Content
- What it is?
- Positive aspects of rigidity
- Disadvantages of rigidity
- Types of rigidity
- Risk factors
- The main causes of occurrence
- Psychophysiological reasons
- Social reasons
- Manifestations in humans
- Detection method
- Ways to overcome
- Videos about rigidity in psychology
In psychology rigidity is, simply put, inability to concede, constructively assess the point of view or emotions of another person. Usually, mental rigidity is also characterized by a lack of empathy.
What it is?
Rigidity has been defined by psychologists as "resistance to the acquisition of new behavioral patterns by retaining old and maladaptive behaviors." It is also seen as an essential component of dysfunctional, that is, negative, perfectionism.
Rigidity can manifest itself in persistence and inability to change habits, inability to change concepts and attitudes, once developed and reinforced by empirical experience.
A specific example of rigidity is “functional fixedness,” which presents a difficulty in understanding new uses for familiar objects. That is, a person cannot use, for example, a knife for other functions than cutting vegetables.
Rigidity in psychology implies the complexity, unreadiness or complete inability of the subject to change the intended program of activity in new situational conditions. This is the ability of the psyche and character of a person to firmly maintain a given attitude of consciousness.
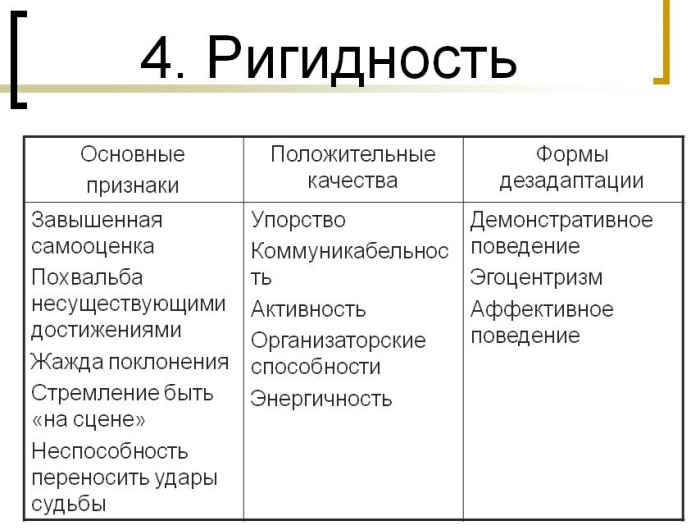
A rigid person is not inclined to change his habits. He is stubborn, tries to defend his tactics in solving everyday problems. He is impressionable, retains his emotional state for a long time. People around him have to put in a lot of effort to distract him from the overvalued idea or convince him.
Positive aspects of rigidity
The dictionary of psychology characterizes a rigid person as a subject, little changeable even under the influence of powerful external influences and incapable of self-regulation.
Moderately expressed personality rigidity expresses the invariability of interests and attitudes aimed at defending one's opinion, on the activity of a position that, under the influence of external forces, only intensifies. She is practical, accurate, true to her principles. Such people are resistant to stress, as they are less susceptible to environmental changes.
Rigidity also has 3 different main stages of severity, although it never has to progress to further stages:
- Stage 1 is a strict perception that makes a person persist in his path and be close to other things.
- 2 - ego protection.
- Stage 3 is part of a person's personality. Its manifestations can be observed even in cognitive processes, that is, in thinking and understanding the world around us.
Three main stages of its development are being investigated:
- rigidity as a neurologically determined feature of individual perception, leading to premature closure;
- rigidity as a defense mechanism against ego-involving stimuli;
- rigidity as a manifestation of basic personality variables observed in the cognitive and social spheres, as well as in perception.
Rigidity, which is described by the first stages of development, can be beneficial to the individual. It makes him resistant to negative environmental influences, allows him to defend his opinion and position, to show non-conformism.
Moderately rigid people are less susceptible to stress, panic, and emotionally more stable than people with flexible and emotional thinking.
Disadvantages of rigidity
The following concomitant and characteristic features of a rigid personality are disadvantages:
- perfectionism;
- dichotomous thinking;
- excessively high self-esteem.
In an attempt to understand perfectionism, psychologists have divided this construction into 2 aspects:
- Positive. Forms self-confidence, ambition and cleanliness, accuracy, professionalism. Positive perfectionism does not seek to put someone “higher” and someone “lower”.
- Negative. Forms self-doubt, in others, excessive skepticism.
Dichotomous thinking is another variable associated with perfectionism and rigid thinking. Simply put, dichotomous thinking is when a person perceives either victory or failure.
American psychologist Saffron et al. 2002 developed a model of 'clinical perfectionism', which they define as' the overdependence of self-esteem on the desire for self-imposed standards in at least one very important area, despite adverse personality ".
Rigidity in psychology is a condition that Riley and Saffron strongly associate with negative perfectionism, because they have similar negative traits.
They assume that people make decisions in a dichotomous way as to whether they meet their high personal standard: either as a complete success or as a complete failure.
Foreign authoritative psychologists Riley and Saffron in 2002. found that dichotomous thinking is present in most people who are qualitatively rated as having "clinical perfectionism." Dichotomous thinking is associated with negative, not positive, perfectionism.
High self-esteem limits experience, disrupts social interaction, and makes it difficult to establish psychological contact with the people around you.
Types of rigidity
In psychology, these 3 main types of personal rigidity are distinguished:
- Cognitive.
- Affective.
- Motivational.
Cognitive rigidity implies the difficulty of restructuring perception and thinking in changed situational conditions. This is the reluctance of the subject to create a new conceptual picture of the world around him when new information arrives that does not correspond to the previous one.
First of all, cognitive rigidity affects the adaptation of the individual to new conditions, which is extremely important in the modern and constantly changing world. Therefore, flexibility of thinking is so often singled out - a trait that is the opposite of rigidity.
Rigidity in psychology is also affective rigidity, that is, the invariability of reactions (affective or emotional) to changing objects of emotions. For example, a person tends to respond to the same stimulus always with one response, regardless of the context.
Motivational rigidity is manifested in the complexity of organizing a system of motives in conditions that require flexibility and behavior change. The rigidity that the subject shows in a given situation largely depends on the complexity of the task, its attractiveness for him, the presence of danger, and so on.
Lazursky A. F. called emotional rigidity in psychology "the stability of emotions." It is characterized as follows: this is the largest time interval for a certain person, during which once the excited emotion is found again, despite the fact that the pathogen has ceased to act, and the circumstances have changed.
Emotional rigidity of thinking is associated with the stability of emotions, with the fixation of attention on any important events, objects or circumstances, failures, offenses, and so on. So, for example, in many personal classifications, psychologists distinguish the so-called "stuck" character - the experience of the same emotions, most often unpleasant.
| Type of rigidity | Description | Example |
| Cognitive | Often the prerequisites for the formation of cognitive rigidity are brain pathologies and traumatic brain injuries. The person becomes incapable of assimilating new information. | A person only uses a fork for food, not realizing that it can be used to open bottles. |
| Affective | Ignoring the context, the response to different emotional stimuli is the same, despite the different context of situations. | I got used to reacting to anger towards myself from different people in the same way: to hide, not to conflict. |
| Motivational | Difficulty in building the structure of the activity and correlating the sequence of the task. | A person finds it difficult to complete a task, for example, solving a problem, if a condition is changed. |
| Emotional | Fixation on certain negative emotions. More often these are emotions experienced in childhood: resentment, anger, failure. | Resentful of peers and introverted due to a single incident in childhood. |
Risk factors
Psychological rigidity is especially noticeable in populations and with anxiety disorders. For example, people who struggle with flexible thoughts, emotions and behaviors are at increased risk of developing a major depressive disorder.
Routine is another factor contributing to the inability to unlearn. Due to the daily routine, employees rarely have enough time to identify outdated methods. Thus, people with responsible work are at risk.
In addition, people are exposed to more and more information, which can lead to sensory overload. Excessive number of meetings, phone and video calls, email, and exposure The Internet, social media and news can lead to an inability to separate relevant knowledge from irrelevant.
Resistance to ignorance also arises from people's fears that risk will lead to critical errors. For fear of making a critical mistake, employees tend to refrain from using new ways of doing business, but prefer to stay on the safe side.
The main causes of occurrence
Rigidity in psychology is a personality trait, which, accordingly, develops at the appropriate stages of development. Children are the most vulnerable. Especially if this is accompanied by psychophysiological or social factors.
Psychophysiological reasons
The psychophysiological risk factor for the development of rigidity is the type of person's temperament. So, the flexibility of thinking is characteristic of the individual style, and as the main carrier of the style characteristics of temperament, therefore, flexibility should be conditioned by temperament.
Flexibility or rigidity of thinking is based on the mobility of the nervous system. The mobility of the nervous system is the speed of the subject's reaction to a change in sign stimuli, adaptation, the ability to change his behavior in accordance with a change in the influencing stimuli.
In the works of V. M. Rusalova shows the relationship between the main properties of the nervous system, temperament and rigidity or flexibility of thinking. Rusalov conducted an experimental study of the relationship between the properties of temperament and the characteristics of creativity according to P. Torrance. He concluded that creativity is due to temperament.
So, for example, temperaments with a less mobile nervous system are subject to rigidity: melancholic, phlegmatic.
Social reasons
Personality rigidity is acquired as a quality, usually between the ages of 3 and 5, when a child identifies with a parent of the same gender.

For a child of this age, the reaction of a parent of the same gender to his actions and self-expression is extremely important. If a child receives a lot of comments, criticism - he decides that he is being treated unfairly, he also decides to become more perfect. To protect his pain, he puts on a cold, tough mask, which gives the impression that a person does not know how to feel, is not capable of a warm relationship.
This feature becomes a characteristic feature of the rigid person, although inside he is a rather sensitive person. In appearance and physique, this manifests itself in maximum proportionality, poise, his body is symmetrical and has some roundness. However, the inflexibility is noticeable, the arms are often crossed at the level of the solar plexus, which is a protective mechanism that allows the rigid to move away from others, not to accept emotions from them, not to feel.
Manifestations in humans
More pronounced rigidity in psychology is characteristic of psychopaths with signs of paranoia. For such individuals, as a rule, conflicts are characteristic, affective capture by the dominant idea. Often a typical example of rigidity is the introverted personality type.
The introverted type is characterized by low contact, isolation, isolation from reality, a tendency to philosophize. Such people love loneliness; enter into conflicts with others only when trying to unceremoniously interfere in their personal life.
They are often emotionally cold idealists with relatively little attachment to people. They have such attractive features as restraint, strong convictions, adherence to principles.
Rigidity in psychology is stubbornness, stubborn defense of one's ideas. Such people have their own point of view on everything, which may turn out to be erroneous, differ sharply from the opinions of other people, and nevertheless they continue to defend it, no matter what.
Thus, the following features are indicative of rigidity. It can be both external behavior and personality traits.
For example:
- Persistently repetitive behavior.
- Difficulty with unmet expectations.
- Perfectionism.
- Compulsions (rituals, repetitive actions).
- Perseverance.
- Concomitant internalizing behavior.
- Obsessions (as in OCD).
Detection method
Attitude flexibility score of 75 self-report points is also used to measure rigidity. However, the most acceptable methodology is the "rigidity questionnaire" developed by American psychologists.
It specifically measures the rigidity of thinking and is part of the Behavioral Rigidity Test. It has good reliability and acceptable performance. The test also gives results on a true-false scale. Lower scores indicate that the person is more rigid.
Example clause: "Once I have made a decision, I rarely change it."
Ways to overcome
Correcting the behavior of people with a high level of rigidity is not an easy task. The strategy of interaction with a person of this type should be based on an implicit belief in the form of a recommendation in order to the individual himself got the impression that the belief comes from himself, and the psychologist only confirmed it right.
For weaning to be successful, employees need to know that weaning initiatives depend on their own thinking and acting. Managers need to put themselves in the shoes of their employees and think about how to motivate and engage them.
These are the main ways for educators and organizational leaders to overcome rigidity:
- Isolation from previous experience.
- Situational awareness.
- Temporal and spatial freedom.
- Promote a culture of forgiveness.
- Reducing the influence of old knowledge over time.
Here is one example of a successful way to overcome rigidity in a combination of ways:
Doppelmayr, one of the leaders in the global ropeway market, planned to develop a radically innovative product. Senior management felt it was necessary to free their employees from preconceptions, assumptions and other biases.
The idea was to refrain from using blueprints and sketches for existing products and start from scratch. Starting with the core team, employees were dispatched to a vacant position on site 1 day per week for approximately 1 year. 
They were located in offices with no telephones to isolate them from their daily activities. This helped the team focus on the new product. During this time, employees had the opportunity to question assumptions about existing products in a secure environment.
Employees did not have to fear negative consequences for critical mistakes. The new product contained several radical innovations and was well received by customers.
Employees are strongly encouraged to get rid of old notes, documents, or other information that might make it difficult to generate new ideas. The interviewees confirmed that this practice really helps them gain new perspectives.
Giving employees islands of spatial and temporal freedom allows them to question routines, habits, and ingrained ways of thinking. This allows employees to forget previous experiences, assumptions and procedures, while at the same time making room for new ideas and behaviors.
Managers must implement and develop a culture that allows employees to make mistakes and blunders during the innovation process. Open-minded and proactive people will especially benefit from a culture of forgiveness that makes mistakes.
Only when employees are confident they can make mistakes will they start thinking and doing things in new ways. Of course, they might fail in the beginning, but there is a new way to think about it: they weren't wrong, they just found one way that doesn't work.
Perhaps the biggest challenge for managers is ensuring that employees don't fall back on old habits and routines. To actively discard old knowledge from the cognitive and behavioral repertoire of members of the organization, managers need to remove the stimulus-response patterns that trigger the use of old knowledge.
For example:
- Rearrange tables, furniture.
- Deliberately disrupt the exchange of information, disable the Internet.
- Block the use of certain incentives and procedures, or change the corporate language by removing terms or phrases that were associated with the old one.
In psychology, rigidity is a factor that significantly reduces the efficiency of employees and students. Managers, educators and organizers are encouraged to take action to prevent and overcome stiffness.
Author: Svitkevich Julia
Videos about rigidity in psychology
Psychological defense mechanisms. Rigid personality: