Content
- Characteristics and properties
- In the first trimester
- In the second trimester
- In the third trimester
- Analysis
- Pathological causes
- Liver disease
- Disruption of the pituitary and hypothalamus
- Disruption of the excretory organs
- Gastrointestinal pathologies
- Dieting
- Decreased symptoms
- Treatment
- Blood Urea Video
Decreased blood urea levels - considered the main component of protein breakdown, a normal, physiological state during pregnancy, caused by a number of reasons. Normally, such a deviation does not harm the baby and gradually recovers after completing breastfeeding, but also considered a sign of malnutrition in a young mother, in which the baby lacks nutrients for full growth and development.
Characteristics and properties
Urea (or carbamide) is an organic compound that appears in the body at the final stage of protein breakdown. By itself, it is not an important element and is not needed for metabolic processes, but it helps to quickly and safely cleanse the body of nitrogen. In the process of protein breakdown in the blood, ammonia compounds are formed, which first enter the liver, and then are excreted from the body by the kidneys along with other decay products.
The highest concentration of the amount of carbamide reaches in the blood and urine, in the study of which specialists are able to determine a number of abnormalities in the body. The level of urea can indirectly indicate the condition and function of the liver and kidneys, and also indicate the likelihood of the development of dangerous pathologies of the pituitary gland or hypothalamus.
Urea is excreted from the body gradually, in several stages. Synthesized in the liver, it circulates in the blood for some time, and then enters the kidneys. Here it is filtered, remaining in the primary urine portion. Some of the urea is then able to re-enter the bloodstream, but most of it leaves the body with secondary urine. At the final stage, urea descends into the bladder, leaving the body together during urination.
A decrease in uric acid levels is observed in all pregnant women and is associated with an increased protein load due to the increased needs of the fetus. If a slowed down protein breakdown and a decrease in urea levels occur against a background of normal functioning of the kidneys, then urea leaves the body along with the kidneys, without provoking any residual phenomena.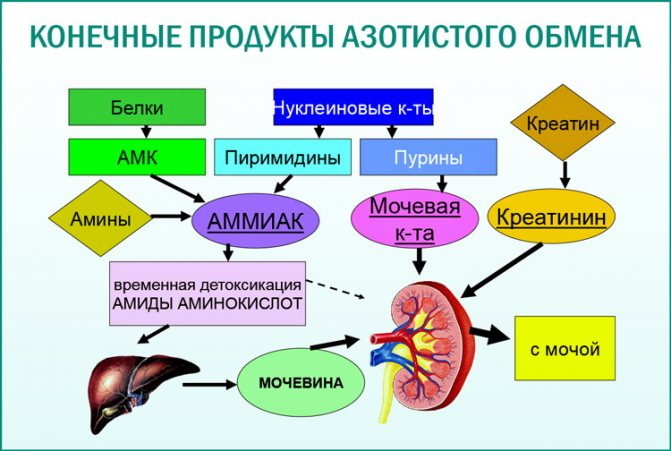
The danger is caused by a decrease in urea indicators, which occurs against the background of slowed down kidney function. In this case, ammonia, which is a protein derivative, and when it enters the liver is transformed into urea, is retained in the body, provoking intoxication and becoming the cause of the development of defects fetus.
Fortunately, this condition is rarely observed, because together with the increasing protein processes due to gestation, the volume of fluid also increases, contributing to the faster withdrawal of potentially dangerous connections.
With a reduced level of urea, an intense protein breakdown occurs, or a significant decrease in the amount of protein is observed, what is caused by pregnancy, lactation, intense physical activity or insufficient amount of protein eaten food.
Pregnancy table:
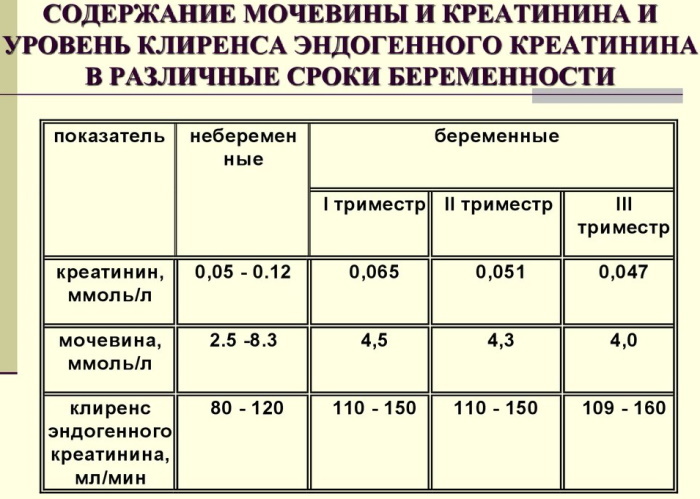
Urea in the blood is lowered during pregnancy due to physiological processes occurring in the body and accompanied by increased protein production. Normally, the urea indicator is 2.5-8.3 mmol / l, but for expectant mothers it shifts slightly to the lower side:
| 1 trimester of pregnancy | 2.5 - 7.3 mmol / L (4.5 mmol / L) |
| 2nd trimester of pregnancy | 2.5 - 7.0 mmol / L (4.3 mmol / L) |
| 3rd trimester of pregnancy | 2.3-6.3 mmol / L (4.0 mmol / L) |
Normally, the concentration of urea in the blood and urine is affected by the work of the liver and kidneys.
In the first trimester
A decrease in blood urea during pregnancy in the 1st trimester in most cases is completely normal and is associated with the development of toxicosis, forcing a woman to abandon most previously consumed foods due to their sudden intolerance.
A vegetarian diet or veganism, which the expectant mother adhered to before pregnancy and kept while waiting for the baby, can also have an impact. In addition, the volume of circulating fluid increases significantly, contributing to a faster removal of uric acid from the body of a young mother. It affects the volume of urea and the activity of progesterone with estrogen, the level of which has increased significantly since the beginning of conception.
In the second trimester
In the 2nd trimester of pregnancy, with the development of the placenta, the level of urea in the blood is equalized, while its indicators are still quite low compared to prenatal tests. Simultaneously with the indicators of urea, the doctor assesses the condition of the pregnant woman's kidneys, which, as at the beginning of pregnancy, continue to actively process fluid.
In the third trimester
At the beginning of the 3rd trimester of pregnancy, the level of uric acid remains quite low, which is associated with an increase in the amount of fluid and active protein metabolism. In addition, during this period, the organs of the excretory system are actively working, trying to remove harmful substances from the body as quickly as possible, preventing their negative impact on the fetus.
Analysis
Urea in the blood is lowered during pregnancy against the background of active kidney function, which is considered completely normal and does not cause doctors to fear for the condition of a young mother. The danger can cause a significant decrease in the amount of uric acid below during pregnancy (below the permissible norms) caused not by natural causes, but by the development of dangerous pathologies. You can determine the level of urea during a biochemical blood test, conducted from venous blood taken on an empty stomach.
In addition to uric acid, the analysis also makes it possible to assess the value of cholesterol, creatinine, glucose and other compounds. Since the results of blood biochemistry, with improper preparation and analysis, can give a false result Of particular importance is the observance of a number of simple recommendations that allow an objective assessment of the state of urea in blood.
- do not give physical activity to the body 24 hours before the scheduled study;
- observe the usual diet (without overusing meat, fish and confectionery);
- in the morning, on the day of donating blood, refuse to eat (it is allowed to drink only water or tea without sugar);
- avoid severe stress.
With urea levels below the interval of 2.5-7.3 mmol / l in the first half of pregnancy and 2.3-6.3 mmol / l in the second half of pregnancy, the gynecologist will prescribe additional tests.
Also, research may be prompted by:
- the resulting muscle weakness along with rapid fatigue;
- loss of appetite;
- painful sensations in the right hypochondrium;
- weight loss;
- swelling of the legs;
- a sharp increase in red blood cells in the second half of pregnancy;
- growth of physical indicators of blood pressure;
- insufficient weight of the embryo or problems in its development;
- gas formation and swelling of the abdomen, as well as belching with air.
