Content
- Indications for research
- Preparation for analysis
- Orthopantomograph
- Stages
- Features for the child
- Dignity
- Flaws
- What is displayed in the picture
- Decoding the results
- In adults
- In children
- Teeth X-ray video
Despite the emergence of advanced technologies, a panoramic X-ray image of teeth is today a popular diagnostic method. used in dentistry. It is used in all cases when it is required to obtain information about the state of the human dentition as a whole and to identify the existing problems of the oral cavity.
Indications for research
X-ray of teeth (panoramic X-ray) is a method of examining internal, invisible during visual inspection, structures of the human body. It is based on the ability of X-rays, passing through tissues and being partially absorbed by them, to create an impression on the film. Although X-rays are a type of radiation that can harm the body, X-rays are completely safe.
This is due to the fact that during the examination:
- the radiation source used generates beams having low energy;
- the exposure time is extremely short (fractions of a second);
- protective measures are applied to limit the area to be exposed;
- in the case of using digital equipment of the latest generation, the dose of radiation received during procedure is 95% of the standard dose received by the patient when using film devices.
For safety reasons, X-ray examinations have no age restrictions and can be performed multiple times in order to:
- obtaining reliable results;
- tracking the dynamics of treatment;
- checking its effectiveness.
Several types of X-ray diagnostics are widely used in modern dentistry:
- periapical, involving examination of 1-2 adjacent teeth;
- palatal (occlusal), in which a single image of the upper or lower row of teeth is obtained;
- bite, providing maximum information about the condition of the crowns on the upper and lower teeth;
- panoramic or orthopanthogram (OPTG).
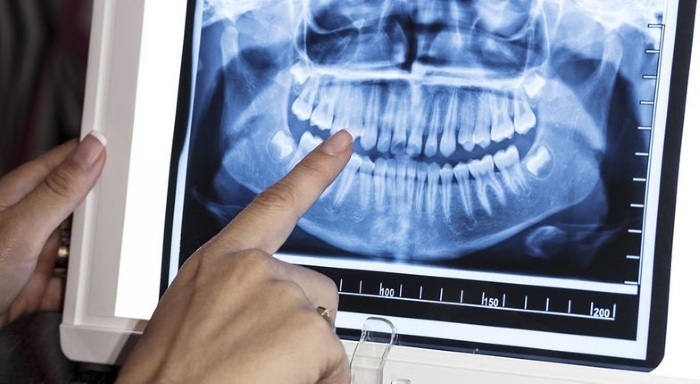
The latter gives an idea of the state:
- teeth;
- gums;
- maxillary sinuses;
- soft tissues surrounding these structures.
Depending on the equipment used, the examination result is displayed on film or displayed on the monitor, allowing you to identify hidden defects and assess the degree of development of pathological process.
In particular, by analyzing a panoramic photograph of an adult, a specialist can determine:
- the presence and location of carious cavities on the surfaces of the teeth;
- deep caries affecting the root;
- diagnose jaw fractures, fractures and dislocations of teeth due to trauma;
- assess the condition of the periodontium and bone septa between the teeth;
- identify benign and malignant neoplasms located in soft tissues;
- explore the maxillary sinuses.
The examination of a preschool child has other purposes and, in particular:
- makes it possible to determine the location of the primordia of permanent teeth;
- find out how their formation is progressing and whether there are any factors that interfere with the normal process of development of the dentition.
Also, an orthopanthogram of a small patient can reveal the presence of:
- impacted (developing with any deviations) teeth;
- inflammatory foci on the roots of milk teeth;
- factors that slow down the process of involution (reverse development) of the roots of deciduous teeth and the eruption of permanent teeth.
Orthopanthogram can be performed before treatment, during treatment, in the field, or as a preliminary procedure prior to other types of examination.
The main indications for its implementation are:
- suspicion of the presence of carious cavities in the interdental spaces;
- the need to determine the exact location of multiple foci of infection at the roots of the teeth;
- periodontitis;
- sinusitis;
- suspicion of neoplasms localized in nearby soft tissues;
- the need to check the quality of treatment;
- fractures of the jaw;
- cases of acute toothache of unclear localization, the cause of which cannot be clarified by visual examination.
In addition, a panoramic examination is mandatory before prosthetics or the installation of implants to determine the appropriateness of such procedures, as well as in order to:
- obtaining information about the degree of tooth decay;
- assessing the condition of the gum bone tissue;
- exclusion of contraindications, which may be an inflammatory process or a neoplasm;
- if it is necessary to make a "bridge" - an assessment of the condition of the teeth on which the structure will be fixed.
For children, the main indications for panoramic radiography are the period of active eruption of molars and the presence of any problems in the formation of the dentition requiring the intervention of an orthodontist (malocclusion, delayed jaw growth, curves teeth).
Preparation for analysis
X-ray of teeth (panoramic X-ray) does not have any special preparation for performing, except for a situation when the patient is a pregnant woman. In that case, she must definitely notify the doctor about the fact of pregnancy and first consult a gynecologist. Everyone else is advised not to wear metal jewelry on the head and neck area (earrings, piercings, hairpins). They will have to be removed before the procedure, as the metal will distort the result of the X-ray.
It is also advisable to thoroughly cleanse the oral cavity from food debris in order to eliminate mistakes, and choose comfortable shoes and clothes to feel as comfortable as possible. You will have to stand still for a few seconds, wearing a heavy lead apron.
Orthopantomograph
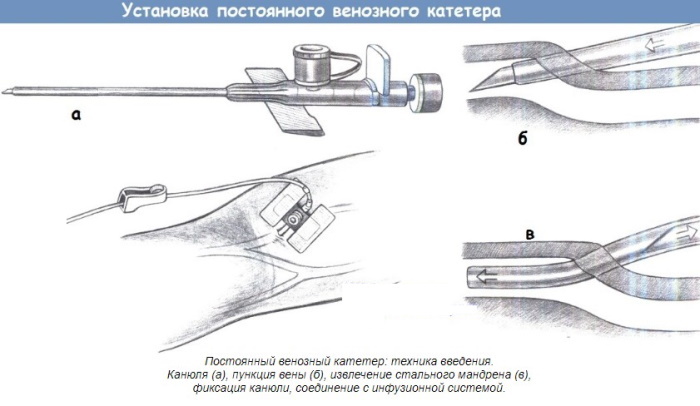
The examination is performed on a special apparatus - digital or film orthopantomograph.
Its main elements are:
- a rotating U-shaped frame, on one side of which there is an X-ray source, and on the other - a receiver: a sensor that transmits information to a monitor, or a cassette with a film;
- temporal clamps, necessary to hold the patient's head in the desired position;
- oral element that fixes the jaw;
- chin rest;
- stabilizing handles;
- Remote Control;
- vertical column with a mechanism that allows you to change the height of the device in accordance with the patient's height.
Stages
The stages of the procedure will be as follows:
| № | Stage | Description |
| 1 | Training | Before performing the procedure, the patient is asked to remove glasses, jewelry, dentures, braces, then put on a protective apron with sewn-in lead plates and a protective collar |
| 2 | Determination of position | The patient should take the following position:
To determine the desired position of the patient's head, new-generation devices use a laser centering, in its absence, the radiologist performs all the actions himself, focusing exclusively on own experience |
| 3 | Finding motionless | The operator offers the patient not to move and starts the equipment. The bed begins to move, describing an arc around the patient's head. After 20-30 seconds, it returns to its original position, the temporal clamps are unclenched |
| 4 | Checking the snapshot | The snapshot is an image of the dentition unfolded in the plane |
When using digital equipment, the result can be printed immediately, if the diagnostics were performed on a film machine, you will have to wait a few minutes for the film to develop.
Features for the child
Performing OPHT on a child does not fundamentally differ from the "adult" procedure, but it is advisable to take an overview image in one of the specialized children's clinics.
In them, as a rule:
- installed devices of small dimensions, corresponding to the growth of the baby;
- the used orthopanthographs give the minimum radiation exposure;
- the staff has acquired the skills of working with children and will be able to carry out diagnostics so as not to frighten the little patient and not form a negative attitude towards the doctor in him;
- the cost of the children's clinic services is slightly lower than the price of the same services for adults.
Dignity
Dental X-ray (panoramic X-ray) is safe for the patient, painless, does not cause discomfort. The duration of the procedure is no more than 5 minutes, and the radiation dose is much lower than when performing "targeted" images.
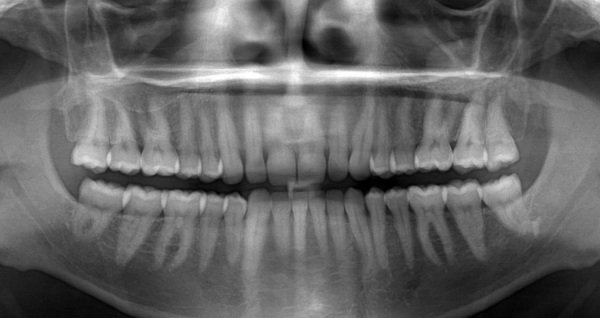
Other benefits include:
- no contraindications;
- high image quality;
- information content of the picture;
- the possibility of a comprehensive assessment of the state of the oral cavity;
- low dose of radiation;
- instant results;
- the ability to examine in more detail any fragment of the image by enlarging it.
Flaws
There are also disadvantages associated with the fact that the image is in the same plane and has a low resolution:
- the impossibility of detecting supernumerary teeth when they are behind the dentition;
- the impossibility of performing some measurements, which may be needed before implantation;
- OPGT is not very informative in cases when it is required to evaluate the bite line.
If it is necessary to obtain this information, the patient is shown other types of radiography (bite, periapical). He may also be offered to perform computed tomography of the teeth. CT allows you to obtain a three-dimensional model of the object of interest, as well as a series of ultra-sharp slices, on which the smallest elements are visible. This technology has no drawbacks, except for the high cost of the procedure.
What is displayed in the picture
Knowing the principle of action of X-rays and the features of the visual display of possible tooth defects, jaw, soft tissues on an X-ray, you can, if desired, independently analyze the result OPGT.
Dental X-ray (panoramic X-ray) is based on the property of X-rays to be absorbed differently by human tissues body and, accordingly, leave in the future on the film, sensitive to X-rays, spots with different coloring.
From these spots the image of the investigated area is formed. The denser the tissue, the more radiation energy they will absorb, respectively, the film of rays will get less, therefore, on an X-ray image, more dense tissues will correspond to areas with a lighter color.
In digital devices, film is not used; instead, sensors are used that convert the residual radiation into an electrical signal. Depending on the signal strength, an image of a certain brightness is obtained on the monitor.
Since all elements of the oral cavity have different densities, they are displayed on the film in different ways:
- X-ray-positive fillings, crowns, dental implants - have a bright white color;
- teeth - white, but translucent, with a grayish tint;
- liquids, soft tissues - painted in gray tones, the intensity of the color depends on the density;
- the cavities correspond to black.
A panoramic image of healthy teeth clearly shows:
- roots of teeth;
- areas with a denser layer of enamel (they look like white spots along the edge of the tooth, brighter than the rest of its tissues);
- "Wisdom teeth" not yet erupted and not even fully formed.
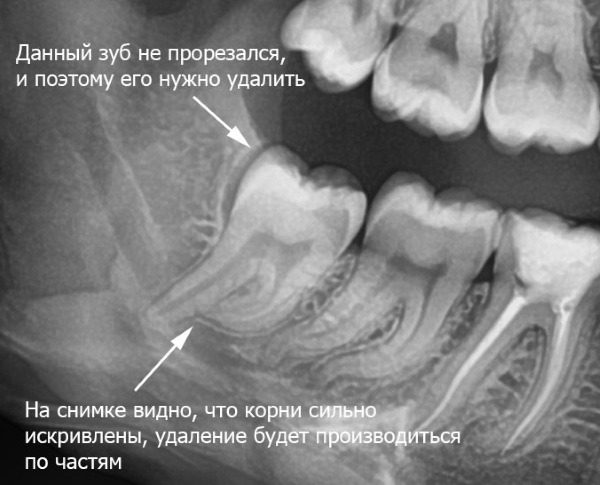
Health of teeth and gums is also said to be:
- a small distance between the upper part of the interroot septum and the place where 2 adjacent teeth meet. It indicates that the tooth is surrounded by a high layer of connective tissue and, therefore, is highly resistant;
- the presence of a light strip surrounding the root of the tooth and indicating that the bone tissue located here has a dense structure;
- uniform coloring of teeth, bone and soft tissue;
- anatomically correct position of the teeth and no crowding.
Decoding the results
Before starting an independent analysis, it is necessary to correctly orient the image, figuring out where its left and where is the right side. For convenience, they are usually labeled with the letters L and R.
In adults
Then you need to try to find: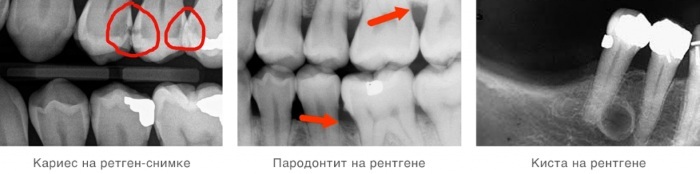
| Part of the review | Description |
| Artificial elements | They differ sharply from natural fabrics in bright white color and have clear contours. Also, on the overview X-ray image, the fasteners of the implants are clearly visible, which makes it easy to assess the quality of work on the installation of dentures. With the help of an overview image, you can find a foreign body "forgotten" there by the doctor: this happens when cleaning the canals and can subsequently lead to serious complications. |
| Caries | The panoramic image is not able to visualize the primary caries, which has not yet caused destruction of the enamel. Fissure and root caries are also not well diagnosed. A defect on the surface of the tooth crown will look like:
|
| Wedge-shaped defects | Non-carious damage to the bone tissue, as a result of which it slightly drops (rises), exposing the neck of the tooth. The defect has the shape of a wedge upon visual inspection and looks like a dark triangular spot near the neck of the tooth in the picture. |
| Paradontitis | This is the name of the inflammatory process, covering the soft and bone tissues located near the tooth and fixing it in the gum. On an X-ray image, the area of the gum affected by periodontitis will have an uneven, bumpy edge, due to the proliferation of connective tissue, which is a direct consequence of the inflammatory process. |
| Periodontitis | Inflammatory process, covering the layer of connective tissue between the tooth root and the gum bone. In the picture, periodontitis looks like a dark spot, contours repeating the shape of the root. |
| Periodontal disease | These are dystrophic changes in the bone tissue holding the tooth, in particular, its thinning. |
| Cyst and granuloma | A cyst is a benign neoplasm, the size of which varies from 1.2 to 2 cm. It is a cavity, a sac of fibrous tissue filled with pus. A granuloma differs from a cyst only in smaller sizes (up to 0.8 cm). Both the one and the other defect is well diagnosed on a panoramic X-ray, representing an oblong darker spot at the root of the tooth. |
| Pulpitis | Inflammation of the pulp - soft tissue located in the central part of the tooth. It is, as a rule, a consequence of caries not cured in a timely manner and bacteria entering the pulp through the carious cavity. On the picture, this pathology will look like a dark spot in the central part of the tooth. |
| Dentikly | Or tartar, dense mineral deposits on the crown of the tooth, which appear on an X-ray image as irregularly shaped and uneven stains. |
| Jaw injuries | Panoramic X-ray also makes it possible to identify a fracture of the jaw, its nature and location. On the picture, the crack will look like a dark, uneven line with clear edges, passing vertically or at a slight inclination from the edge of the jaw to the dentition. On the overview image, you can also see the dislocation of the tooth: its displacement relative to other teeth. |
| Malignant neoplasms | If untreated, some benign neoplasms (cysts, granulomas) can change and be reborn into a carcinoma of the jaw - an aggressive malignant tumor that in a short time is able to occupy neighboring areas. On an x-ray, the carcinoma appears as a black spot with clear edges. |
| Wisdom teeth | Sometimes "eights" (as dentists call them) have to be removed, even if they are completely healthy and do not cause any trouble to the patient. The indication for removal is their incorrect (horizontal) location: in this case, it causes harm to the rest of the teeth, provoking their crowding and causing the appearance of various neoplasms. An overview snapshot will help you figure out if you need to delete it. |
| Diagnostics of the maxillary sinuses | Although the assessment of the maxillary sinuses is not expected when taking a panoramic image, sometimes OPGT can reveal benign neoplasms (cysts) that appear as a lighter, transparent spot or foreign body that is bright white and small sizes. |
In children
OPGT of a child has its own characteristics: on it you can see not only the existing milk teeth, but also the rudiments of permanent teeth, who still have to cut through and determine how likely certain problems in the development of dentoalveolar have about this view: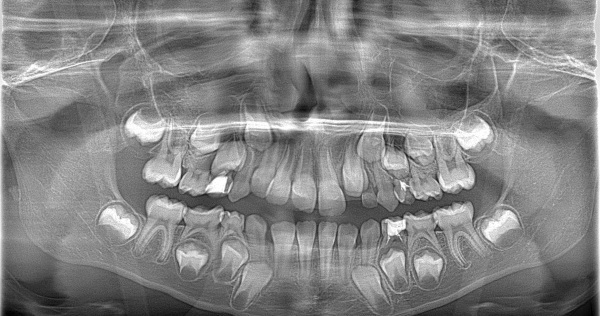
With a panoramic shot, you can:
- to determine the presence of supernumerary (extra) teeth, even if they still exist only in their infancy;
- diagnose the reason for the absence of some teeth in a child in order to determine the appropriateness of treatment and choose the optimal strategy.
The following options are possible:
- tooth rudiments are present, but do not erupt (impacted teeth), there is no place for them. The child may be assigned to wear a bracket system, which will expand the dentition and form gaps for missing teeth;
- the rudiments of teeth are absent, there is adentia - the pathology of the development of the dentoalveolar system. Depending on the appearance of the dentition, everything is left as is (the teeth are closed, look aesthetically pleasing) or, with clearly visible gaps, braces are put on to fix them with the aim of installing them in the future implants.
Panoramic X-ray is a painless, quick and relatively inexpensive procedure that evaluates the a snapshot of the condition of the teeth, gums, adjacent soft tissues and, having identified possible pathologies, choose the optimal method treatment.
Teeth X-ray video
Panoramic X-ray: