Content
- Initial manifestation of the disease
- Other symptoms
- The main causes of the development of the disease
- How is it developing
- Forms and degrees
- Treatment in adults
- Medicines
- Inhalers
- Folk remedies
- Diet
- Complications
- Asthma Videos
People prone to allergies and inflammatory diseases of the bronchi and lungs need to know symptoms of bronchial asthmahow it starts, what types of medical care exist in the treatment and prevention of seizures, and the presence of complications in adults. It is also important to adhere to a diet, which is aimed at avoiding foods that provoke an allergic reaction of the body.
Initial manifestation of the disease
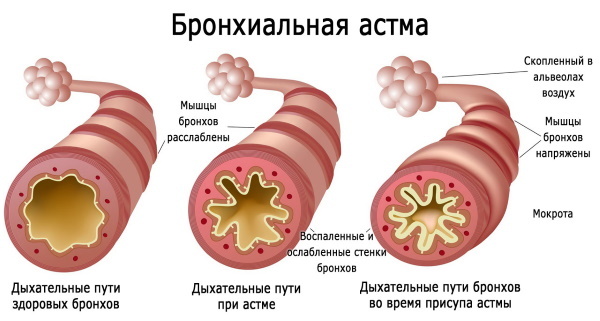
Bronchial asthma refers to chronic inflammatory diseases of the respiratory system of a non-infectious nature. It is characterized by altered bronchial reactivity, cyclic course with the development of obstructive syndrome, asthma attacks and dry unproductive cough. At its basis, the decisive role is played by the allergic component and a malfunction of the immune system.
Asthma (symptoms in adults and how it begins, people study, fearing the first signs of shortness of breath) has a completely clear and definite symptomatology and is characterized by gradual development. Its onset is preceded by a number of harbingers of the disease, which can be mistaken for malaise, a viral infection.
Attention should be paid to such phenomena as:
- An attack of suffocation, which occurs at night against the background of general calmness, after physical exertion, prolonged stay in highly polluted places, during flowering, when moving from a warm room to a cold, sharp smells. It is characterized by suddenness.
- Dry, unproductive cough.
- Rapid shallow breathing.
- Whistling dry wheezing.
- Forced position during an attack: sitting, legs hanging, hands resting on the bed.
- The state of health worsens in dry weather and improves in rain.
- Difficulty breathing is observed under stress.
- Sometimes skin manifestations: rash, urticaria.
These symptoms are characterized by the fact that they stop after the disappearance of the irritating factor.
Among the typical symptoms of asthma, such manifestations can be observed:
- Rapid breathing without wheezing or shortness of breath.
- Desire to draw more air into the lungs.
- Fatigue and increased anxiety.
- Chronic cough for no apparent reason.
- Hoarseness of voice.
Other symptoms
Asthma at the initial stage of its development in adults does not have a serious effect on the body. But then a number of symptoms appear, indicating that a violation of the functioning of organs and systems begins.
How they can be identified, indirect signs say:
- Shortness of breath, shortness of breath at rest.
- Feeling weak. Any movement only increases shortness of breath. The man takes a forced pose.
- Acrocyanosis and cyanosis of the skin.
- Tachycardia: 90-120 beats per minute.
- Changes in the nails (like a watch glass) and phalanges of the fingers (like a drumstick) are dystrophic in nature.
- Headaches with dizziness due to respiratory distress.
- Increased tendency to allergic reactions and diseases of the skin and mucous membranes.

Asthma in adults. Symptoms
It is necessary to distinguish the phenomena of chronic bronchitis with obstructive syndrome from asthma symptoms:
| Chronical bronchitis | Bronchial asthma | |
| Flow | Stable | A sudden exacerbation in the form of an attack (several minutes-hours) with a violation of the general condition of the body. |
| Cause of occurrence | Infections: bacterial, viral. | Inhalation of airborne allergens. Seizures often occur at night. |
| Dyspnea | It is characteristic of obstructive bronchitis. | The main symptom. It manifests itself with any degree of the disease. |
| Cough | Dry alternates with wet. | Dry |
| Sputum | Mucopurulent, greenish, in large volume. | Vitreous, at the end of the attack a small amount. |
| Temperature | Periodically | No |
| Emotional response to an attack | No | Fear of death. |
The main causes of the development of the disease
Factors contributing to the development of asthma:
- Allergens: food, household, fungal, pollen, animal hair.
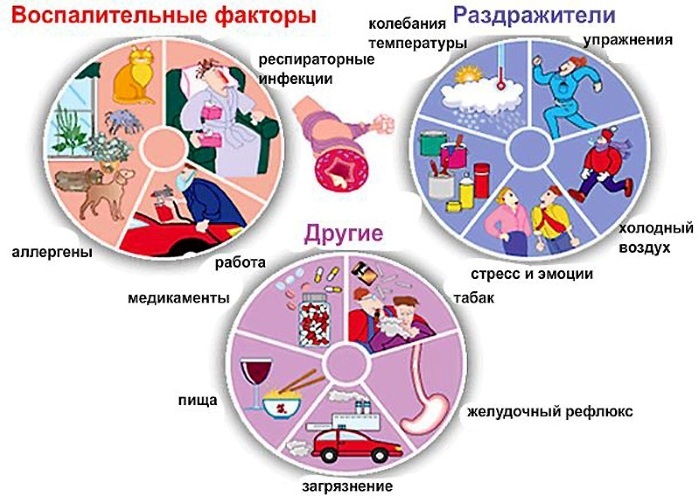
- Pharmacological preparations: based on aspirin and analgin, beta-blockers, dyes.
- Chronic bronchitis and frequent upper respiratory tract infections.
- Professional: smoke, chemical gaseous substances.
- Waste production.
- Smoking.
- Meteorological: dry climate, sudden changes in temperature, atmospheric pressure.
- Physical exercise.
- Disorders of the endocrine system.
- Psychoemotional disorders.
These reasons, with the help of a different mechanism of action, lead to an increase in the release of mediators (histamine, acetylcholine), which cause spasm of the smooth muscles of the bronchopulmonary system.
How is it developing
Asthma (symptoms in adults and how it begins, mechanisms of development and pathology options) is described in numerous textbooks for medical institutions.
There are immunological and non-immunological with clinical and pathogenetic variants of the disease:
- Atopic (allergic). Available in 1/3 of patients. Allergen related.
- Infection-dependent, in which asthma attacks occur with an exacerbation of a chronic infection in the lungs.
- Aspirin as a result of long-term use of aspirin or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Physical effort.
- Dyshormonal. In its occurrence, disturbances in the work of the endocrine system during menopause, adrenal insufficiency are involved.
- Neuropsychic.
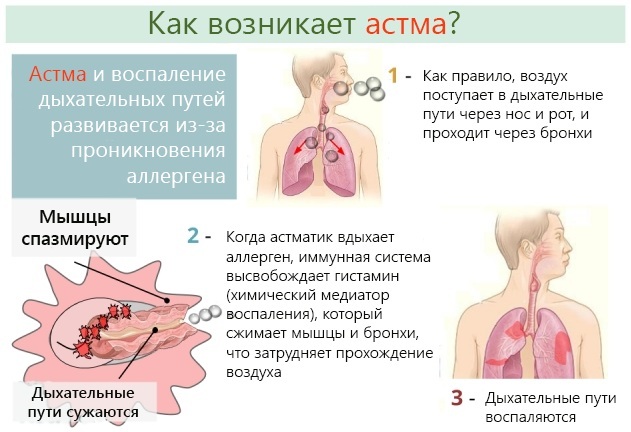
Sometimes in patients, bronchial asthma develops with a combination of two options: aspirin and dyshormonal, atopic and infectious-dependent.
The mechanism of development of different variants of asthma is based on inflammation of the bronchial wall, which violates the integrity of the epithelium and leading to its desquamation, and an increase in the sensitivity (reactivity) of the respiratory ways. As a result, there is a restructuring of the bronchopulmonary system. At the same time, the number of mast cells, eosinophils and T-lymphocytes increases, which secrete substances that contribute to the occurrence of an allergic and inflammatory reaction of the body.
With the restructuring of bronchial tissues, the basement membrane thickens, collagen is deposited under the epithelium, smooth muscle muscles and mucous glands are hypertrophied, their number increases, new ones are formed vessels. These changes lead to irreversible consequences of the air exchange function in the lungs, the development of bronchial hyperreactivity and obstructive syndrome.
The inflammatory process is associated with an increase in the activity of bronchial smooth muscles in relation to irritants: cold air, smoke, strong odor, and increased secretion of mucus by epithelial cells of the bronchi. Violation of mucus removal from the lumen of the bronchioles is associated with eosinophils, which damage the cilia of the epithelium, making the evacuation of mucous secretions unproductive.
Forms and degrees
According to the international classification, asthma is divided into:
- Allergic.
- Non-allergic.
- Mixed type.
- Unspecified.
All patients are divided into categories, depending on the causes of the development of the disease, which are called phenotypes.
Phenotypic forms of asthma:
- Allergic. It begins in childhood, and is associated with a hereditary factor: in relatives manifestations of respiratory or skin allergic diseases. Immune inflammation of the bronchial tree is characteristic. Treatment is based on the use of corticosteroids.
- Non-allergic (aspirin) develops in the body of an adult. It is not associated with allergies and a burdened history. Inflammatory changes in the bronchial tree develop under the influence of leukotrienes. Glucocorticosteroid therapy is ineffective.
- Persistent airway constriction is associated with uncontrolled asthma symptoms. With this form, there is a restructuring of the walls of the bronchi. The disease is difficult to treat.
- With a belated onset, which mainly affects women of advanced age. An increased dose of corticosteroids is required.
- Against the background of excess weight (obesity). It is characterized by a severe course and moderate allergic inflammation of the bronchi.
 The degree of asthma depends on the symptoms of the disease and the data obtained during instrumental examination (peak flowmetry, spirometry):
The degree of asthma depends on the symptoms of the disease and the data obtained during instrumental examination (peak flowmetry, spirometry):
- Light intermittent. There are no signs of asthma between attacks.
- Mild persistent with weekly exacerbations, often at night.
- Moderate persistent: daily attacks.
- Severe persistent is manifested by constant symptoms. Sleep and physical activity are disturbed.
Treatment in adults
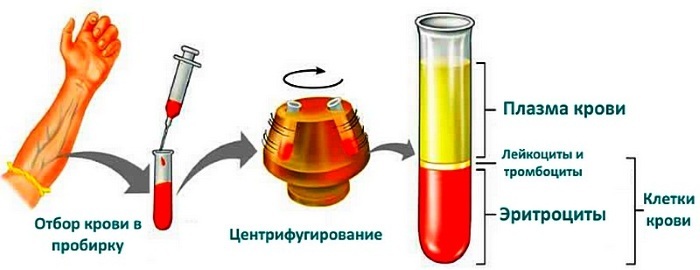
Asthma (symptoms in adults, how it starts and what types of drugs are used, many are trying to find the answer to these questions on the Internet, instead of consult a doctor) has a complex etiology, and only a qualified person can establish the true cause of the pathology, as well as prescribe an effective drug therapy doctor. And most often, this is possible after collecting anamnesis, blood tests, allergological tests, instrumental studies.
Drug therapy is determined by the quality and effectiveness of:
- Well controlled.
- Partially controlled.
- Uncontrolled, in which drugs do not help.
When the patient's condition changes, his body's resistance to the treatment being carried out, the treatment regimen, doses and drug intake should be changed.
Medicines prescribed to patients are divided into:
- Basic, which help control the course of the disease, reduce the frequency of exacerbations.
- Symptomatic are ambulance drugs, relieve bronchial spasm.
Medicines
Chronic inflammation in bronchial asthma is characterized by the involvement of eosinophils and mast cells in the pathological process. Basic drugs help stop the progression of the disease.
They are used daily for:
- Monitoring the frequency and duration of symptoms.
- Expansion of the lumen of the bronchi.
- Prevention of status asthmaticus and complications.
Basic therapy drugs include:
- Glucocorticosteroids: fluticasone, budesonide, beclomethasone, triamcinolone. These medicinal substances increase the production of β2-adrenergic receptors, which inhibit the pathological action of allergens, reduce inflammation and mucosal edema. They have minimal side effects. The dosage is calculated based on the patient's condition and the severity of the symptoms.
-
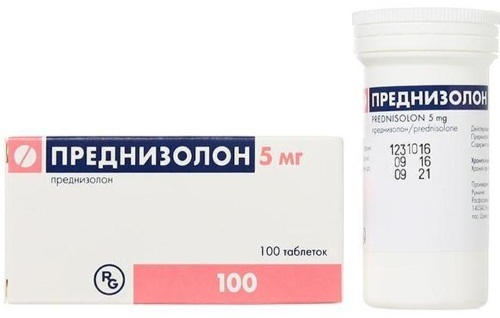
Systemic glucocorticosteroids: methylprednisolone, prednisolone, betamethasone, dexamethasone. They are used in the form of tablets or intravenous administration with ineffective therapy with other drugs. They have multiple side effects.
- Mast Cell Stabilizers: cromoglycic acid, nedocromil, intal. They act on mast cells, release histamine substances. Suppress bronchospasm in response to an allergic attack. They help to reduce the activity of the bronchi in winter, thereby reducing the duration of attacks and their frequency of occurrence.
- Leukotriene antagonists: montelukast, zafirlukast. The use of these drugs reduces the dosage of rapid-acting β2-adrenergic agonists. They have an anti-inflammatory effect, reduce the reactivity of the bronchopulmonary system, increase the secretion of mucus. They are prescribed for aspirin asthma, for the prevention of bronchospasm during physical exertion.
- Β2-adrenergic agonists: salbutamol, preparations based on salmeterol, fenoterol. Provide prolonged (up to 12 hours) expansion of bronchioles, inhibit the production of leukotrienes, prevent inflammation and reduce allergic reactions.
- Xanthines(long-acting theophyllines): neophylline, theopec, theophylline.
- Combined: Long-acting β2-agonists and corticosteroids.
- Mucolytic drugs: mukaltin, ACC. Liquefy phlegm, promote its excretion.
- Antibiotics taken when joining the bacterial flora.
- Antibodies to immunoglobulin E: xolar.
Symptomatic drugs do not affect the development of the disease. Their use is justified to relieve suffocation during an attack.
Distinguish:
- Short-acting anticholinergics: atrovent, irravent, spiritiva. The active substance of the drug binds to m-cholinergic receptors, promotes their blockade, and stops the passage of a nerve impulse. This effect leads to a decrease in the tone of the smooth muscles of the bronchi and suppresses their reflex contraction. The lumen of the bronchioles expands, which facilitates the excretion of sputum after an attack.
- β2 agonistsshort and long acting: salbutamol, berotek, serevent. The active component of the drug interacts with beta-2-adrenergic receptors, helping to relax muscle fibers. As a result, the lumen in the bronchi increases, gas exchange improves.
- Theophylline fast and long (theotard) action. They relax the muscles of the bronchi, dilate the blood vessels in the lungs, thereby increasing the percentage of oxygen in the patient's blood. By acting on mast cells, they prevent the release of active proteins, and, consequently, edema and spasm of the bronchial tree.
- Sympathomimetics. Their task is to reduce the permeability of the bronchi and reduce the manifestations of edema. Most effective for exercise asthma. Overdose causes tremors of the muscular system, an unstable emotional state.
- Glucocorticosteroids: flixotide, beklazon. They are used for status asthmaticus and for inhalation by means of a nebulizer.
- Combined: berodual, seretid. Fast action. Effective in inhalation.
Inhalers
Pocket inhalers are used to relieve the symptoms of an attack when the tablets cannot be taken.
The following varieties are available:
- Powder: a single dose of medication is administered. They are more often used for pediatric therapy.
- Aerosol, when used by the patient, a breath is taken at the time of spraying the drug.
 Some medicinal substances are injected through a nebulizer. Therapy using the device allows you to deliver a therapeutic dose of the drug in the form of an aerosol directly to the bronchial tree. It is very effective during an exacerbation when a large dose of bronchodilators is required. The drug practically does not enter the bloodstream, thereby reducing the side effect on other organs.
Some medicinal substances are injected through a nebulizer. Therapy using the device allows you to deliver a therapeutic dose of the drug in the form of an aerosol directly to the bronchial tree. It is very effective during an exacerbation when a large dose of bronchodilators is required. The drug practically does not enter the bloodstream, thereby reducing the side effect on other organs.
Pharmacological groups of symptomatic therapy:
- Β2-short-acting adrenergic agonists: salbutamol, fenoterol. When combined with M-anticholinergics: ventolin, berotek, atrovent. They are used to relieve an attack. Rapidly expand the airway lumen. Valid for up to two hours.
- Long-acting inhaled glucocorticoids: becotide, beklazon, pulmicort. Reception daily. Reduces inflammation in the bronchi.
- Combined. They contain medicinal substances with different effects on the bronchopulmonary system: anti-inflammatory, bronchodilator, antibacterial. Produced under trade names: symbicort, seretid, foster, intal. Reduce obstructive syndrome, increase expiratory volume.
- Xanthines: aminophylline, doxophylline, theophylline. Their use reduces the edema of the mucous membrane of the bronchioles, activates microcirculation, relieves the inflammatory reaction.
Folk remedies
In asthma, as an adjuvant to relieve symptoms, medicinal herbs are used:
- Plantain, Rosyanka, Violet and Fennel in equal dosage.

- Anis, Elecampane, Mother and stepmother, Thyme in 1 volumetric measure.
- Pine buds, Plantain, Mother and stepmother.
- Thyme, Mother and Stepmother, Violet, Elecampane, Anise.
- Thyme, Strawberry, Sage, Melissa.
Prepare these fees in the form of an infusion. Take 1/4 cup 3 times daily before meals.
With obstructive syndrome, inhalation over steam of boiled potatoes can be used.
Diet
Asthma (symptoms in adults, how it starts and what food is associated with, all this information can be obtained from a pulmonologist and allergist) requires the development of a proper nutritional regimen to reduce the impact allergen.
Diet principles (in order of decreasing requirements):
- Prohibited:
- fish;
- seafood;
- caviar;
- fatty meat (duck, goose, pork);
- fried foods and smoked meats;
- honey;
- legumes;
- tomatoes;
- yeast dough;
- eggs;
- chocolate and sweets;
- Strawberry;
- citrus;
- apricots;
- raspberries;
- melon;
- nuts;
- currant;
- alcoholic drinks.

- Limit use:
- salt and sugar;
- muffins;
- decoys.
- The diet is based on:
- dietary meat (rabbit, turkey, chicken);
- hated soups;
- porridge;
- salads;
- doctor's sausage and sausages;
- rye or bran bread;
- biscuit and oatmeal cookies;
- dairy products;
- compotes, decoctions, infusions;
- mineral water.
- Compliance with the diet: food intake is fractional, warm. Dishes are steamed, stewed, boiled, baked in the oven. You can't eat at night.
Complications
Asthma (symptoms in adults, how it begins, all this can be found in the medical literature) has a different nature of the course, and doctors do not always manage to timely diagnose and prescribe drug therapy that relieves symptoms.
In these cases, complications develop:
- Cor pulmonale, in which the right atrium and right ventricle are enlarged and there is a risk of acute pulmonary failure.
- Emphysema of the lungs, pneumosclerosis, respiratory failure.
- Lung atelectasis.
- Subcutaneous emphysema.
- Spontaneous pneumothorax.
- Disorders of the endocrine system.
- Neurological disorders.
The most serious complication is status asthmaticus. It is characterized by a decrease in the effectiveness of drug therapy and an obsessive cough without sputum discharge.
There are 2 forms:
- Anaphylactic. A large number of allergic mediators are released, resulting in an acute severe attack of suffocation. This process occurs in patients with drug sensitivity.
- Metabolic. Associated with the blockade of β-adrenergic receptors against the background of the phenomenon of overdose from taking sympathomimetics during infections of the bronchopulmonary system, adverse weather, after abrupt withdrawal corticosteroids. Symptoms increase gradually.
Status asthma goes through several stages:
- Initial is characterized by pain in the muscles of the shoulder, chest, and abdominal wall. The viscosity of the sputum increases due to hyperventilation and loss of moisture on expiration, which leads to blockage of the bronchiole lumen.
- In the posterior inferior regions, areas of the "silent lung" are formed. Wheezing is heard at a distance, but absent on auscultation. The patient's condition worsens. Tachycardia, increased blood pressure, and acidosis are observed.
- Hypoxic-hypercapnic coma with increasing shortness of breath and cyanosis, depression of consciousness, convulsions.
Asthma, as a manifestation of a disease of the bronchopulmonary system, begins in adults in accordance with different mechanisms of development and a person's predisposition to certain kinds of stimuli. Timely detection of the disease and the initiation of treatment at an early stage by a pulmonologist relieves symptoms and makes the prognosis more favorable.
Asthma Videos
All about bronchial asthma: