed, both longitudinal and transverse. The arch of the foot, devoid of depreciation, is unable to protect the intervertebral disks of the cervical region from concussion and destruction;
- The underlying osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine. If the elasticity in the lower back is broken, do not wait for good protection from the cervical region.
Symptoms of cervical spine osteochondrosis

Symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis photo
Signs of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine are very diverse, but they can all be grouped into local and remote manifestations.
To local symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis include:
- Drawing and aching muscle pains, of low intensity, intensifying after prolonged sitting, for example, when working in the office and behind a computer;
- A crunch when you move your neck. The most strongly it is felt when performing morning exercises, in the event that you plug your ears with your fingers. Then the bone conduction of sound exceeds air, and when the neck turns the crunch is heard well. This symptom indicates the appearance of osteophytes, which violate the congruence( accuracy of fit) of cartilages and vertebrae;
- Pain in the neck, as with movement( mostly abrupt).These pains are called cervicago, by analogy with the "lumbago" in the lower back, which is called lumbago. Such pain already refers to the radicular manifestations of osteochondrosis. They occur with a sharp shaking of the nerves, which occurs when laughing, coughing, sneezing, straining. This pain resembles neuralgia, and is similar to an electric shock due to its strength and suddenness. Most often it occurs in the thoracic spine;
To remote attributes include:
- Headaches with osteochondrosis. Occur discreetly, resemble a "helmet" or "helmet", often are symmetrical. Their intensity is low, they can be associated with movement, but not necessarily. Often they "pass" to the head from the nape, and accompany a sedentary lifestyle.
- Conducted sensitivity disorders. Often occur at night - waking up, a person feels that his fingers are numb. Most often these are little fingers and half of the ring finger, on the side of the little finger. To restore sensitivity, you need to move your hands, neck and change your pose.
This is due to the infringement of the roots of the cervical plexus at the points where the nerves exit. It is important that the roots are infringed for the most part by the spasmodic muscles of the neck that are adjacent to the vertebrae.
Cervical osteochondrosis, the symptoms of which we have disassembled, can be complicated by the instability of the cervical spine. In this case, the height of all intervertebral discs in the cervical region will be uniformly reduced, and the neck acquires "pathological mobility", or a tendency to the appearance of pain and various deformities during movement.
In this condition, frequent occurrence of infringement of roots of nerves arises and the risk of development of protrusions and hernias increases.
The role of muscle spasm
There is a secondary muscle spasm called myofascial tonic syndrome. This condition can occur in various parts of the spine, wherever there are striated muscles.
As a result of the decrease in the height of the intervertebral discs and the growth of marginal osteophytes, the muscles "tighten", and their blood supply deteriorates.
Accordingly, the venous outflow decreases. This situation leads to muscle edema and their chronic spasm, which is manifested by pain and stiffness in the neck and back.
Diagnosis of the cervical osteochondrosis
In typical cases, the osteochondrosis of the cervical spine proceeds with the symptoms described above. Therefore, the main stage of diagnosis was and remains the identification of patient complaints, the establishment of the presence of concomitant muscle spasm with the help of simple palpation of muscles along the spinal column.
The diagnosis of osteochondrosis can be confirmed by X-ray examination:
- "X-ray" of the cervical spine, moreover with functional tests for flexion-extension does not show cartilage, as their tissue passes X-rays.
Despite this, by the location of the vertebrae, it is possible to draw general conclusions about the height of the intervertebral discs, the general rectification of the physiological flexure of the neck-lordosis, and the presence of marginal growths on the vertebrae with prolonged irritation of their surfaces with fragile and dehydrated intervertebral discs. Functional tests allow to confirm the diagnosis of instability in the cervical spine;
- Magnetic resonance and X-ray computed tomography is shown to clarify the internal structure of cartilage and the formation of protrusions and hernias.
Thus, the diagnosis of the complication of the disease is accurately exposed, and the result of tomography is an indication for the surgical treatment of a hernia in the neurosurgery department.
Treatment of cervical osteochondrosis, preparations

Treatment of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine has always been complex: first, acute pain is removed with the help of medications, then when cervical osteochondrosis( pain decreases), physiotherapy and massage techniques join, and after relieving this aggravation, the phase of the secondaryprevention, which aims to prevent repeated exacerbations.
Sometimes a patient is given a spa treatment.
The main groups of medicines for relief of acute pain are:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs( "Xefokam", "Movalis").Stop the inflammatory component;
- Muscular relaxants of central action( "Midokalm", "Sirdalud").Reduces the tone of spasmodic muscles, reduces pain, stiffness in muscles;
- B vitamins( "Milgamma") - contribute to the improvement of trophism of nervous tissue;
- Preparations for improving microcirculation of capillary blood -( Pentoxifylline, Trental) - improve the outflow and normalize muscle function.
These drugs are administered either by mouth or intramuscularly for greater efficacy. The goal is to remove the acute pain syndrome. Then, 2-3 days later they switch to taking pills, actively apply ointments or gels, which are rubbed into the neck and back.
At the second stage physiotherapy methods are added - electrophoresis with vitamins and hydrocortisone, massage, underwater traction and Charcot's shower, acupuncture methods.
Sometimes prescribed drugs - chondroprotectors, but when they are taken inside their effectiveness is still not proven. Only the intra-articular introduction of an articular fluid substitute can reduce the crunch, facilitate movement and eliminate pain. But with osteochondrosis, this technique, worked out on large joints, is almost not used.
Operative treatment is performed with pronounced compression by protrusion or hernia of the sensory or motor spine. Indication for the operation will be non-curable, severe pain during the month that will not be treated, or progression of weakness in the muscles of the hands, widening the zone of sensitivity decrease, and confirmation of the diagnosis of protrusion and hernia with MRI or CT.
Gymnastics for cervical osteochondrosis
 Gymnastics for osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is nothing more than the rational observance of motor activity and the maintenance of a healthy lifestyle: after all, osteochondrosis occurs in all people without exception, beginning with childhood, and even here and in some cases it is considered "variant of the norm ".
Gymnastics for osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is nothing more than the rational observance of motor activity and the maintenance of a healthy lifestyle: after all, osteochondrosis occurs in all people without exception, beginning with childhood, and even here and in some cases it is considered "variant of the norm ".
Since there is no such person who, especially in adulthood, would not have signs of osteochondrosis, then the goal of gymnastics is to leave only objective, roentgenological signs of the disease, and eliminate all complaints.
It is known that even an elderly and old person can not complain about his neck and back, but only if he has given enough time for prevention.
Prevention of cervical osteochondrosis
Perhaps, on the example of osteochondrosis, one can deduce those principles of prevention that are shown to everyone, and as a result we will get the rules for a healthy lifestyle. Here they are:
- Free movement, without unnecessary burdens, exercises without load, only with the mass of your body;
- Drinking plenty of clean water, as with age, dehydration of cartilage tissue occurs;
- Conservation or normalization of body weight;
- Occupation such types of load, which reduces the load on the back( swimming);
- Discarding bad habits;Interleaving mental load with physical. Every hour and a half of mental work is recommended to change the type of activity to physical work;
- Prevention of hypothermia of the neck, back and waist, especially in the spring - autumn season.
Only when these simple recommendations are followed, the osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, the symptoms and treatment of which we have disassembled in detail, will not bother you for many years.