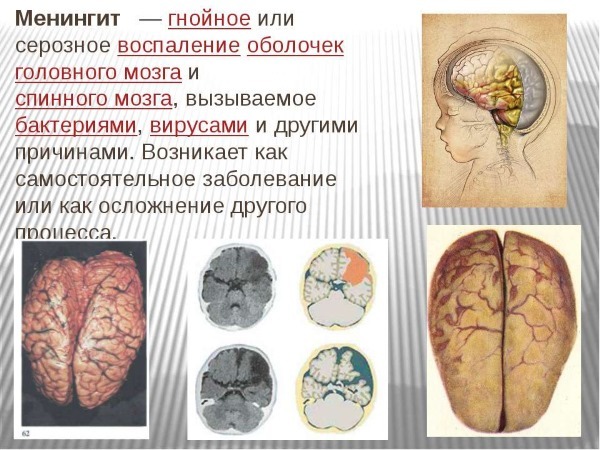
Serous meningitis - a disease characterized by inflammation in the cerebral cortex. Upon detection of the symptoms must be urgent examination and treatment. Meningitis in children is more common than in adults, but in any age the disease is extremely difficult. The probability of a full recovery, with no consequences for this form of meningitis is more than 80%.
The content of the article:
- 1 The causes of serous meningitis in children
- 2 transmission path
- 3 Symptoms of serous meningitis
-
4 Clinic of certain forms of serous meningitis
- 4.1 Acute lymphocytic choriomeningitis
- 4.2 tuberculous meningitis
- 4.3 Fungal meningitis in AIDS
- 5 Serous meningitis in mumps
- 6 incubation period
- 7 The primary diagnostic methods
- 8 Specific methods of diagnosis
- 9 Serous meningitis treatment
- 10 Rehabilitation
- 11 Prognosis and complications of serous meningitis
- 12 Video of serous meningitis
The causes of serous meningitis in children
Serous meningitis began to develop after the pathogen enters the body. It can be viral, bacterial and fungal origin. But what would be the nature of occurrence of the disease in the course of the disease does not occur dying brain cells and pus formation. Therefore, this type of meningitis, while timely and correct treatment, leaves no complications.
The most common pathogens:
- enteroviruses and adenoviruses;
- mononucleosis pathogen (infectious);
- herpes infection;
- influenza viruses and measles;
- bacteria of tuberculosis and syphilis (less common).
- fungal pathogen (happens very rarely).
Meningitis is not always infectious nature, sometimes its development can be triggered by, the process of tumor or cyst in the brain. In this case, the child is not contagious.
If the disease is contagious nature, the infection does not always occur in contact with the pathogen in the body.
Development of meningitis can occur if the child:
- Immunity greatly reduced. This may be a result of disease, congenital immunodeficiency or prematurity.
- Complication of infectious diseases.
- Violation of the functioning of the brain.
- Generic or personal accidents.
In newborns may be infected in the womb. Once infected, the disease develops rapidly and requires medical treatment in a hospital. Importantly, it is not necessary to begin treatment on their own. In meningitis for the successful outcome of the disease is important every hour.
transmission path
Meningitis is developed after exposure of the pathogen into the body and further into the cortex. The infection can occur in several ways. Depending on how the infection occurred, will depend on the speed of disease development.
Ways of getting a virus, bacteria or fungus:
| The main ways of infection | How do you get infected | notes |
| Contact | Infection enters the body in communication with the carrier through a handshake kissing | When this infection may develop disease within the first 3 days |
| Domestic | The causative agent settles on the surrounding objects and products by sneezing patient. With them she had ingested a healthy baby | At observance of hygiene measures can prevent infection. If they are absent, then the disease will manifest itself not later than 10-14 days |
| Air | When chihe and cough virus can get directly into the airways | The symptomatology may appear within 2 weeks |
| Water | Infection may be in the pool and the water is populated when ingested in the body | The disease can make itself felt within 3 days |
| Infection | When viral, fungal or bacterial pathogens may be through the blood vessels, together with the blood get to the brain, it will be the beginning of the disease | Depending on the degree of severity of primary disease (that is the cause of meningitis) depends on the rate of development of inflammation in the brain. |
| Animals and insects | On the subject of on food or other signs of infection may be transferred to the legs of insects may enter with animal fur. Pets are also susceptible to the disease and can be sources of infection. Also bloodsucking (mosquitoes and ticks) may be carriers of infecting and stings | Upon infection by the bite of the first meningitis symptoms manifest within 6 hours after infection |
| through blood | If improperly disinfection of instruments in a hospital or poor blood test, the agent can get through blood transfusions, treatment of teeth, in the capture assays of the vein. And also in contact with the virus into open wounds in the production of scratches or abrasions. | The infection quickly reaches the localization and the first symptoms during the first day. |

The disease is difficult to avoid. Since the sick person can be contagious from the time of infection, but the symptoms it may not appear for 14 days. All this time, he will be the distributor of the disease. But hygiene measures (clean hands and fruits) reduces the risk of infection.
Symptoms of serous meningitis
Aseptic meningitis (symptoms in children varies depending on the type of disease) in the first days of the manifests pronounced symptoms. Although no full survey can be confused with the occurrence of severe cold.
The main symptoms of serous meningitis:
- High temperature 38-40 degrees, which is accompanied by fever, delusions and hallucinations. Sometimes the temperature can be reduced without the use of drugs and to rise again to a high point. Medicines do not help to reduce the temperature.
- Dizziness and headache, which is localized in the forehead and temple. Painkillers are not able to reduce it.
- Pain in the eyes. When moving the pupils a sense of enhanced and increased headaches. The child becomes easier in a darkened room.
- Hearing loss with tinnitus and a feeling muted.
- Disrupted the functioning of the digestive tract (vomiting, diarrhea, occur after abdominal pain).
- Children with nezarosshim fontanel is its swelling.
- The child becomes restless, not sleeping, perhaps the appearance of cough and cold.
- The hallmark is throwing the head back and pressing his knees to his stomach. Kid is located in the lateral position.
The child's age affects the brightness of the symptoms. Toddlers up to 3 years, virtually no immunity, so the signs are clearly expressed and appear quickly.
To clarify, it is a disease of meningitis, or it may be that disease during additional tests:
-
symptom Lesage. Kid in a suspended state (it has to be kept under the armpits) begins to pull his legs to his stomach in a bent position.
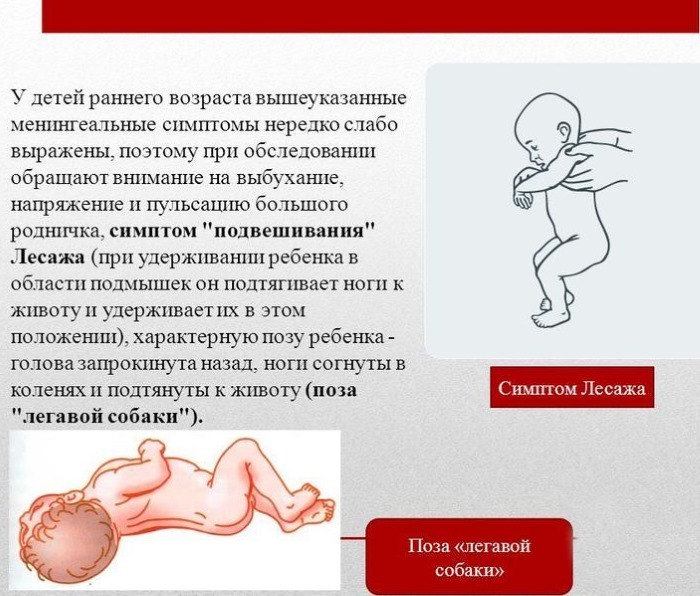
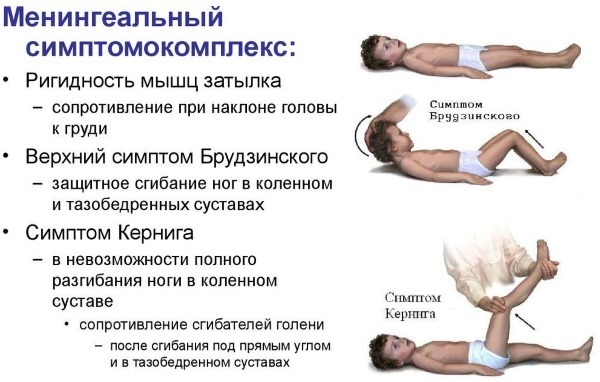
Serous meningitis - a dangerous disease. Symptoms in children can be defined in different ways. - symptom Kernig. The child does not straighten the raised leg (it is at an angle of 90 degrees).
- symptom Brudzinskogo. When straightening the first leg, the child automatically flexes more second. Or pressed against his chin to his chest the baby immediately flexes his feet.
- symptom spondylitis. When stroking the front of the arc occurs contraction of facial muscles.
- symptom Pulatova. When lightly pressed in the parietal or occipital area, there is a strong pain.
- symptom Mendel. When light pressure near the temporal region, and pain.
If the tests are carried out and give a positive result has the above symptoms, you should immediately call the emergency care. Treatment will be assigned after complete examination and identification of the pathogen.
Clinic of certain forms of serous meningitis
We have examined the major signs of the disease. But the disease can occur in several forms. To correct destination therapy specialist must find out what kind of meningitis. It can be pre-determined by additional symptoms.
Acute lymphocytic choriomeningitis
Aseptic meningitis (symptoms in children with lymphocytic choriomeningitis infection and disease progression in an acute form expressed clearly) in this case develops due to the mice. They distinguish infection with mucus, urine and feces.
The agent may be in the product, the water and on objects.
Upon infection, the child is not only an inflammation of the meninges, also disrupts the blood vessels of the brain ventricles. The disease is similar to the occurrence of influenza. The difference is a positive response to additional tests (Lesage, Kernig).
The disease usually occurs with 2 stages. Initially, the symptoms of influenza appear, then the condition becomes much worse, and there are all the signs of meningitis. With timely handling in the hospital, the treatment has a favorable outcome.
tuberculous meningitis
Tuberculous meningitis develops due to ingestion of Koch's bacillus. In most (over 75%) is a complication of pulmonary tuberculosis, kidney, genital. The pathogen enters the brain through the blood vessels. Risk of disease is that during TB treatment meningitis can become chronic.
Brightness symptoms appear in 14-21 days after the onset of illness. To the basic symptoms added malfunction of the optic nerve (decreased vision, strabismus, hurt one's eyes). If there is no proper treatment is started at this point in the week, it may lead to death.
Fungal meningitis in AIDS
Serous meningitis caused by fungi in the presence of the AIDS patient, often stale and almost without symptoms.
In children, the main symptoms are lethargy, somnolence, headache tolerant.
Explicit symptoms of meningitis often absent. Accurate diagnosis pediatrician can supply following a complete examination.
Serous meningitis in mumps
Meningitis often develops on the background of infectious diseases of bodies which are not accompanied by purulent complications. Symptomatology meningitis may be intertwined with the features of the original disease. Or appear before the symptoms of the underlying disease.

When mumps pronounced symptoms of meningitis (temperature up to 41 degrees with intolerable headache, cramps). Fever and severe headache are not amenable to reduction. Self-treatment is contraindicated. Only pediatrician can prescribe a comprehensive treatment of meningitis and the original disease.
incubation period
Aseptic meningitis (symptoms in children can occur after 3 hours after infection, or 3 weeks) It has a different incubation period, which depends on the type of disease and the immune status in child.
The latent period of meningitis in various forms of flow:
| form of the disease | The incubation period (days) |
| Acute | 5-12 |
| tubercular | Up to 21 |
| Fungal AIDS | Up to 21 |
| In mumps | Up to 30 |
The incubation period in children can occur completely asymptomatic. Sometimes parents can note the weakness of the baby, irritability and poor sleep. After the end of the latent period of the disease symptoms evident.
The primary diagnostic methods
When you call in a specialist hospital performed the initial examination of the child. From the words of the parents found out symptoms (headaches, vomiting, psychological state). Performed additional testing (Lesage, Kernig).
The temperature is measured and evaluated by the general condition of the child. And his response to sounds and light.

Complete diagnostics with a primary inspection may not be possible. Since the purpose of treatment is necessary to identify the cause of the disease and the causative agent. As well as the primary diagnosis is not always possible to carry out full, sometimes a child may be in an unconscious state, making it difficult to conduct tests and medical history. To this end, the pediatrician is assigned a specific diagnosis.
Specific methods of diagnosis
For approval or denial therapist disease is assigned a set of procedures. Since the treatment of meningitis must be installed, which was the root cause of the disease. If it is a complication of an infectious disease, as long as it is not eliminated, the therapy does not bring positive results.
General diagnosis of serous meningitis:
- Investigation of cerebrospinal fluid. This type of diagnosis helps to determine the presence of 90% and meningitis pathogen. During the procedure, the composition is determined not only material, but also its rate of leakage from the needle. To determine infection resulting liquid dye reagents, and sent to the crop. The procedure can not be performed if there is damage to the skin in the area of the fence, cramps and the critical condition of the child.
- To diagnose the disease and taken the throat mucus. On it is possible to identify an inflammatory process, as well as the causative agent. But this type of procedure is not 100%.
- Total and complete blood count.
- Urine and feces help identify the source of the disease if the infection has spread from the digestive tract or urinary canal.
- MRI or CT scan of the head. With it, it is determined which zones are involved and how strongly marrow.
-
Echoencephalography and electroencephalography. When carrying out their activity in the brain is determined.

- Fundus examinationAnd determining the functioning of the optic nerve. Normally the reaction to light, the pupil becomes narrower, and moves following the movable object. In meningitis the pupil does not show any reaction.
- head x-ray. Especially necessary if meningitis began to develop as a result of head injuries.
- Checked for the presence of skin rashes. It may indicate measles disease.
Pediatrician determined by a set of necessary procedures. With the right combination, it turns out, completely determine the type of disease and pathogen. Only after that it will be assigned to treatment with the selection of the right medication.
Serous meningitis treatment
Serous meningitis symptoms in children who have been described above, lends itself only to medical treatment. Traditional recipes improvement will not bring, but can lead to the death of a child. The therapy is carried out only in a hospital ward in separately allocated. When a serious condition requires constant monitoring, this patient was placed in the intensive care unit.
Depending on the cause of the disease and the causative agent can be assigned to drugs:
- Antibiotics. If the disease is bacterial in nature. They destroy pathogens and prevent their growth and reproduction: ceftriaxone; amoxicillin; tseftizidim.
- Antiviral agents, when viral pathogen. Depending on the type of virus, there is the selection of medications: acyclovir; interferon; arpetol.
- When the fungal infection are appointed antifungals: fluorocytosine.
- To reduce the heat required intake of antipyretics paracetamol; ibuprofen.
- In the presence of seizures, you must take medications: diazepam; detomidine; seduksen.
- For removal of headaches and aching joints required reception analgesics. In conjunction with the general therapy, they help to stabilize the patient's condition: analgin; Nospanum; Drotaverinum.
- Because loose stool and vomiting may occur dehydration. To prevent it is necessary to restore the water-salt balance with regidratov: rehydron; saline.
- To speed up the withdrawal of the infection from the body requires use of diuretics. It will also reduce the swelling of the limbs and organs: furosemide; acetazolamide; Lasix.

- Medications for the restoration of the digestive tract. For preventing vomiting and watery stools: smectite; polisorb.
- After recovery, you need to drink vitamin complex to raise the immune system: immunoglobulin.
- If the disease is caused by tuberculosis, requires reception: ftivazid; isoniazid; rifamlitsin.
antihistaminic drugs (Suprastinum, fenistil, zodak) are assigned to reduce the likelihood of an allergic reaction and reduce the temperature of acceleration. The recovery period are assigned means to restore brain health and stress relieving (glycine, pirotsetam).
Therapy takes place in a darkened room, until a crisis passes, required bed rest. If the child is in serious condition, the necessary drugs are administered by injection and intravenous lines. While improving the appointed suspensions and tablets.
Rehabilitation
As long as the child is not a positive trend of recovery has been marked, the treatment will take place in a hospital. After stabilization pediatrician may allow dolechitsya at home. It is necessary to strictly observe all appointments and keep taking medicines for hours.
After recovery, the child will be under the supervision of a neurologist to 2 years.
If there were complications to other organs, it is necessary to monitor and other specialists (a gastroenterologist, a cardiologist). During this period, you must take immune-boosting drugs, stick to your diet. Also banned heavy physical exertion and long being under direct sunlight. In compliance with all measures a full recovery is recorded after 2 years.
Prognosis and complications of serous meningitis
With timely detection of the disease and the treatment delivered correctly, the disease progresses without complications. Child after recovery returned to normal life. But if the disease was hidden and was not immediately recognized, it can stay the consequences of meningitis. The most dangerous is fatal. He most often occurs at untimely treatment of tuberculosis forms.

Complications from the disease:
- paroxysmal headache;
- sleep disturbance, up to insomnia;
- impaired perception of new information;
- loss of vision and hearing;
- delays in psychological development;
- seizures;
- loss of coordination, and involuntary contraction of muscle groups.
Subject to all conditions in the rehabilitation period, complications can be stopped after 5-6 years after recovery. To this end, in addition to watch specialists and carry out the necessary therapeutic games and physical activities.
Serous meningitis is most dangerous in children up to 1 year. But because the symptoms pronounced, the disease is impossible to miss. Parents should monitor their condition in children after serious illnesses. If you suspect meningitis, call the emergency care.
Author of the article: Svetlana Kotlyachkova
Registration of the article: Lozinski Oleg
Video of serous meningitis
doctors advice about the disease aseptic meningitis:



