Content
- With venous bleeding
- Training
- Bandage application
- On the shoulder
- On the forearm
- On the shin
- Care procedures after
- With arterial bleeding
- Training
- Bandage application
- On the shoulder
- On the forearm
- On the shin
- Care procedures after
- Contraindications
- Possible complications
- Compression bandage video
Large blood lossthat can lead to the death of the victim is one of the most serious complications after injuries associated with damage to the main or peripheral vessels. Meanwhile, mastering the skills of applying a pressure hemostatic bandage, which may save someone's life, is not a difficult task, the main thing is to know its algorithm.
How you apply a bandage depends a lot on:
- bleeding intensity (weak, medium, strong);
- localization and size of the wound, its condition (clean or clogged);
- the type of bleeding, which is determined by which vessels were destroyed during the injury.
In accordance with this criterion, bleeding is distinguished:
- capillary;
- venous;
- arterial;
- mixed.
Capillary bleeding associated with a violation of the integrity of small peripheral vessels - capillaries, does not pose a danger to life. To eliminate it, it is enough to treat the edges of the wound with an antiseptic, apply a gauze napkin and fix it with a bandage that does not impede blood circulation in the limb.
All other types of bleeding are not so harmless; in the absence of help, they can lead to critical blood loss and death of the victim.
With venous bleeding
Venous bleeding is called bleeding that occurs when the vessels (veins) are damaged, along which blood moves from the capillaries to the heart.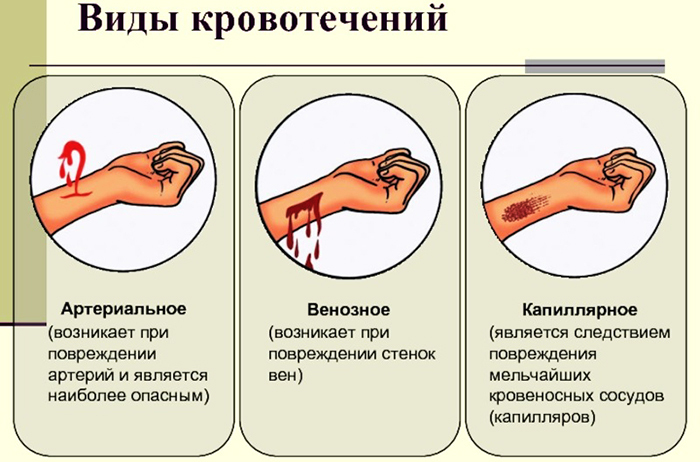
In addition to an open wound at the site of the passage of a vein, signs of venous hemorrhage are:
- dark cherry color of blood that pours out in an even, continuous slow stream;
- complete absence or extremely weak pulsation (periodic increased bleeding);
- since the venous blood flow is directed from the periphery to the center, when you press on the area of the body below the wound, the bleeding weakens;
- pale skin tone of the victim;
- increased blood pressure;
- acceleration of the pulse.
Applying a pressure bandage (the algorithm must be clear and consistent) is one of the main methods of stopping venous bleeding, applicable in the framework of first aid.
Training
In order to protect against possible infection (especially if you have to provide assistance to a stranger), wear rubber gloves.
Further, in preparation for the subsequent application of the bandage, it is recommended:
- Free the affected area of the body from clothing (cut with scissors, tear).
- Treat the skin around the wound with an antiseptic or a damp cloth (if it is heavily soiled) with movements directed away from it. If an arm or leg is injured, lift it up.
- Lay down or sit down the patient in a position that is comfortable for him.
It should be remembered that there are a number of actions that may seem necessary to an inexperienced person, but in fact can lead to increased bleeding or other undesirable consequences.
In particular, you cannot:
- remove fragments of clothing adhered to the wound or previously applied bandage soaked in blood;
- try to clear the wound from blood clots and blood clots;
- remove dirt particles, metal, wood, glass fragments from the wound surface, any large objects stuck in it;
- rinse the wound itself with water or an antiseptic;
- lubricate it with oil, any ointments, sprinkle with powdered medicines;
- put cotton swabs directly on the wound (it will be difficult to remove cotton fibers later).
Bandage application
Applying a pressure bandage (the algorithm for its implementation is simple) is a method of stopping bleeding.
To create such a bandage, a dressing will be required, which must be in the first-aid kit of a motorist or in its absence, any possible analogue: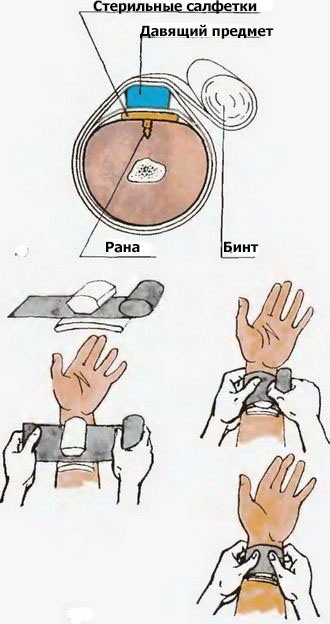
- a gauze pad or a small piece of clean cloth, preferably one that absorbs moisture well;
- pelot - a dense roller to create pressure. In its absence - a bandage, a piece of fabric rolled into a tight roll;
- bandage, long and narrow piece of fabric, braid, tape.
Further sequence of actions, in accordance with the requirements of dysmurgy (a discipline that studies the technique of applying bandages and splints) consists of the following stages:
- By pressing on the vein below the wound, stop the blood.
- Apply a gauze cloth to the wound and press firmly. If necessary (severe bleeding) - place one more napkin on top, remove the old one.
- Secure the napkin with 2-3 turns of the bandage.
- Place the pelot on a napkin fixed with a bandage so that it is located along the damaged vein (along the arm or leg) and also press it. If the victim is conscious, you can ask him to keep the roller pressed, otherwise an assistant will be needed.
- Fix the pelot with a bandage.
On the shoulder
The bandaging process depends on where the wound is located.
For example, if above the elbow it is necessary:
- Make several turns (rounds) of the bandage to secure it.
- Continue bandaging in a spiral in the direction from the elbow to the shoulder joint, the next turn half overlaps the previous one. On each round, the bandage is pulled tight and tight.
- Continue bandaging until the roller is completely covered and securely fixed.
- Above the wound, make several circular turns, after which the bandage is fixed, tied or sealed with tape.
If the wound is close to the shoulder joint, another type of bandage called a spike bandage is used.
To apply it you need:
- Perform several circular rounds of the bandage around the bicep to secure it to the body.
- Lead the bandage along the back and return through the armpit of the healthy hand to the affected area
- Move onto the shoulder and make another 1 turn around it.
- Wrap the bandage twice more around the body according to the same algorithm and fasten it on the back.
On the forearm
If the wound is located on the forearm, after pretreatment:
- Close the wound with a gauze pad, which is fixed with several turns of the bandage around the arm.
- Place a thick roller on the napkin along the forearm and press it down with your hand.
- Fix the bandage in several circular rounds in the wrist area, and then in a spiral lift up the arm to the elbow bend. The pressing force gradually increases. When bandaging, it is necessary to apply a bandage with an overlap: the previous turn is partially overlapped by the next one.
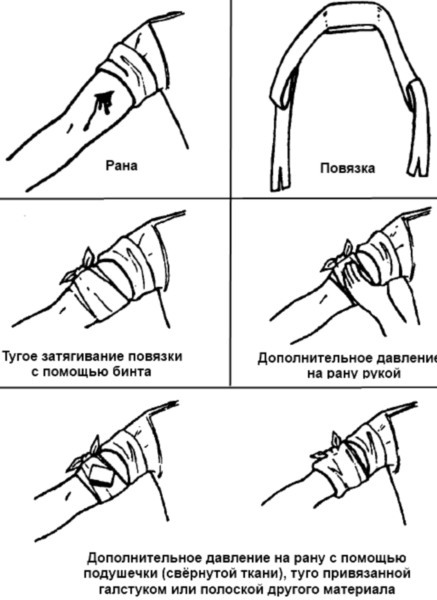
- Fix the bandage in the elbow area (tie or glue).
On the shin
Applying a pressure bandage (the bandaging algorithm on a small area of the lower leg is performed according to the same principle as in the case of the forearm) on a large area of the lower leg is performed in the form of a spiral.
To create such a dressing, you must do the following:
- After applying a napkin and a roller along the leg, fasten the bandage in several circular rounds just above the foot.
- Pull the bandage up in a spiral. At each turn, it is pressed against the front of the lower leg with one hand, and twisted with the other.
- The result is a pigtail-shaped bandage, the end of which is fixed in a convenient way.
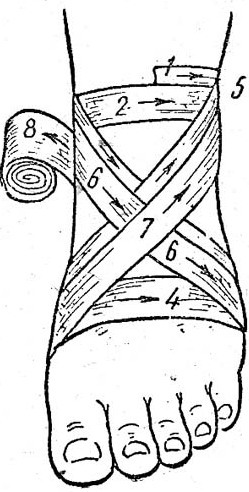
Signs of a properly applied bandage are:
- stopping bleeding;
- reliable fixation of the roller (it does not move);
- moderate pressure on the entire body area under the bandage.
At the same time, the following are unacceptable:
- blue in the face;
- pallor of the skin;
- numbness;
- tingling sensation, indicating a complete cessation of blood circulation. In this case, the bandage will have to be applied again, with less bandage tension.
The bandaging is repeated if the bandage is too weak (slipping, not giving hemostatic effect). In this case, it is advisable to impose a new bandage on the existing old one. The same should be done if the bandage is all soaked in blood: removing the old bandage, you can disturb the wound, remove the already formed blood clot and increase blood loss.
Care procedures after
If the bleeding has stopped, the victim must be taken to the hospital as soon as possible. If it is impossible to do this, you should give the limb a comfortable position and lay the victim on his back or on his side, raising his legs by 30-45 cm relative to the head. You can put ice in a plastic bag or any cold object on top of the bandage. If the patient is conscious, you can offer him a drink (if there is no suspicion of internal bleeding).
The final stop of bleeding should be dealt with by the doctor after the patient is taken to the hospital.
For this purpose, a number of procedures are performed:
- Removing the old bandage.
- Cleaning the skin around the wound.
- Wound surface treatment: removal of foreign inclusions, antiseptic procedures. They can be supplemented by the administration of anti-tetanus serum when the wound comes into contact with the ground or metal.
- Medical examination.
Depending on the recommendations of a specialist, methods can be used to completely stop the blood:
- mechanical: ligation or stitching of damaged vessels;
- physical: the use of high or low temperatures, laser, plasma scalpel;
- chemical: treatment with substances that cause protein coagulation and vasospasm;
- biological: blood transfusion, wound tamponade with a hemostatic sponge, use of a fibrin film.
After the final stop of bleeding, a dressing and a mandatory examination are performed, the purpose of which is to identify possible hidden damage. If the patient's condition is satisfactory and the wound is not dangerous, he may be allowed to go home. In case of large blood loss or the presence of injuries to internal organs, the victim should be in the hospital under the supervision of a doctor.
With arterial bleeding
Arterial bleeding is called bleeding that occurs when large vessels (arteries) are damaged that transport blood from the heart to all structural elements of the body. This type of injury poses the greatest threat to life, since it is associated with profuse and rapid blood loss.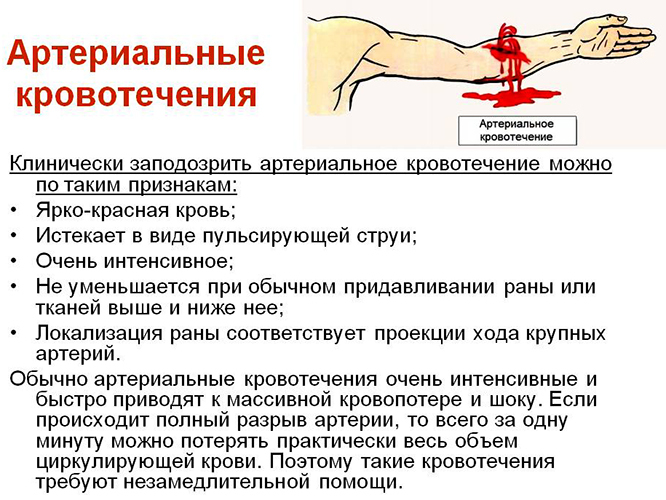
The main signs of arterial hemorrhage:
- blood of a bright scarlet hue;
- the blood does not flow out, but beats with a fountain (in the first minutes: then, as the blood volume decreases and the blood pressure falls, the blood is poured out in a stream, as if a vein is damaged);
- well noticeable pulsation (weakening and strengthening of the jet), coinciding with the beats of the heart;
- a decrease in the intensity of bleeding when the artery is squeezed;
- rapid blood loss, expressed in pallor of the skin, increased heart rate, drop in blood pressure, fainting.
Training
Since with arterial bleeding, only several minutes, the preparatory period is reduced to a minimum, in particular, the preliminary cleaning the wound.
Recommended:
- Freeing the area with the existing wound from clothing: it is necessary to make sure that this is indeed arterial bleeding.
- Compress the artery above the wound; if it is impossible to find it, press the wound itself tightly with the palm of your hand.
Bandage application
If the artery is damaged, blood flows out under high pressure, for this reason, the pressure bandage will be ineffective. The only way to prevent large blood loss and death of the patient is to apply a tourniquet. But it should be borne in mind that touring several times increases the risk of undesirable consequences. This can be avoided through the correct implementation of the procedure and competent subsequent actions, depending on where the wound is located.
On the shoulder
In case of a wound on the shoulder that caused arterial bleeding, it is necessary:
- Pinch the axillary artery as tightly as possible. You can determine its position by the beat of the pulse at this point. To stop the blood, the victim's hand is lifted up, pulled back as much as possible, the fingers are placed in the armpit and press the artery to the head of the humerus.
- Apply a tourniquet. The best option is the Esmarch elastic tourniquet, which has a perforation that facilitates fixation. In its absence, you can use any available means: a rubber hose, a towel, a strip of fabric, a belt.
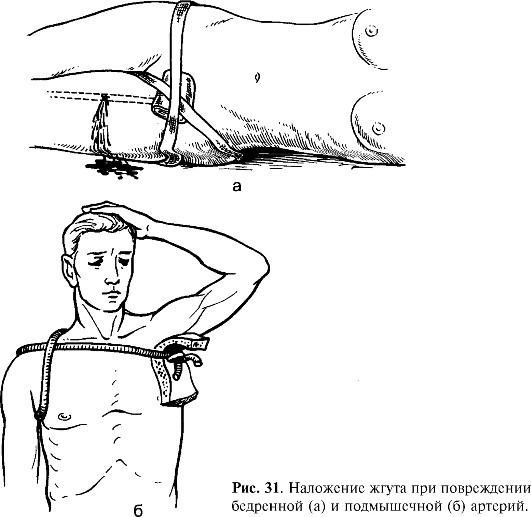
The algorithm for applying not pressing, but a tourniquet dressing will be based on the following rules:
- the place of imposition is 5-7 cm above the wound;
- the tourniquet is not applied to the naked body: if there is no clothing in the desired area, it is necessary to make several turns of the bandage;
- the tourniquet is applied with the most possible tension;
- The 1st turn of the tourniquet is immediately fixed. Then another 2-3 turns are performed with a slight downward shift;
- the end of the harness is fixed in any way
A sheet of paper is placed under the tourniquet with the exact time of application and the name of the victim indicated on it.
In the absence of a tourniquet, it can be replaced with a cloth tied in the form of a ring and a twist, which is subsequently fixed with a bandage.
With a correctly applied tourniquet:
- the bleeding stops;
- there is no pulse on the limb below the tourniquet;
- the skin of the hand below the tourniquet becomes pale.
If the bleeding is not stopped, and the skin of the limb has acquired a bluish color, then the tourniquet was applied incorrectly and squeezed a vein, not an artery. In this case, the procedure will have to be repeated. At the same time, moderate pain is considered normal and not dangerous.
After the blood has stopped, wound tamponade is performed.
For this:
- Its cavity is completely and as tightly filled with a bandage so as to achieve direct contact with the damaged artery.
- After applying a tampon, it is necessary to press on the wound with maximum effort for 3 minutes, then apply a pressure bandage on it, having previously cleansed the skin in this area of the shoulder.
- Bandaging is performed from the elbow, above which several circular rounds are made.
- The bandage rises up the shoulder, overlapping with each subsequent turn 1/3 or half the width of the bandage already applied.
- A bandage is fixed 5-7 cm above the wound site.
Sometimes the described measures are enough to form a blood clot and stop bleeding, which makes it possible to loosen the tourniquet, but this must be done very slowly, controlling the condition of the wound. If bleeding has resumed, the tourniquet is tightened again.
Since the tourniquet completely compresses the blood vessels and nerve endings, it can lead to the development of tissue necrosis and the need for amputation of the arm. For this reason, you should control the time during which the tourniquet is on the limb. An interval of 1 hour in warm weather and half an hour - if the victim is forced to be in the cold, is considered safe.
If during this period it was not possible to obtain qualified assistance, you must:
- Pinch the artery.
- Loosen the tourniquet.
- Perform a light massage of the remaining furrow from it.
- Wait about 10 minutes, during which blood circulation should be restored. This is indicated by the warming of the fingers, the normalization of the color of the nails, the appearance of a paler spot on the skin after strong pressing on it.
- Tighten the tourniquet again, slightly moving it from its original location (up or down).
- Fix (write down) the reset time.
- Take measures to ensure that the tourniquet is clearly visible (do not bandage or cover with clothing).
It must be remembered that when reapplying, the tourniquet time is halved. The next time the tourniquet will have to be removed after 30 minutes (in summer) and after 15 minutes (in winter).
In case of large blood loss, reapplication of the tourniquet can cause hemorrhagic shock, therefore, in this case, the procedure is performed extremely carefully or not at all.
On the forearm
In case of violation of the integrity of the arteries on the forearm, it is necessary to find the brachial artery, which is a continuation of the subclavian artery, and press it tightly against the humerus, placing the palm on the inside or outside of the shoulder and squeezing it fingers.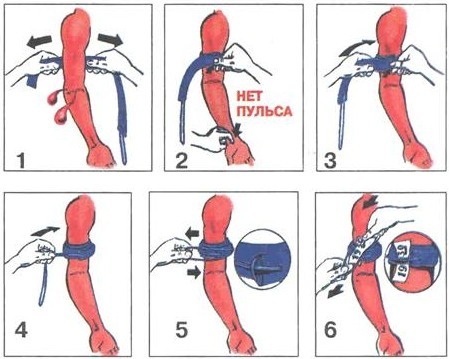
Since in the forearm area the artery passes between the bones, it is impossible to clamp it here, for this reason, the tourniquet is applied to the upper third of the shoulder, but as close to the wound as possible, according to the algorithm described higher. A bandage after tamponade is applied from the wrist, around which several circular tours are made, to the elbow, and fixed above the wound. Subsequent actions are as described above.
On the shin
In case of leg injuries leading to arterial hemorrhage, it is necessary to temporarily stop the bleeding by pressing the popliteal artery against the popliteal fossa.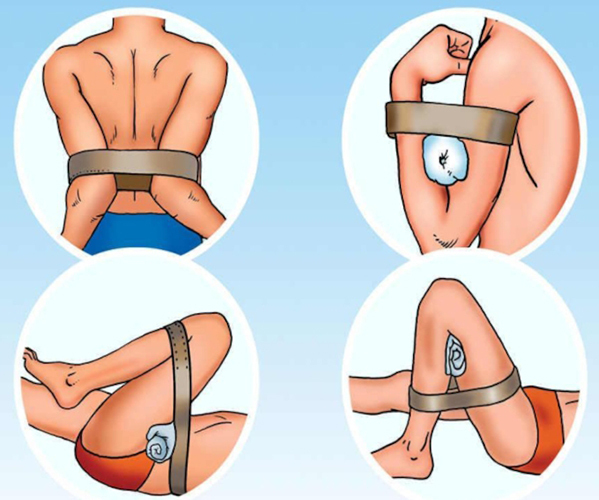
Next, apply a tourniquet to the thigh. After stopping the blood, the wound is tamponed and bandaged in the direction from the ankle joint to the knee with circular or spiral bandaging. Further actions are the same as for a hand injury.
Care procedures after
Before the arrival of an ambulance, it is necessary to carefully monitor the condition of the victim and the time elapsed since the application of the tourniquet. In order to ensure the maximum blood supply to the internal organs, which most need oxygen and the flow of nutrients, with a reduced blood volume substances, the patient is placed on his side or back so that his legs are raised by 20-30 cm relative to the head, and the wounded limb is located as much as possible higher.
After the victim is delivered to the hospital and examined by a doctor, the following actions are performed:
- Treatment of the wound surface: its cleaning and disinfection.
- Replacing the tourniquet and tampon.
- Restoration of the integrity of the artery walls, usually performed by suturing the vessel. As additional measures, the above physical, chemical, biological methods of stopping blood can be used.
- To normalize blood circulation, the victim is given a blood transfusion. He should be examined in order to identify possible fractures of the limbs and injuries of internal organs. Over the next few days, the patient is in the hospital.
Contraindications
Applying a pressure bandage, the algorithm of which is not complicated, is an effective and relatively safe method of stopping bleeding. However, there are situations when it can harm a person, increasing blood loss, or be ineffective.
A pressure bandage should not be used when:
- the presence of a large foreign body stuck in the wound;
- clogging of the wound surface with small objects with piercing and cutting properties: fragments of glass, metal, wood;
- open fracture and the presence of bone fragments in the wound.
In all these situations, pressure on the vessels can injure them even more and, as a result, lead to an increase in blood loss.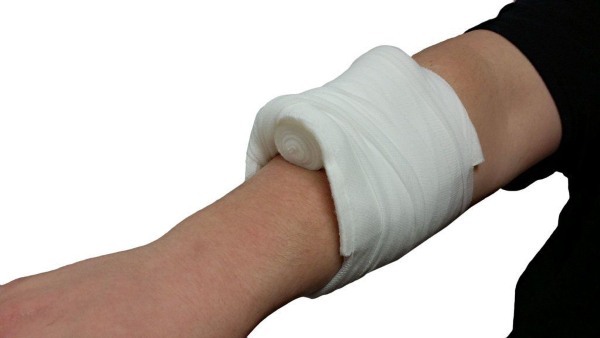
Also, this method of emergency assistance will be ineffective for:
- injuries to the arms and legs, leading to arterial hemorrhage;
- very severe venous bleeding;
- a low level of platelets in the victim (poor blood clotting);
- traumatic limb amputation.
Possible complications
If the bandage or tourniquet is too weak, the bleeding cannot be stopped and the victim will continue to lose blood, which threatens him with the following complications:
- the development of anemia;
- a sharp drop in blood pressure;
- heart attack;
- stroke;
- various diseases of internal organs, as a result of their prolonged oxygen starvation;
- death (with blood loss accounting for more than 20% of the total blood volume).
With an excessively tight bandage or incorrectly (for too long a period of time) a tourniquet is applied, the following complications are possible, which usually appear when trying to remove the bandage (tourniquet):
| Complication | Description |
| Turnstile shock | Intoxication of the body during penetration of the destroyed muscle fibers into the bloodstream from the wounded arm (leg). Usually manifests itself:
|
| Paresis | Decreased muscle strength associated with prolonged compression of nerve fibers. Among the external manifestations:
|
| Paralysis | Complete immobilization of a limb is a consequence of damage to peripheral nerve endings responsible for motor activity |
| Amyotrophy | Dystrophic changes in muscle fibers, a decrease in muscle volume, which developed due to prolonged immobility |
| Limb ischemia | Weakening of blood circulation in them due to blockage of blood vessels |
| Limb necrosis | Tissue death as a result of prolonged (over 2 hours) lack of blood flow. In case of necrosis, the only way to save the patient's life is to amputate the injured arm (leg) |
A relatively mild complication can be considered a slow healing of the wound and its frequent suppuration.
No one is immune from injuries that cause large blood loss. With the knowledge of the algorithms and the ability to apply a pressure and tourniquet bandage, the victim's chances of saving life and health increase many times over.
Compression bandage video
Stopping venous bleeding by applying a pressure bandage:



