Sometimes, in the kidneys, under the influence of certain factors, multiple or single fluid cavities are formed that can be located in any renal department. The kidney cyst - this is the name for such formations, is usually formed due to the clogging of the nephron tubule.
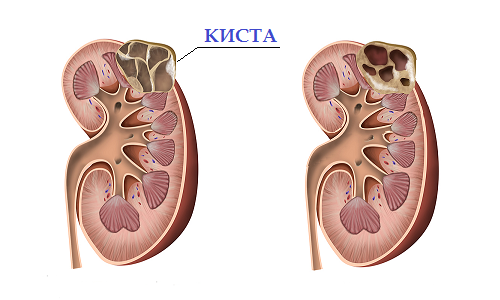
In general, the renal cyst is a benign tumor-shaped cavity of a rounded shape, inside which is a slightly cloudy or clear liquid. The cyst is limited to a capsule with thin walls that are formed from connective tissue cells. Such a disease is acquired or inherent in nature. In a number of cases, the kidney cyst is associated with a congenital renal anomaly, in which several similar formations appear in the parenchyma of the organ. Then kidney polycystosis is diagnosed.
As the pathology of
appears In the cystic walls there are no pain receptors, therefore, formation is usually not manifested. Although in general the kidney cyst is manifested in accordance with its size. At small sizes the development of renal cystosis passes unnoticed, without any characteristic symptomatology. With the growth of tumor formation, its pressure on the pelvis or ureter starts, which is accompanied by certain symptoms. This may be aching tenderness, heaviness or a feeling of discomfort in the lumbar region. Localization of the pain syndrome is caused by the location of cystic education.
Often, a characteristic feature of the pathology are frequent exacerbations in the form of inflammatory processes in the calyx, pelvis and other kidney tissues. Similar pathological conditions are manifested by fever and chills.
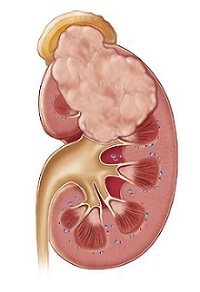 If the kidney cyst reaches a large size, it leads to abnormalities of the urine flow and causes stagnant urine in the tissues of the kidney. This circumstance predisposes to the emergence of all sorts of secondary infections. Then to the main symptomatology signs like fever and rising temperature, chills and weakness are added. At the same time, pain sensations often radiate into the genital area and groin. Secondary infectious processes are often manifested by cloudiness of urine or changes in its hue. Often infectious processes develop not in the renal parenchyma, such complications can appear in the cystic cavity. Then in the inflamed formation begins an abscess, which is characterized by an acute pain syndrome, a rapid urination process, accompanied by painful sensations, and an increase in temperature.
If the kidney cyst reaches a large size, it leads to abnormalities of the urine flow and causes stagnant urine in the tissues of the kidney. This circumstance predisposes to the emergence of all sorts of secondary infections. Then to the main symptomatology signs like fever and rising temperature, chills and weakness are added. At the same time, pain sensations often radiate into the genital area and groin. Secondary infectious processes are often manifested by cloudiness of urine or changes in its hue. Often infectious processes develop not in the renal parenchyma, such complications can appear in the cystic cavity. Then in the inflamed formation begins an abscess, which is characterized by an acute pain syndrome, a rapid urination process, accompanied by painful sensations, and an increase in temperature.
If the festering and inflamed cyst of the kidney is broken, then the clinical picture is supplemented by signs of an acute abdomen:
- Abrupt tension of the anterior wall of the peritoneum;
- Pain syndrome is localized in the region of the waist and the entire abdomen.
If the renal cystosis develops for a long time, then this course is accompanied by symptoms of chronic failure: hematuria( the presence of bloody impurities in urine), hypertension, an increase in the volume of excreted urine, the amount of which gradually comes to naught.
For congenital renal cysts, development is more common( in mature or even retirement age).
Warning! If a suspicious symptom is found, immediately consult a urologist who will prescribe the proper examination and the necessary diagnostic procedures.
A characteristic for pathology is the tendency to frequent relapses of genitourinary infectious diseases. Cystic kidney affected by a cyst is prone to hemorrhages, a growing cyst can put pressure on the organs located next to the kidney. If the liquid accumulates in the kidney, it adds weight, which is manifested by painful heaviness and the presence of protein, red blood cells and white blood cells in urine. When palpation, a certain densification is felt in the retroperitoneal cavity, arising in connection with the growth of the organ affected by the cyst. Although it is possible and asymptomatic development of pathology, when the patient learns about it by accident, when ultrasound passes.
Causes of development of renal cystosis
 The kidney is a whole complex of different pipes, through which the liquid moves continuously. When, under the influence of pathogenic factors, some of the pipes overlap, then under the pressure of blood it expands. A cavity with a liquid is formed in the tube, which later forms into a renal cyst. Usually, according to this scheme, a simple or solitary cyst is formed. In general, the main cause of cystic formations is the pathologically rapid growth of epithelial cells in the renal tubules, which is facilitated by various parasitic and infectious pathologies, injuries and heredity, etc.
The kidney is a whole complex of different pipes, through which the liquid moves continuously. When, under the influence of pathogenic factors, some of the pipes overlap, then under the pressure of blood it expands. A cavity with a liquid is formed in the tube, which later forms into a renal cyst. Usually, according to this scheme, a simple or solitary cyst is formed. In general, the main cause of cystic formations is the pathologically rapid growth of epithelial cells in the renal tubules, which is facilitated by various parasitic and infectious pathologies, injuries and heredity, etc.
There are many factors contributing to the development of pathology, but all of them are divided into primary and secondary. If the kidney cyst is congenital, the factors that determine it are related to the genetic apparatus, since cases of familial disease are frequent, when renal cystosis is observed in several generations in a row. Often congenital pathology is caused by infectious or traumatic factors affecting the fetus in the phase of embryonic development. Many experts believe that renal cystosis can develop in the presence of congenital connective tissue disorders. In this case, it is rather difficult to determine whether a pathology belongs to a particular group( acquired or congenital form).
That's interesting! According to statistical data, the formation of renal cystosis is more likely than others for patients over 50 males.
Acquired disease most often has an infectious etiology when the kidney cyst is formed due to a recent inflammatory or infectious process in the calyx or kidney parenchyma( pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, urolithiasis, kidney tuberculosis, prostate adenoma, hemodialysis).Often the cause of the occurrence of cysticosis is any trauma, which resulted in the formation of parenchyma hematoma. The hereditary pathologies such as Hippel-Lindau disease( cystic formations in the brain, liver or eyes) or tuberous sclerosis( a tendency to benign tumorous formations) can also act as a cause of renal cystic disease. Today there is no strictly formulated classification of the causes that cause the development of cystosis in the kidneys, therefore, from the whole variety of theoretical assumptions, everyone has the right to exist. Because of this, prevention and selection of therapeutic measures are significantly complicated.
Classification of the disease
The kidney cyst can develop in various forms. An important distinction of such cystic forms from each other are intracavitary septa - in simple cysts they are absent, and if the cyst refers to complex forms, there are partitions inside it, the presence of which increases the risk of malignancy of the formation. In addition, renal cysts are single or multiple.
Among the individual forms also distinguish:
- Spongy form - pathology of a hereditary nature, characterized by a special structure of kidney tissues, similar in structure to the sponge;
- Parapelvic cyst - the kidney cyst is located in a dangerous proximity to the pelvis;
- Multicystosis - a similar pathological form is manifested in that it looks like a brush of grapes and consists of a number of bubbles filled with liquid;
- Dermoid formation - this cystic form refers to congenital pathologies and is characterized by ectodermic contents like epidermis, teeth, hair, fat or bones, etc.
According to the nature of the fluid filling the cyst, the formations are divided into infected, serous( solitary) and hemorrhagic. The contents of the infected cyst are rich in pathogenic microorganisms, the liquid in the formation of serous character is characterized by a yellowish tint and transparency, and the contents of hemorrhagic formation contains bloody impurities, since such a cyst is formed due to hemorrhage. In a solitary( serous) cyst, a syphonic or purulent mass may be present. The kidney cyst is also classified according to localization. If the cystic formation is formed in the cortical layer of the kidney, it is called cortical. In the kidney tissues a parenchymal cyst is formed. Near the pelvis appears okololohanochnaya, and under the renal capsule - subcapsular cyst. All varieties of renal cystic lesions are divided into several categories:
- Category I is probably the most common category, including benign, simple cystic formations that are easily diagnosed by MRI or ultrasound. Usually they differ in the small size and absence of symptoms;
- II category - education, with some structural changes like partitions, as well as infected, calcified and hyperdense cysts;
- III category unites cysts prone to malignancy. Such formations are characterized by poor limitation( on ultrasound images, MRI), have thick septa and an external capsule, are treated with removal;
- IV category are cysts that are characterized by a large amount of fluid and have an uneven surface. On x-ray examinations, these formations accumulate a contrast agent in themselves, which indicates the malignant nature of the cyst. Such formations must be deleted.
Therapeutic measures
Pharmaceutical preparations can not make so that the kidney cyst completely resolves, they will only alleviate the symptoms and improve the patient's condition a little. To this end, patients are prescribed drugs that reduce blood pressure and stop the pain syndrome, as well as remedies that eliminate infectious processes and symptoms of urolithic pathology, restoring the salt balance.
If the cystic formation is due to a genetic etiology, the kidneys of the patient lose the ability of urinary concentration, so they have a water imbalance. Such patients need to drink at least two liters of fluids per day. Patients usually have hypertensive signs, so they are shown drugs that reduce blood pressure, ACE inhibitors. With the development of the infectious process, long-term antibiotic therapy with penicillin and cephalosporin series, as well as aminoglycosides( tetracycline, ciprofloxacin, erythromycin, levomycetin, etc.) is prescribed. Because such cystic forms are accompanied by excessive edema, patients need to minimize salt intake and take diuretic drugs.
Among surgical methods, laparoscopic removal is considered to be the most gentle, minimally invasive method that does not cause complications.
If the kidney cyst is an acquired pathological condition, then complete rest with bed rest is shown. With minor bleeding, it is necessary to take anesthetic medication. In the case of joining the infectious process( enterobacterial or staphylococcal inflammation), antimicrobial treatment and surgical intervention are resorted. With a small size of the formation, cystic drainage is carried out followed by sclerosing. From the cystic cavity, the contents are sucked through the needle and filled with a sclerosing substance( alcohol, etc.), which adheres the cystic walls.
This therapeutic technique is considered to be the most effective and sparing today. If the formation develops to a considerable extent, surgical removal is applied, which is done by percutaneous or laparoscopic method.


