White spots on the skin, especially noticeable in dark-skinned people, are an unpleasant cosmetic defect that provokes a decrease in self-esteem and consternation when communicating with other people. Vitiligo suffers up to 1% of all people.
And although this skin disease is completely unresponsive, it can signal a serious malfunction in the human body. At the same time, the possibility of transferring the genes responsible for the development of vitiligo to subsequent generations is not ruled out.
Contents of
- 1 Vitiligo - what is it? The causes of vitiligo - why do spots appear?
- 3 Symptoms of vitiligo, photo, initial stage
- 4 Vitiligo in children
- 5 Treatment of vitiligo, preparations
- 5.1 Frequently asked questions about vitiligo
Vitiligo - what is it?
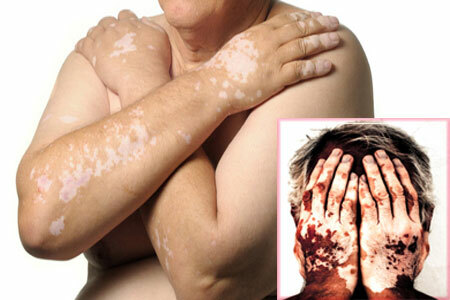
Vitiligo is a disease in which the pigment melanin completely melts in some areas of the skin, giving color to the skin. In this case, the skin completely discolored on the affected areas, which is most noticeable in dark-skinned people.
Periodic appearing spots of white and milk color have a variety of shapes and are capable of peripheral growth and gradual fusion. The hairs growing on white spots also become discolored. Any damage to the skin( cracks, peeling) is absent. Often, white spots spontaneously disappear and reappear - the disease has a chronic, recurrent nature.
Most often, vitiligo( leukoderma) first appears at the age of 10-30 years. The disease is more often diagnosed in brown-eyed people, blue-eyed and green-eyed people are less prone to this skin pathology.
Leukoderma can occur in any area of the skin, including the scalp and neck, the beard and mustache zone in men, the perineal region. On the face of vitiligo appears white spots near the nose, on the cheeks. However, most often discolored foci occur on the hands, elbows and knees. Cosmetic discomfort is experienced by those patients who have vitiligo localized on the face and exposed areas of the body.
Localization of depigmented foci distinguishes several types of leukoderma:
- Mucous - damage to the mucous membranes;
- Segmental - a lesion of the skin innervated by a separate spinal or cranial nerve;
- Focal - 1-2 white spots on different parts of the skin;
- Generalized - defeat of the face and limbs( acrofascial vitiligo), focal lesion of the skin throughout the body( vulgar vitiligo, with damage to more than 80% of the skin - total vitiligo).The causes of vitiligo - why do spots appear?
The true cause and mechanism of focal depigmentation of the skin is completely unclear. However, doctors identify several factors that have a leukoderm development:
- Autoimmune failure - the immune system starts producing antibodies that destroy melanin;
- Genetics - inheritance of the gene responsible for the development of vitiligo, does not indicate the inherent nature of the disease and does not guarantee a 100% incidence;
- Endocrine pathology - severe fluctuations in human hormonal background( diseases of the ovaries, thyroid, adrenal and pituitary) can provoke skin depigmentation;
- Violated trophism of skin - burns, traumas that start the scarring process, form foci of vitiligo on the affected areas, and the autoimmune component of the recovery process leads to the spread of pathology;
- the atony of the gastrointestinal tract and the liver - a violation of the absorption process in the intestine leads to a lack of minerals( manganese, zinc, magnesium, copper) necessary for the synthesis of melanin;
- Toxic effects - Some medicines, substandard cosmetics and household chemicals containing phenol and formaldehyde can cause leukoderma.
The impetus for the appearance of white spots can be a stressful situation, an infectious disease, intoxication( for example, in the workplace), mechanical damage to the skin( including prolonged friction), tanning, regular skin contact with synthetic tissues.
Vitiligo can occur against a background of a chronically occurring process in the human body and even in helminthic invasion.
Symptoms of vitiligo, photo, initial stage

Symptoms of vitiligo, photo
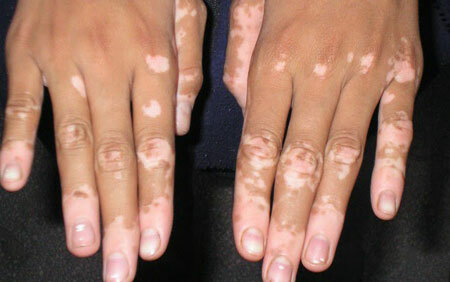 Diagnosis of leukoderma is based on the characteristic changes in the skin. Signs of vitiligo:
Diagnosis of leukoderma is based on the characteristic changes in the skin. Signs of vitiligo: - Discolored spots first pink, then milky white( less often with bluish tinge);
- The contour of rounded spots is often somewhat pigmented, which further causes contrast;
- Foci are capable of peripheral growth and fusion;
- Often, small foci of hyperpigmentation appear within the discolored spots;
- Sometimes there is a raised shaft along the edge of the spots;
- In the decolorization zone, sweating is decreased, hypo-function of the sebaceous glands is noticeable;
- Hair is discolored on affected areas;
- White spots react poorly to cold and other irritants( muscle and vascular reflexes decrease).
Several stages of the flow of vitiligo are distinguished:
The initial stage of
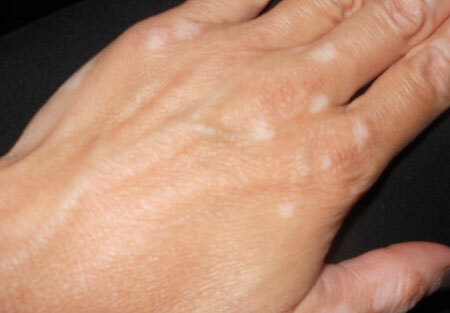
vitiligo photo the initial stage of
1-2 small spots with a size of 0.2 - 0.3 cm appear on the body. Skin discoloration spots are hardly noticeable and often remain without the necessary attention. Depending on the characteristics of the body, the disease can go to any of the following stages.
Stationary stage
The appearance of a spot for a long time does not increase in size, new foci do not appear.
Progressing stage
On the progression of the disease indicates the appearance of new depigmented spots, the growth of the emerged focus for 3 months. Sudden increase in the size of long-formed spots. The development of leukoderma can be either slow( new foci appear within a few months) or lightning( increase in the size and number of spots within a few weeks).
Stage of repigmentation
The discolored foci partially or completely restore healthy color. However, repigmentation is most often observed in the emergence of vitiligo on the basis of medication or temporary exposure to chemical agents.
With endocrine disorders in the body and chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, vitiligo spots rarely regress.
With prolonged course of vitiligo it is often observed nest alopecia( focal alopecia) and earlier graying. Scleroderma, flat lichen, various kinds of dermatitis and psoriasis are often attached.
Vitiligo in children
Leukoderm is very rarely diagnosed in children under 10 years old. Disease often affects girls in their teens. An important role is played by the increased emotionality of the child. Frequent stressful situations, negative experiences not only provoke a leukoderma debut, but also contribute to its progression.
The clinical picture of vitiligo completely coincides with the manifestations of the disease in adults.
Vitiligo in a pregnant woman does not affect the development of the fetus and does not guarantee the appearance of the disease in the newborn. White spots in a small child most often indicate the development of allergic dermatitis, multicolored lichen or psoriasis.
- These diseases from vitiligo are distinguished by the presence of peeling.
Treatment of vitiligo, preparations
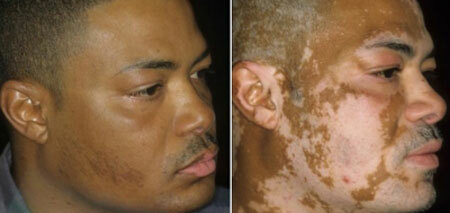
Treatment of vitiligo, photos before and after
Although sometimes cases of complete cure for vitiligo, a reliable treatment method, restoring the function of melanin synthesis and completely eliminating relapse of the disease, are registered, doctors have not yet invented. However, the treatment of vitiligo is necessary to prevent exacerbation and prevent major changes in the body.
Treatment Scheme includes:
- In case of localized form( lesion area not more than 20%) - ointments Hydrocortisone, Triacort, Esperson, Fluorocort, in their ineffectiveness appoint Sinalar, Tacrolimus, Dermovain, Elokom;
- In generalized form, tableted corticosteroids are shown: Dexamethasone, Prednisolone, Triamcinolone( with prolonged intake, they depress immunity and increase the risk of diabetes mellitus!);
- Ultraviolet therapy - narrow band( with small foci) and broadband( more effective) course of 20-100 sessions for 2-3 procedures per week;
- Photosensitizing agents( combined with ultraviolet therapy) - Beroksan, Meladinin, Psoberan, Metoksalen are prescribed for increased sensitivity to ultraviolet radiation( there are a number of serious contraindications!);
- Irradiation of foci by laser or monochromatic light - give the best result than narrow band ultraviolet therapy, the course - 20-60 sessions;
- Vitamin-mineral complexes - must contain vit. E and C, group B, pantothenic, folic and alpha-lipoic acids;
- Placental preparations( melagenin plus) - the most effective for localized vitiligo;
- Technologies of transplantation - transplantation of donor skin with activated ultraviolet pigment synthesis, melanocyte autotransplantation - not available to all patients due to high cost;
- It is compulsory to treat the concomitant pathology of the endocrine glands and the gastrointestinal tract.
Treat vitiligo at home with a diet that restores metabolism and saturates the body with iodine, iron, copper and zinc. In food, most include seafood and fish, buckwheat, walnut, legumes, figs, cherries, parsley, apricots, celery and pear.
If possible, it is necessary to exclude prolonged exposure to sun and any skin trauma.
Frequently Asked Questions about Vitiligo
Often people avoid contact of vitiligo patients due to a complete lack of knowledge of the disease. And many patients with leukoderma try to mask the skin defect with cosmetic means. Each person who has encountered( himself or in the family) with vitiligo should know the answers to the following questions.
Is Vitiligo transmitted, is it contagious?
The categorical answer is no, under no circumstances is it contagious. Vitiligo is a violation of skin pigmentation, not an infectious disease.
What is dangerous vitiligo?
Leukoderma - a sign of a serious disruption of the body. Vitiligo patients are more susceptible to the development of diabetes mellitus, thyroid pathology, psoriasis and alopecia, immune disorders. Often, this disease reduces vision( progressive myopia).
And most importantly - the inferiority complex can cause long-term depression and noticeably affect a person's personality.
What are the ways to treat vitiligo?
Most often, the basis of treatment is taken individually selected course of corticosteroids in the form of ointments or tablets.
However, the best result is achieved only with a comprehensive therapy - medication, laser therapy or UFO, taking photosensitizing drugs, vitamins and diets. A full-fledged treatment of the concomitant disease is mandatory.
Can I get rid of vitiligo, what is the duration of therapy?
To achieve the effect, a correctly selected treatment regimen is carried out for 6-12 months. However, with a long-term disease, therapy does not even have a minimal effect in 20% of patients. Spontaneous recovery occurs only in 5% of cases.