Under atopic dermatitis, otherwise called neurodermatitis, is to be understood as an allergic skin reaction due to a genetic disorder of the immune response.
An important role in the development of atopic dermatitis in children is played by insufficiently developed function of the gastrointestinal tract. It is the correction of genetics and GIT functionality that should be considered for the prevention and treatment of this disease.
Contents of
Causes of atopic dermatitis in a child
- 1.1 Stages of development of the disease
- 4 Diet for atopic dermatitis in children
- 4.1 Possible complications
- 5 Recommendations to parents
Causes of atopic dermatitis in a child
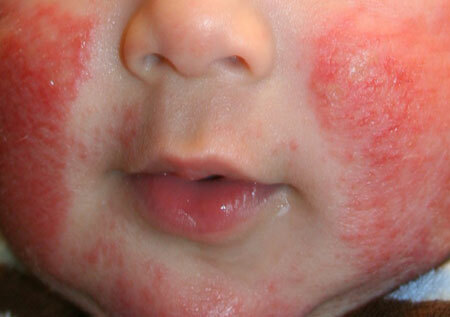
Atopic dermatitis in children, photo
Symptoms of atopic dermatitis in children are provoked by an inadequate immune response to foreign proteins against a background of genetiction predisposition( atopic dermatitis or other allergic reactions in the parents).The reason for this may be:
- excessive use of pregnant conditional-allergic products( cocoa, citrus, eggs, nuts, etc.) and the appearance of specific antibodies in the fetus;
- immaturity of the gastrointestinal tract - undigested protein fragments enter the blood, on which sensitization is formed;
- hypersensitivity to the skin and mucosa of the respiratory tract - dry climate causes dryness of the skin and mucous membranes, which provokes an increase in its sensitivity to allergens in the air, baby creams, clothes( see photo).
Once-formed antibodies cause exacerbations of the disease even without direct contact with a sensitizing agent or product.
Stages of development of the disease
Atopic dermatitis in an infant appears only after 2 months. The following stages of the disease are determined according to the age criterion and the specificity of the clinical manifestations:
- 1 stage - infantile neurodermatitis - is observed up to 2 years, characterized by pronounced inflammation, wetness;
- Stage 2 - infantile atopy - is fixed before puberty, papules are formed against the background of increasing dryness of the skin;
- Stage 3 - juvenile neurodermatitis - manifestations first appear in adolescents, and exacerbations can persecute a person and in adulthood, an inflammatory reaction replaces signs of lichenification and vascular skin disorders.
Symptoms of atopic dermatitis in children, photo

The tactics of treating atopic dermatitis in children directly depends on its symptoms and stage. At different ages, neurodermatitis gives a characteristic clinical picture.
1 stage
Atopic dermatitis in the initial stage is manifested by marked inflammation of the skin. Typical localization - skin folds( intertrigo), forehead and baby cheeks.
For this age period, characteristic hyperemia, edema and rapidly forming foci of wetness, which are then covered with dairy scabs.
Often the inflammation spreads to the scalp and neck. Strong itching can provoke scratching and suppuration of cracks. The baby is disturbed by sleep, and the slightest discomfort causes concern. Often, infantile neurodermatitis is accompanied by thrush in the mouth.
2 stage
In a child under 10 years old, the focus of the neurodermatitis is located in the skin folds behind the ears, on the delicate skin of the flexor surface of the wrist and ankle, on the neck under the nape.
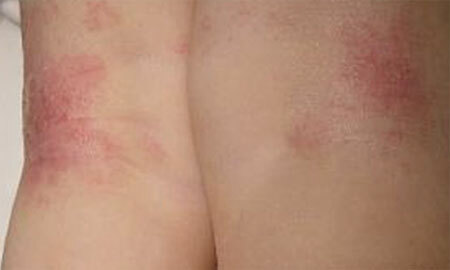
photo of the second stage of dermatitis
In this case, the pronounced dryness of the skin, expressed by ecdysis, and disturbed pigmentation( dark and light areas of the skin) comes to the fore.
The atopic face of a child: grayish dull skin, pigmented spots around the eyes, an additional crease of the lower eyelid. During this period, the condition of the child may worsen by severe allergic reactions - Quinck's edema, bronchial asthma, urticaria.
3 stage
In adolescence, the pathological changes in the skin have signs of lichenization - a focal thickening of the skin with pronounced flaking, an intensified cutaneous pattern.
Predominantly changed areas are located on the face and neck, upper limbs. In severe cases, the lesion of the skin of the trunk is fixed.
Treatment of atopic dermatitis in children
Only an allergist doctor after careful examination of the anamnesis( detection of allergic reactions in parents), carrying out special allergic tests and examining the child's blood for antibodies can make an accurate diagnosis and differentiate the neurodermatitis from psoriasis, eczema and other skin diseases.
Although atopic dermatitis is a chronic pathology, often with appropriate therapy, its symptoms disappear by the time the body grows up. However, sometimes the disease manifests itself as exacerbations in adulthood.
The therapeutic regimen for atopic dermatitis includes the elimination of allergens, diet and complex medication.
Drug therapy
Carried out by courses lasting 1-1.5 months and includes the use of the following:
- antihistamines;
- vitamins and preparations of zinc;
- immunosuppressors, suppressing the hyperactivity of immune cells;
- antibiotics( with attached infection);
- soothing;
- gastrointestinal drugs( normalization of the stomach, intestines, liver);
- corticosteroids( in severe cases, with frequent exacerbations).
Drug treatment is prescribed by a qualified dermatologist-allergist, taking into account the features of the disease course and the patient's condition.
External means
Their application is aimed at minimizing pathological skin manifestations:
- anti-inflammatory talkers;
- drying agents and antiseptics - point-wise when wetting at stage 1;
- moisturizing - with severe dryness of the skin in 2 stages of the disease;
- external corticosteroids - hormonal cream with atopic dermatitis, as well as internal corticosteroids, is appropriate only if other agents in the acute phase are ineffective and lasts no more than 1 week.
Local use of alcohol-containing liquids is strictly prohibited.
Physiotherapy
Phototherapy is especially effective in atopic dermatitis. Irradiation with ultraviolet increases the effectiveness of the use of Psoralen( PUVA-therapy).
Bioresonance treatment is also often prescribed, however, no studies of the effectiveness of this method in the treatment of neurodermatitis have been conducted.
Diet for atopic dermatitis in children
 Diet for one year
Diet for one year
Babies in this period can be given fruit purees and juices from pears, apples, currants. Safe among vegetables are zucchini, potatoes, different kinds of cabbage. In the course of complementary foods, only one new product should be introduced into the diet each week.
From cow's milk it is desirable to refuse, giving preference to natural feeding and special infant formulas, which correspond to the age of the child. From drinks you can give pure water, compotes and slightly brewed tea.
Diet after the year
The diet menu for atopic dermatitis at this age can be made more varied by including various vegetable soups, boiled lean meat( rabbit, turkey, veal), pumpkin, cucumbers, greens, rice, oatmeal, semolina, buckwheat porridge.
The choice of fruit is best spent with the attending physician, since many of them are potential allergens. Vegetables must be processed thermally - they can be boiled, baked in the oven, cooked for a couple.
Dairy products need to be removed from the diet except for a small amount of cottage cheese, homemade yogurt and curdled milk. The menu should not have sausages and sausages, preserves, eggs, fatty broths and fried foods, smoked products, honey, bright fruits( red apples, strawberries, citrus fruits).After the research on the main allergen menu can be significantly expanded.
Dietary restrictions apply not only to children, but also to the mother during breastfeeding. All products that increase the histamine content in the blood are excluded from the diet:
- smoked meat,
- nuts,
- chocolate,
- marinades,
- eggs,
- honey,
- vinegar,
- yeast,
- products with chemical dyes and preservatives.
In the menu with atopic dermatitis must prevail:
- green apples,
- cabbage and zucchini,
- lean meat,
- buckwheat groats, pearl barley and corn.
Possible complications of
Along with a cosmetic defect, atopic dermatitis can be complicated:
- Long-lasting non-healing cracks;
- Bacterial, fungal or viral infection: streptodermia, pyoderma, cutaneous candidiasis( including multicolored lichen), herpes;
- Candidiasis of the mouth( in infants);
- Atopic march in 5-7 years - severe allergic pathologies - asthma, allergic rhinitis in a child, etc.
Recommendations for parents
- Observe the optimum airflow in the children's room - + 23 ° C, 60% humidity and more.
- Elimination of allergenic things from the situation - carpets, feather pillows.
- Removal of mold in the bathroom( mold fungus - aggressive allergen).
- No pets are required: cats / dogs, birds, fish( fish food is also allergenic).
- Revision of washing powder, soap and detergent to exclude sensitization.
- Children's clothing is only cotton.
- Hypoallergenic child care products - lanolin or baby soap without chemical flavors, neutral moisturizers.
- Preservation of the child's psychological rest, exclusion of scratching.
- Vaccination only for a healthy baby.
- Treatment of helminthiases and chronic tonsillitis.