Pathological causes
Urea in the blood is lowered during pregnancy, both due to the increased amount of fluid in the body, and due to pathological reasons, including:
- hepatic pathologies;
- kidney disease;
- problems in the stomach and intestines;
- insufficient amount of protein in the diet of a pregnant woman;
- disruption of the pituitary gland and hypothalamus;
- the use of certain drugs.
 If the deviations in the amount of uric acid are caused by improper diet, toxicosis or adherence to a vegetarian diet, the doctor will prescribe the woman a special diet, including foods rich in protein, drugs that relieve the severity of toxicosis, or explain the danger of compliance during this period vegetarian food. With pronounced toxicosis, which prevents the expectant mother from eating normally and can cause significant damage to the unborn baby, a pregnant woman will be placed in a hospital, where intravenous injections will be prescribed drugs.
If the deviations in the amount of uric acid are caused by improper diet, toxicosis or adherence to a vegetarian diet, the doctor will prescribe the woman a special diet, including foods rich in protein, drugs that relieve the severity of toxicosis, or explain the danger of compliance during this period vegetarian food. With pronounced toxicosis, which prevents the expectant mother from eating normally and can cause significant damage to the unborn baby, a pregnant woman will be placed in a hospital, where intravenous injections will be prescribed drugs.
Some of the most common abnormalities that cause low uric acid levels include:
Liver disease
The most common reason for a decrease in uric acid is associated with its inadequate work in processing proteins and leading to a metabolic disorder.
The decrease in urea here may be due to:
- cirrhosis;
- hepatitis;
- the development of malignant neoplasms.
The development of these pathologies leads to a decrease in protein metabolism, due to which urea is formed in a small quantity and is accompanied by severe pain in the right hypochondrium, yellowing of the skin and dyspeptic phenomena.
In addition to pathologies, medications can also worsen liver function and, as a result, reduce urea, including:
- all drugs with acetylsalicylic acid;
- cephalosporin antibiotics;
- drugs containing tetracycline;
- cytostatics.
In addition to hepatotoxicity, a number of these drugs are dangerous for a young mother and her unborn baby and can negatively affect the development of the fetus.
Disruption of the pituitary and hypothalamus
Acromegaly caused by hypothalamic disease leads to an increase in growth hormone (growth hormone) suppressing the production of urea and manifested by the growth of the facial part of the cranial bones, hands and stop. Most often, this disease is triggered by a pituitary tumor, in which a pregnant woman needs a consultation with a neurosurgeon and endocrinologist. With the growth of a neoplasm in the second trimester of pregnancy, the neoplasm is removed through the nasal passage, which is considered the most gentle method.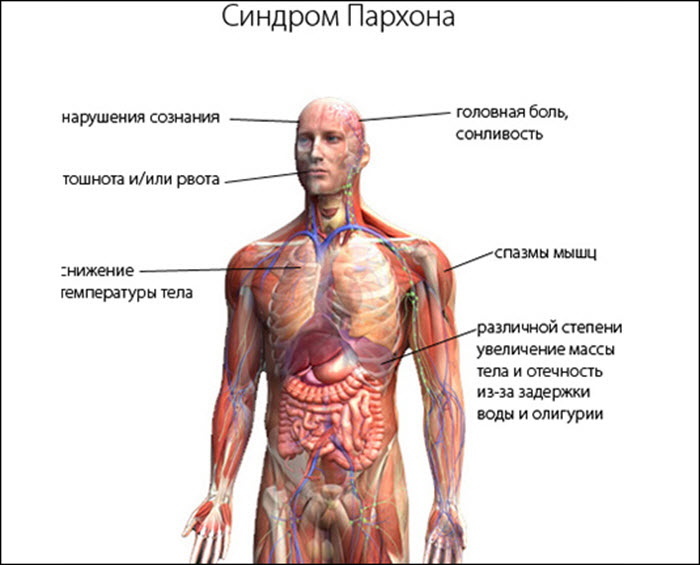
The second reason provoking a decrease in uric acid is associated with Parkhon's syndrome, in which there is an increased release of vasopressin, which is considered an antidiuretic hormone. With this pathology, the level of sodium and urea falls, and the disease itself is accompanied by a sharp weight loss, convulsions and vomiting. Treatment here is carried out with vasopressin antagonists, as well as a significant reduction in the amount of fluid consumed.
Disruption of the excretory organs
With kidney diseases, including nephrotic syndrome, there is a decrease in urea in the blood of a pregnant woman, which occurs against the background of edema, loss of proteins and an increase in lipid levels. Enhanced excretion of protein contributes to a significant decrease in the level of uric acid, as well as other abnormalities in the biochemical analysis of blood.
Gastrointestinal pathologies
Irritable bowel syndrome is accompanied by a deterioration in the absorption of proteins and other nutrients, along with anemia, vitamin deficiency, diarrhea and a constant feeling of fatigue. A decrease in carbamide is also accompanied by chronic pancreatitis, since the inflammatory process in the pancreas negatively affects the metabolism of proteins. In this case, a violation of the biochemical parameters of the blood occurs against the background of pain in the middle of the stomach and nausea.
Dieting
Urea in the blood is lowered during pregnancy in most cases due to malnutrition, in which there are no foods saturated with protein, which is necessary for the full development of the child.
A vegetarian diet is considered one of the common factors that lead to a decrease in the amount of carbamide in the blood. Since protein is found most of all in meat products that have excluded animal food, the expectant mother deliberately provokes a decrease in urea that is dangerous for the baby.
If a woman is considered an ardent opponent of the consumption of meat products, she needs to include in the diet a substitute food, including:
- milk and dairy products;
- legumes and soybeans;
- walnuts;
- eggs;
- buckwheat;
- mushrooms.
 Protein food cannot be completely excluded from the diet during pregnancy, since protein is vital for the health of the baby, and its absence can lead to various developmental pathologies.
Protein food cannot be completely excluded from the diet during pregnancy, since protein is vital for the health of the baby, and its absence can lead to various developmental pathologies.
Deviations in urea levels caused by the use of any medications will require careful adjustment of the dosage or replacement of the drug with an analogue, not accompanied by such side effects effects.
Decreased symptoms
Blood urea is lowered during pregnancy in only 20% of all known cases and can negatively affect both the general condition of a pregnant woman, and also have a significant impact on condition of the fetus.
So, faced with a decrease in uric acid, an expectant mother can find out:
- severe swelling of the legs;
- small weight gain;
- very high hemoglobin levels in the second and third trimester;
- increase in physical indicators of blood pressure.
At the same time, on the control ultrasound, clear signs of intrauterine growth retardation are visible, which will force doctor to be wary and prescribe additional tests, according to the results of which the appropriate treatment.
When taking medications, it is also important to remember that the high level of urea, which is often found with impaired renal function, also negatively affects the condition of the expectant mother. Such a uremic syndrome can be a consequence of both an infectious disease and develop as a result of vaccination, therefore, a young mother should be very careful about her state of health and protect herself from viruses and infections. Vaccination should also be postponed until the end of labor.
A sudden increase in urea can also be associated with burns, leukemia, bleeding or intestinal obstruction, and since urea itself is a fairly toxic substance, it can significantly affect the health of a woman and her baby.
Treatment
Treatment with a low level of urea should be prescribed by a doctor, taking into account the condition of the expectant mother and the presence of concomitant diseases. If the low level of carbamide is of a physiological nature and is caused by a malnutrition, the expectant mother is prescribed a special diet.
If, as a result of the diagnosis, any concomitant disease was detected, in the second trimester of pregnancy, corrective medication is carried out, and in some cases, surgical treatment.
Potential therapy options also include:
- treatment and restoration of the liver;
- normalization of the digestive tract;
- regulation of metabolic processes in the body;
- detoxification activities.
During treatment, a pregnant woman should be under the strict supervision of a doctor, and a specialist will evaluate the effectiveness of therapy based on the results of biochemical blood tests.
A decrease in the amount of urea in the blood during pregnancy is completely normal and is caused by an increase in protein metabolism and the amount of fluid circulating in the body. The danger can only be caused by a very low level of urea in case of impaired kidney function, indicating a delay in the body of decay products and arising from pathologies of the liver, gastrointestinal tract and pituitary gland.
Blood Urea Video
Blood urea: