What is it? Otitis is an inflammation of various tissues that form the ear - depending on the localization of the inflammatory process, the forms of the disease are distinguished: internal, middle and external. Moreover, the latter option is most often encountered. To fully understand what otitis and its varieties are, it is important to consider the anatomy of the organ.
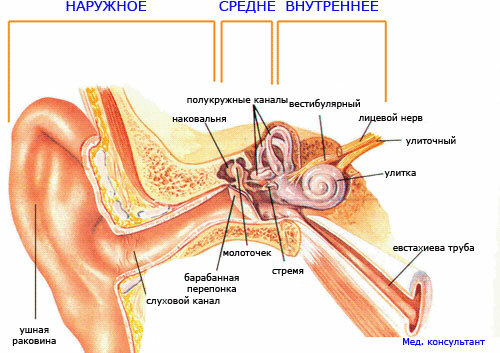
The ear is divided into 3 departments:
- outer ear;
- middle ear;
- inner ear.
The outer ear consists of the auricle and the external auditory canal. Inflammation of these structures will relate to the external form of the disease.
The middle ear is formed by an eustachian tube, a tympanic membrane and a tympanic cavity. The inflammatory process can capture all these structures, but traditionally middle otitis is called inflammation of the tympanum.
The inner ear is represented by a labyrinth. Its inflammation( labyrinthitis) is an internal otitis.
Contents
- 1 Types and causes of otitis
- 2 Symptoms of otitis in adults by disease form
- 3 Diagnosis of otitis
- 4 How to treat otitis media in adults?
- 4.1 Home treatment for adults
- 5 Prevention of otitis
Types and causes of otitis
The following external otites are distinguished:
- Inflammation of skin diseases of the auricle such as erysipelas, eczema, herpes, dermatitis;
- Inflammation of cartilage - perichondritis. Its cause is infection, more often Pseudomonas aeruginosa, when wounded;
- Inflammation in case of infection of the skin of the external auditory canal - diffuse otitis media;
- An otohematoma with infection. This extensive hemorrhage due to trauma( often observed in the mentally ill);
- Furunculosis is an inflammation of the sebaceous glands of the external auditory canal when staphylococcus or other microbes get into the roots of the hair. It often develops by combing the auditory canal and active purging of sulfur;
- Mycosis is a fungal infection of the skin when it grows mold fungi. It affects people living in damp, dusty, dark rooms.
The otitis media of the middle ear differs depending on the place of development of the inflammatory process:
- eustachiitis - inflammation of the eustachian tube;
- myringitis - an inflammation of the tympanic membrane( almost always associated with inflammation of the tympanic cavity);
- acute catarrh and inflammation of the tympanum;
- mastoiditis is an inflammation localized in the mastoid process( bone structure of the skull).As a rule, it is a continuation of otitis media with insufficient treatment.
Mean otitis, according to the nature of the course, is divided into acute and chronic. At acute, at first there is a catarrhal inflammation which then passes in purulent.
The causes of acute otitis media are quite diverse. In almost all cases, it is a phased penetration of the infection from the throat and nose with colds, flu and other acute respiratory viral infections. This is the so-called tubbar way.
First, the inflammatory process passes from the nasopharynx into the associated Eustachian tube. It is very narrow, and when the inflammatory edema develops it quickly overlaps completely, which leads to a decrease in pressure in the tympanic cavity.
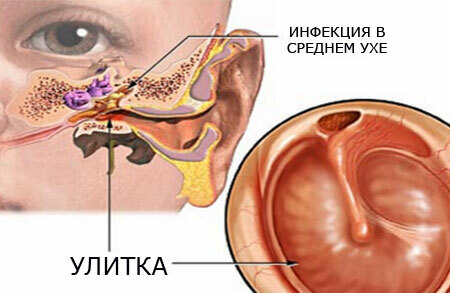
Because of this, from the blood vessels into the ear cavity begins to stretch the transudate - the liquid part of the blood. In the future, this fluid can dissolve, and can be inflated - this is facilitated by the penetration of infection from the nasopharynx along the Eustachian tube. The most common pathogens are pneumococcus and hemophilic rod.
Rarer causative factors are:
- sudden pressure drops when washing the nasal cavity with too much fluid under high pressure, strong blowing, taking off and landing the aircraft, diving to depth in diving;
- infection can be penetrated through the bloodstream of influenza, measles, typhoid fever, scarlet fever, tuberculosis, as well as trauma to the tympanic membrane;
- prolonged hypothermia in combination with a reduced response of the immune system and a general weakening of the body. This leads to otitis caused by the saprophytic microflora of the tube and pharynx, which in healthy people is not dangerous. The path of infection can be observed in tuberculosis, HIV, syphilis, diabetes mellitus.
Chronic otitis media of the middle ear can also be catarrhal and purulent.
The causes of the chronic form are:
- untreated or severe acute otitis, especially with infectious diseases: influenza, bark, scarlet fever;
- nasal breathing disorder caused by curvature of the nasal septum, adenoids, allergic rhinitis;
- decrease in body resistance, inhibition of the immune system in cases of blood diseases, diabetes, infectious processes;
- reception of drugs that depress immunity( corticosteroids and cytotoxic drugs).
The following factors can cause the introduction of infection into the labyrinth with development of internal otitis:
- chronic otitis media;
- injury;
- meningitis;
- mumps;
- syphilis.
Symptoms of otitis in adults according to

The nature of clinical symptoms and their severity depends on the course of the disease( acute or chronic) and the localization of the inflammatory process within the hearing organ.
External otitis media are characterized by the following features:
- manifestations of specific skin diseases in the form of bubbles with crusts with herpes, bright red redness in face, wetness with eczema, etc.;
- perichondritis is manifested by reddening, tuberous edema, sharp soreness of the auricle;
- diffuse form is manifested by itching of the skin, purulent discharge from the ear, painfulness when pressing on the tragus;
- othematoma looks like a soft tumor of blue-purple color, more often painless;
- furunculosis is accompanied by severe pain that spreads to the neck, teeth, into the eye area, amplified by pressure on the tragus, pulling the ear, chewing movements and conversation, and also at night, especially if you sleep on a sick ear. Upon examination, it is possible to detect an exaggeration of the skin with translucent yellow purulent contents, sharply painful when pressed;
- mycoses in the beginning are asymptomatic, with the germination of the mycelium deep into it there is a strong itch, an unpleasant smell, noise and stuffiness, mild pain, hearing loss.
Average otitis media presents a greater health hazard than external otitis media. Therefore, early diagnosis with subsequent therapy is required.
Signs of otitis in adults in the emergence of acute forms depend on the localization of the inflammatory process. Thus, eustachiosis is characterized by the appearance of noise and pronounced ear congestion.
A specific symptom of eustachyitis is autophony, in which the patient's own voice resonates in the patient's ear. If the inflammation occurs against the background of ARI, the temperature is raised, in other cases, eustachyte is not accompanied by a significant change in health and fever.
Inflammation of the tympanum is clinically divided into 2 stages: before the breakthrough( perforation) of the tympanic membrane and after the breakthrough. In the first stage appears and grows shooting pain in the ear, which extends to the temple and the crown;gradually the hearing decreases.
The temperature rise may rise to 39.0 ° C as the suppuration in the tympanic cavity develops, as well as against the background of acute respiratory viral infection, especially influenza. There is general weakness.
The second stage is characterized by a sharp decrease in pain in the ear, improves overall health, body temperature decreases. Stuffiness and discomfort in the ear persist for a while. Gradually, there is a restoration of hearing.
Mastoiditis as a complication of acute otitis media is manifested by a recurrent deterioration of the condition:
- pulsating pain in the ear and behind the ear, above the mastoid process;
- increases body temperature;
- worsens hearing.
The otitis media of the middle ear of adults, upon transition to a chronic course, is manifested by the presence of permanent serous or purulent discharge from the ear, deterioration of hearing, regular noise. At an exacerbation there is a headache and a pain in an ear, vydeleny becomes more.
The appearance of a sharp odor of the pathological secret indicates the connection of the inflammation of the temporal bone, which is a severe form of otitis - epitimpanitis.
Often this is an indication for emergency surgery;there is a serious threat to purulent lesions of the brain.
Labyrinthitis( internal otitis media) is characterized by the appearance of symptoms indicative of a lesion of the vestibular apparatus:
- by the appearance of severe dizziness, which is more often paroxysmal. It increases when the position of the head changes, sneezing;
- impairment of coordination and balance;
- nausea and vomiting of a central character.
Also noted pallor, increased heart rate and a sharp deterioration in hearing.
Diagnosis of otitis
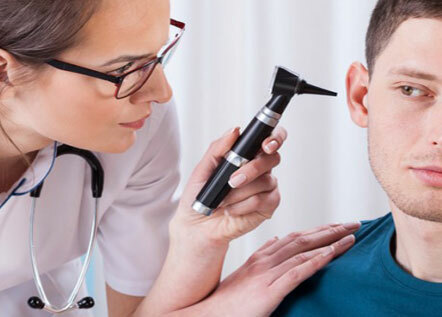
Otitis of all forms is identified based on a survey, identifying complaints and characteristic symptoms. Specific diagnosis is the examination of the ear departments with otoscopy, which is performed by an ENT doctor.
Complement this study by examining the nose, determining the severity of the hearing. Blood tests and bacteriological examination of the ear being separated( seeding) for the detection of infectious agents are also shown.
Instrumental methods use radiography, computed tomography of temporal regions.
How to treat ear otitis in adults?

When treatment of symptoms characteristic of otitis media, treatment is performed by an ENT doctor. The principles of treatment depend on the location of the inflammatory process. So, in some cases, enough drug therapy, and in others - it requires surgical intervention.
Treatment of external otitis is based on the following provisions:
- Inflammatory skin diseases of the ear are treated according to the principles of treating these diseases on other parts of the body. With herpes, antiviral ointments are used, with eczema - hormonal ointments, etc.
- With perichondritis, cold and compresses with Burov's fluid are used at the beginning, when a pus appears, surgical dissection.
- Ottohematoma - extraction of liquid with a syringe followed by tight bandaging.
- For furunculosis, antibiotics are taken from the first day, such as erythromycin, rulid, augmentin. At the same time, a tamponade of the ear canal is produced locally - laying cotton wool, dry or moistened with a solution of boric alcohol, lubricate the furuncles with iodine.
With a deterioration in overall well-being, prescribe aspirin, ibuprofen, paracetamol. Warm the ear with a "blue" lamp. The ruptured abscess is opened surgically by a small incision.
- Diffuse otitis externa means rinsing with a warm solution of furacillin or boric acid, the aural passage is lubricated with lapis or zelenium solution. Also used warming compresses with Burov's fluid, ointment with prednisolone, hydrocortisone.
If itching is prescribed sulfatiazolovuyu or yellow mercury ointment, menthol in peach oil. Polidex and Otof drops are effective. Carry out physiotherapy - UHF, UFO, especially shown in chronic course.
- Treatment of mycoses is the administration of antifungal drugs topically and inwardly. Locally, a solution and cream of clotrimazole, exotherin, lamilicol are used with preliminary purification of the ear passage with hydrogen peroxide.
Inside - nystatin, diflucan. At an itch accept suprastin, dimedrolum, zirtek, klaritin.
With an average acute otitis treatment is carried out as quickly as possible - to eliminate potential complications. Therapy consists in the initial elimination of the causes leading to ear inflammation - acute respiratory viral infection, influenza, cold, etc.
Simultaneously, a catheterization of the auditory tube is performed to purge, normalize the intra-arterial pressure and inject anti-inflammatory solutions. An air massage of the tympanic membrane is also shown.
From medicines use: otrivin, naphthyzine, galazolin, which need to drip into the nose, from the side of the patient's ear. After instillation, turn the head to the side of the affected ear. Used UHF and tube-quartz.
Treatment of otitis media without suppuration:
- Every day a catheterization of the tube is performed with the administration of hormones and antibiotics.
- Make warming compresses, laying in the external ear canal turundas moistened with alcohol and glycerin and closing the auditory hole with cotton wool soaked in Vaseline. Compress has a warming and anti-edematous effect.
- Inside is taken with paracetam, ibuprofen.
- During this period, you can use drops from otitis, in adults use drops of Otipax, Otofa, Polidex.
Antibiotics for otitis in adults add to the treatment of acute middle form with the development of purulent inflammation. The use of Augmentin has proven successful. Also effective are Rulide, Amoxiclav, Cefazolin.
Puncture( paracentesis)
If antibiotic therapy proves to be ineffective, surgical treatment is used. With an average otitis it consists in carrying out a paracentesis - a puncture of the tympanic membrane with a pronounced purulent process.
After surgery or spontaneous breakout of the membrane, catheterization of the auditory tube is performed with the introduction of hormones and antibiotics, as well as infusion of dimexide, antibiotics into the tympanum( when the drug gets to the destination, the patient feels its taste in the mouth).
After the penetration of the membrane, the use of ear drops is contraindicated. It can lead to severe pain, due to irritation of the mucosa of the tympanum.
Treatment of mastoiditis begins with the appointment of antibiotics, the use of UHF.In the absence of improvement within 1 to 2 days, surgical treatment is performed - trephination of the mastoid process. In severe conditions trepanation is carried out immediately after treatment.
Treatment of chronic form
Treatment for otitis media in chronic course is somewhat different. First of all, they are aimed at combating the inflammatory process and its consequences, and in the second - on the causative factor, becauseits role in the chronic process is secondary( in contrast to the acute course).Therefore, apply:
- washing the ear with warm solutions of furacillin, hydrogen peroxide, boric acid, aerosol oskikorta;
- washing with solutions of antibiotics with hormones;
- infusion of solutions of dimexide, atopy, quinazole, furacillin, solutions of antibiotics, protargol into the external auditory meatus;
- dusting of the ear canal with boric acid powders;
- the general antibacterial therapy is shown only at exacerbations of process and rise in temperature;
- physiotherapy: UFO, laser therapy, in the absence of pus and sprouting, polyps - UHF;
- in the occurrence of chronic purulent epitimpanitis is carried out surgical treatment.
Treatment of internal otitis is the administration of antibiotics, diuretics, vitamins. On the 6th-8th day, the disease is sanitized( cleansing).Otherwise, the risk of hearing loss is high.
Home treatment for adults
At home, otitis treatment is allowed after consultation of an ENT doctor and the setting of a final diagnosis. With medium otitis, warming compresses with vodka are recommended for 6 hours.
For this, cotton wool is impregnated with vodka or diluted with half alcohol and applied to the ear. Outside, "warm" with dry cotton wool and reinforce with a bandage.
Home treatment can complement the heating of the ear with a Sollux lamp, a "blue" lamp.
Prevention of otitis
Prophylactic measures of otitis are:
- Refusal of active and deep cleansing of the ears, which leads to mucosal trauma. Otolaryngologists recommend using cotton buds to remove sulfur from the external auditory canal without penetrating it;
- Removal of adenoids, sanation of the mouth, pharynx;
- Prevention of ARVI, influenza;
- Strengthening immunity and hardening.