Content
- Characteristics and properties
- The table is ok
- Increase symptoms
- Reasons for the increase
- Renal failure
- Diabetic ketoacidosis
- Osteosarcoma
- Hypoparathyroidism
- Multiple myeloma
- Vitamin D overdose
- Severe bone injuries
- Drug overdose
- Nephritis
- Acromegaly
- Features of the diet
- How is it determined
- How to bounce back
- Insulin replacement therapy
- Surgery
- Antibiotic therapy
- Hemodialysis procedure
- Calcium and Vitamin D Therapy
- Video about phosphorus in the body
Increased inorganic phosphorus levels in the composition of human blood indicates the possible presence of a chronic disease of internal organs, or is the result of systematic abuse of products containing this mineral.
Characteristics and properties
Inorganic phosphorus is a vital microelement that is a nutrient base for the cellular structure of the entire body. The normal concentration of this mineral ensures a stable energy metabolism in tissues, balanced development of skeletal muscles and bones of the musculoskeletal system, supporting them strong and healthy. An excessive increase in this trace element in the composition of venous and peripheral blood while maintaining the usual diet indicates a pathological state of the organs of the endocrine, excretory or digestive systems.
The following biochemical properties of inorganic phosphorus are distinguished, which are manifested in the human body:
- is directly involved in the process of growth and division of cells responsible for the transfer of genetic information from parents to offspring;
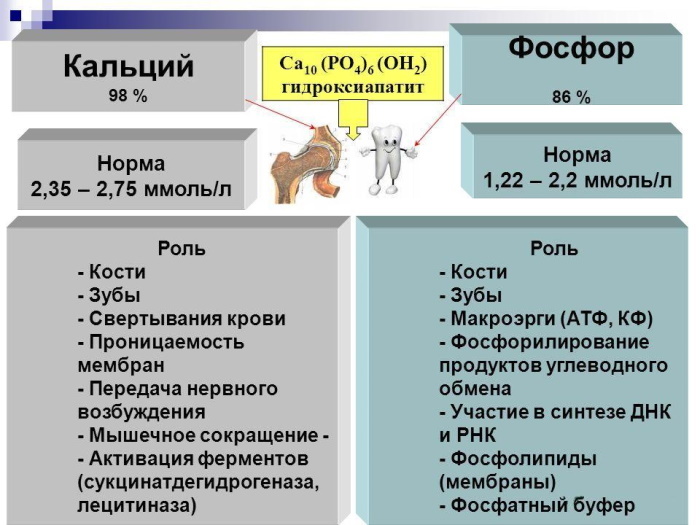
- is part of the bone tissue of the skeleton (in this part of the musculoskeletal system, on average, at least 85% of all reserves of inorganic phosphorus are concentrated);
- forms the basis of nucleic acids;
- creates a full-fledged mineral framework for the development of gums and teeth, and also maintains these parts of the jaw apparatus functionally healthy;
- ensures stable functioning of the heart muscle and kidneys;
- participates in physiological processes for the accumulation and release of intracellular energy (for example, during heavy physical labor, sports activities or prolonged fasting);
- is responsible for the timely transmission of nerve impulses from the centers of the brain to the peripheral parts of the musculoskeletal system and tissues of internal organs;
- simplifies the process of breaking down starch compounds and lipids into pure food energy.
 Inorganic phosphorus in the blood is increased when there is an imbalance of other minerals associated with it in the human body. For example, chronic calcium deficiency can cause a gradual rise in phosphate concentration.
Inorganic phosphorus in the blood is increased when there is an imbalance of other minerals associated with it in the human body. For example, chronic calcium deficiency can cause a gradual rise in phosphate concentration.
The table is ok
The table below provides information on the indicators of the norm of the level of inorganic phosphorus in the blood in children, adult men and women.
| Age indicator | Normal level (unit of measure mmol per 1 liter of blood) |
| Newborn babies | 1.45 to 2.91 |
| Child aged 10 days to 2 years | 1.29 to 6.5 |
| Children from 2 to 9 years old | 1.03 to 1.87 |
| Child from 9 to 15 years old | 1.07 to 1.74 |
| Patients in the age category from 15 to 60 years old, regardless of gender | 0.78 to 1.42 |
| Men and women over 60 | 0.74 to 1.32 |
The highest level of inorganic phosphorus is observed in the blood of infants. A child who experiences a systematic deficiency of this mineral loses the ability to fully absorb calcium and vitamin D. Over time, this leads to the development of rickets and complications associated with skeletal deformation.
Increase symptoms
Inorganic phosphorus in the blood is increased in those clinical situations when a person already has one or several diseases of internal organs. Symptoms of an imbalance in this mineral depend on what kind of disease the patient is diagnosed with. Considering the fact that an increase in the concentration of inorganic phosphorus in the blood causes pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, endocrine glands and kidneys, most people have the following signs of health problems:
- dizziness;
- loss or complete lack of appetite;
- nausea that is present on a full and empty stomach;
- discharge of vomit;
- feeling chills;
- feverish condition;
- confusion of consciousness;
- impaired cognitive function;
- frequent urination;
- cramping pain inside the abdominal cavity in the area of \ u200b \ u200bthe intestines and stomach;
- diarrhea;
- heartburn;
- increased gas formation;
- frequent belching and constant rumbling in the stomach;
- quick fatigue after doing physical work or other activities that do not involve high energy costs;
- darkening of the enamel of the teeth with further destruction of the jaw apparatus;
- osteoporosis of bone tissue;
- degenerative changes in the structure of the musculoskeletal system caused by changes in the mineral composition of the skeleton.
Conducting a laboratory blood test for the content of inorganic phosphorus without fail indicated for people who have been diagnosed with acute or chronic diseases of bones, kidneys, and parathyroid glands.
Reasons for the increase
Inorganic phosphorus in the blood is elevated for 2 main reasons. These are concomitant diseases of the body or features of the diet of a person whose body is faced with an increase in the concentration of phosphates.
These are concomitant diseases of the body or features of the diet of a person whose body is faced with an increase in the concentration of phosphates.
Renal failure
Renal failure is a pathological condition of the patient's body, in which the kidneys completely or partially lose their physiological function to cleanse the blood from metabolic products. This organ stops the process of producing urine, along with which toxic substances should be excreted. In this regard, mineral components, including phosphates, begin to accumulate in the patient's body.
The occurrence of this cause, which provokes the growth of inorganic phosphorus in the blood, is associated with the influence of the following factors:
- malignant neoplasms in the tissue structure of the kidneys;
- diabetes;
- autoimmune kidney damage;
- blockage of the ureters with stones;
- congenital anomalies of the structure of the kidneys;
- loss of large amounts of blood;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- poisoning of the body with chemical toxins and biological poisons;
- unauthorized administration of drugs with nephrotoxic properties.
An increase in the level of phosphorus in the blood, which is caused by kidney failure, can be fatal. Patients with this pathology need urgent hospitalization with the passage of complex treatment in the hospital of the nephrological or therapeutic department.
Diabetic ketoacidosis
Inorganic phosphorus in the blood is elevated if a person suffers from diabetic ketoacidosis. This is a dangerous complication that occurs in patients with type I diabetes. Diabetic ketoacidosis is characterized by a severe course with an immediate manifestation of pathological symptoms. In this case, an increase in the level of inorganic phosphorus in the blood occurs simultaneously with an increase in the concentration of ketone bodies.
The mechanism of development of this causative factor triggering phosphate imbalance is as follows:
- The patient's body does not have enough insulin to convert glucose into food energy.
- In search of alternative sources of energy, the process of breaking down fat stores is activated.
- As a result of physiological fat burning, a by-product is formed in the form of ketone bodies, which are acidic in origin.
- There is a gradual increase in the number of ketone bodies that destroy the internal structure of the kidneys.
- The damaged organs of the excretory system cannot cope with the utilization of excess amounts of phosphorus, causing its accumulation in the blood and tissues of internal organs.
Diabetic ketoacidosis is a common cause of sudden onset of coma. Together with hyperphosphatemia, the prognosis for the patient is unfavorable.
Osteosarcoma
Osteosarcoma is a primary tumor of the bone tissue of the skeleton, which occurs due to the mutation of its cells. A distinctive feature of this disease is the rapid development of an extraneous neoplasm. In the process of bone decay, the balance of calcium and phosphorus is imbalanced towards an increase in the concentration of the last mineral. In most cases, osteosarcoma affects the long bones of the upper and lower extremities. About 50% of all tumors are found in the knee joint area.
Patients who have been diagnosed with an increase in the level of inorganic phosphorus in their blood are examined for osteosarcoma without fail. In the early stages of its development, an extraneous neoplasm does not manifest any pathological symptoms, gradually capturing bone and bone marrow. The first painful sensations, accompanied by an inflammatory process, arise at the stage of tumor metastasis to the adjacent muscles and soft tissues. The concentration of phosphates increases in proportion to the progression of the oncological process.
Hypoparathyroidism
Hypoparathyroidism is a serious condition of the patient's body, which develops against the background of complete or partial dysfunction of the thyroid gland, as well as the parathyroid glands. As a result of the pathology of these organs in the blood serum, there is a decrease in the concentration of parathyroid hormone. This leads to the development of hypocalcemia, a rapid increase in the level of inorganic phosphorus while maintaining optimal magnesium levels. Hypoparathyroidism is accompanied by convulsions of the lower extremities and individual parts of the body, increased irritability of the nervous system, tetany with the risk of sudden death.
Multiple myeloma
Multiple myeloma is a dangerous disease of the hematopoietic system, which has a malignant origin.
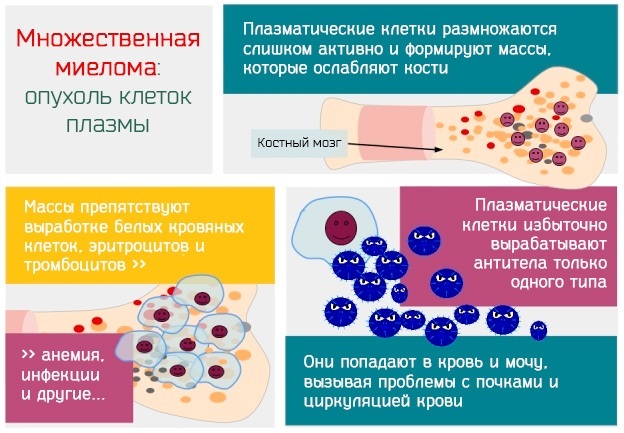
The pathology is characterized by uncontrolled division of plasma cells (B-lymphocytes), spreading in the structure of the bone marrow. The result of this disease-causing process is the destruction of the hematopoietic system of the patient with metastasis of the tumor neoplasm to the bone tissue. An increase in the level of inorganic phosphorus in the blood is detected already at 2-3 stages of this disease.
Vitamin D overdose
Not only vitamin D deficiency is dangerous for human health, but also an excess of this substance. Unauthorized intake of this biological supplement in the form of tablets or liquid solution leads to an overdose, which disrupts the absorption of calcium and phosphorus. Against the background of an excessive concentration of vitamin D in the blood serum and body tissues, a proportional increase in the level of phosphates is observed. In especially severe cases, kidney damage and impaired urine flow are not excluded.
Severe bone injuries
Traumatic injuries of the musculoskeletal system associated with bone fractures are accompanied by a local inflammatory process. In such situations, it is possible to increase the level of phosphate in the blood. Medical practice shows that the effect of this causative factor provokes an increase in the concentration of phosphorus, but not to critical limits.
Drug overdose
An increase in the level of phosphate in the blood is possible in people who are undergoing therapy with phosphorus-containing medicines. In this case, the patient's excretory system cannot cope with the function of removing phosphates from the body. It is possible that, against the background of an increase in the concentration of phosphorus, the patient develops concomitant symptoms associated with an overdose of drugs of this category. Timely cessation of taking phosphorus-containing medicines allows you to stabilize the patient's condition.
Nephritis
Nephritis is a generalized medical term to define several kidney diseases at once, the development of which leads to damage to the renal glomeruli, destruction of their tubules, or interstitial tissue.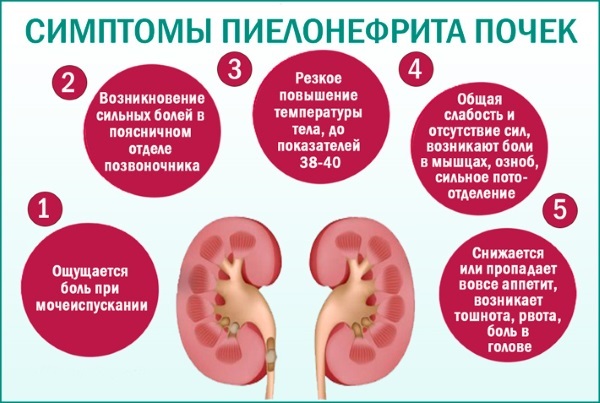 As the disease progresses, there is a decrease in the functional activity of the kidneys in terms of cleaning the blood from excess phosphates. This leads to the fact that the level of inorganic phosphorus is constantly or periodically detected in the human body. The danger of nephritis is the high risk of developing kidney failure.
As the disease progresses, there is a decrease in the functional activity of the kidneys in terms of cleaning the blood from excess phosphates. This leads to the fact that the level of inorganic phosphorus is constantly or periodically detected in the human body. The danger of nephritis is the high risk of developing kidney failure.
Acromegaly
Acromegaly is a disease of the endocrine system that occurs due to dysfunction of the pituitary gland. The development of this pathology is characterized by an increase in the volume of bone tissue of the feet, hands, and cranium. Abnormal growth of the skeleton is caused by an excessive concentration of growth hormone, which is synthesized by the anterior pituitary gland. This disease causes an imbalance of calcium and phosphorus in the patient's body, which leads to an increase in phosphate levels.
Features of the diet
Men and women whose diets are dominated by the following types of foods on a daily basis are at risk of experiencing hyperphosphatemia:
- ocean fish and seafood;
- beans;
- green pea;
- chicken;
- beef;
- cereals;
- chicken eggs;
- vegetable fats.

To minimize the risk of increased blood phosphorus levels from overuse of certain species food, it is recommended to balance your diet by making an individual menu for every day weeks.
How is it determined
Determination of the level of phosphate in the patient's blood is carried out using a laboratory test called colorimetry with the substance ammonium molybdate. Venous and capillary blood is used as biological material. Before visiting the laboratory, do not eat food for 2-3 hours. Otherwise, you may receive distorted diagnostic results.
It is allowed to drink plain water without carbon dioxide, dyes and other additives. Blood sampling for analysis is performed in the morning. The results of the study are known after 1-2 days. The average cost of this analysis is 415 rubles.
How to bounce back
The method of restoring normal parameters of inorganic phosphorus in the blood depends on what kind of disease provoked an increase in its concentration.
Insulin replacement therapy
Insulin replacement therapy is prescribed for patients diagnosed with type I diabetes mellitus. For more effective control of glucose levels in the blood, patients are transferred to injections with this hormone, the deficiency of which causes diabetic ketoacidosis with all the ensuing consequences. The dosage regimen for insulin is determined by the endocrinologist on an individual basis, depending on the results of a clinical study of the patient's blood.
Surgery
Surgical intervention is indicated for patients suffering from osteosarcoma of the upper or lower extremities who have undergone a course of drug therapy, but have not achieved a positive effect. The surgeon performs the removal of the tumor from the structure of the bone tissue. If a malignant neoplasm has grown through the thickness of the bone, its excision is impossible, then a decision is made to amputate the limb. After the operation, the patient undergoes a course of chemotherapy to prevent recurrence of the disease and the spread of degenerated cells to other parts of the musculoskeletal system.
Antibiotic therapy
A conservative method of treatment with the use of antibacterial drugs is indicated for patients in whom a high level of inorganic phosphorus in the blood is caused by nephritis. In this case, a prerequisite for the use of antimicrobial agents is the inflammatory process of a bacterial origin. The type of antibiotic is selected by a nephrologist or therapist, depending on the strain of the microorganism diagnosed in the patient.
In most cases, the following drugs are used:
- Biseptol (89 rubles);
- Nitroxoline (99 rubles);
- Metronidazole (69 rubles);
- Amoxiclav (336 rubles);
- Cephalexin (74 rubles);
- Hikontsil (113 rubles);
- Ospamox (77 rubles).
The duration of the therapeutic course with the above antibiotics is from 10 to 15 days.
Severe forms of nephritis of bacterial etiology will require repeated administration of these drugs after 1-2 weeks of a break. After elimination of the inflammatory process, restoration of reduced renal function, a gradual normalization of the level of phosphorus in the blood serum occurs.
Hemodialysis procedure
This method of treatment to restore the concentration of phosphates to the normal limit is prescribed for patients suffering from chronic renal failure. With kidney dysfunction in terms of blood purification from metabolic products and toxic substances, hemodialysis is required. The patient's venous system is connected to an artificial kidney apparatus, which chemically removes harmful compounds from the body for 1-2 hours.
Patients with renal failure become lifelong dependent on hemodialysis. This procedure is performed in specialized medical centers. The frequency of artificial blood purification from excess concentration of inorganic phosphorus is 1-2 times a week, depending on the state of the kidneys.
Calcium and Vitamin D Therapy
Medication for calcium and vitamin D is prescribed for patients who have elevated phosphate levels due to a severe bone fracture.
In this case, the following drugs are used:
- Calcium-D3 Nycomed (300 rubles);
- Complivit Calcium D3 (224 rubles);
- Calcium D3 Classic (510 rubles).
The dosage regimen with the above medicines should be determined only by the attending physician, since an excess of vitamin D and calcium in the blood leads to the opposite pharmacological effect.
An increase in inorganic phosphorus in the blood serum is an alarming symptom that indicates severe disorders in the work of the kidneys, organs of the endocrine system, pathological condition of the bone tissue of the musculoskeletal apparatus. Normalization of the level of this substance is possible only after the elimination of the underlying disease that causes an imbalance of trace elements in the body. In the course of treatment, antibiotics, surgery, medicinal calcium and vitamin D, and hemodialysis are used.
Video about phosphorus in the body
Phosphorus - value in the body: