Intrauterine infections (IUI) are pathologies of newborns in which infection of the embryo occurs in the womb or during childbirth. This concept cannot be used as a diagnosis. When making a diagnosis, it is allowed to use the term "congenital infection".
Intrauterine infections in newborns may not have clinical manifestations. In this case, the diagnosis is confirmed by a history of genital and other infections in the mother.
Symptoms are more common if the child has had TORCH infections. These include toxoplasma, rubella, herpes simplex virus, cytomegalovirus. Infection is also possible with other pathogens, such as HIV, hepatitis B and C, mycoplasma.
The main symptoms of intrauterine infection include: developmental delay during gestation, icteric syndrome, pathology of the central nervous system, exanthema, diseases of the circulatory system, enlargement of the liver and spleen. These manifestations can be noted with any type of infectious agent.
Since the symptomatology of various IUIs is very similar, an examination is carried out to make a diagnosis, determine the pathogen. These include: microscopic, cultural, immunoassay, molecular biological studies. IUI therapy is carried out with the help of immunoglobulins, antiviral, antibacterial agents, as well as immunomodulators.
Record content:
-
1 Types of intrauterine infections
- 1.1 Cytomegalovirus
- 1.2 Neonatal herpes
- 1.3 Toxoplasma infection
- 1.4 Neonatal candidiasis
- 1.5 Syphilis
- 1.6 Rubella
-
2 Symptoms
- 2.1 Cytomegalovirus infection
- 2.2 Herpetic infection
- 2.3 Toxoplasma infection
- 2.4 Candidiasis
- 2.5 Syphilis
- 2.6 Rubella
- 3 Causes of intrauterine infections
- 4 Diagnostic measures
- 5 Prophylaxis
- 6 Treatment
- 7 Intrauterine Infection Videos
Types of intrauterine infections
In neonatology, there is a classification of IUI by the type of pathogen. These include:
- caused by viruses (hepatitis, herpes lesions, rubella, cytomegalovirus infection);
- provoked by bacteria (tuberculous or syphilitic lesions, syphilis, listeriosis);
-
caused by parasites and fungi (mycoplasmosis, toxoplasmosis, chlamydia, candidiasis).
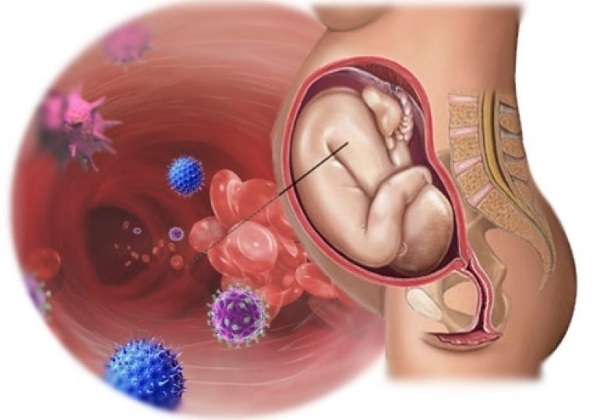
In the protocol of intrauterine infections there is such a definition as TORCH syndrome.
This concept includes major infections:
- T (Toxoplasmosis) - toxoplasma;
- O (Other diseases) - other infections;
- R (Rubella) - rubella;
- C (Cytomegalovirus) - cytomegalovirus infection;
- H (Herpes simplex virus) - herpes simplex virus.
Other (O - Other) pathogens include hepatitis B and C virus, mycoplasma, syphilis, HIV, candida fungus, human papillomavirus (HPV) and others.
Cytomegalovirus
Cytomegalovirus infection (CMVI) is a common pathology, the causative agent of which affects patients only in immunodeficient conditions. The incidence in newborn patients is 0.2-2.5%.
Cytomegalovirus belongs to the DNA-containing viruses of the Herpesviridae family. The pathogen is able to change its DNA. It is not active in the external environment.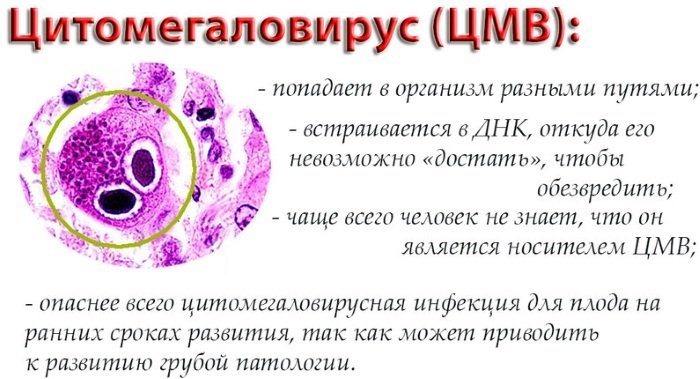
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) affects pregnant women due to reduced immunity. Patients working in public places (doctors, waiters, salespeople and other professions), who often gave birth, are especially susceptible. CMVI is transmitted from a sick person to a pregnant woman or during invasive manipulation of the fetus.
There are 2 types of CMVI:
- primary (the mother becomes infected for the first time);
- secondary (re-infection).
The primary form of CMVI is much more severe than the secondary one. The mother has no protective antibodies. Secondary infection has a milder course. The virus affects the fetus to a lesser extent, since the mother has protective antibodies.
Neonatal herpes
Herpetic infection is a common condition among adults. The causative agent is considered a representative of the Herpesviridae family: herpes simplex virus (HSV) types 1 and 2. The prevalence of HSV is 7-40%.
Types of infection:
- HSV-1 - the causative agent of labial herpes;
- HSV-2 is the causative agent of genital herpes.
A high risk of herpes infection in a newborn baby is possible with an exacerbation of genital herpes in the mother 1 month before delivery.
Toxoplasma infection
Toxoplasma infection is caused by the causative agent Toxoplasma or Toxoplasma gondii. It belongs to the intracellular parasites of the Sporozoa class. The main host and source of the pathogen is the cat. 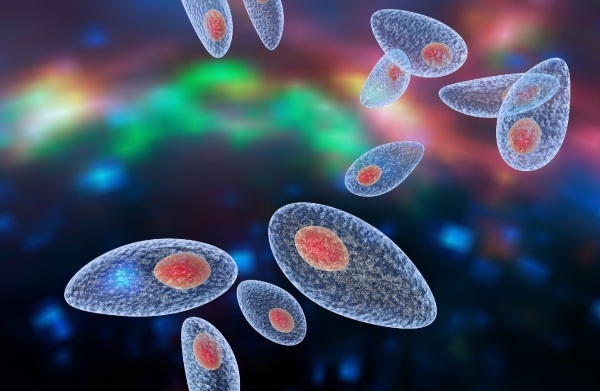 Cats secrete Toxoplasma oocysts with feces, carry them around the house. Infection occurs alimentary (through dirty hands, food).
Cats secrete Toxoplasma oocysts with feces, carry them around the house. Infection occurs alimentary (through dirty hands, food).
Neonatal candidiasis
The incidence of candidiasis in newborns and babies in the first month of life is 15-30%. The causative agent is a fungus of the genus Candida (Candida). There are 10 types of candida. Most often found: albicans, tropicalis, krusei, parapsilosus, globrata.
Candidiasis develops due to:
- diabetes mellitus in the mother during gestation;
- prematurity;
- surgical intervention during pregnancy, resuscitation measures;
- re-treatment with antibiotics, especially in conjunction with immunosuppressive drugs;
- neutropenia;
- carriage of candida.
Syphilis
The causative agent of the disease is treponema pale - Treponema pallidum. The incubation period is 3-4 weeks. Has a primary and secondary flow period. Fetal infection occurs with early latent form and secondary syphilis in a pregnant woman. The probability of having a baby with congenital syphilis is 80-85%.
Rubella
Intrauterine damage to the fetus occurs when the mother is sick with rubella. The causative agent of rubella is the rubella virus, or Rubella virus, belonging to the Togaviridae family, the Rubivirus genus.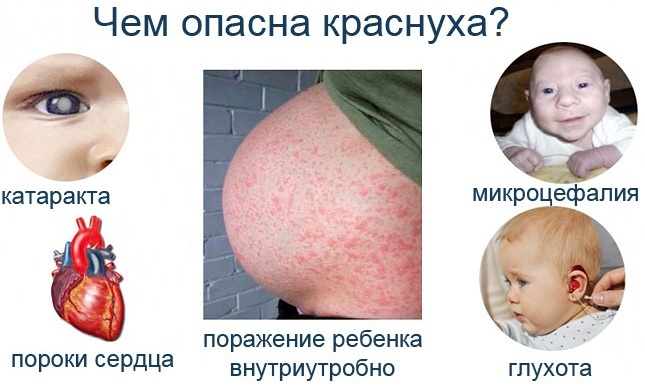
The greatest risk of intrauterine infection is observed in the first trimester of gestation and is 80%. In the 2nd trimester, the probability of congenital rubella is 10-12%, in the 3rd trimester - 3-8%. The pathogen can cause fetal malformations.
Symptoms
Intrauterine infections in newborns have similar manifestations after birth. The consequences of the disease may differ.
The main symptoms of IUI are:
- delayed development of the fetus in the womb;
- enlargement of the liver and spleen;
- icteric syndrome;
- exanthema;
- disorders of the heart and blood vessels;
- pathology of the central nervous system.
The similarity of symptoms does not give an accurate diagnosis, for this reason, diagnostic tests are necessary.
Cytomegalovirus infection
Cytomegalovirus during pregnancy may be asymptomatic, but ARVI manifestations are also possible. The patient may have a high fever for 1 month. CMV has no specific symptoms.
When the fetus is affected in utero, the following are noted:
- Blastopathy (0-14 days) - frozen pregnancy, miscarriage, the appearance of genetic defects.
- Embryopathies (15-75 days) - malformations, miscarriage.
- Early fetopathies (76-180 days) - an inflammatory reaction of the generalized type, provoking fibrosclerotic deformities, termination of pregnancy.
-
Late fetopathies (from 181 days) - a manifest inflammatory reaction (hepatitis, encephalitis, thrombocytopenia, pneumonia).
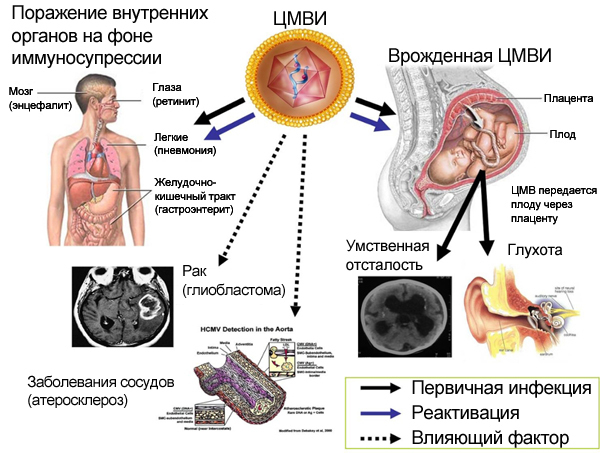
Despite the consequences, CMV is less dangerous compared to enteroviruses, rubella and other pathogens. Cytomegalovirus has less teratogenic effect.
With primary CMVI, the following symptoms are noted:
- thrombocytopenic purpura;
- icteric syndrome;
- enlargement of the liver and spleen;
- microcephaly;
- lack of weight;
- prematurity;
- inflammatory liver damage;
- inflammation of the brain tissue;
- chorioretinitis.
Even with an asymptomatic course of CMVI in a child, sensory deafness, delayed psychomotor development, cerebral dysfunction, and neurological symptoms are possible in the future.
Herpetic infection
On the eve of childbirth, the mother may have genital herpes with severe itching, burning, swelling of the labia and vagina. Also, a pregnant woman can suffer labial herpes: a rash on the lips, accompanied by oozing, itching. There are 3 forms of neonatal herpes infection.
These include:
- localized - damage to the skin, eyes; single or multiple vesicular elements are possible; systemic inflammation is not observed; with eye damage, optic nerve atrophy, blindness in severe cases is possible.
- generalized - celebrated on the 5-10th day of the baby's life; sepsis occurs (sluggish sucking, regurgitation, increase or decrease in temperature, respiratory arrest); the liver and adrenal glands are affected; there is an increase in the spleen, a decrease in blood sugar, an increase in blood bilirubin, DIC syndrome; elements on the skin may be missing.
- central nervous system damage - meningoencephalitis, encephalitis, high temperature, tremor of the extremities, lethargy, convulsions, poorly controlled, subsequently a change in cerebrospinal fluid (cytosis); there are no rashes on the skin.
Toxoplasma infection
In pregnant women, there is a limited and generalized form of toxoplasmosis. The generalized inflammatory form of pathology is manifested by damage to the lymph nodes, heart, liver, muscles.
Fibrosis or calcification of damaged tissues is possible. Such a clinic is possible with immunodeficiencies. Many women do not have symptoms of toxoplasmosis. The disease is diagnosed using serological tests.
With intrauterine infections in the fetus (newborn), the following clinic is possible:
- at 0-8 weeks - malformations, embryonic death (anencephaly, hydrocephalic syndrome, stillbirth, absence of eyes, enlargement of the liver, spleen, spontaneous abortion).
- at 8-18 weeks - brain damage in the form of hydrocephalic syndrome, calcifications, damage to the liver, eyes, convulsive syndrome.
- at 18-24 weeks - icteric syndrome, anemia, hepatosplenomegaly, thrombocytopenia.
- at 24-40 weeks is asymptomatic during the neonatal period, after a few years hearing loss, mental retardation, epileptic seizures, chorioretinitis are possible.
Candidiasis
Candidiasis in pregnant women is manifested by damage to the mucous membranes, skin or genitals. When the skin is involved in the process, swelling, cracks are possible. If the mucous membrane of the oral cavity is damaged, there is a cheesy plaque, burning sensation, and swelling. The most dangerous is genital candidiasis. At the same time, there is a white cheesy discharge from the vagina, edema, burning, itching.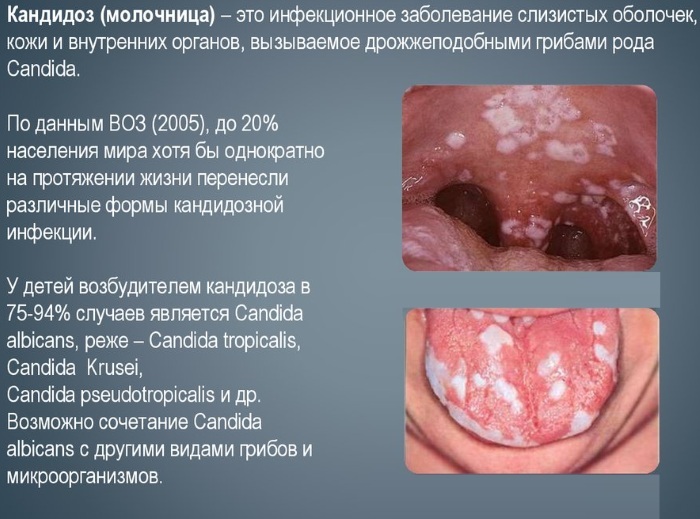
Manifestations in infants and fetuses:
- generalized form with damage to internal organs, death is possible;
- damage to the eyes;
- damage to the skin, mucous membranes, genitals;
- damage to internal organs without spreading the pathogen throughout the body (CNS candidiasis, carditis, pneumonia, hepatitis, nephritis).
Syphilis
During pregnancy, pale treponema often affects the genitals. Erosion, ulcers are noted. After the incubation period, hard chancres are revealed (after 3-4 weeks).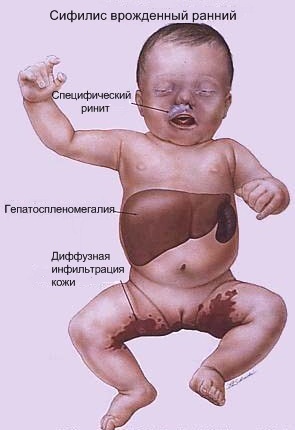
After 6-7 weeks, abundant maculo-nodular (sometimes papular) formations appear on various parts of the body and mucous membranes.
In the latent period, the rashes disappear, after which they appear again. Possible development of neurosyphilis and damage to internal organs.
In newborns, the following symptoms are noted:
- syphilitic pemphigus;
- diffuse Gochsinger skin infiltration;
- specific rhinitis;
- osteochondritis of Wegner's long tubular bones;
It is also possible to damage the brain, deformation of the skull (the skull is enlarged, there is a predominance of cerebral part, low location of the auricles, wide bridge of the nose, wrinkled face), an increase in the abdomen with venous network.
Rubella
A pregnant rubella is difficult. A small rash on the body, reddening of the throat are revealed. The patient has a high fever.
In the fetus and newborn, the following consequences are possible:
- heart defects;
- cataracts, blindness;
- deafness.
The brain is also affected, microcephaly, microphthalmia, and dilated fontanelles are noted.
Other manifestations:
- glaucoma, vestibulopathy;
- skeletal defects;
- hepatosplenomegaly;
- pathology of the urinary system.
Sometimes a woman gives birth to a dead fetus, a premature baby.
Causes of intrauterine infections
The emergence of IUI contributes to the illness of the mother during the gestation of the embryo. The pathogen enters the fetus through the placental organ. In some cases, infection of the amniotic fluid occurs.
Also, infection is possible during childbirth. When passing through the birth canal, the child comes into contact with foci of infection. Less commonly, the fetus becomes infected during invasive prenatal diagnosis.
These include:
- amniocentesis;
- cordocentesis;
- chorionic villus biopsy.
Also, transmission of infection is possible with the introduction of blood products to the fetus.
IUI factors include:
- gynecological diseases - colpitis, STDs, inflammation of the ovaries and tubes;
- during previous pregnancies (miscarriage, threat of termination, placental abruption);
- the presence of infectious diseases.
The place of work of a pregnant woman is very important. When the patient is in crowded places, the risk of IUI increases.
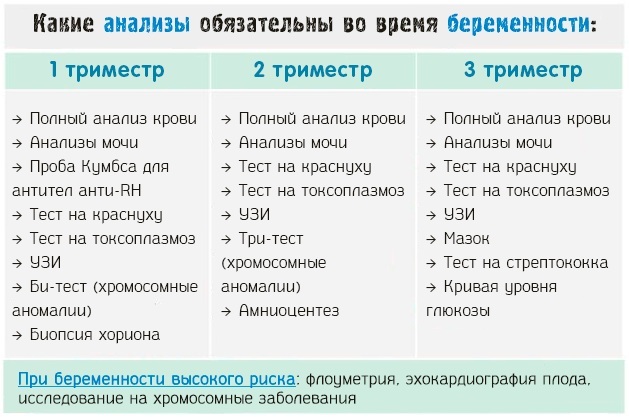
Diagnostic measures
Diagnostic measures include examination of the pregnant woman, collection of anamnestic data on diseases, previous pregnancies, abortions. With a burdened history, the woman is sent for examination.
List of diagnostic procedures at IUI:
- microscopic examination of a smear from the genital tract, urethra, bacteriological culture on the flora from the vagina, PCR examination of scraping;
- analysis of TORCH infection;
- serological studies;
- invasive prenatal diagnosis (if the woman is at risk);
- Fetal ultrasound;
- Doppler study of placental blood flow;
- cardiotocography.
After the child is born, microbiological (virological, bacteriological), molecular biological (DNA hybridization, PCR), serological (ELISA) examination methods are performed. If necessary, ophthalmoscopy, neurosonography, echocardiography, hearing examination are prescribed.
Examination of a pregnant woman is carried out on the basis of an antenatal clinic or a maternity hospital. It is also possible to carry out diagnostics in a paid clinic at the place of residence.
Examination cost in Moscow:
| Study type | Cost, rub.) |
| Microscopic examination of a smear from the genital tract | From 900 |
| Bacteriological culture on flora from the vagina | 130-500 |
| PCR study of scraping | 600-800-3000 |
| TORCH infections | From 1300 |
| Serological tests (determination of antibodies) | From 4500 |
| Invasive prenatal diagnosis | from 700 to 52500 |
| Doppler study of placental blood flow | From 400 |
| Fetal ultrasound | From 500 |
| Cardiotocography | From 450 |
If there is a suspicion of IUI, it is necessary to contact the gynecologist at the site. If complications of pregnancy occur: strong uterine tone, bleeding or spotting from the vagina, early labor, drainage of water, you should call an ambulance.
Prophylaxis
Intrauterine infections in newborns can be prevented by planning a pregnancy. Before conception, you need to undergo an examination for the presence of genital infections (STDs, TORCH, HIV, hepatitis, syphilis), treat all chronic and infectious (including sexual) diseases in both partners.
During gestation, you should not change your sexual partner, go to public places. If you change your sexual partner during gestation, you should be tested for infections. If possible, avoid invasive perinatal diagnosis. If you suspect an infectious disease, you should contact a gynecologist for examination and treatment.
Treatment
Intrauterine infections in newborns are treated with drugs that kill the pathogen. In addition, symptomatic therapy is used to alleviate the child's condition. Together with the newborn, the mother is also treated, if necessary.
Essential drugs for IUI:
| Disease | Medicines for the newborn / mother | Child / mother dose |
| CMVI | Cytotect |
|
| Herpetic infection | Acyclovir |
|
| Viferon | Kid 150000ME 1 time per day for 5 days. | |
| Toxoplasmosis | Spiramycin | Pregnant woman up to 1 g 3 times a day, the course is 2-3 weeks. Treatment throughout all pregnancies at intervals of 14 days. |
| Tindurin | Child - 1 mg / kg (2 divided doses), short-acting sulfonamides - 0.1 / kg (3-4 doses). repeat after 2 weeks | |
| Spiramycin | For a child, 150,000-300,000 U / kg - a daily dose in 2 doses, a course of 10 days. | |
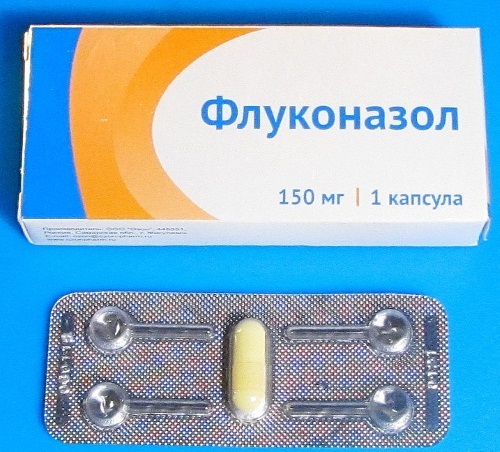
| Candidiasis | Fluconazole | For babies - daily dosage - 5-8 mg / kg body weight once a day. The duration of therapy is determined by the clinic. After the symptoms disappear, therapy is canceled. The most common form is a dose of 8-10 mg / kg. Mothers with genital candidiasis - clotrimazole suppositories 1-2 per day. Fluconazole 1 capsule every 3-7 days or once. |
| Syphilis | Procaine-Penicillin | Mothers with primary syphilis 1.2 million each IU daily, 10 days (20 days with secondary) |
| Novocaine penicillin salt | Mothers with primary syphilis, 600,000 units 2 times a day for 10 days (20 days for secondary). | |
| Novocaine penicillin salt | For a child, the daily dose for the first six months is 100,000 U / kg of body weight, after 6 months - 50,000 U / kg of body weight. |
IUI is treated in the pathology of newborns or the intensive care unit, depending on the condition of the baby. Drug therapy is quite effective. Traditional medicine and other non-traditional methods of treatment are not used, as this does not help.
Intrauterine infections without treatment lead to death from the spread of an infectious agent, an inflammatory reaction, and tissue necrosis. IUI in newborns provoke malformations of the heart, genitourinary apparatus and other systems, depending on the species. Almost all IUIs cause damage to the central nervous system. Possible hepatitis, cirrhosis of the liver, COPD, insterinary nephritis.
Article design: Vladimir the Great
Intrauterine Infection Videos
Doctor about intrauterine infections:



