Content
- What breasts are considered small
- Aesthetic parameters
- Breast structure in normal conditions and with micromastia
- Types of micromastia
- Possible reasons
- Constitution
- Heredity
- Hormonal pathologies
- External factors
- Correction methods
- Hormone therapy
- Plastic surgery
- Possible complications
- Video about micromastia
Breast growth is one of the main signs of puberty, observed in girls aged 12-14 years. At this time, mammary glands begin to gradually develop from small nodules, the active formation of which stops by about 20-25 years.
Depending on hereditary and constitutional factors, women may have small, medium or voluminous bust that becomes the cause pride or provoking the appearance of complexes, or there is a complete absence of breasts associated with the development of micromastia due to hormone deficiency or intrauterine growth disorders.
What breasts are considered small
Small breasts are mammary glands, the volume of which varies from AA (0) to A (size 1), which is considered an absolute norm and does not prevent women from leading a normal lifestyle. The small size here can be caused by both anatomical or genetic reasons, and occur under the influence of external factors that have a negative impact on the formation of dairy glands.
Unlike normal indicators, micromastia, or underdevelopment of the mammary glands or sudden loss of volume, is considered a pathological condition, diagnosed both at the age of 15-16 years (hypoplasia), and at a later time, due to breastfeeding, sudden weight loss or age-related changes. It is also possible the development of amastia - atrophy of the mammary glands, due to the absence of a glandular layer in them.
A large number of girls with breasts from 0 to 1 size consider their bust ugly, or not large enough, and may look in themselves signs of pathology, while their mammary glands are fully formed and may have a miniature appearance due to genetic reasons.
Today in mammological practice there is no exact concept of "small breasts" or micromastia, but objectively, the underdevelopment of the mammary gland is associated with a discrepancy between its appearance and the desired size and form.
Determining the volume of the mammary glands is quite simple, for this you need to measure them with a tape measure and calculate the difference between the two values:
- determine the volume of the breast at its highest point (at the level of the nipples);
- measure the circumference of the body under the bust.
After subtracting the second from the first number, you get the difference that accurately determines the size of the breast. There are 6 full breast sizes from 0 to 6. Normally, for a miniature neckline, the indicator should be at least 10-11, which is typical for a zero bust volume (AA). Lower values may mean the development of micromastia and require an appointment to a mammologist, tests and ultrasound diagnostics.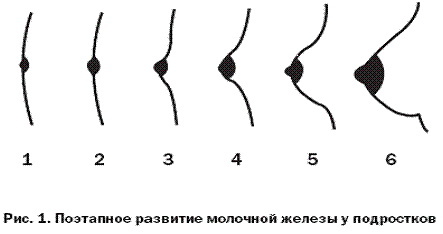
The asymmetry of the bust is also considered negative, in which one of the mammary glands is much more developed than the other.
Aesthetic parameters
Ideal for perception is a bust with paired breasts, which have a conical shape with a small top - the nipple. When an imaginary axis is drawn through the center of the breast, above and below it, it should have uniform bulges and the same mass, which is found with a virgin type of gland.
Scientists have also deduced the ideal parameters for breasts characteristic of women of average height and corresponding:
- base width 12-13 cm;
- interthoracic distance (or intermammary interval) of 4 cm;
- areola diameter of 3.5-4.5 cm with a nipple diameter of 0.8 cm;
- the optimal distance from the intramammary fold to the nipple is 7-8 cm;
- the distance from the center of the sternum to the nipple is 9-11 cm.
Breast structure in normal conditions and with micromastia
Why a woman has small breasts is a question that a mammologist can answer, focusing on the results of analysis, visual examination and ultrasound.
The female mammary gland is a paired organ located in the center of the rib cage and attaches to the base of the pectoral muscles (large and dentate), approximately at the level of 3 - 6-7 ribs. The upper part is covered with skin, and inside there is adipose tissue, which is largely responsible for the volume of the bust.
Under the fatty layer is the glandular part covered with connective tissue.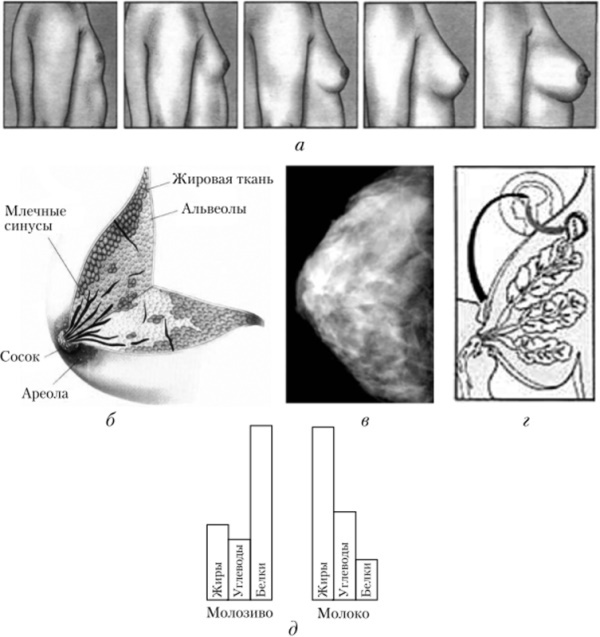
Visually, the mammary gland can also be divided into 15-20 glandular lobules, separated by layers of adipose and connective tissue.
The areola (or areola) is located at the level of the 5th intercostal space, and the nipple is placed in its center. The shape of the areola and nipple are always individual, and the color has a pronounced pigmentation. Also in the areola are the sebaceous and sweat glands and 12 Montgomery tubercles, which are considered accessory glands and increase their volume while waiting for the baby.
The size and shape of the mammary glands is not constant and repeatedly undergoes significant changes:
| At 10-11 years old | The active growth of the mammary glands begins, associated with an increase in the blood estrogen content. At this moment, upon examination, the mammologist can detect glandular tissue at the site of the future breast, which is actively starting its development. |
| At the age of 13 | The mammary gland is actively developing. The areola and nipple of the breast also increases in size, and the bust itself can cause pain when touched. Discomfort is especially increased during menstruation, accompanied by swelling of the mammary glands. |
| 16-17 years old | The mammary glands are fully formed and have a firm and toned "virgin appearance". Their growth is still ongoing and will end by about 20-25 years. |
| 20-25 years old | The breast has acquired the maximum size genetically determined for it and is fully ready to perform its main functions of breastfeeding the child. |
| Pregnancy period | Breast size increases significantly due to exposure to the hormone oxytocin and preparation of the body for breastfeeding. At the end of lactation, breast size most often returns to pre-pregnancy size, but it can also increase or, on the contrary, decrease. |
| After 45-55 years | Due to a gradual decrease in the amount of adipose and glandular tissue, as well as a decrease in the production of estrogen, a gradual decrease in breast volume occurs. It is also possible to preserve the volume of the bust due to the replacement of the glandular connective tissue. |
| After 55 years | Age-related ptosis and the onset of menopause negatively affect the condition of the mammary glands, leading to a gradual loss of elasticity and skin coiling. This process can occur earlier and be associated with both very large breasts and sudden sudden weight loss. |
| 80 years and older | The chest sags completely and loses its original shape. Also, during this period, the risk of developing oncological neoplasms in the mammary glands increases. |
With micromastia, postpubertal underdevelopment of the mammary glands is observed, in which:
- The volume of the breast is no more than 200 mg, which is significantly less compared to standard mammary glands. This symptom is due to a disruption in the normal process of development of the mammary glands, forcing them to remain at the level of a teenager.
- There is an asymmetry of the mammary glands, in which the right or left breast develops much faster than the other.
- Decreases breast sensitivity caused by underdevelopment of fibers and nerve receptors.
- One of the mammary glands associated with the development of Poland's syndrome is missing.
Types of micromastia
Why a woman has small breasts is a question that a mammologist can answer after diagnosing the pathology of the development of the mammary glands.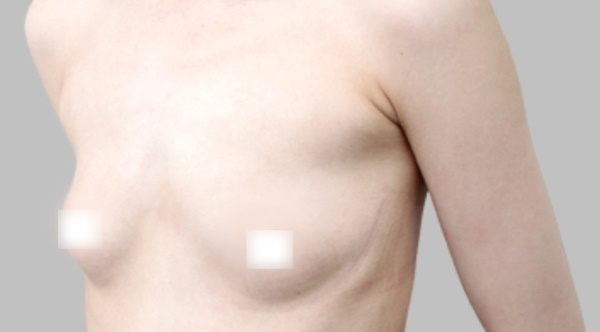
The formation of the bust begins in the prenatal period, with the appearance of two ribbon-like thickenings of the epithelium, arising in the axillary region. These folds are called "milk lines" and gradually expanding, transforming into mammary glands, approximately 2 months before the birth of the child.
The nipple is formed for the first time in 2 years of a baby's life and, starting from 3 years old, gradually increases in volume. If this process is violated, a pathology arises - an "inverted nipple", in which the nipple does not rise above the mammary gland, but is pulled into it or be at the level of the skin.
The active development of the mammary glands in girls begins in adolescence and ends at about 17-18 years old, but during menstruation, they swell. In the intervals between cycles, the formation of new milk ducts, an increase in the bloodstream, capillaries and the diameter of the nipple are possible.
Micromastia can develop at any stage of the formation of the mammary gland and can be both unilateral and bilateral. Hypoplasia is most commonly associated with chromosomal abnormalities such as Turner syndrome, and unilateral caused by intrauterine abnormalities (Poland syndrome) due to impaired fetal blood circulation.
Distinguish also:
| Congenital micromastia | It is caused by heredity and intrauterine development of the fetus and is usually combined with other genetic abnormalities. |
| Primary micromastia | The cause of which is hormonal imbalance during puberty. |
| Secondary micromastia | Associated with age-related changes, breastfeeding, sudden weight loss or the influence of negative environmental factors (ecology, trauma). |
| Aesthetic micromastia | Providing a woman with psychological discomfort, but not associated with congenital or hormonal pathologies. |
There are also 5 stages of development of the mammary glands, while patients with micromastia go through only the first 2 of them:
| Stage 1 | The mammary glands are not expressed. The glandular tissue is completely absent, and the diameter of the nipple does not exceed 2 cm. | Age up to 10.5 years |
| Stage 2 | There is a slight increase in the breast caused by the appearance of glandular tissue. The size of the nipple is more than 2 cm in diameter. | 10.5-11.5 years |
| Stage 3 | The mammary glands acquire the shape of a cone, slightly protruding above the surface of the chest without clear contours of the base. The nipple and areola begin to darken gradually. | 12.5-13 years old |
| Stage 4 | The areola and nipple darken, and also begin to protrude above the surface of the mammary gland. | 13.5-14 years old |
| Stage 5 | The breast takes on a mature appearance with the nipple protruding above it. The border between areology and breast tissue is smoothed out. | 15-16 years old |
Possible reasons
Why a woman has small breasts is a question that can be answered by studying hereditary relationships and the constitutional structure of the patient. The process of growth and development of the mammary glands is individual in each case, and the development of micromastia can be overestimated by several factors:
Constitution
Very slender girls with a thin, petite physique in most cases are distinguished by the presence of a miniature bust (no more than 2 sizes), which is due to their constitutional body structure. The mammary glands here, like the whole body, do not have a sufficient volume of adipose tissue, which is directly responsible for their volume.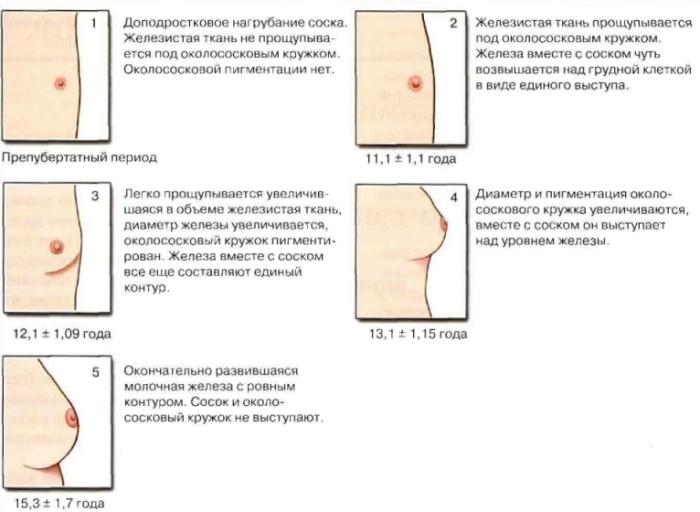
This condition is not a symptom of micromastia, and during pregnancy, due to the production of the hormone oxytocin, the mammary glands increase and the breast reaches its maximum size.
Heredity
One of the reasons for a small bust is also a hereditary factor. If in a girl's family all female relatives suffered from micromastia or had a small bust (0-1 size), then a similar anomaly will repeat in each subsequent generation. Unlike other factors, the genetic predisposition does not lend itself to correction and the only possible way to increase the bust here will be plastic surgery.
Hormonal pathologies
Breast growth is directly related to an increase in the girl's blood hormones estrogen, responsible for puberty. Estrogens affecting the ovaries contribute to the development of secondary sexual characteristics, and their lack leads to the development of micromastia and slowed development of the mammary glands.
An insufficient amount of estrogen in most cases is associated with thyroid problems and requires appropriate treatment and supervision and an endocrinologist.
An increase in androgens and testosterone in the girl's blood, which contribute to the formation of a figure, can also provoke the development of micromastia. for the male type, as well as operations on the genitals and ovaries carried out in puberty, which completely changed the hormonal background.
External factors
Smoking, drinking alcohol during adolescence negatively affects breast growth.
It also provokes the appearance of micromastia:
- poor ecology and severe air and water pollution;
- constant hypothermia of the body;
- lack of adequate nutrition, including a lack of vitamins and minerals, which does not allow the body to receive sufficient building material for the formation of the body.
Active sports activities and related injuries can also slow down or completely stop breast growth, leading to the fact that the pectoral muscles are well pumped, thereby interfering with the full development of milk glands.
Correction methods
Why women have small breasts is a question that an endocrinologist can answer by conducting a study of hormonal levels. Today, medicine knows several options for the treatment of micromastia, selected after a full examination and depending on the factor that provoked the development of the pathology
Hormone therapy
Hormone replacement therapy is considered one of the most effective treatments for micromastia prescribed by a mammologist. A full examination allows you to identify the most suitable drug that does not cause side effects. effects and contributes to an increase in the blood level of estrogen, which is responsible for the formation of the mammary glands.
In most cases, a woman is prescribed hormonal contraceptives containing oxytocin, estrogen and progesterone, stabilizing hormones, normalizing the menstrual cycle and activating growth breasts.
In addition to drugs, it is also prescribed:
- Foods containing foods rich in phytoestrogens, which, when accumulated in the body, turn into full-fledged estrogen. These herbs include, in particular, flaxseed oil, fennel seeds and hop cones, used to make herbal infusions and teas.

- Folic acid tablets, which saturates the body with vitamin B9 and has a beneficial effect on the female body.
It is also recommended to include foods that promote breast growth:
- white cabbage, carrots and beets;
- pomegranates, apples, cereals and nuts;
- dairy;
- avocados and bananas;
- herring.
Regular sexual intercourse also helps to activate the production of estrogen.
Plastic surgery
Augmentation mammoplasty is considered the most effective method of breast augmentation, helping to restore the bust even in the case of hereditary and intrauterine development of micromastia.
Modern endoprostheses are completely safe, have a round or anatomical shape and are filled with silicone gel or saline, which allows them to give the bust a beautiful and natural shape.
Augmentation mammoplasty is performed after 18 years of age on a fully formed breast and in the absence of contraindications for surgery. Surgical intervention is also preceded by a difficult preparatory stage, when, in addition to taking tests, a woman together with a doctor chooses the method of intervention, selects the appropriate implant and undergoes 3D modeling, which allows you to imagine how it will look new bust.
Mammoplasty takes 1.5-2 hours, is performed under general anesthesia, and the place of the incision is determined individually:
- next to the armpit;
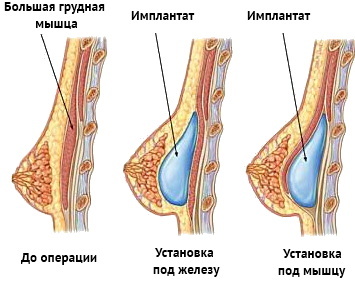
- with an incision along the edge of the thoracic areola;
- in the chest fold.
Over time, the bust drops slightly and hides the suture from the operation.
The rehabilitation period after mammoplasty takes 4-6 weeks, and the result can be assessed 6 months after the operation.
Possible complications
A small bust is not considered a pathology, does not interfere with breastfeeding and looks very sexy under clothes. Despite the stereotype in society about the beauty of large breasts, some Hollywood stars on by their own example, they proved that a bust of size 0 or 1 is not only beautiful, but also very sexually.
Kate Moss, Gwyneth Paltrow, Charlize Theron and Keira Knightley are not only not shy about their small breasts, but also are removed naked, and also allow themselves to show on the red carpet in dresses with a deep neckline.
Unlike a fully formed small breast, micromastia is considered a pathology and is accompanied by a number of complications, including:
- Difficulties during lactation caused by underdevelopment of the mammary glands and milk ducts.
- Problems in sex life associated with the lack of sensitivity of the mammary glands and nipples.
- Psychological discomfort that causes depression and prevents women from freely visiting swimming pools and beaches.
Small breasts are a feature of the development of the female body or pathology, which often becomes the cause of the appearance of psychological discomfort and complexes about their attractiveness. The mammary glands can stop growing due to hereditary, environmental or hormonal reasons, but they can be corrected can only be a full-fledged hormonal treatment or plastic surgery, which helps in any, even the most difficult cases.
Video about micromastia
Formation of the female breast: