Leukocytosis blood is a change in the level white bodies in the blood. This is not a pathology, but the body's response to diseases and irritants.
Often, an increase in the concentration of white cells is only a temporary phenomenon due to natural changes (bearing a child, poor-quality food). Large shifts in the leukocyte formula may indicate serious pathological processes when treatment is urgently required.
Record content:
- 1 Views
-
2 Stages and degrees
- 2.1 Neutrophilic
- 2.2 Lymphocytic
- 2.3 Monocytic
- 2.4 Eosinophilic
- 2.5 Basophilic
- 3 Symptoms
- 4 Reasons for the appearance
- 5 Diagnostics
- 6 When to see a doctor
- 7 Prophylaxis
-
8 Treatment methods
- 8.1 Medications
- 8.2 Traditional methods
- 8.3 Other methods
- 9 Possible complications
- 10 Video about leukocytosis
Views
Leukocytosis is true (with an absolute increase in the level of white cells).
Other forms:
- Distributive. The circulating pool becomes larger than the parietal pool. But there is no absolute increase, the hematopoietic organs are almost not irritated.
- Hemoconcentration leukocytosis leads to thickening of the blood due to a decrease in water in it. The level of red blood cells also increases.
Due to its occurrence, it is divided into:
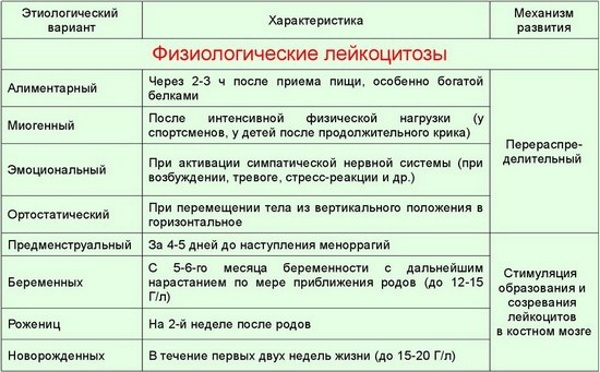
- Physiological. This type of disease does not harm a person; it periodically appears even in healthy people. Physiological leukocytosis is divided into subspecies:
- digestive appears after eating (after 2 hours);
- myogenic - due to heavy physical exertion;
- premenstrual;
- stressful;
- arising after X-ray examinations, physiotherapy;
- in newborns (first week of life);
- in pregnant women.
- Pathological. It occurs due to inflammation, infectious, purulent processes, due to the reaction of the bone marrow to tissue deformation, provoked by circulatory disorders or toxic poisoning.
- Short-term. It occurs after a sharp increase in leukocytes in the blood. Hypothermia, stress becomes the reason. Then the condition is short-lived and disappears after the factor that provoked it.
The concentration of leukocytes is moderate, high, hyperleukocytosis.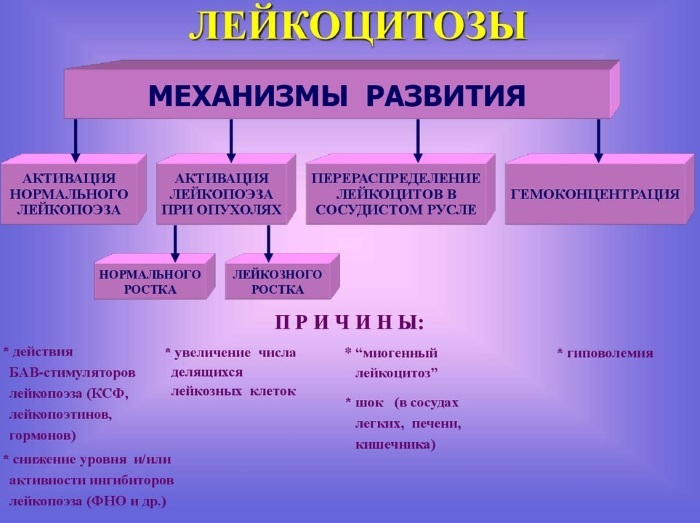
Also, the syndrome is divided into several types according to the types of white bodies (their increase in percentage over the norm):
- Neutrophilic (more than 75). Leukocytes enter the bloodstream from the bone marrow. As a result, their number increases dramatically. White molecules are rapidly redistributed in the vessels, and most of them pass into the circulating pool.
- Lymphocytic (up to the age of seven, the norm is 55, in adults more than 38). It is also called lymphocytosis. There is an increased supply of white cells from the organs of lymphocytopoiesis.
- Monocytic (more than 10). Increased monocyte levels. The beginning of the restoration of hematopoiesis.
- Eosinophilic (more than 5). Eosinophils enter the bloodstream from the bone marrow.
- Basophilic (over 1). A gradual increase in the concentration of basophils and leukocytes.
Leukemia is divided into two types. Acute is characterized by rapid development and extinction, inflammatory lasts for a long period. For adults, the condition is more dangerous, since the level of leukocytes recovers more slowly than in children.
Stages and degrees
Leukocytes exist in five different forms. By their name, the type of leukocytosis is also named.
Neutrophilic
More common than others. It can last for days or weeks. It depends on the cause and severity of the process. A rapid release of neutrophils is observed during exacerbation of diseases. Intoxication is accompanied by toxic granularity of leukocytes.
Neutrophilic leukocytosis is regenerative, when all types of granulocytes increase equally. Immature cells appear in the blood. The degenerative form is characterized by an uneven ratio of neutrophils. At the same time, the level of segmented ones decreases, and the level of stabs increases. This is accompanied by degenerative disorders in the cells.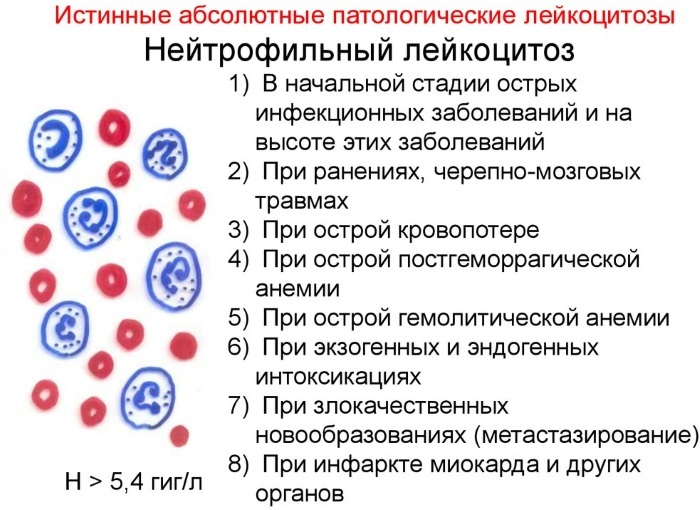
True leukocytosis is caused by disease. In addition to mature cells, there are blast and young cells in the blood, indicating a severe course of pathology. Under stress, great physical exertion, transistor leukocytosis is diagnosed. It is characterized by the absence of symptoms. True leukocytosis lasts several minutes or hours.
When making a diagnosis, a nuclear shift (a change in the ratio of mature and young neutrophils) is taken into account. If to the left, the number of new forms increases in the blood. Their decrease indicates a shift to the right.
The cause is infectious pathologies and their exacerbation, croupous pneumonia, influenza bronchopneumonia, and severe poisoning. A small nuclear shift to the left indicates a mild course of diseases and infections, a hypergenerative (enhanced) - a possible unfavorable outcome.
Lymphocytic
This form is characterized by a rapid increase in the number of white bodies. At the same time, the symptoms are pronounced. During the preparation of smears, some of the cells are damaged, forming Gumprecht's shadows. The bone marrow does not always contain tumor inclusions or interstitial infiltrates. Neoplasms without cellular mutations are highly aggressive.
At first, leukocytosis is almost asymptomatic. Signs are nonspecific - weight loss, lack of appetite, fatigue. The white blood cell count is highly variable. It depends on the clinical stage. The brighter the symptoms, the more leukocytes. The survival period is 4-6 years, but if a malignant tumor was found at an early stage, then more than ten.
Monocytic
This is a malignant process in which the normal composition of the blood changes. There is a sharp increase in the level of monocytes. The chronic form of leukemia is more common in older people. If the number of myelocytes is further increased, then this indicates myelomonocytic leukemia.
In acute monocytic cancer, cell division occurs, which stopped the disease at the very beginning. Tumors are made up of blasts (progenitor cells). The chronic form is accompanied by a partial retardation of cellular development. At the same time, the blood formula remains almost unchanged.
Eosinophilic
It can be determined only after receiving the results of a general blood test. The number of eosinophils in it greatly increases. The form does not have its own symptoms, all the signs refer to the disease that provoked leukocytosis. It can form as an independent disease or manifest as a consequence.
The mutation begins in embryonic, stem cells, mature blood cells. Since it is impossible to distinguish clonal division from reactive division, the diagnosis "eosinophilic syndrome" placed if there is a history of chromosomal abnormalities (Klinefelter's, Down's syndrome), in other cases - leukemia.
The formation of a state takes place in three stages. First, blast cells are transformed into eosinophils and begin to mutate. At the second stage, their maturation stops at the initial stage.
Unripe eosinophils can no longer self-destruct, they begin to actively divide. In the third stage, many white blood cells appear that are unable to function normally. Abnormal cells occupy a large volume and begin to displace healthy ones (including platelets). This causes the appearance of new lesions.
Basophilic
Basophilic leukocytosis is a rare condition. Development mechanism: clonal degeneration of bone marrow cells, hyperproduction of basophils. With their simultaneous increase with eosinophils, they are highly likely to indicate a blast transformation of chronic myeloid leukemia.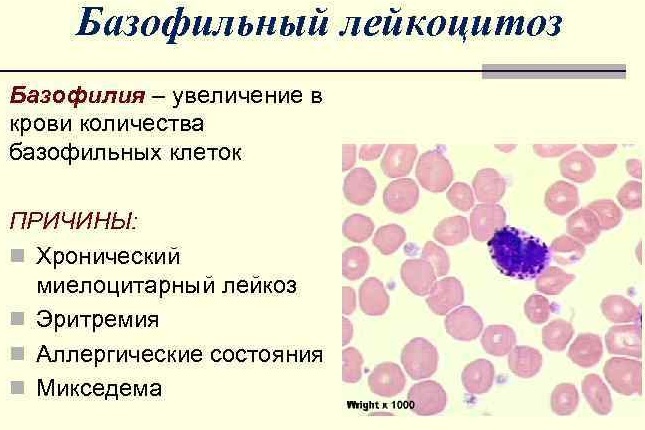 This is the final stage of pathology with a high risk of death.
This is the final stage of pathology with a high risk of death.
Symptoms
Leukocytosis of the blood is not a disease, but a condition accompanied by some symptoms. Constant fatigue appears, persists for a long period. This is accompanied by lethargy, weakness. Hemorrhages can occur spontaneously. In this case, bright bruises are formed.
Other symptoms:
- high temperature that cannot be brought down;
- heavy sweating;
- frequent dizziness, fainting;
- the appearance of bruising;
- rapid weight loss;
- deterioration of vision and appetite;
- hard breath;
- pain in the abdomen (may radiate to the legs).
Depending on the factor that caused the leukocytosis, characteristic symptoms appear.
For example, pulmonary oncological processes are characterized by:
- dyspnea;
- coughing up blood;
- hypoxia;
- sternum pain.
With brain cancer, memory lapses, impaired speech and vision, and epileptic seizures appear. In other cases, internal organs increase in size, joint pain occurs.
Reasons for the appearance
Leukocytosis can be triggered by smoking, contact with carcinogens, chemotherapy, genetic changes during the period of embryo maturation. Common causes are infections and weak immunity.
In this case, a specific pathogenic microorganism can provoke different types of disease:
- Bacterial infections. A distinctive feature is the appearance of immature neutrophils. In the acute form, leukocytosis reaches its peak on the second day, then gradually the number of cells is normalized. In chronic syndrome, they are at the upper limit or slightly exceed it. With bronchitis, angina, pyelonephritis, the increase in leukocytes is insignificant. It becomes high against the background of strong purulent processes and generalized infections.
- Viral infections. They cause an increase in the level of lymphocytes, which trigger the production of immunoglobulins, which are necessary to suppress the infection. In persistent infections, mild lymphocytosis can last for years.
-
Helminthic invasions. It most commonly causes eosinophilic leukocytosis. It develops on the fifth day, but reaches its peak only on 35-40 days. Then it gradually decreases to normal.
Physiological blood leukocytosis
| Types of leukocytosis | Causes of occurrence |
| True | Tissue irritation:
Increased excitability of the nervous system. Excessive production of estrogens, glucocorticosteroids, somatotropic and adrenocorticotropic hormones. |
| Redistributive | Physical activity, the introduction of chemotaxis into the blood from the lesions, the release of catecholamines. |
| Hemoconcentration | Dehydration of the body. |
| Physiological |
|
| Pathological | Occurs in the background:
|
| Neutrophilic |
Due to infection:
Due to non-infectious reasons:
|
| Eosinophilic |
Connective tissue pathologies (arthritis, fasciitis, vasculitis). |
| Basophilic |
Infectious pathologies:
Blood pathologies:
|
| Monocytic |
|
| Lymphocytic |
|
| Hyperleukocytosis | Develops against the background:
|
Diagnostics
Blood leukocytosis is an increase in the concentration of white cells above normal. For this, a little liquid is taken from a vein. In the presence of violations, the concentration of leukocytes in the blood will be high.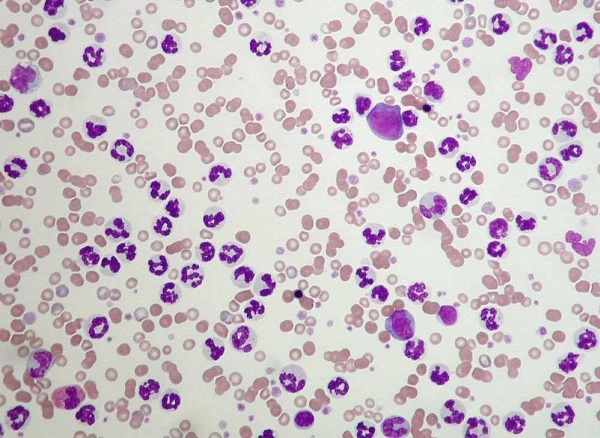
If there is an inflammatory process, the indicators of CRP and ESR, autoantibodies will be increased. The percentage of leukocytes is taken. A blood smear gives an idea of the presence and condition of neutrophils, mononuclear cells, Botkin-Gumprecht shadows, presepsin is measured.
To determine the infectious agent of the disease, a bacterial culture is done. With the help of enzyme immunoassay, the presence of antibodies (immunoglobulins M and G) to helminths, viruses, bacteria is detected. PCR helps detect their DNA. Then the temperature is measured, the skin and mucous membranes are examined.
This is followed by additional mandatory examinations:
- X-ray. If leukocytosis is caused by pneumonia, then infiltrates, areas of darkening are detected in the lungs. When affected by arthritis, bone erosion, osteoporosis, narrowing of the inter-articular gap are visible. If osteomyelitis is the cause, areas of necrosis and thickening of the periosteum are visualized in the images.
- Ultrasound. With pyelonephritis, an enlargement of the kidneys, the calyx-pelvic area is visible on the screen. Infectious mononucleosis is characterized by hepatosplenomegaly. Then on the ECG there is an effusion in the pericardial area, vegetation on the valves.
- Histology. Trepanobiopsy and sternal puncture are performed. With leukemia, hyperplasia of granulocytic cells and many blasts is found in biomaterials. An aspiration biopsy of the enlarged lymph nodes is required to detect lymphomas. In the presence of a disease, lymphocytic hypercellularity, large particles of Berezovsky-Sternberg, proliferation of collagen are found in them.
- MRI and CT. Appointed to determine the nature of the lesion, its boundaries. More often performed with contrast.
- Bone marrow biopsy. The material is taken with a thin needle. The study helps to make a correct diagnosis.
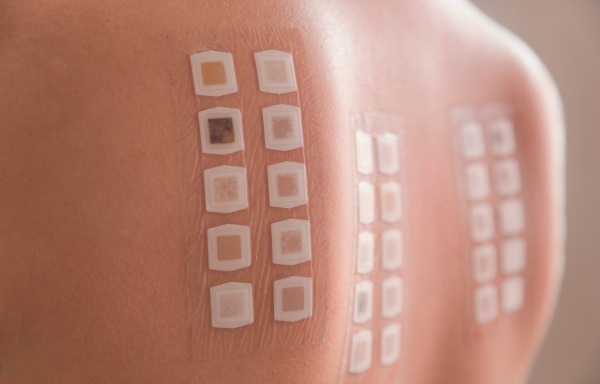
If an allergen is the cause of the disease, then an ELISA is done to measure the level of immunoglobulin, basophilic tests are performed.
Allergy skin tests include:
- prix tests;
- application;
- scarification;
- provocative - conjunctival, inhalation, nasal.
However, blood tests are becoming the most effective. If you have a compulsory medical insurance policy, leukocytosis is diagnosed in polyclinics free of charge. If there is no equipment for histology, then the blood is sent to the regional center. These answers come within two weeks, the rest are ready in 1-2 days. The hardware diagnostic methods are recorded in advance.
An urgent examination can be carried out in any private medical center. The cost depends on the region, equipment, doctors' qualifications. On average, in Moscow, an appointment with a hepatologist is 3500 rubles, an ultrasound scan is 800-2200 rubles, an x-ray is 1500 or more (depending on the area under study). In provincial cities, the price of services is much lower.
When to see a doctor
Leukocytosis is treated by a hematologist, but the primary examination is carried out by a therapist. They turn to him after the appearance of constant weakness, rapid fatigue, loss of appetite and weight.
After receiving blood results, if the number of leukocytes is increased and this is not associated with the physiological form of the syndrome, you should consult a doctor. As well as with visible abnormalities on X-ray, ultrasound, after disappointing histology results. Then additional consultation with an oncologist will be required.
Prophylaxis
To prevent leukocytosis, it is necessary to lead a healthy lifestyle, exclude bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol), and regularly undergo preventive examinations. It is necessary to timely treat diseases (especially infectious, bacterial), eat right. Eat 5-6 times a day, in small portions.
Exclude from menu:
- roast;
- spicy;
- fatty;
- marinades;
- conservation;
- flour;
- confectionery.

The diet should contain lean fish and meat, fresh vegetables and fruits, compotes. It is important to drink enough water - 2.5 liters each. Sleep - at least 8 hours, provide the body with good rest. Hiking in the fresh air daily.
Treatment methods
Treatment of leukocytosis should be comprehensive. First of all, drug therapy is prescribed. It is aimed at eliminating the cause that caused the increase in leukocytes. If treatment is impossible (for example, in cancer patients), chemotherapy is given.
The drugs and the course are selected individually. The minimum course is 4 chemotherapy procedures. This can stop the development of pathological processes. Blood transfusion is also used as a treatment. Folk remedies are used as an aid.
Medications
Blood leukocytosis is not a disease, but its consequence. Therefore, for treatment, funds are selected that will eliminate the cause of the appearance of this condition.
Can be assigned:
- Antibiotics (cephalosporins, macrolides, penicillins) - "Amoxicillin" (400 rubles), "Amoxiclav" (700 rubles). Prescribed to prevent and treat infection. This can sometimes help prevent sepsis. Antibiotics are taken in a course of 7-14 days. Then the drug is changed.
- NSAIDs - Ibuprofen (60-120 rubles), Piroxicam (140 rubles), Paracetamol (70-140 rubles), Diclofenac (80-250 rubles). Reduces and relieves inflammation, which automatically lowers the white blood cell count.
- Antacids ("Gevikson", "Almagel", "Gastal" - they all cost an average of 260-310 rubles). Reduces urinary acid levels.
- Antihistamines (Loratadin (30 rubles), Suprastin (130 rubles), Tavegil (250 rubles), Erius (650 rubles). Helps eliminate allergies.
-
Glucocorticosteroids ("Dexamethasone" (140-190 rubles), "Prednisolone" (110-180 rubles)). They help to remove inflammation, reduce the level of leukocytes.
Treatment of newborns becomes more difficult if the child's body reduces symptoms, responding in a peculiar way to therapy. In infectious processes, expectorant drugs, anti-inflammatory in the form of sprays, drops, tablets, can be additionally prescribed. All prices are approximate.
The cost of drugs varies, depending on the type, dosage, manufacturer, region of sale.
Traditional methods
Blood leukocytosis is an increase in leukocytes in it. Folk remedies as an independent direction for treatment are not used. Used only as an auxiliary direction.
Recipes:
- A decoction of lingonberry leaves or berries. Take 1 tbsp. l. raw materials, poured with a glass of boiling water, and the product is infused for 15 minutes. Then it is filtered, drunk three times a day.
- Birch buds are brewed in the same way. But the product is kept for half an hour. The infusion is drunk 3 times a day.
- Take leaves and berries of wild strawberries, cook for five minutes. Then the product is filtered, drunk during the day.
- You can make infusions from a mixture of horsetail, motherwort, knotweed, blackthorn berries, linden. Drink the remedy daily.
- Bitter wormwood is collected, crushed. Take 3 tbsp. l. herbs, pour 0.6 l. boiling water. The remedy is infused for an hour. You need to drink it 3 times a day, 15 drops.
- Drink green bean juice in the morning.
- Eat pollen with honey (2 tsp. l. in a day).
Folk remedies help to reduce the level of leukocytes, which speeds up drug treatment. Even as a preventive measure, lemon balm leaves can be added to tea every day.
Other methods
It is extremely rare that leukopheresis is done, when excess leukocytes are extracted using an apparatus procedure. The resulting purified blood is poured back to the patient or sent to a donor center.
In oncology, chemotherapy and radiation are prescribed. In this case, special drugs are used (for example, "Filgrastim", "Leykeran"). If leukemia is diagnosed, then a bone marrow transplant may be performed. When the cause of the increase in white blood cells is uremia, detoxification is performed.
However, there is no common standard dosage. All medications (including those for chemotherapy) are selected individually. It depends on age, weight, gender, current diseases.
One of the important directions for the treatment of blood leukocytosis is diet. It is selected individually, but the general rules include the inclusion in the menu of dairy and legumes that help increase hemoglobin, enriched with vitamin B6.
Kidneys and liver are completely excluded, and meat is consumed as little as possible and in small quantities. Remove synthetic sauces, foods with dyes, preservatives, food additives from the diet. It is recommended to eat more greens, nuts, fresh fruits, vegetables.
Possible complications
In children, leukocytosis is treated faster than in adults. But if you do not start therapy at the initial stages, then this can lead to serious complications - peritonitis, purulent-septic processes (phlegmon, abscess, etc.), spread of metastases, development of immunopathological pathologies (dermatomyositis, lupus erythematosus and etc.).
With basophilic leukocytosis, the prognosis is poor - the risk of the thermal stage of the disease increases.
Blood leukocytosis is the body's response to diseases, physiological processes. Some forms of the syndrome are safe for health and do not require treatment. The level of leukocytes is restored as soon as the cause disappears. However, the prediction of the quality of life is not based on the presence of leukocytosis and its type, but on the factors that caused this condition, its stage and the patient's condition.
Video about leukocytosis
Doctor about leukocytosis:



