Content
- What is a dental nerve and what does it look like
- Where is located, structure, functions
- Causes of nerve inflammation
- Signs of inflammation
- When to remove a nerve
- Dental nerve removal techniques
- Dental nerve removal
- Partial depulpation
- Causes of toothache after dental treatment
- Can a dental nerve die on its own?
- How to kill a dental nerve at home, relieve pain
- Arsenic drugs
- Arsenic-free drugs
- Vinegar essence
- Baking soda and salt solution
- Propolis
- What to do is strictly prohibited
- How long will a tooth live without a nerve?
- What is the threat of poor-quality treatment
- Dental nerve video
In dairy and permanent teeth are nerve fibers, which provide moderate sensitivity of tooth enamel in response to external stimuli in the form of cold or hot drinks, foods with a sour, salty or sweet taste. Timely prevention of dental diseases allows you to maintain the health of dental nerves, prevent their damage by the inflammatory process with further removal.
What is a dental nerve and what does it look like
Dental nerve (pulp or lat. "Pulpis dentis") is a very loose and rather soft tissue of the connective type, which consists of many peripheral nerve fibers, thin-walled lymphatic and blood vessels. All structural elements of molars are located inside the dental crown, and are also located in close proximity to each other.
Outwardly, the dental nerve resembles a thin white thread with an admixture of ichor. In conditions of acute inflammation of the pulp, its nerve fibers can acquire a pink, burgundy or red color, which indicates an increase in local blood circulation and the development of pathological processes in the root part molar.
Where is located, structure, functions
The nerve in the tooth is under the double protection of its surface membranes. The pulp, composed of many peripheral nerve fibers and blood vessels that feed the molar, is surrounded by a dense layer of enamel and dental dentin.
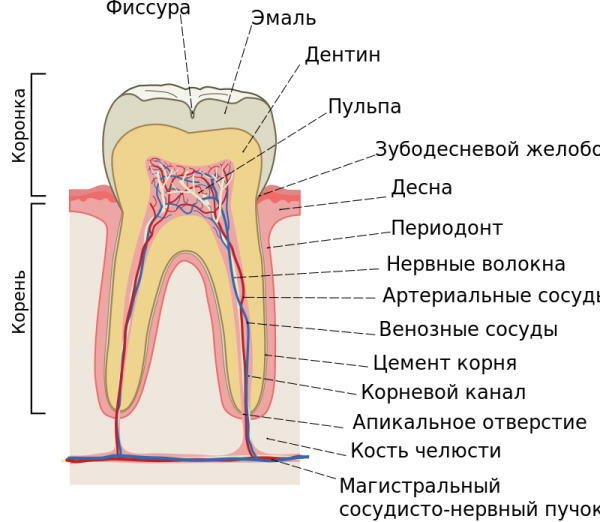
Directly the nerve itself is hidden in the periodontal groove. The lower part of the nerve plexuses of the molar is concentrated in the root canals, which run through the entire root structure of the tooth, and then connected to the main neurovascular bundle of the upper or lower jaw, depending on the location incisor.
The table below details the main functions of the dental nerve:
| Functions of the nerve endings of the teeth | Characterization of the physiological properties of the pulp |
| Blood circulation and innervation | The blood supply and sensitivity of the teeth is provided by the multiple venules and arterioles of the jaw. Entering the cavity of the dental chamber through an opening in the molar canal, a single bundle of vessels and branches of peripheral nerves forms smaller sections of capillaries and nerve plexuses. A sufficient level of innervation and blood irrigation of the tooth tissues maintains their stable mineralization and supply of nutrients. |
| Plastic | The plastic function of the pulp is realized due to the physiological activity of odontoblasts. The latter components are directly involved in the formation of the protective layer of dentin, which is located on top of the neurovascular bundle. The pulp is able to stimulate the regeneration processes for the partial restoration of dentin tissues destroyed as a result of the carious process. |
| Protective | The dental nerve has the function of self-defense against the negative effects of external and internal factors. Tooth pulp macrophages neutralize pathogenic microorganisms that try to penetrate into the tooth through damaged areas of enamel and dentin, and also utilize dead cells. Lymphocytes localized inside the pulp carry out the synthesis of IgG-type immunoglobulins and provide a sufficient level of the body's immune response in response to infectious invasion. Fibroblasts stabilize the balance of the liquid intercellular substance of the dental pulp, the presence of which contributes to the passage of a full-fledged metabolism in the structure of the neurovascular bundle. |
| Trophic | The trophic function of the dental nerve is realized due to the peculiarities of the construction of the system of blood vessels that surround its fibers. Rapid inflow and outflow of blood, as well as lymphatic fluid inside the molars is ensured by the following factors:
In conditions of increasing tissue inflammation, the vascular branches of the dental nerve have the ability to directly bypass local blood flow. This is manifested in the ejection of blood from arterial vessels straight into the venous bed without its transit distribution inside the capillaries. This manifestation of the trophic function allows the pulp to get rid of excess blood that has flowed into response to the inflammatory process, as well as to prevent the development of acute pulpitis with further loss tooth. |
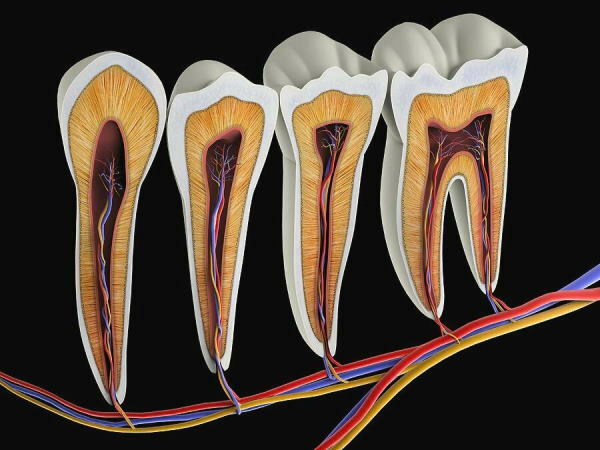 The realization of the sensory function of the pulp tissues is felt every day by all inhabitants of the world who have preserved teeth. The smallest nerve fibers, localized inside the crown of the molar, provide its sensitivity when drinking, eating food with various biochemical properties. With the destruction of enamel or dentin, the sensory function of the dental nerve becomes more pronounced, which leads to pain.
The realization of the sensory function of the pulp tissues is felt every day by all inhabitants of the world who have preserved teeth. The smallest nerve fibers, localized inside the crown of the molar, provide its sensitivity when drinking, eating food with various biochemical properties. With the destruction of enamel or dentin, the sensory function of the dental nerve becomes more pronounced, which leads to pain.
Causes of nerve inflammation
The nerve in the tooth is located under the dentin sheath, the integrity of which ensures its protection from the effects of pathogenic microflora of the oral cavity.
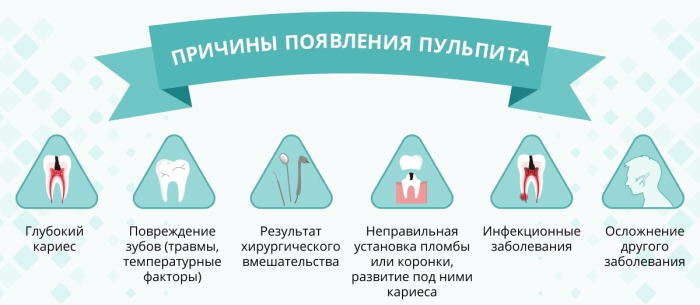
Pulp inflammation occurs for the following reasons:
- mechanical damage to the crown or root of the tooth;
- deep caries;
- penetration of infectious microorganisms into the tooth chamber;
- acute or chronic pulpitis;
- severe hypothermia of the body;
- medical error made by the dentist during the performance of therapeutic manipulations;
- periodontitis.
 In dental practice, there are occasional cases when the inflammation of the pulp occurs due to its infection by the hematological route. In this situation, bacterial microorganisms destroy the tooth from the inside. The infection penetrates into the pulp along with the flow of blood from other body tissues affected by the invasion of pathogenic microbes.
In dental practice, there are occasional cases when the inflammation of the pulp occurs due to its infection by the hematological route. In this situation, bacterial microorganisms destroy the tooth from the inside. The infection penetrates into the pulp along with the flow of blood from other body tissues affected by the invasion of pathogenic microbes.
Signs of inflammation
The nerve in the tooth is located deep in the crown, surrounded by enamel and a dense layer of dentin.
Inflammatory lesion of the pulp is manifested by the following symptoms:
- acute pain inside the tooth, which increases sharply at night;
- painful reaction to the use of cold, hot food and drinks;
- the formation of a flux in the root part of the tooth, which indicates the development of nerve inflammation, accompanied by an accumulation of pus;
- a feeling of pulsation inside the molar;
- the spread of pain to half of the face, their localization in the submandibular or temporal region of the head;
- swelling of the gum tissue in the area of the tooth with an inflamed nerve.
In most cases, teeth with inflamed nerves have external defects in the form of damage to the enamel and dentin tissues, which have been destroyed by the carious process. Acute or chronic pulpitis can also be triggered by mechanical crown amputation.
When to remove a nerve
The nerve in the tooth is deep enough. The decision to remove the pulp is made by the dentist-therapist based on the results of a preliminary examination of the patient's jaw apparatus using the X-ray method. Violation of the integrity of dentin with the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into the cavity of the tooth chamber or soreness during percussion is the basis for complete or partial depulpation molar.
Dental nerve removal techniques
Treatment of acute and chronic pulpitis involves the use of two main therapeutic methods. This is a devital extirpation or vital amputation of the dental nerve. The method of dental therapy depends on the general condition of the patient's tooth.
Dental nerve removal
During the complete removal of the dental nerve, the neurovascular pulp bundle is destroyed. This method of treating the inflammatory process is carried out in 2 stages.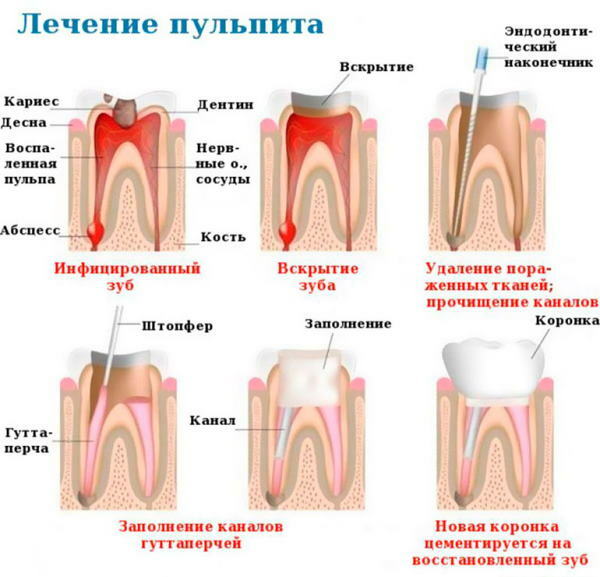
The process of removing the intradental nerve is as follows:
- The patient receives local anesthesia.
- Using a hand excavator, the dentist removes the surface tissues of the tooth, destroyed by caries.
- Mechanical removal of damaged dentin is performed.
- The pulp chamber is opened.
- Devitalizing paste is applied inside the tooth.
- A sterile cotton wool layer is applied on top of the drug.
- A temporary filling based on powder dentin is being installed.
- The patient is scheduled for the next date of the dental appointment.
- After 3-4 days, the patient again comes to the dentist.
- The doctor removes the temporary filling, removes a cotton swab and the remains of devitalizing paste from the tooth.
- Access to the neurovascular branches of the molar is expanded.
- Complete removal of the pulp is carried out using dental instruments.
- Mechanical cleaning of the pulp chamber and root canals with their antiseptic treatment with medicinal solutions is performed.
- The filling and complete sealing of the tooth with the restoration of its architecture is carried out.
To carry out devital extirpation with complete removal of the pulp, pastes based on chemicals from the group of paraformaldehydes and anesthetics are used. Arsenic is practically not used at present.
Partial depulpation
Vital amputation of the dental nerve makes it possible to preserve the partial function of nerve fibers and blood vessels that supply tissues. In this case, the effect of prolonging the life of the molar after dental treatment is achieved, the risk of complications is prevented.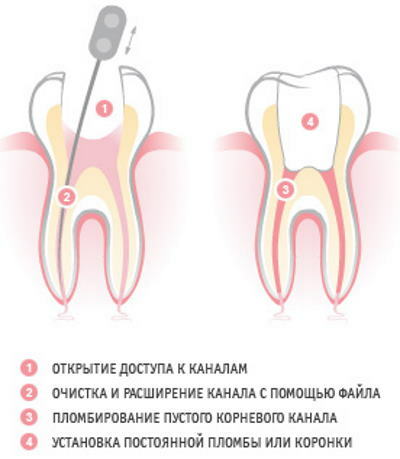
Partial depulpation is carried out as follows:
- An X-ray of the affected tooth is taken.
- The patient receives local anesthesia.
- With the help of a hand excavator, the dentist removes the surface layer of tissues damaged by caries.
- Dentin is machined with access to the pulp chamber.
- The neurovascular bundle of the tooth is removed.
- Mechanical cleaning of the inner cavity of the molar is carried out.
- Filling and complete sealing of the tooth is performed.
- A repeated X-ray of the molar root is performed to control the treatment performed, to timely detect errors that can lead to the development of complications.
After partial removal of the dental nerve, its root pulp remains fully viable, continuing to synthesize secondary dentin. The use of this method of therapy requires a high level of qualifications and professionalism from the doctor. Most dentists practice complete root depulpation, minimizing the risk of complications.
Causes of toothache after dental treatment
The appearance of acute or aching toothache after dental treatment can occur under the influence of the following causal factors:
- carious tooth cavity and root canals are not processed well enough;
- the doctor preserved the pulp, despite its inflammation;
- during mechanical processing of tissues, perforation of the tooth root occurred;
- a bacterial infection has entered the pulp chamber;
- there was a development of a local allergic reaction in response to the constituent components of drugs that were used for antiseptic treatment of dental canals;
- too high a filling has violated the architecture of the tooth and bite;
- prolonged mechanical processing of tissues led to their overheating;
- after a certain period of time, there was a natural shrinkage of the filling material;
- in the process of filling the dental cavity, the doctor did not comply with all standards of sterility, or did not ensure high-quality sealing of the molar;
- metal debris of a drill or a needle for removing a nerve remained inside the tooth.
The painful sensations that appeared after filling the tooth are the basis for an early visit to the dentist. A timely visit to the doctor will eliminate the factor of medical error and prevent the development of complications.
Can a dental nerve die on its own?
The death of the pulp without therapeutic procedures by the dentist is really possible. The death of the dental nerve occurs against the background of a prolonged inflammatory process. Before the pulp completely stops performing its functions, a person experiences excruciating pain for a long period of time, suffers from swelling of the gum tissue. At this stage, there is a strong destruction of the crown of the tooth, which can lead to its complete loss.
How to kill a dental nerve at home, relieve pain
There are several ways to get rid of toothache on your own, which are based on taking medication, as well as using alternative methods.
Arsenic drugs
In modern dentistry, arsenic-based drugs are practically not used due to the high level of toxicity and a large number of side effects. The safest medicines in this group are devitalizing pastes Devit-ARS and Pulpicide, which contain arsenic anhydride. For the necrosis of the pulp, a small amount of these drugs is put into the diseased tooth.
The average therapeutic dose of arsenic paste is the size of a millet grain. After the introduction of the arsenic medication, a temporary filling should be installed on the tooth, since the spread of the drug through the oral cavity is not allowed. After 1-3 days, the remnants of the paste are removed from the diseased tooth, and its further stay in the molar structure leads to a toxic effect and destruction of the crown tissue.
Arsenic-free drugs
As arsenic-free drugs for relieving pain at home, medicines from pharmacological group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, namely:
- Ketanov;
- Tempalgin;
- Diclofenac;
- Analgin;
- Ketorolac.
During an attack of acute toothache, these drugs are taken 1 tablet 2-3 times a day. The maximum duration of therapy with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs is 5 days. During this period of time, a person should seek help from a dentist.
Vinegar essence
The use of vinegar essence to relieve toothache and nerve necrosis is a popular method of treating acute or chronic pulpitis. To achieve a therapeutic effect, 1-2 drops of this substance are applied to the surface of the diseased area of the tooth with signs of caries.
Vinegar essence is a powerful preservative that destroys bacterial microorganisms that provoked acute inflammation of the pulp, but at the same time causes the death of nerve endings. Over time, this also leads to the complete destruction of the tooth tissue, which occurs already without pain.
Baking soda and salt solution
This method of getting rid of toothache and necrosis of the pulp is more humane, but has a less pronounced effect. To prepare a therapeutic solution, you will need to take 1 tsp. l. table salt and baking soda.
These ingredients dissolve in a glass of warm water. After that, the person performs a rinse of the oral cavity with the retention of this agent near the diseased tooth. This therapeutic procedure should be performed every 30 minutes. until the complete disappearance of pain and inflammation inside the tooth chamber.
Propolis
Bee propolis has unique properties, and its effect on the neurovascular bundle of the tooth resembles a devitalizing paste based on formaldehyde. This method of getting rid of toothache has been used at all times and historical eras. It is enough to take a small piece of bee propolis and then put it inside a tooth affected by caries.
After 8 hours, this beekeeping product is removed from the oral cavity. In case of recurrence of toothache, the procedure is repeated. A side effect of getting rid of pulpitis with propolis is complete tooth decay. As a result, the patient has a dead root instead of a tooth, which will eventually require surgical removal.
What to do is strictly prohibited
It is strictly forbidden to engage in self-treatment of sick teeth, using the advice of friends, as well as improvised materials and tools. Such actions will still lead to the dentist's chair, but with the risk of complete loss of the injured molar.
How long will a tooth live without a nerve?
The lifespan of a tooth after complete depulpation depends on many factors. Of great importance is the fact at what stage of the inflammatory process the appeal to the doctor was performed, and the level of qualification of the specialist is also important. On average, a tooth with a removed nerve retains its integrity from 1 to 10 years.
After this period of time, the upper part of the molar begins to collapse. The next stage of treatment is the installation of a post, strengthening of the dental tissue with fiberglass or closing with a crown. In dental practice, there are cases when a high-quality cured tooth with complete depulpation remains intact for 20-25 years.
What is the threat of poor-quality treatment
Conducting poor-quality dental treatment with complete or partial removal of dental pulp is fraught with the development of the following complications:
- inflammatory damage to tissues located in the circumference of the root of a diseased tooth;
- the formation of cystic formation, which occurs due to chronic periodontitis;
- periostitis (this complication also occurs under the name "flux" or inflammation of the periosteum);
- aching or sharp pain caused by irritation of dentin with drugs that were used in the process of antiseptic treatment of dental canals;
- perforation of the tooth with further opening of bleeding from the injured root area;
- inflammation of the pulp against the background of its bacterial infection.
The most serious complication of poor-quality treatment of a diseased tooth is its forced removal due to acute inflammation or tissue suppuration in the periosteum region. In most cases, similar consequences develop in the first 1-3 days after the filling is installed.
The dental nerve is a plexus of peripheral nerve fibers, blood and lymph vessels, which are located under the layer of enamel and dentin. This part of the teeth perform trophic, protective and sensory functions. The pulp nourishes the molar tissues with useful substances, provides them with a sufficient level of mineralization, takes part in the formation of an acute immune response in response to bacterial invasion.
Inflammation with further death of the dental nerve occurs due to the development of deep caries, which destroys the enamel of the crown, and then penetrates deep into the dentin. Treatment of acute or chronic pulpitis involves the complete removal of the neurovascular bundle of the tooth, or its partial amputation while preserving some of the functions.
Dental nerve video
Tooth nerve extraction: