Content
- Classification
- Features of pathogenesis
- Symptoms and Signs
- Causes
- Diagnostics
- Blood testing
- Hormone Spectrum Data
- Electrocardiogram results
- Treatment methods
- Choosing a medication course
- Home therapy
- Possible consequences and complications
- Video about hypokalemia
To ensure the normal functioning of the human body, it is necessary balance of essential micronutrients, including potassium. If the level of potassium in the blood falls below 3.5 mmol / L, we are talking about the development of hypokalemia. Electrolytic imbalance manifests itself in mild symptoms, therefore, additional diagnostic results are needed to clarify the diagnosis and treat potassium deficiency. The most common causes of the disease are not only comorbidities, but also the use of certain medications, sometimes uncontrolled.
Classification
Maintaining the balance of essential substances is extremely important for the well-coordinated work of the whole body, since deviations from generally accepted norms lead to serious health problems. Potassium is the main intracellular element - the concentration is approximately 80-90% in the form of ions, which ensures the membrane potential of cells and the transmission of nerve impulses. In addition, potassium is a sodium antagonist, ensures the removal of excess fluid from the body along with toxins and toxins.
A drop in K + homeostasis below the boundary limit results in the appearance of numerous severe organ and systemic disorders, often posing a threat to the patient's life. The greatest danger of hypokalemia is associated with heart rhythm failures, as indicated by altered ECG parameters. In addition to the heart, in conditions of intracellular deficiency of potassium ions, the liver and kidneys, brain, endocrine and nervous systems are unable to function normally.
From the point of view of the content of potassium ions in the blood serum, the clinical signs of a pathological condition are divided into two stages:
| Type of hypokalemia | a brief description of |
| Easy | Within 3-3.5 mmol / l. Mild potassium loss is rarely signaled by special clinical symptoms, so people are not even aware of the problem. |
| Heavy | Below 3 mmol / L. The fall in serum potassium is accompanied by a syndrome of muscle weakness, paralytic intestinal obstruction, the development of respiratory failure and hypotension. |
The fact of chronicity of potassium deficiency leads to a violation of the concentrating ability of the kidneys, which is manifested by excessive urination (polyuria), as well as secondary polydipsia (severe thirst). The state of pseudohypokalemia, which develops asymptomatically and does not require treatment, is distinguished into a separate category. Obtaining a false test result can be triggered by overestimated levels of leukocytes, actively absorbing K + ions. A similar situation is typical for leukemia or severe infections. In addition, long-term storage at room temperature increases the concentration of potassium in the sample taken for research.
Features of pathogenesis
Hypokalemia (the symptoms of the cause and treatment of the pathology require special attention) is closely related to the diet. If a sufficient amount of an important micronutrient does not enter the body with food, the problem of metabolic balance arises. A lack of potassium disrupts the intercellular exchange of biological fluids, the contractile function of muscles (including the heart) suffers, and the production of complex enzymes slows down. The regulation of potassium balance is provided by chemical and hormonal substances, and the excess amount is excreted in sweat and urine.
Potassium deficiency is accompanied by an increase in the potential of cell membranes (hyperpolarization), which leads to a decrease in the excitability of myocytes and neurons. As a result, the process of chain inhibition of neurons starts with a decrease in the permeability of cell membranes for sodium and potassium ions. Violation of the equilibrium potential makes it difficult to transmit nerve impulses in synapses (points of contact between neurons) of the conduction system of the heart muscle. As a result, the muscle tone of the vessel walls decreases, which is signaled by the malfunctioning of the internal organs.
What happens due to the development of hyopkalemia:
- ectopic (gastric) rhythms appear in the heart;
- the ability of the kidneys to concentrate water decreases;
- the production of the hormone insulin (pancreas) is suppressed;
- the secretion of aldosterone secreted by the adrenal glands decreases;
- hydrogen accumulates in cells, intracellular acidosis develops.
The result is the suppression of cellular respiration, as well as the initial phase of glucose breakdown (glycolysis). In the results of the pathological examination, traces of dystrophic changes are observed in almost all structures of the internal organs. The heart, kidneys and liver are most severely affected.
If the cause of the metabolic imbalance is caused by improper diet, the stabilization of the temporary disturbance is solved by insulin, the secretion of which is stimulated by food. However, a prolonged process of rapid loss of urine or sweat without replenishment with a sufficient amount of potassium leads to the appearance of signals of persistent hypokalemia.
Symptoms and Signs
In the case of a mild course of potassium deficiency pathology, there are no symptoms, and the increase in clinical manifestations is not caused by the level of K + concentration, but by the rate of decrease in this indicator. If it falls below 3 mmol / L, the first signal is a feeling of muscle weakness against the background of psychoemotional lability and imbalance.
Hypokalemia (symptoms, causes and treatment are described in this article) in elderly patients is more often severe, as well as in people with heart and kidney diseases.
In this case, a reduced level of potassium circulation is manifested by a wider range of general symptoms:
- signs of apathy, drowsiness and persistent fatigue, leading to loss of vigor and loss of performance;
- the appearance of muscle twitching, tremors of the limbs, tetanic cramps with pain in the muscles (more often - the calf);
- a decrease in blood pressure indicators, a violation of the heart rhythm with the appearance of arrhythmia and a slowdown in the pulse;
- due to constant thirst, diuresis increases - the daily volume of urine can exceed 3 liters, which leads to polyuria;
- failure of the digestive system is manifested by loss of appetite, frequent nausea, flatulence, diarrhea or constipation.
The elements of the cardiac conduction system are especially sensitive to the constant lack of K +, which is manifested by interruptions in the heart rhythm, symptoms of tachycardia. With the development of hypotension, patients complain of frequent dizziness, tinnitus. Traces of the cardiopulmonary action of hypokalemia are easy to notice on the ECG; they are usually used to identify the latent course of the disease. Among the permanent signs of potassium deficiency on the ECG include the appearance of frequent ventricular extrasystoles, prolongation of the QRS complex, as well as changes affecting the ST segment, T and U waves.
In addition to the myocardium, dystrophic changes affect the structures of skeletal muscles, causing myopathy, which is fraught with gradual atrophy of muscle tissue with its subsequent degeneration. The catastrophic result of systemic myopathy is the aseptic form of skeletal muscle necrosis (rhabdomyolysis), which is massive in old age.
The chronic course of hypokalemia affects the functions and structure of the nervous system, the functions of its central, peripheral and autonomous branches suffer. Signs of dysfunction include anxiety-depressive manifestations, hypochondriacal and senestopathic disorders, a number of sensory failures that cause paresthesia (face, limbs), increased sensitivity or its loss. The fact of paralysis of the respiratory muscles, confusion of consciousness, a decrease in mental activity is not excluded.
Causes
Hypokalemia is caused by the rapid loss of potassium due to increased functions of the excretory system (urine, sweat, stool). Pathology does not arise by itself, its symptoms are mainly the result of other disorders, and the reasons are associated not only with a decrease in the amount of potassium entering the body. Therefore, early diagnosis and treatment of the disease at an early stage can reduce the risks to life by normalizing the potassium balance.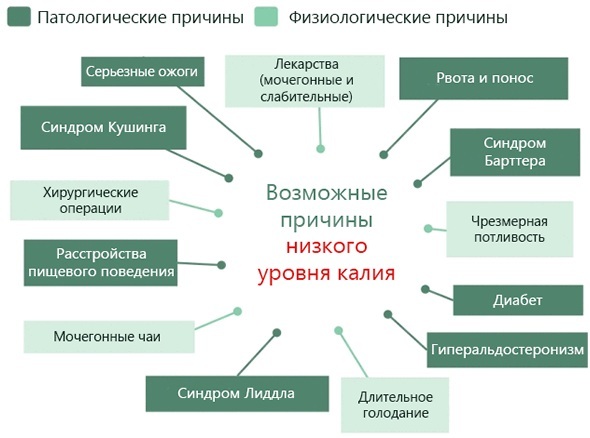
The entire spectrum of causes of hypokalemic dystrophy can be divided into several groups.
Non-renal causes of K + loss include the following factors:
- insufficient micronutrient content in food due to excessive enthusiasm for diets with limited potassium-containing foods;
- fluid loss as a result of chronic diarrhea due to intestinal dysfunction or uncontrolled intake of laxatives;
- excessive physical exertion, causing the loss of large amounts of an important trace element with sweat;
- migration of ions from the extracellular space into cells with enhanced synthesis of protein and glycogen after leaving a diabetic coma;
- evacuation of potassium from the gastrointestinal tract with intestinal obstruction or infection with the formation of fistulas, continuously removing large volumes of intestinal fluid.
Physiological causes of hypokalemia can be considered reversible to a certain extent. Pathological disorders of intracellular deficiency of potassium ions are mainly associated with the development of systemic kidney diseases. There are a lot of them, information on some of the disorders is presented below.
| Problem | Short description |
| Bartter-Gitelman syndrome | The increased outflow of potassium along with sodium is caused by a malfunction of the renal tubules due to impaired water-salt metabolism. A rare genetic syndrome is associated with excessive production of aldosterone with high excretion of K +. |
| Liddle syndrome | The reason for the excretion of sodium and potassium is in the increased activity of the sodium channel epithelium against the background of arterial hypertension and metabolic alkalosis. Potassium losses are due to inadequately high sodium reabsorption.
|
| Hypokalemic periodic paralysis (HPP) | It is characterized by the lethargy of the skeletal muscles, which leads to the loss of reflexes of deep-lying tendons, as well as the response to stimulation (electrical). Hypokalemia is manifested by abnormally low potassium levels. |
| Metabolic alkalosis | The pathological disorder develops against the background of an increase in the level of bicarbonate in the blood, which is accompanied by the loss of acids and alkaline solutions. Impaired gastrointestinal motility with excessive urination leads to potassium deficiency. |
Hypokalemia (symptoms, causes and treatment are described in the article for informational purposes only) should be under the constant supervision of a specialist. Among the factors provoking hypokalemic dystrophy are also the consequences of debilitating diseases, surgical interventions. The danger of metabolic imbalance increases after abundant infusion of medicinal solutions, leading to the replacement of potassium and its increased excretion.
Of the drug causes of hypokalemia, therapy with certain medications should be noted - diuretics, beta-adrenomimetics, antibiotics, theophylline. Fluid loss is also observed with hypomagnesemia, massive burns. To make a diagnosis, it is important to take into account that in the case of large fluid losses, the amount of plasma decreases, but the level of potassium in it may not deviate from the norm, despite the intracellular deficiency of this trace element.
Diagnostics
Hypokalemic disorder in itself is not a disease, but in order to normalize the electrolyte balance, it is necessary to establish the cause of its occurrence. Therefore, patients with suspected hypokalemia will have to consult with doctors of various specialties - nephrologist, gastroenterologist, endocrinologist, cardiologist. During the examination, the doctor must be informed about all medications taken, not forgetting about diuretics, insulin, beta-agonists.
Particular attention is paid to an overview of symptoms, including muscle tone, episodes of vomiting or diarrhea, pulse and heart problems. To make the correct diagnosis and prescribe adequate therapy, the doctor will need the results of an additional examination.
Blood testing
In the course of laboratory tests, the basic acidic parameters of blood are determined - the pH value, partial pressure of CO2, the amount of true and standard bicarbonates. Diagnostics is necessary for the timely detection of alkalosis and acidosis, which require medical correction. For a more detailed study of the composition of the blood, the results of biochemistry are important; according to the analysis of urine, the renal cause of hypokalemia is differentiated from the extrarenal one.
The main type of diagnostics of pathology is to determine the concentration of K + ions in the plasma, the result should be less than 3.8 mmol / l. Together with the history data, the cause of the pathology can be determined by also assessing the level of potassium in the urine sample.
Hormone Spectrum Data
Measuring the level of the hormone aldosterone (regulation of water and electrolyte balance) and renin (an enzyme produced by the kidneys) allows you to calculate the ratio between substances. The activity of renin affects the functioning of the kidneys, its presence in the blood, allowing the diagnosis of renal diseases.
Electrocardiogram results
Hypokalemia (the attending physician knows the symptoms, causes and treatment of the disorder) is detected on the basis of ECG data, which is a decisive factor for detecting gystrophy.
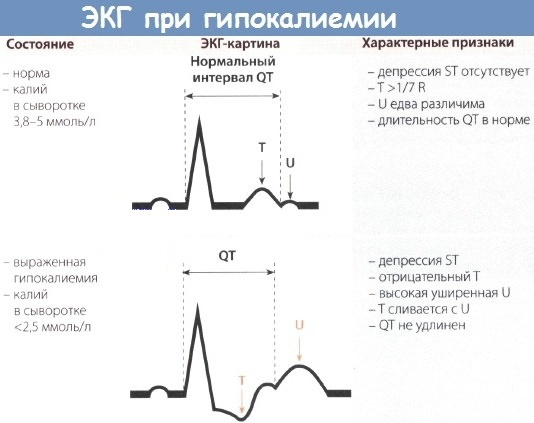
The following points indicate the development of a pathological condition:
- signs of thickening or inversion of the T wave;
- the appearance of a sharpness on the U wave;
- a decrease in the peak of the SN segment;
- an increase in the length of the QT interval;
- the appearance of ventricular extrasystoles.
A severe degree of electrolyte imbalance is manifested by signs of paroxysmal tachycardia of the ventricular type. In some cases, the disturbed heart rhythm results in atrial fibrillation.
To identify a benign formation on the surface of the adrenal cortex, instrumental research methods are used - ultrasound, CT. In the presence of renal diseases, ultrasound diagnostics is carried out with the connection of Doppler ultrasonography. The cost of a specific type of diagnosis depends on the category of the medical institution, so the price must be specified additionally.
Treatment methods
After determining the cause of the deficiency of the main intracellular element, the doctor prescribes a therapeutic course to stabilize the potassium balance in the body. The method of treatment depends on the type of pathology (renal, gastric, or other) that caused the loss of potassium. In case of a serious condition, the patient goes to the intensive care unit, where intensive therapy is carried out.
Choosing a medication course
At the initial stage, you should stop taking medications that provoke hypokalemic dystrophy. Intravenous potassium solution is considered a high-risk procedure. Therefore, it is preferable to choose a non-invasive method for normalizing the potassium balance together with the relief of life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias.
The doctor chooses the specific treatment tactics based on the diagnostic results:
- therapy of a mild, implicit form of hypokalemia is based on the treatment of the disease that caused it;
- with a severe form of intracellular deficiency of K + ions, enhanced therapy with potassium preparations is prescribed.
For oral administration of drugs containing potassium, a certain dosage is selected, since too high doses of the element can irritate the gastrointestinal tract and cause bleeding. Oral administration of a solution of potassium chloride in the case of metabolic alkalosis can quickly (after 1-2 hours) increase the concentration of an important trace element. However, the solution has a bitter taste and poor tolerance. For the treatment of metabolic acidosis, the dosage of potassium bicarbonate and citrate is selected.
To reduce renal excretion of potassium ions, treatment is enhanced by taking potassium-sparing diuretics. However, this method is not acceptable for patients suffering from kidney pathologies and diabetes mellitus or disorders of the autonomic nervous system.

Hypokalemia (symptoms, causes and treatment are interrelated) is considered a serious condition, and in some cases, the disease can be fatal. For this reason, a severe form of electrolyte imbalance is preferably treated with intravenous potassium solutions.
The concentration of a trace element in the solution depends on the place of drug intake:
- peripheral vein - no more than 40 mmol / l;
- central vein - no more than 60 mmol / l.
In the absence of paresis, as well as threatening arrhythmia, it is important to monitor the infusion rate (up to 20 mmol / h). In the case of a rapid intravenous intake of potassium chloride, the patient will need careful observation - monitoring the results of the ECG and motor function. In patients with arrhythmia, as a rule, replenishment of the deficiency of K + ions contributes to the normalization of sinus rhythm. If this does not happen, antiarrhythmic drugs (flecainide, propafenone, amiodarone) are connected. Defibrillation is the only treatment for ventricular fibrillation.
As alternative drugs for the treatment of mild hypokalemia, Panangin tablets (93-165 rubles) are used, as well as its cheaper analogue Asparkam (40-105 rubles). However, you should be aware of the danger of self-medication, because potassium-containing tablets can be bought over the counter without a prescription. A lack of potassium is equally harmful as an excess of it, therefore, to eliminate the main cause of a pathological condition, you must consult a doctor.
Home therapy
If the potassium imbalance is not the cause of serious illness, it can be restored by normalizing the diet. To replenish the reserves of an important element for health, the doctor will recommend a special diet program that includes foods containing potassium and helping its full absorption.
In the diet, it is necessary to increase the content:
- dairy products, beef, fish;
- buckwheat, wheat and oat groats, rice;
- vegetables - potatoes, cabbage, tomatoes, carrots;
- vegetable greens and beet tops;
- dried fruits, especially dried apricots, dates, raisins, prunes.
Bananas are famous for the highest potassium content, do not forget about honey and nuts, the use of melon and watermelon. In order to preserve the trace element in food as much as possible, nutritionists advise baking foods rich in it. When boiling food, most of the potassium remains in the water, and it is more useful to eat fruits and recommended vegetables fresh or squeeze juice from them.
Possible consequences and complications
The consequences of untreated hypokalemia are catastrophic. Without immediate treatment, ventricular fibrillation due to electrolyte disturbance is extremely likely to be fatal. Arrhythmia, which in some cases is asymptomatic, is considered an equally formidable complication. The patient turns to the doctor only when obvious symptoms appear - lack of air, fading or interruptions in the heart rhythm, which can lead to cardiac arrest.
Patients with weakened intercostal muscles and diaphragm develop symptoms of respiratory failure due to impaired circulation of gas in the lungs. The gastrointestinal tract often reacts to hypokalemic dystrophy by the development of intestinal obstruction, when semi-digested food masses cannot move freely in the space of the digestive tract.
Rare complications of severe potassium deficiency include extreme destruction of muscle tissue (rhabdomyolysis). With prolonged metabolic imbalance of K + ions, chronic renal failure develops, and neoplasms of a benign type (cysts) appear in the kidneys. Signs of cystic changes often go unnoticed due to the asymptomatic course.
To avoid serious pathologies, including hypokalemia, it is important not to miss the symptoms of even an implicit lack of potassium. Moreover, the signs of hypokalemic dystrophy can be disguised as clinical manifestations of other disorders. If the causes of the disease are not associated with organ or systemic pathology, timely treatment will eliminate the threat of dangerous consequences.
Video about hypokalemia
Causes, mechanism of development of hypokalemia: