CT scan allows you to get a complete picture of the work and state of the human body. This is one of the modern diagnostic methods by which all organ systems are examined.
Record content:
- 1 Computed tomography what is it?
- 2 The principle of operation of the tomograph
-
3 Types of computed tomography with and without contrast
- 3.1 Multispiral CT
- 3.2 CT with 2 radiation sources
- 3.3 Angiography
- 3.4 PAT
- 3.5 Contrast enhancement
- 4 What organs are examined by computed tomography?
- 5 Indications for tomographic examination
- 6 Contraindications and side effects
- 7 Preparation and conduct of the survey
- 8 Decoding the results
- 9 Which is better - CT or MRI?
- 10 Why shouldn't CT scan during pregnancy?
- 11 How often can tomography be done?
- 12 Cost of CT diagnostics
- 13 CT video
Computed tomography what is it?
Computed tomography is an instrumental type of diagnosis based on the passage of X-rays through the patient's body. Unlike conventional radiography, CT allows you to obtain a volumetric image (cut) of the area under study. Diagnostics is performed using a special device - a tomograph.
The principle of operation of the tomograph
The very first tomographs were of a sequential type - the patient was placed in a machine, then X-rays scanned a part of the body. Then the table with the patient was moved and a second picture was taken.
For an informative result, you need a lot of images, so the procedure on a sequential tomograph today it is almost not used due to the long time of the procedure and the large number radiation.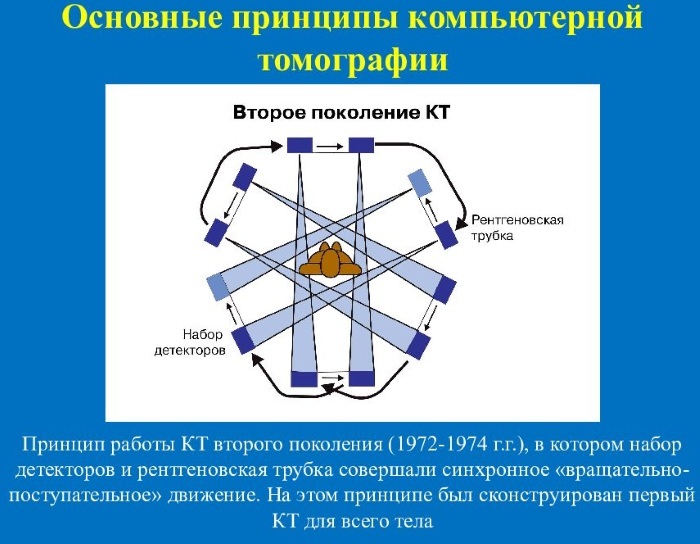
Most often, spiral tomographs are installed in clinics, which allow you to obtain an image in a shorter time and, due to this, minimize the amount of radiation.
A spiral tomograph is a large square or rectangular apparatus, in the center of which there is a tunnel - a patient is placed in it on a special moving table in a supine position. The tomograph is equipped from the inside with sensors and an X-ray emitting tube - it rotates 360 degrees around its axis and shines through the patient's body.
Next, the image is formed:
- X-rays penetrate the tissues of the body and reach the opposite part of the ring, where the detectors are located.
- Due to the fact that X-rays pass through layers of tissues of different density and thickness, the detectors capture the strength of the energy of the beam and the angle at which it was sent.
- The information received is collected and analyzed by the central processor of the tomograph (most often it is located in another room with the control panel).
- The photographed tissue sections are formed into a complete volumetric image.
- The result is recorded on a CD or other medium, and then the doctor decrypts the results of the study.
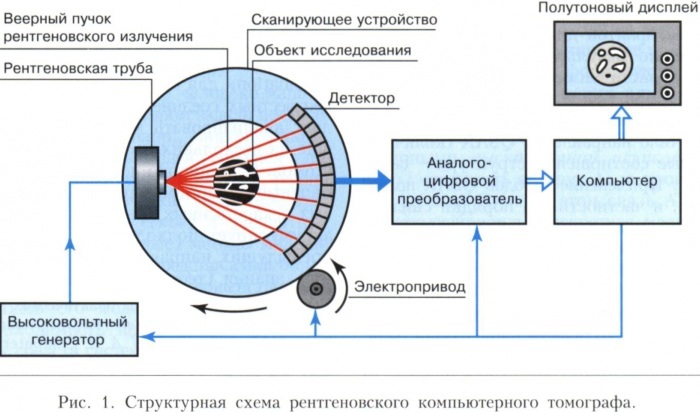
The principle of operation of a computed tomograph
The doctor performing the procedure regulates the rotation speed of the tube, the radiation power, and the movement of the table. The specialist is sure to be in another room, but he fully coordinates the entire scanning process.
Types of computed tomography with and without contrast
Computed tomography is an extensive diagnostic method that has several types. They have the same principle of operation, but differ in the way they are carried out.
Multispiral CT
A multislice (multislice) tomograph has several rows of detectors, allowing to obtain up to 300 images of the examined area per 1 revolution of the X-ray tube and examine up to 64 layers fabrics.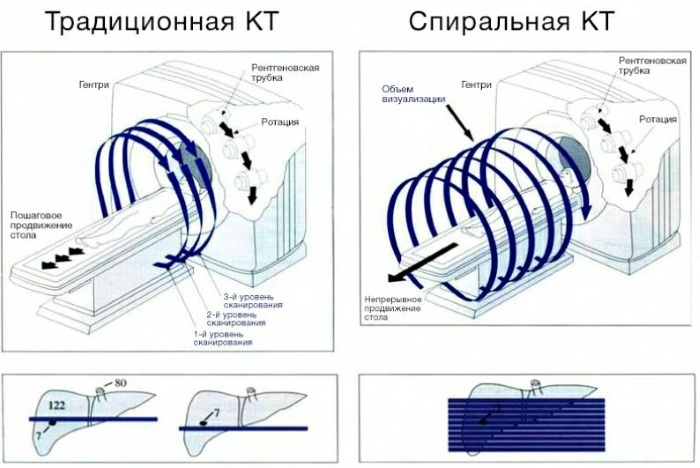
This makes it possible to significantly reduce the time of diagnosis and the amount of radiation exposure of a person and to obtain a more detailed image. Most often, multispiral computed tomography is performed for acute injuries and urgent cases.
CT with 2 radiation sources
The tomograph with 2 radiation sources belongs to the types of multispiral CT. It was developed for examining moving objects (heart) in order to assess the functioning of the organ in a state of movement and rest.
Since the period of time in which the heart muscle is at rest is only a few milliseconds, then one the X-ray tube is not able to capture this moment, and for this they use a tomograph with 2 tubes working with a small time difference. A tomograph with 2 sources of radiation allows you to accurately determine the presence of pathologies of the heart and nearby vessels.
Angiography
Angiography is a method of vascular contrast examination. To do this, a special contrast agent is injected into the patient's vein (most often it contains iodine) and a tomographic examination is performed.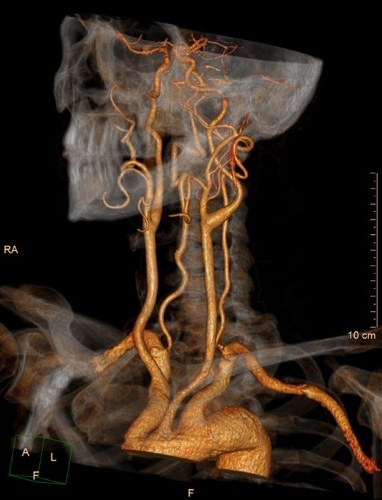
This method allows you to assess the state of the coronary and peripheral vessels, to identify the presence of blood clots and other pathologies of the vascular system and heart. Also, angiography is used to examine the vessels of the internal organs.
Before the angiography, the patient is prescribed a biochemical blood test to identify the presence of some contraindications. Additionally, consultations of narrow specialists may be required.
PAT
Positron emission tomography involves the use of radionuclide drugs and the registration of the radionuclide in body tissues. This method does not give an idea of the structure of the organ, but it allows you to determine its functioning. At the same time, the radiation dose will be slightly higher than during conventional tomography.
The essence of PET is to monitor the body's metabolism in almost real time. The patient is injected with a radioactive substance that is absorbed by tissues with a very high metabolic rate - cancerous.
After absorption of a radionuclide, pathological cells emit gamma rays, which are recorded by a tomograph. After that, the computer processes the received data and shows in which area of the body the changed cells are located.
With the help of PET, it is possible not only to detect cancerous tumors, but also to reveal metastases.
Contrast enhancement
The introduction of a contrast agent, which tends to accumulate in tissues and make them more visible for radiation, allows you to better visualize the internal organs and structures of the body and more accurately determine their structures and borders. Additional contrasting during CT is used to detect cancer tumors, kidney and gallbladder stones, and blood clots.
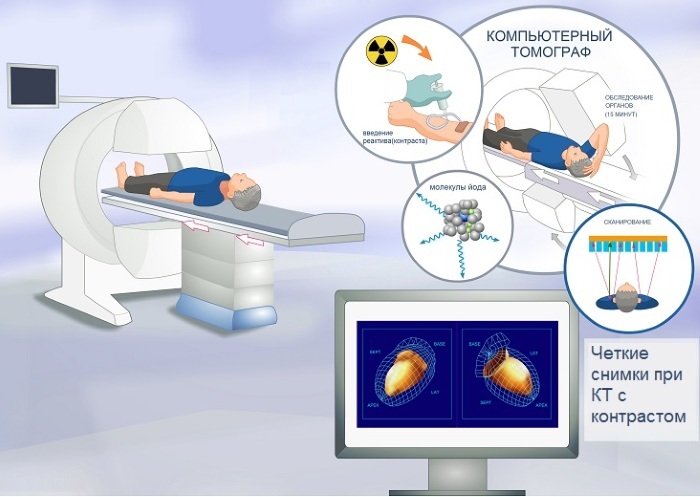
As in the case of angiography, a blood test and consultation of narrow specialists are prescribed before the CT scan with amplification.
What organs are examined by computed tomography?
Computed tomography is a detailed method of examining almost all organs of the human body and detecting many diseases:
| An organ or area of the body | What can be identified |
| Brain and Skull | Tumors, strokes, vascular pathologies, traumatic brain injury. |
| Temporomandibular joint | Oncological diseases, diseases of teeth and jaw, trauma. |
| Chest organs: heart, lungs, esophagus, mammary glands | Tumors, lymph node pathologies, inflammatory diseases, pathological changes in the structure of organ tissues. |
| Abdominal and pelvic organs (digestive tract, pancreas, liver and biliary organs, spleen, kidneys and bladder, reproductive organs) |
|
| Spine and joints | CT allows you to accurately determine the presence and degree of development of a disease of the musculoskeletal system:
|
| Paranasal sinuses | Inflammation in the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses, polyps and other masses, trauma and congenital structural features of the nasal septum. |
| Limbs | Thrombosis, inflammatory and infectious lesions of muscles, joints, tendons, varicose veins, trauma. |
Indications for tomographic examination
Computed tomography can be prescribed for the following complaints and indications (there may be several of them at once):
- persistent headaches;
- frequent loss of consciousness for no reason;
- impaired cognitive functions of the brain (attention, memory);
- convulsive conditions;
- head injuries of various kinds;
- suddenly developed mental disorders;
- persistent pain in the spine, neck or joints;
- injuries of the musculoskeletal system and some internal organs;
- with suspicion of cancer, vascular disorders, internal bleeding;
- in the event of an emergency brain examination (in case of a stroke or injury);
- before installing dentures, in the treatment of complex dental diseases;
- In the preoperative period.
Also, CT is prescribed to confirm or refute the alleged diagnosis (not established exactly after ultrasound, conventional X-ray and analysis), to evaluate and control the results treatment. In some cases, the tomograph is used for complex operations, during which computer visualization of the operated area is required.
Contraindications and side effects
Computed tomography does not cause side effects, despite the fact that when it is performed, the patient receives the amount of radiation 3 times more than with conventional radiography. This increases the rate of development of cancerous tumors and some other diseases, but their danger is several times higher than with CT.
A relative contraindication for CT without contrast is pregnancy or suspicion of pregnancy. Also, the procedure is prohibited for people with a very large body weight, since the tomograph table has a weight limit.
Contrast-infused CT is prohibited under the following contraindications:
- cases of allergy to X-ray contrast agent during previous CT scan;
- renal failure;
- diabetes;
- diseases of the endocrine system (in particular, damage to the thyroid gland);
- myeloma;
- bronchial asthma;
- pregnancy or suspicion of it;
- too serious a patient's condition;
- some mental abnormalities (as the patient may have a hysterical or panic attack);
- too agitated state of the patient (since it will be difficult for him to maintain a stationary position).

Children are not prohibited from undergoing computed tomography, but often before the procedure, the child is injected with sleeping pills so that he lay quietly (since children are afraid of closed spaces and can rarely remain immobile for a long time). Sleeping pills are administered only with the consent of the parents.
Preparation and conduct of the survey
Computed tomography does not require special and complex preparation - the patient needs to wear comfortable clothes (so that it does not restrict movement and does not cause discomfort - otherwise you will have to constantly move during the study, straightening clothes) and remove metal objects and jewelry from body.
The mobile phone must be turned off or left in the doctor's room - radiation from the device may affect the accuracy of the diagnostic results.
When performing CT with contrast, it is necessary at least 3-4 hours in advance. stop eating, as its interaction with the iodine preparation can cause nausea, vomiting and other symptoms. But in no case should you come for a contrast study on a completely empty stomach.
When examining the organs of the genitourinary system, it is necessary that the bladder be filled - for this, 1-2 hours before the study, it is required to drink several cups of any liquid.
If the patient takes any medications and has chronic diseases, then it is imperative to download about this from the doctor conducting the examination.
The procedure goes as follows:
- The doctor asks the patient about the presence of chronic diseases, medication intake and cases of allergy to iodine preparations.
- If there are no contraindications to the procedure, then the patient is taken to the room where the tomograph is located and placed on the conveyor table.
- At this stage, a contrast agent is injected, if necessary (the patient can feel warmth in the body, no discomfort should arise).
- The doctor leaves the room, and the table begins to move into the tomograph, so that the area of the body being examined is in the center of the gantry (a ring in which there is a spiral with an X-ray tube).
- During the procedure, the table may move slightly forward and backward; the doctor fully coordinates the entire process through the control panel and, if necessary, gives the patient instructions (for example, to hold his breath or not to swallow) through the speakerphone. The patient also has the opportunity to speak with the doctor, and if it is impossible to follow any instructions, he must tell about it.
- Scanning takes from 5 to 60 minutes. After that, the conveyor table is pulled out, and the patient has the opportunity to stand up.
- The results of the examination are given to the patient in 1-3 hours.
In some cases, a contrast agent can be injected through a liquid - for this, the patient is given a glass of water with the drug dissolved in it before the procedure.
Decoding the results
The doctor who ordered the examination is responsible for decoding the CT scan results.
When looking at a snapshot, depending on the area of interest, he looks at the following:
- the size of the organ and the presence of its damage;
- the presence of cysts, abscesses, foreign bodies;
- the presence of stones in the kidney or gallbladder, biliary tract;
- proliferation of tissues of internal organs (it can be endometriosis, tumors); the presence of seals;
- presence of fluid or pus in body cavities;
- the presence of an aortic aneurysm;
- the presence of intestinal obstruction (whether there are diverticula or other causes of this condition);
- swollen lymph nodes;
- the presence of blood clots in the vessels, the size of the vessels (narrowed or not);
- the integrity of bones, joints and vertebrae.
Different pathologies in the picture look different: they can be darkened or, conversely, highlighted.
In order to decipher the image as accurately as possible and make the correct diagnosis, the doctor must thoroughly know the density, color and shade, the shape of a particular organ, vessel or other area body. Also, in the process of decoding, the doctor uses pictures of the “norm” and compares the CT results with them, performed in different projections.
Which is better - CT or MRI?
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is based on the effect of a magnetic-electric field, which, like X-rays, penetrates the tissues of the body. However, the magnetic field does not emit harmful radiation and does not adversely affect the body.
Both diagnostic methods have a high level of information content. But CT is more effective in examining bone-cartilaginous structures (since hard structures retain X-rays better than soft ones), vessels and some internal organs.
When diagnosing soft tissues, cancerous tumors, brain structures, MRI will be more accurate. But in the presence of contraindications or the impossibility of carrying out one or another method of examination, CT and MRI can be interchangeable. The type of examination should be selected only by the attending physician.
Why shouldn't CT scan during pregnancy?
X-rays negatively affect the fetus, causing various congenital malformations and developmental disorders. Also, radiation can cause the risk of developing cancer in the child in the future.
When examining a pregnant woman, doctors try to make a diagnosis using ultrasound or MRI. However, in rare cases (if it is vital), CT is indispensable - then the pregnant woman is examined, but cover the abdomen with a special lead “apron” that traps X-rays and minimizes the impact radiation.
Breastfeeding women are not contraindicated for CT, but doctors recommend expressing 1 portion of milk after the procedure and not feeding the baby with breast milk for 24 hours.
How often can tomography be done?
Computed tomography (with or without contrast) for diagnostic purposes can be performed 1-2 times a year with a difference of 6-12 months. It will not cause any harm to health and will not cause complications due to exposure to X-rays.
If necessary (to assess the results of treatment or control of cancerous tumors, for vital indications) the number CT examinations performed per year can be increased to 4-6 - in this case, the increased amount of X-ray radiation will be justified.
Cost of CT diagnostics
Computed tomography is an expensive procedure, the cost of which starts from 3000 rubles. Depending on the area being examined, the type of CT scan and the injection of contrast agents, the price will rise.
Approximate prices for different types of CT:
| CT of the brain and sinuses without contrast | 3000-4000 rub. |
| CT of the brain and sinuses with contrast | 5000-6000 rub. |
| CT scan of the chest with contrast | RUB 6000-7000 |
| CT of the abdominal and retroperitoneal organs with contrast | RUB 6000-8000 |
| CT angiography (various vessels) | RUB 6000-12000 |
| CT scan of soft tissues, bones and joints without contrast | RUB 3000 |
| CT scan of soft tissues, bones and joints with contrast | 5000-6000 rub. |
| Multispiral CT | From 10,000 rubles. |
Also, the cost of the procedure depends on the region, equipment and reputation of the clinic.
Computed tomography allows you to accurately determine the presence of a disease or assess the state of the internal structures of the body. This method is much more informative than ultrasound and radiography, but it has its own contraindications and features.
Article design: Vladimir the Great
CT video
About computed tomography:


