Leukemia is a serious cancer, which is characterized by a malignant lesion of blood cells. In adults, the main symptoms of the disease are dysfunctions of the immune system, increased fatigue, and slow regeneration of epithelial cells.
In medical terminology, leukemia is also found under the names: leukemia, leukemia. To confirm the diagnosis, the method of biochemical analysis of venous blood is used.
In modern hematology, it is customary to refer to leukemia as a large number of blood diseases associated with the pathological state of the cellular apparatus responsible for the synthesis of leukocytes.
The main characteristic features of leukemia include the presence of malignant clones, which in most cases are produced by immature bone marrow cells of the hematopoietic type. Unlike other pathologies of the hematopoietic system, leukemia belongs to the category of neoplastic diseases.
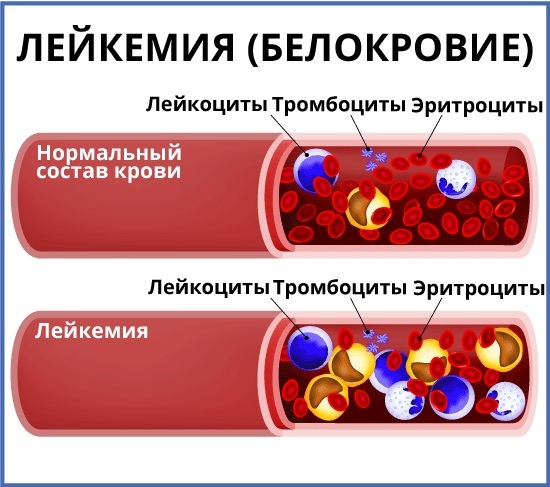
The progression of leukemia is due to the fact that the malignant clone continues uncontrolled cell division, increasing the number of mutated cells. In this regard, the blood of a sick person gradually loses its physiological functions.
This leads to disruption of the work of internal organs and all body systems. According to the latest scientific research, leukemia can be acute, chronic and latent. The latter type of the disease can develop over 50-60 years.
Record content:
- 1 Views
-
2 Stages and degrees
- 2.1 Latent stage
- 2.2 Acute stage
- 2.3 Remission
- 2.4 Relapse
- 2.5 Terminal stage
- 3 Symptoms
- 4 Reasons for the appearance
- 5 Diagnostics
- 6 When to see a doctor
- 7 Prophylaxis
-
8 Treatment methods
- 8.1 Medications
- 8.2 Traditional methods
- 8.3 Other methods
- 9 Possible complications
- 10 Video about leukemia
Views
Symptoms of leukemia in adults largely depend on the type of this disease. At the first stage of the examination, the patient is prescribed a blood test to establish the concentration of leukocytes, as well as to determine their malignant origin.
Based on the current symptoms and the results of other examination methods, the attending physician classifies leukemia into an acute or chronic form. Then, depending on the type of malignant leukocyte lesion, the type of leukemia is determined.
The table below describes in detail the main types of leukemia, as well as their distinctive features.
| Types of leukemia | Characteristics of the disease |
| Acute myeloid leukemia | It is one of the most common and common blood cancers. The development of the disease lies in the fact that the bone marrow synthesizes an excess of special cells - blasts. In healthy people, they are involved in the fight against infectious agents, but in this case, blasts are initially produced by malignant ones, unable to perform the protective function of the body. In some cases, the bone marrow also produces abnormal red blood cells and platelets, which gradually crowd out full blood cells. Malignant lesions of the blood and the hematopoietic system are always accompanied by acute symptoms and a rapid deterioration in the patient's well-being. |
| Acute lymphocytic leukemia | In oncology, this type of leukemia is also found under the abbreviated designation "ALL". A distinctive feature of this type of blood cancer is that the malignant cells spread in the spongy tissue of the bone marrow. In most cases, the disease affects immature blood cells. Lymphocytes are the object of malignant lesions. Unlike other types of leukemia, this type of disease is characterized by rapid development and requires urgent therapy. |
| Chronic lymphocytic leukemia | This type of oncology of the blood and hematopoietic system is characterized by a very slow development. Bone marrow tissues consistently produce a small number of lymphocytes, which do not help a person fight infections, but, on the contrary, disrupt the function of the blood. This disease most often occurs in elderly people. Modern methods of therapy make it possible to restrain the progression of the disease with the help of medications. |
| Chronic myeloid leukemia | This type of leukemia belongs to the category of the most rare oncologies of the blood and hematopoietic system. There is a slow replacement of healthy leukocytes with malignant blood cells. In most cases, this type of leukemia is a consequence of the patient's lifestyle, the conditions of daily work, contact with toxic substances of chemical etiology. Chronic myeloid leukemia mainly occurs in adults. This disease practically does not affect children. |
Determining the type of leukemia is the main condition for a comprehensive examination of the patient. After the diagnosis is made, the attending physician forms a course of effective therapy, which includes chemistry preparations, cytostatics, as well as other medicines and hardware treatment methods.
Stages and degrees
From the moment when the first signs of leukemia begin to appear, it takes from 1.5 to 2 months.  All this time, mutations of the tissues of the bone marrow and blood cells occur. In this regard, the following stages of leukemia are distinguished.
All this time, mutations of the tissues of the bone marrow and blood cells occur. In this regard, the following stages of leukemia are distinguished.
Latent stage
The latent stage of the development of the disease is characterized by a pre-leukemic state of the body. A person does not yet feel significant changes in the work of internal organs and systems, there is no pathological symptomatology. Despite this, disorders in the work of the bone marrow are already occurring, and malignant cells begin to enter the blood.
Acute stage
Following the latent form of the development of the disease, the first leukemic attack occurs. In most cases, this occurs 55-60 days after the onset of the first mutations.
The patient feels acute symptoms associated with the dominance of oncological blood cells. The saturation of signs of pathology depends on the type of disease. In most cases, it is at this stage that people first seek medical help, after which they are given an appropriate diagnosis.
Remission
After completing a properly formed course of instrumental and drug therapy, leukemia may recede. Separate complete and incomplete remissions. In the first case, there is an absolute recovery of the body, the functions of the bone marrow are normalized, doctors are able to cleanse the blood of malignant cells.
The stage of incomplete remission requires further treatment, since the effect of partial reduction of mutated cells is achieved, but not complete recovery.
Relapse
This stage of leukemia is also called the stage of the secondary attack. Relapse occurs after a stable remission, which indicated a gradual recovery of the patient.
The secondary attack is accompanied by repeated manifestation of acute symptoms and deterioration of the functions of all internal organs. With a relapse, there may be a rapid progression of the disease, which did not occur before. The stage of the secondary attack indicates a poor prognosis for recovery.
Terminal stage
This is the stage of irreversible changes in the tissues of the bone marrow and the cellular composition of the blood. This stage is characterized by uncontrolled progression of leukemia, which cannot be contained with the help of modern methods of therapy.
Malignant blood cells saturate the tissues of internal organs, form internal bleeding and foci of necrotic process. The final stage of the terminal stage is the onset of death. In this period, the patient is shown symptomatic therapy aimed at alleviating the general well-being.
Leukemia (symptoms in adults are acute, and a blood test allows you to detect an ailment in a timely manner) is a disease which responds well to drug and hardware treatment if it was diagnosed at the latent stage development.
In this case, doctors get more time that can be used to suppress the malignant activity of the bone marrow.
Symptoms
The first signs of leukemia appear only after the blood is saturated with a large number of abnormal cells.
In this case, the sick person begins to experience the following symptoms:
- a febrile condition that resembles the acute phase of influenza or ARVI;
- blanching of the skin, which indicates a critical decrease in the level of red blood cells;
- an unreasonable increase in body temperature, which can be kept within subfebrile values, or reach indicators of 38-39 degrees Celsius (while a person completely lacks signs of a cold or infectious diseases);
- increased sweating of the body, most acutely manifested at night;
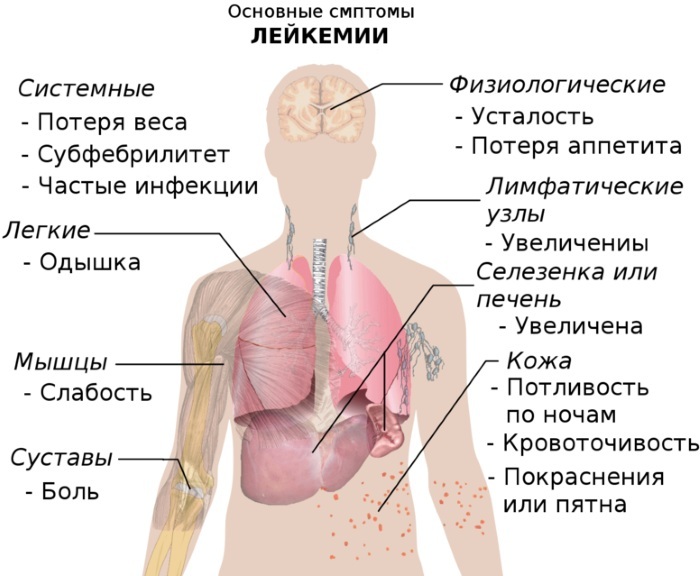
- decreased ability to work and fatigue, which appears even after performing minor physical exertion;
- increased fragility of blood vessels and the presence of a large number of bruises on the body, which appear from the slightest pressure on the skin;
- headache and dizziness attacks;
- frequent and profuse nosebleeds (this sign of leukemia indicates that an abnormal a change in the cellular composition of the blood affected not only leukocytes, but also led to a violation of the level of healthy platelets);
- aches in the bones of the lower extremities and joints;
- feeling of weakness in the muscular system of the musculoskeletal system;
- shortness of breath and heart palpitations that appear when walking fast or doing something physical activity (this symptom indicates a critically low level of red blood cells and progressive leukemia);
- slow healing of cuts, scrapes and other minor skin injuries;
- a decrease in general immunity and an increased tendency to infectious, viral and fungal diseases;
- attacks of spasmodic pain in the center of the abdominal cavity;
- an increase in the tissues of the spleen and liver, which indicates their saturation with abnormal leukocytes.
Leukemia (symptoms in adults are always dynamic, and a blood test shows a decrease in the normal level of hemoglobin) is a disease, the typical symptom of which is progressive anemia. The latter ailment is a concomitant pathology that occurs due to radical changes in the cellular composition of the blood.
Reasons for the appearance
Until now, oncologists cannot come to a consensus on why the human hematopoietic system fails and begins to produce malignant cells.
There are only general factors, the influence of which can lead to the development of leukemia:
- prolonged exposure to radioactive or other ionizing radiation;
- hereditary predisposition of the body;
- previous bruises and mechanical damage to bone tissue;
- long-term use of drugs, the active components of which can affect the biochemical composition of the blood;
- improper diet, the presence of bad habits;
- living in conditions with an unfavorable environmental situation;
- bacterial, viral and fungal infections of the chronic form of the course;
- daily contact with chemicals with toxic properties (the effect of constant poisoning occurs).
In people over 70, leukemia can develop as a result of age-related changes in the organs of the hematopoietic system. Determining the factors that caused leukemia is an important step in diagnosing the disease.
Diagnostics
Leukemia (symptoms in adults appear at an acute stage, and a blood test is one of the most informative methods of examination) Is a disease that does not require the use of a large number of instrumental and laboratory methods.
A person with suspected leukemia is assigned to undergo the following types of tests:
- donation of peripheral blood to identify its cellular composition;
- trepanobiopsy of the iliac tissue, or a puncture from the anterior wall of the sternum (performed using anesthesia).
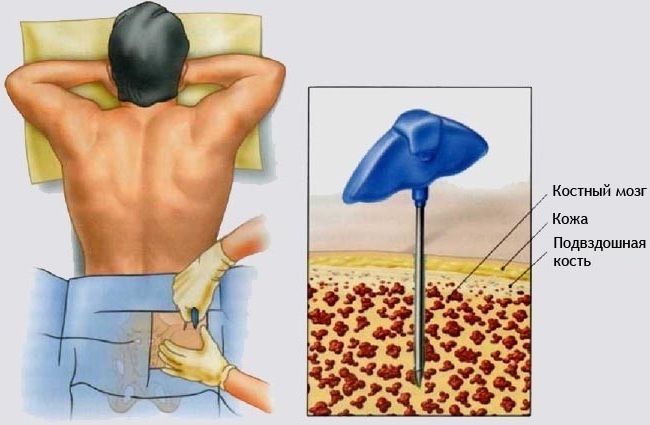
The above diagnostic methods enable the doctor to obtain comprehensive information about the health of the blood and bone marrow tissues. According to the results of the examination, the form and type of leukemia is determined. The average cost of diagnostics is 8500 rubles.
When to see a doctor
A visit to a doctor should take place in the first 1-2 days after a person has discovered painful symptoms that resemble the development of leukemia. This is especially true of those people who are over 70 years old, or had blood relatives in the family who had previously died of leukemia. Leukemia is treated by an oncologist and hematologist.
If these specialists are not available in the district hospital, then you should seek help from a therapist. The doctor of this profile will perform an initial examination, prescribe a blood test, and in case of suspicion of leukemia will be written out by a referral to an institution whose doctors specialize in the fight against malignant diseases blood.
Prophylaxis
In order to minimize the risk of leukemia, the following prevention guidelines are recommended:
- stop drinking alcoholic beverages, smoking and taking drugs;

- balance the diet, which should include only natural and environmentally friendly clean meat, ocean fish, fresh fruits and vegetables, greens, chicken eggs, dairy products, cereals cereals;
- avoid contact with heavy metals and chemicals with toxic properties;
- drink only purified water that does not contain harmful impurities;
- provide the body with moderate physical activity, play sports, spend more time in the fresh air;
- timely treat inflammatory diseases of bacterial, viral and fungal origin.
One of the important methods for the prevention of leukemia is the annual routine medical examination. Analysis of peripheral blood will allow timely detection of changes in its cellular composition, pathological growth of abnormal leukocytes.
Treatment methods
Leukemia (symptoms in adults are always acute, and a blood test can determine the possible presence of disease) is treated by the timely use of medication therapy and surgical interference. Cytostatics are used as medicines.
Medications
Medicines belonging to the category of cytostatic therapies are the main drugs that slow down the uncontrolled division of malignant cells.
In the process of treating leukemia, the following cytostatics are used: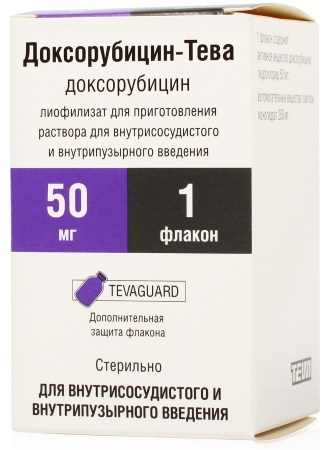
- Doxorubicin Is a medicinal product, which by its nature is of origin is semi-synthetic anthracycline antibiotic of antitumor spectrum of action (the average cost of a medication is RUB 1550 for 50 mg);
- Fluorouracil - This is an antineoplastic agent that is an antagonist of pyrimidone, and also belongs to the pharmacological category of antimetabolites (the price of the drug is 930 rubles. for 10 ml);
- Hydroxycarbamide - This is one of the most effective cytostatic antimetabolites, which is able to suppress the synthesis of tumor cells (the average cost of a drug is 1139 rubles. for 50 capsules);
- Cyclophosphamide Is an anticancer drug with a cytostatic effect, which has alkylating properties (the price of a medicine in pharmacies varies from 880 to 950 rubles).
The dosage of the above drugs is determined by the attending physician individually, depending on the type of leukemia, the stage of development of the disease and the age of the patient.
Traditional methods
Traditional medicines are not used in the treatment of malignant blood diseases, since they do not carry a positive therapeutic effect.
Other methods
In combination with drug therapy with drugs of the cytostatic group, the method of bone marrow transplantation is used. This is a surgical operation that involves the transplantation of stem cells from a healthy person to a patient with leukemia.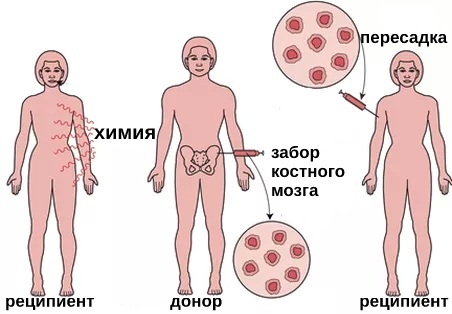
Intravenous infusion of cellular material can be performed, which is able to restore the functioning of the patient's hematopoietic system, or surgical bone marrow transplantation.
In the latter case, no more than 5% of the biological material is taken from the donor's pelvic bones, which is subsequently implanted in the patient. All surgical procedures are performed under general anesthesia, and their average duration is 2 hours. During the implementation of this method of treatment, only bone marrow or stem cells from a compatible donor can be used.
Possible complications
Failure to see a doctor, ignoring the progressive symptoms of leukemia, or an improperly formed course of therapy can lead to the development of the following complications and negative consequences for the patient's body:
- the spread of malignant cells in the tissues of internal organs (metastasis);
- damage to the lymph nodes;
- opening of local internal bleeding;
- tissue necrosis of the liver, lungs, intestines, spleen;
- painful thinness, accompanied by a rapid loss of adipose and muscle tissue;
- osteomyelitis of the bones of the face and jaw;
- stomatitis and bleeding of the gums, which will subsequently lead to the loss of teeth;
- a decrease in the protective functions of the immune system and the body's tendency to frequent infectious diseases;
- bacterial blood poisoning with the development of acute septic shock;
- the onset of a lethal outcome.

Leukemia in adults is a serious cancer, the main symptoms of which are: fever, chills, excessive sweating, frequent nosebleeds, prolonged low-grade body temperature, shortness of breath and palpitations, aching muscles, bones and joints. One of the diagnostic methods for detecting leukemia is a blood test.
With the help of this examination method, abnormal blood cells can be identified in a timely manner even before the stage of manifestation of acute symptoms of the disease. Treatment of the disease involves the use of cytostatics or surgical bone marrow transplantation from a compatible donor.
Video about leukemia
What is leukemia and its signs:



