Content
- Definition in psychology
- What is feedback for?
- Feedback types in communication
- Feedback in training
- Constructive enterprise feedback
- Rules
- How to get feedback
- Feedback video
Feedback is a fundamental aspect of everyday learning that is being studied by modern psychologists. Researchers from all over the world, such as New Zealand, USA, Sweden, Netherlands, UK and Germany, recognize the importance of feedback. Scientists even describe her as one of the most influential factors in teaching. In the list of factors influencing the process of learning and business interaction, it also ranks higher than, for example, the quality of training and the organization of business negotiations.
Definition in psychology
Duinhower in 2010 defined feedback as information that is provided by an external agent regarding some aspect of execution tasks for students and is designed to change the cognition, motivation and behavior of the student in order to increase productivity.
Feedback is presented in the works of the influential foreign psychologist Eric Berne, who called stroking the manifestation of attention to a person. In turn, feedback can be not only positive - sympathy, support, praise, but also negative, so-called "kicks" - criticism, insults, and so on.
Feedback affects emotions, and emotions affect learning. Moreover, positive and negative feedback can affect the emotions of the recipient in different ways. However, research papers rarely provide a clear definition of positive and negative feedback.
What is feedback for?
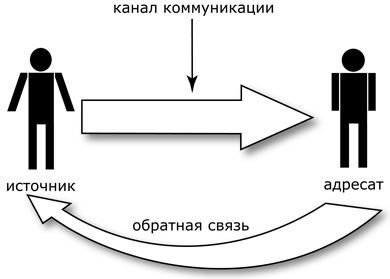
Feedback is (in the psychology of communication) an important tool for establishing psychological contact between people.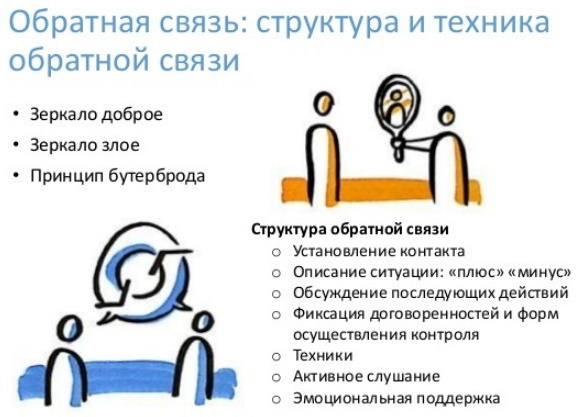
Feedback is necessary to understand whether adequate contact has been established between the source of information, the speaker and the recipient of the information. It is important that when communicating, the recipient understands the meaning of the message, which the sender of the information means. This is the main rule of successful psychological contact.
In the learning process, the feature of feedback is highlighted that it narrows the gap between the current performance and the goal. In this context, it is customary to talk about effective, learning-enhancing feedback.
Feedback functions:
- establishing psychological contact in communication;
- motivation of students;
- activation of emotions;
- conveying the meaning of the message.

While learning, giving useful feedback can be more difficult than most people think. The existing body of knowledge shows that more than one third of all feedback interventions have a negative impact on learning
An exception is the work of positive psychologists Lozada and Heefe (2004), who define positive feedback as an expression of support, encouragement, or appreciation, and negative feedback as an expression disapproval.
The context in which the feedback is provided is important and can also influence the emotions that the learner experiences. For example, a student might experience a negative emotion, such as shame, in response to a positive assessment from a teacher. The fact is that the student's interest in the subject can be negatively assessed by his peers and the teacher's encouragement will not increase motivation, but will cause negative emotions.
Feedback is (in the psychology of communication) one of the criteria for successful communication. For example, the emotions experienced by the person receiving the feedback are influenced by their relationship with the person who leaves the feedback. This forms, according to social psychologists, a kind of context.
Social psychologists emphasize that any communication has content and relationship. For example, a student who has a good and trusting relationship with the teacher will experience negative feedback in a different way than a student who does not trust the teacher. In the first case, the student will be depressed, will be more worried.
It is therefore not enough to distinguish between positive and negative feedback from the perspective of the feedback provider. The recipient of the feedback also experiences emotions and builds constructs.
Thus, feedback can evoke positive and negative activating and deactivating emotions. These emotions will affect learning in a predictable way.
In general, positive feedback evokes positive emotions, while negative feedback evokes negative emotions. But this is not always the case, because the impact of feedback is also determined by the context and relationship with the feedback provider.
It is desirable that the feedback evoke activating emotions or be embedded in a context that generates a vast emotional space. This can be achieved by providing positive reviews more often than negative ones.
Feedback types in communication
Feedback in communication can be presented according to 2 classifications: by sign (negative and positive) and by the degree of formality (formal and informal), as well as by activity (effective, destructive).
Thus, there are 6 types of feedback in communication:
- positive;
- negative;
- formal;
- informal;
- effective;
- destructive.
Praise is one of the most common forms of feedback. Praise can initially be described as a type of positive feedback. Despite this, this type of feedback can have both effective and destructive effects.
The bottom line is that for effective praise, you need to accurately indicate the subject of positive feedback. Spontaneous praise can be perceived differently by the recipient and cause spontaneous changes in behavior or activate unwanted behaviors.
Feedback can serve multiple purposes and take many forms. Informal feedback can provide information about understanding the relationship between students in the classroom.
Informal feedback can be spontaneous. Therefore, informal feedback requires rapport with students and workers to effectively encourage, train or guide them in their day-to-day management and learning decisions. This can happen in the classroom, over the phone, in an online forum, or in a virtual classroom.
Feedback is (in production psychology) predominantly formal feedback that contributes to improving the literacy of students and employees, and also stimulates, motivates them to form professional skills.
Formal feedback is planned and systematically incorporated into the process. Formal feedback, usually associated with assessment tasks, includes assessment criteria, competence or achievement of standards and is recorded for both the student and the organization as proof of.
Each of the types of feedback has its place in improving student learning and improving the efficiency of employees of the enterprise. Therefore, where possible, courses should provide opportunities for different types of feedback.
| Communication type | Example |
| Positive | Praise, approval, handshake, example, encouragement. |
| Negative | Reproach, disapproval, punishment. |
| Formal | Apprentice grade, employee bonus, reward, salary. |
| Informal | Approval, praise, handshake, smile, kiss. |
| Effective | Increasing productivity, efficiency of performed activities. |
| Destructive | Reducing productivity, the efficiency of the activities performed. Most often arises from the recipient's misinterpretation of the praise. |
Feedback in training
In teaching, feedback is given by both the teacher and the learners. The specificity is that the effectiveness of joint activities depends on the person giving feedback. In addition, a different classification is already in force here.
Feedback in training is also divided into:
- formative;
- final.
The purpose of formative assessment is to monitor student learning to provide continuous feedback, which can be used by teachers to improve their skills, and students - to improve their learning.
Therefore, formative feedback is best given at the beginning of the course, but before the final grades. Formative feedback helps students improve and prevents them from repeating the same mistakes again.
The purpose of the summative assessment is to assess student performance at the end of a unit by comparing it to a standard or benchmark.
Thus, the final feedback consists of:
- detailed comments related to specific aspects of their work, clearly explaining how the score was obtained;
- additional constructive comments on how you can improve the work.
Teachers no longer need to be the only experts on a course. With basic instruction and ongoing support, students can learn to give quality feedback, which is highly valued by their peers. Providing students with regular opportunities to voice and receive feedback from peers enriches their learning experience and develops their skill set.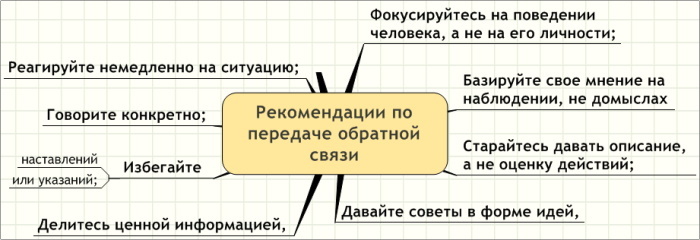
Feedback is (in the psychology of learning) one of the main tools for increasing the effectiveness of the educational process. Self-feedback from students and learners is the ultimate goal of feedback for any learning.
While providing feedback, teachers have the opportunity not only to guide students but also to teach self-assessment skills and goal setting, which makes them more independent without loss of effectiveness learning.
To help students achieve autonomy, teachers can:
- clearly define and explain learning objectives and criteria for success;
- simulate the application of criteria for the successful completion of tasks;
- provide opportunities for self-feedback;
- teach students to use feedback to determine next steps and set goals;
- give time for introspection, reflection and reflection.
Constructive enterprise feedback
This type of feedback is specific, problem-focused, and observational. It is most appropriate in a formal environment at an enterprise. Constructive feedback is effective - that is, it increases the performance of subordinates.
There are four types of constructive feedback:
- Negative feedback - corrective comments about past behavior. Focuses on behavior that has not been successful and should not be repeated.
- Positive feedback - supporting comments about past behavior. Focuses on behavior that has been successful and needs to be continued.
- Negative feedback - corrective comments on future performance. Focuses on behavior to avoid in the future.
- Positive feedback - supporting comments about future behavior. Focuses on behaviors that will improve performance in the future.
Rules
Feedback is more effective after small victories. People are most receptive to feedback when they get positive results, but there is still room for improvement. Their progress gives them the confidence they need to consider new approaches.
Conversely, critical (even constructive) feedback will be ineffective after a major victory. When a team wins a big win, they want to celebrate. This is not the right time or place to discuss what the team could do better.
Critical feedback will be ineffective after failure. Just as a big victory is a time to celebrate, a big loss is a time for reflection. Only after everyone has the opportunity to understand the mistakes on their own and understand the future, can the mistakes be productively considered and planned to fix them.
Begin criticism with an honest compliment. Opening the conversation with an honest compliment disposes the employee better and allows the other person to acquire a willingness to ponder new ideas.
Don't be disappointed in people. Expressed disappointment, resentment and obvious dissatisfaction with employees will only reduce their confidence in themselves and, as a result, the results of their work.
Listen to the end first before giving feedback. You must fully understand the situation before commenting.
Behavior should be criticized, not a person. When giving feedback, you need to focus on changing the other person's behavior, not their character. The reason is simple: it is difficult to force someone to do something else, and to force someone to become someone else is completely impossible.
Timeliness of feedback. Don't wait for the "right moment" to comment on the other person's failures. It rather overwhelms the person who then, after a lot of comments, is usually defensive and less likely to change their behavior.
Feedback should be specific. General comments make people feel good for a few minutes, but they don't change their behavior. Concreteness tells the other person what works and what doesn't.
How to get feedback
In psychology, there are several rules that will help establish feedback in any team and interpersonal relationships.
These are the following positions:
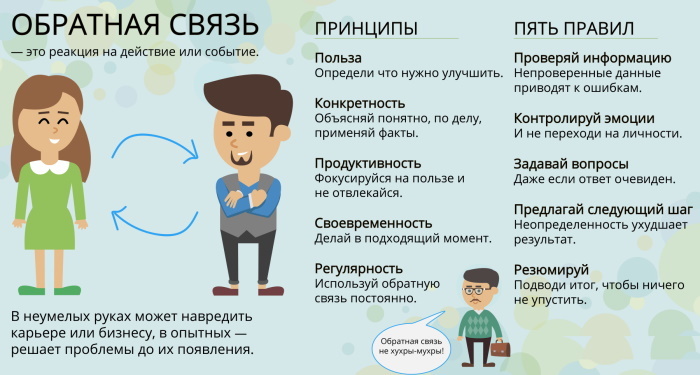
- Create an environment that is safe for feedback.
- Create review standards.
- Provide the ability to choose a feedback channel.
- Correct criticism must be maintained.
- Reviews should be helpful.
- It is necessary to compile a list of solutions in accordance with employee feedback.
Employees need to feel safe and know that if they give feedback, they will not face negative consequences. It starts with building trust and is reinforced by how the feedback is received.
Different employees will have different levels of comfort in both providing and receiving feedback. It is important to show respect and not impose feedback. Create feedback standards. This is what the feedback should look like.
For example:
- Who gives feedback?
- Who gets it?
- How often does this happen?
- What does it look like?
- What is the purpose of feedback?
Practice and consistency are key. Practice leads to excellence. When feedback occurs regularly, it becomes expected.
Feedback culture has more than one way to give or receive feedback. People prefer to receive feedback in different ways, and different situations require different feedback channels.
So, for example, there can be the following types:
- Interpersonal or anonymous;
- One on one or all against all;
- One against the group;
- Face to face or in writing.
Maintain positive feedback and constructive criticism. Everyone loves positive reviews. But focusing only on the good can be risky: you can ignore problems and slow down the professional growth of employees.
It is necessary to formulate solutions to problems based on feedback from other employees. Let them know when you make a decision or change based on someone else's feedback.
A feedback culture assumes that the leader responds and acts in accordance with the feedback. Employees need to understand that feedback is worth their time. Don't underestimate the value of feedback.
Thus, feedback is an important tool outlined by psychologists to drive performance. activities in any team: both students and employees, and can also be used to improve interpersonal communication.
Author: Svitkevich Julia.
Feedback video
Psychological personality types. Correct Feedback: