Content
- Stages of fainting
- Types of fainting
- Causes
- First aid rules
- When to see a doctor
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Possible consequences
- Prevention of fainting
- Fainting videos
Fainting with open eyes in medicine is usually called short-term loss of consciousness, for 1-2 minutes, associated with violation of cerebral circulation and a sudden loss of muscle tone due to vegetative-vascular reasons, caused by strong stuffiness in a public place, an unpleasant smell of paint, or a sudden change in body position.
In most cases, this condition does not pose a threat to human life and health, with the exception of various injuries arising from a fall, but it can also be caused severe disorders of cerebral or cardiac circulation, as well as a sudden onset of epilepsy, requiring careful research and timely treatment.
Stages of fainting
Fainting with open eyes in most cases does not exceed 30 seconds in duration (maximum 2-3 minutes) and is divided into 3 consecutive states:
- Perisyncopal (pre-assembly) the period lasts from 23-30 seconds to 1 minute and is accompanied by sudden weakness, dizziness, the appearance of blackheads before the eyes and tinnitus. If a person who has felt lightheadedness and dizziness manages to sit down with his head down or lie down, then the fainting itself may not occur. Otherwise, the intensity of unpleasant symptoms increases, leading to loss of consciousness and a sharp fall, accompanied by a high likelihood of head injury or other injuries. With a slow course of the stage, a person manages to grab a handrail or other firmly standing object with his hand, which protects him from falling and subsequent injury.
-
Fainting period begins with a complete, deep loss of consciousness, accompanied by loss of muscle tone. At the same time, the reaction of the pupils to light is slowed down, breathing, most often shallow, the pulse is slowed down. Due to impaired cerebral circulation, seizures that are not related to the symptoms of epilepsy may occur.
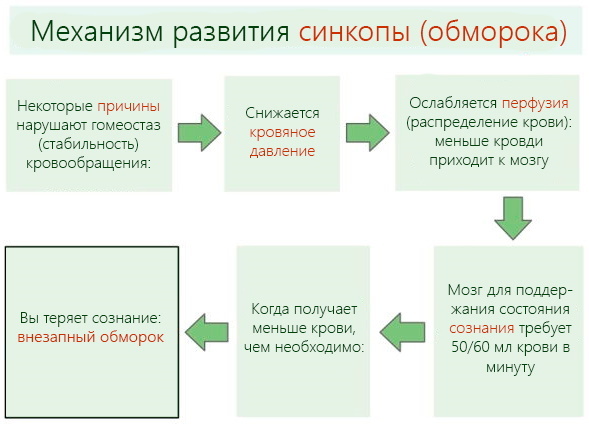
Fainting with open eyes - Post-syncope (or post-syncope) the period lasts 2-3 minutes, but it can persist for several hours. Here, a patient who has experienced a recent fainting has a slight weakness and dizziness, a slight decrease in the physical parameters of blood pressure and instability of movements are also possible. The patient perfectly remembers and understands that he has just experienced a loss of consciousness, which makes it possible to exclude the possibility of a head injury obtained during the fall and its characteristic retrograde amnesia.
Types of fainting
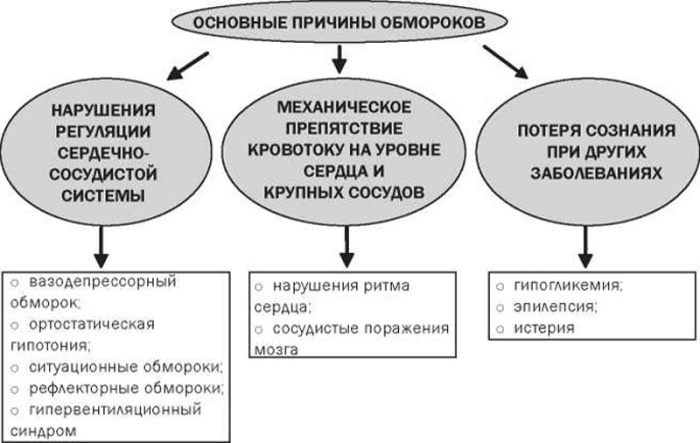
Fainting with open eyes can occur for various reasons, becoming both a consequence of vegetative-vascular disorders and problems caused by dysfunction of the heart and blood vessels.
Experts distinguish between:
| Vasovagal syncope | It occurs for vegetative-vascular reasons in perfectly healthy young people with a strong cough, sneezing, fright, while in a very stuffy place, or because of the type of blood. Appears in a standing position and if a person manages to sit up when dizziness appears, then fainting may not take place. |
| Cerebrovascular syncope | It is caused by pinched vessels in the cervical spine and can occur in people suffering from scoliosis or osteochondrosis. The appearance of fainting in this case occurs due to a sharp turn of the head and compression of the vertebral artery, leading to impaired cerebral circulation. |
| Irritative syncope | It is associated with irritation of the vagus nerve in the receptor zones and occurs in patients with hyperkinesia of the biliary tract and gastric ulcer. Also, this type of fainting can occur as a reaction of the body to FGS or sudden pain when swallowing. |
| Cardio- and arrhythmogenic syncope | It is most common in patients with cardiovascular rhythm disturbances, and is also observed in 13% of patients with diagnosed myocardial infarction. Unlike other syncope conditions, it has no precursors, arising instantly, and is characterized by a strong violation of heartbeats against the background of deep loss of consciousness. It differs from fainting spells that have arisen for vegetative-vascular reasons and a difficult exit from it, during the time of which the patient who has just woken up suddenly falls into a new, unconscious condition. |
| Orthostatic syncope | It develops when trying to transition their horizontal to vertical state and is typical for the elderly, debilitated patients and those suffering from autonomic disorders. A sharp change in body position here leads to severe dizziness and loss of consciousness, but does not pose a danger to human life. The occurrence of this type of fainting is also typical for persons suffering from:
Orthostatic fainting is also possible when taking antidepressants, antipsychotics and antihypertensive drugs. |
 Depending on the cause that led to the fainting state, you can also distinguish:
Depending on the cause that led to the fainting state, you can also distinguish:
- Hypoglycemic syncope occurring in persons with diabetes mellitus and caused by a sharp decrease in blood glucose levels. This condition is considered the most dangerous and can lead to the death of the patient.
- Epileptic syncope. Caused by an epileptic seizure and lasting much longer than normal loss of consciousness. With such a fainting spell, a person comes to his senses for quite a long time, and in case of loss of consciousness, he may bite his tongue or make an involuntary emptying of the bladder or rectum.
- Medication-induced fainting caused by taking certain medications and their intolerance.
- Situational fainting, arising from a sharp increase in intrathoracic pressure, which appears during bowel movements after constipation, diving, lifting weights.
- Anemic syncope associated with a lack of red blood cells in the body and is most common in the elderly, as well as pregnant women and those on a vegetarian diet.
- Bettoleptic syncope. Associated with chronic pathologies of the respiratory system.
- High-altitude syncope. They arise when a person gets to a height due to a violation of cerebral blood supply.
- Fainting associated with prolonged immobility and the absence of the necessary muscle contraction, which corresponds to full blood circulation. Most often, this type of syncope occurs in persons forced to stand motionless for a long time.
Causes
Until the beginning of the 20th century, one of the signs of a girl's good manners was the possibility of losing consciousness in time, thereby avoiding discussion of sensitive problems. This was also facilitated by specific women's clothing, such as corsets with a whalebone, squeezing the ribs and diaphragm and disrupting oxygen metabolism, restricting nutrition and reading women's novels. Such a pathology, quite common in high society, was completely unusual for ordinary peasant girls who wore looser clothes and spent a lot of time in nature.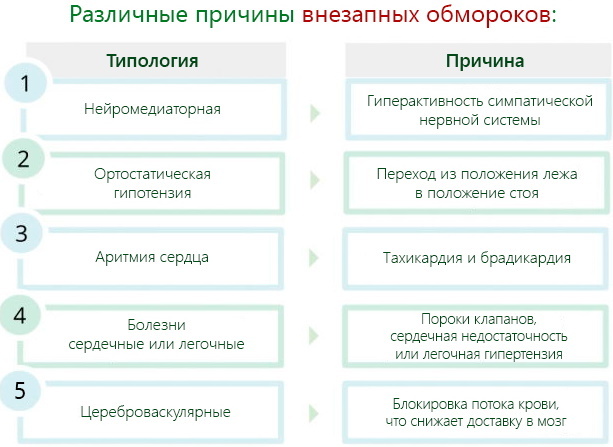
A modern, healthy woman most often faints due to vegetative-vascular disorders, severe migraines and menstrual bleeding associated with:
- insufficient amount of iron in the blood caused by profuse blood loss;
- gynecological pathologies or hormonal imbalance, accompanied by a low contractility of the uterus and severe pain, traditionally stopped by anesthetic drugs.
One of the main reasons for loss of consciousness in women is also pregnancy caused by problems with cerebral circulation, due to the strong pressure of the grown uterus on the inferior vena cava.
Possible venous congestion is quite common in late pregnancy and requires a woman to:
- do as few inclinations as possible;
- choose loose clothes for yourself;
- do not tie collars and scarves around the neck;
- stop sleeping on your stomach.
Fainting during pregnancy can also appear due to anemia caused by the additional consumption of iron by the body for the growing embryo. Here, the main prevention of the condition should be aimed at maintaining an optimal level of hemoglobin, through specialized drugs and diet, since after childbirth, iron deficiency anemia that occurs during pregnancy is only worsens.
Fainting with open eyes most often occurs spontaneously, due to:
- a sharp decrease in blood pressure indicators;
- long standing on your feet;
- nervous or physical exhaustion;
- overheating caused by heat or sunstroke;
- being in a very hot or stuffy room;
- increased body temperature;
- emotional stress, characterized by severe burnout, fatigue and nervous tension;
- severe pain that appears;
- arrhythmias;
- instability of the psyche;
- the onset of menstrual bleeding;
- poisoning with carbon monoxide or acid;
- lowering the level of dextrose in the blood.
Sudden loss of consciousness can also be caused by serious neurological disorders, such as:
- severe and prolonged migraine;
- stroke;
- transient ischemic attack.
In rare cases, a person can also lose consciousness due to narcolepsy, a disease characterized by sudden attacks of daytime sleep with complete muscle relaxation.
First aid rules
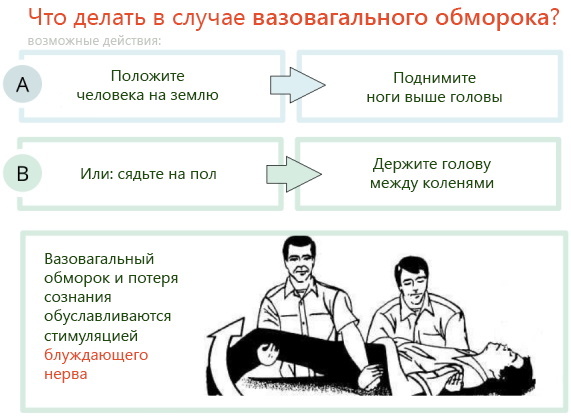
If he feels the harbingers of fainting, a person should immediately sit down with his head bowed as low as possible or lie down. If this is not possible, you need to try to grab a nearby handrail or a solidly standing object, which will help prevent a fall and avoid possible injury.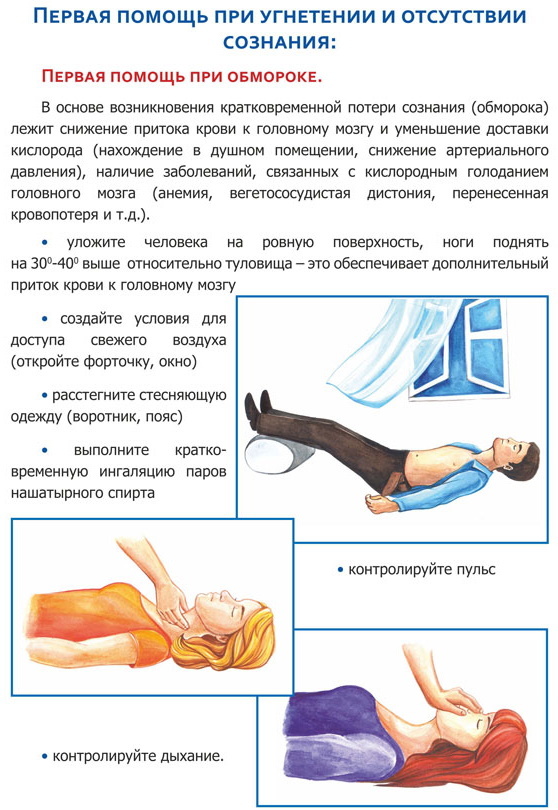
Strangers who see a person who has fainted should:
- Place the victim on his back and turn his head to one side. In the absence of such an opportunity, the patient should be seated, leaning against the wall and tilting his head as low as possible so that the shoulders touch the knees.
- To improve oxygen access, you need to loosen the belt on the victim's trousers, remove the scarf or unbutton the shirt collar. If you faint in a hot room, you must immediately open a window or remove the victim to fresh air.
- A cotton pad dipped in ammonia and brought to the nose will help a person recover. If there are no such drugs at hand, then the victim's face should be sprayed with cold water, and then rub the earlobes, temples and chest of the person who has lost the creation.
In case of severe fainting (if all of the above actions could not help the victim to recover), an injection of ephedrine or phenylephrine should be given. In case of arrhythmia, the use of antiarrhythmics is indicated, and in case of cardiac arrest, atropine is injected intravenously and an indirect cardiac massage is performed.
When to see a doctor
Fainting with open eyes that arose for the first time and caused by fear, pregnancy, being in a stuffy room or nervous overload does not require a visit to the doctor.
You need to contact a specialist if:
- loss of consciousness lasted more than 3 minutes, and before that it was repeated several times;
- the first fainting occurred after 40 years of age;
- an injury was sustained in the fall;
- a person suffers from diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular pathologies;
- before fainting, the heart rhythm was disturbed or severe pain suddenly occurred;
- involuntary defecation or emptying of the bladder occurred in an unconscious state;
- the victim developed shortness of breath, which did not bother him until he lost consciousness.
Diagnostics
At the appointment, the doctors will examine the patient, as well as ask about the history, concomitant diseases, lifestyle and symptoms that preceded the onset of fainting, and then prescribe:
- KLA, as well as research biochemistry, the amount of sugar and possible anemia;
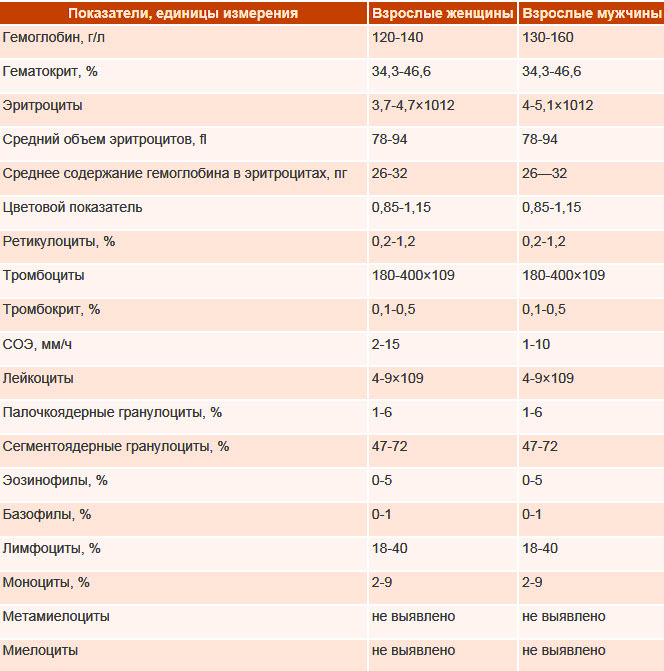
- sampling of feces, for the detection of hidden blood;
- ECG;
- Ultrasound of the heart and blood vessels;
- Doppler ultrasonography of blood vessels;
- magnetic resonance imaging and CT.
If there is a suspicion of a possible dysfunction of the heart and blood vessels, the patient will be offered hospitalization, for observation in a hospital, as well as additional research.
According to the results of the studies obtained, the doctor should be alerted if:
- there were abnormalities in the ECG;
- found changes in the structure of the heart;
- there are symptoms characteristic of heart failure;
- found low blood pressure;
- there was shortness of breath, which appeared a few minutes before and remained after loss of consciousness;
- a significant decrease (more than 30%) in the number of erythrocytes in the blood is alarming;
- diseases characteristic of old age appeared;
- in the family history of the patient, sudden deaths associated with problems in the work of the heart were found.
Treatment
The need for treatment and corrective therapeutic procedures are prescribed depending on the reasons for the loss of consciousness:
- It is not necessary to prescribe therapeutic measures for vasovagal, reflex fainting. If the loss of consciousness has occurred due to fear or fatigue, it is recommended to simply exclude the provoking factor, and also avoid visiting stuffy rooms with a large number of people.
- The anemia that caused the loss of consciousness needs adjusting the diet and taking iron-containing drugs.
- With low blood pressure, it is necessary to maintain optimal water balance in the body, eat small meals and regularly consume caffeinated drinks. You should also not try to abruptly change the position of the body, and when trying to get out of bed, you should first sit down and cross your legs, and also strain your arm muscles.
- Fainting triggered by taking medications can be prevented by replacing the drug, as well as the timely intake of a vitamin-mineral complex.

Specific therapy is prescribed for cardio-, arrhythmogenic and glycemic syncope, requiring immediate medical or surgical measures.
- In the first case, the patient will be offered appropriate drug therapy, and, if necessary, the installation of a cardioverter-defibrillator that corrects the heart rate.
- In the second case, a patient with diabetes mellitus will have to monitor blood glucose levels daily and apply supportive insulin therapy.
With an unknown specificity of frequent fainting, the patient is prescribed a course of b-blockers that reduce neurovascular excitability and increasing the level of autonomic resistance, as well as sedatives (root extracts valerian and mint). In some cases, the use of tranquilizers is also indicated.
Possible consequences
Fainting with open eyes is dangerous not only by short-term loss of consciousness, but also by the risk of receiving various injuries, including craniocerebral ones, during a sharp fall.
TBI - damage to the soft membranes, nerve endings, vessels or bone tissues of the skull, is considered the most dangerous consequence of fainting and is divided into:
- shaking of the "gray matter" is the easiest consequence, without brightly grown disturbances in work of the brain, the signs of which appear immediately after a person leaves syncope states;
- injury of the "gray matter";
- compression of the brain, accompanied by the presence of a hematoma;
- axonal diffuse damage.
When a traumatic brain injury occurs in a person in a post-faint state, the following is observed:
- coma;
- sopor;
- damage to nerve endings;
- hemorrhage.
Any of these signs requires immediate hospitalization of the victim.
Prevention of fainting
For people with a tendency to frequent fainting, experts recommend covering the floor in the apartment with carpet, as well as avoiding prolonged standing on their feet. With such a pathology, it is best to walk on the ground or grass, avoiding asphalt paths if possible.
The prevention of syncope also includes:
- prevention of stressful situations, hunger and increased fatigue;
- dosed physical activity to help avoid overwork;
- hardening water procedures;
- stabilization of the rest and work regime;
- compulsory night sleep for at least 8 hours;
With a tendency to fainting, one should not abruptly change the position of the body from horizontal to vertical. It is also important to maintain blood vessels in a normal state and control blood pressure, since a sharp change in blood pressure can cause fainting.
Fainting with open eyes is a fairly common pathology that occurs in people at any age and is associated with impaired cerebral circulation. The pathology that appears due to severe pain, stuffiness, a sharp change in body position or nervous exhaustion requires special attention to one's own health, normalizing sleep and rest, and, if necessary, conducting a thorough medical examination, capable of detecting severe heart pathologies at an early stage and vessels.
Fainting videos
Causes and treatment of fainting: