Content
- Views
- Diffuse
- Dystrophic
- Focal cicatricial
- Metabolic
- Cicatricial cardiosclerosis
- Reasons for the appearance
- Symptoms
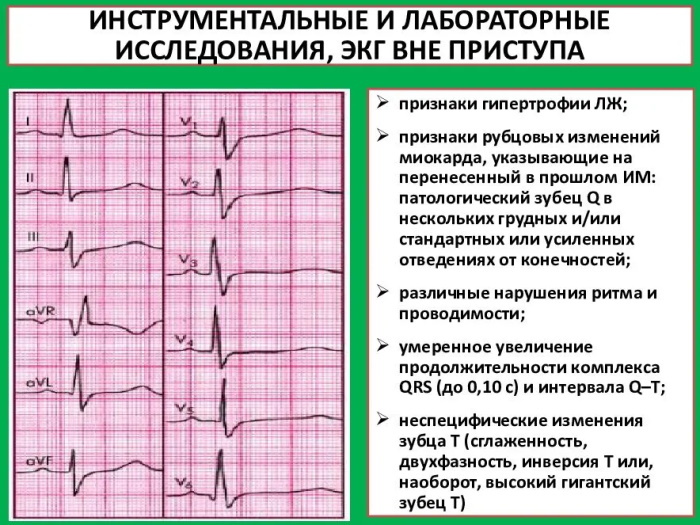
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Drug therapy
- Surgery
- Stem cells
- Diet and physical activity
- Possible complications and prevention
- Video about cicatricial changes in the myocardium
Cicatricial changes in the myocardium - mark on the heart or cardiosclerosis resulting from any disease. Well visible on the ECG, such changes are quite dangerous and can become a trigger for slowing down the cellular myocardial metabolism, which can provoke a heart attack or coronary heart disease, which can lead to fatal the outcome. In structure, the scar itself is the dead cells of the heart muscle, replaced by fibrous (connective) tissue much stiffer than muscle and therefore unable to provide a full reduction of the myocardium, ensuring gas exchange and blood flow.
Pathology can occur at any age, becoming a consequence of the development of atherosclerosis caused by blockage of blood vessels along the reason for the appearance of cholesterol plaques that appear in people with metabolic disorders or leading the wrong image life.
Views
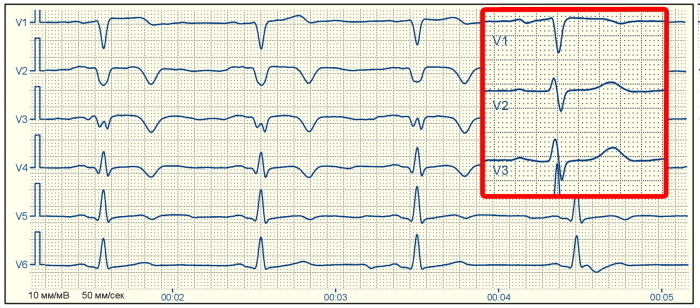
Cicatricial changes on the ECG can be detected:
| In the left ventricle | In this case, the ECG will noticeably:
In this case, the connecting fibers cannot generate signals. |
| In the bottom wall | In this case, the monitor will show the pathological Q, marked in the second standard lead. |
| In the partition area | The diagnostic Q value will be placed in leads V1, V2, and the R waves in V1,2,3 are low or undetectable. |
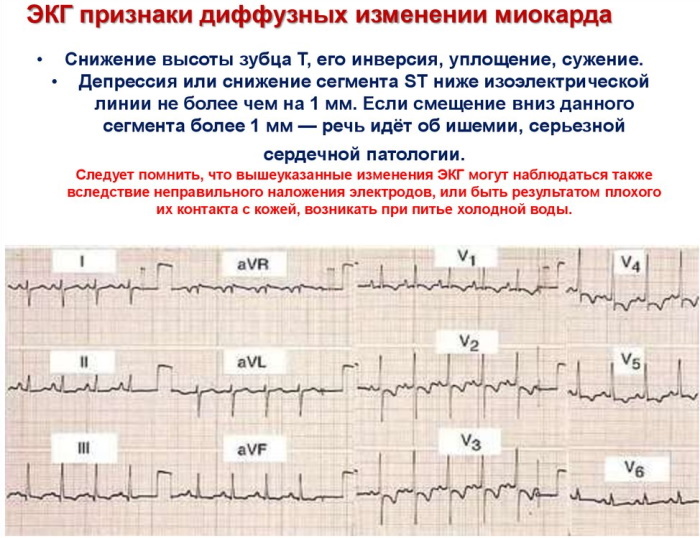 Moderate changes in the myocardium can occur due to common physiological reasons, and even appear in outwardly perfect healthy person or child due to strong shocks suffered the day before research. In this case, the changes are not dangerous and go away on their own after a good rest and sleep. The danger is caused only by cicatricial changes, accompanied by poor health associated with inconsistency of the outflow of the myocardium to physiological reasons, disrupting blood circulation and leading to blockage arteries.
Moderate changes in the myocardium can occur due to common physiological reasons, and even appear in outwardly perfect healthy person or child due to strong shocks suffered the day before research. In this case, the changes are not dangerous and go away on their own after a good rest and sleep. The danger is caused only by cicatricial changes, accompanied by poor health associated with inconsistency of the outflow of the myocardium to physiological reasons, disrupting blood circulation and leading to blockage arteries.
Depending on the course and development of pathology that interferes with normal cardiac activity, they differ:
Diffuse
Most often arising due to the development of the inflammatory process, they affect the entire muscle at the same time, leading to disruption of the work of all its cells and necessary for adequate oxygen supply, metabolic processes.
The trigger for the development of diffuse change can be:
- alcohol abuse;
- increased physical activity;
- chronic stress;
- frequent hypothermia;
- chronic infections.
With timely detection of the disease, in most cases it is possible to normalize cardiac activity, preventing the development of ischemia or death.
Dystrophic
They develop in the left ventricle, and are associated with nutritional deficiencies due to:
- disorders of the liver and kidneys;
- iron deficiency anemia;
- nervous overstrain;
- diabetes mellitus or disruptions in the endocrine system;
- improper nutrition, leading to vitamin deficiency;
- dehydration of the body, occurring against the background of poisoning;
- chronic diseases or infectious pathologies;
- alcohol or drug intoxication.
Such disorders can occur in perfectly healthy people, as well as children, students and schoolchildren.
Focal cicatricial
Cicatricial changes of a local nature can be found in persons who have previously had a heart attack, while areas of cardiosclerosis on the film will be clearly visible.
Their main cause is considered to be a high level of cholesterol in the blood, leading to the development of atherosclerosis and arising in persons suffering from:
- diabetes mellitus;
- obesity;
- frequent physical or emotional stress;
- increased blood pressure;
- alcohol or nicotine addiction.
Quite insignificant changes in the myocardium that appear when there is an imbalance in the body of potassium and sodium ions, which are necessary for relaxation and contraction of the heart muscle.
Such a pathology arises when:
- angina pectoris;
- arterial hypertension;
- heart defects;
- pancreatitis;
- inflammatory processes in the vascular wall;
- infectious diseases.
Cicatricial cardiosclerosis
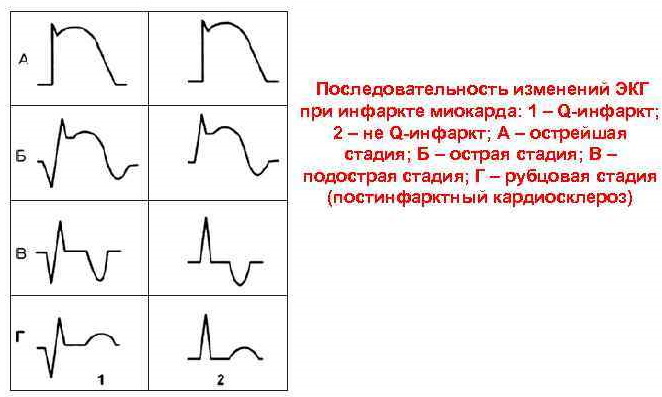
The most dangerous is the cicatricial cardiosclerosis that has arisen as a result of a previous heart attack, which is subdivided into: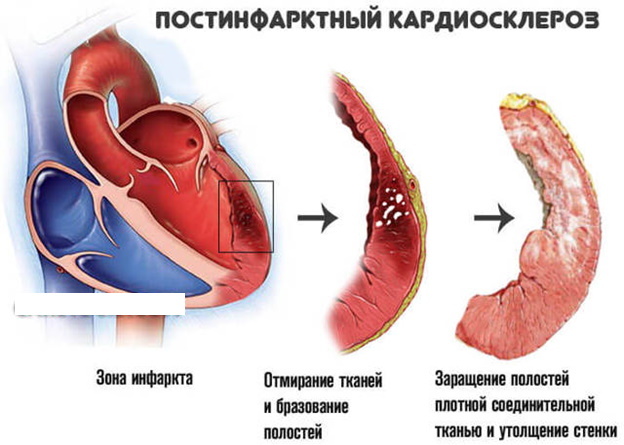
| Focal cardiosclerosis | Most often it occurs as a consequence of myocardial infarction and is characterized by the appearance of scars of various sizes over the entire area of the heart muscle. |
| Diffuse cardiosclerosis | It accompanies chronic ischemia and is associated with an even distribution of connective tissue throughout the heart. |
| Postinfarction cardiosclerosis | It occurs after a heart attack and is manifested by the formation of foci of connective tissue, provoking a violation of cellular metabolism and impaired blood circulation. |
| Atherosclerotic cardiosclerosis | A slow, chronic process that accompanies ischemia and is associated with the development of atherosclerosis, gradually blocking the lumen between the vascular walls. |
| Postmyocarditis cardiosclerosis | It is typical for young patients and is associated with previous infectious pathologies. |
| Congenital cardiosclerosis | A rare form of the disease caused by genetic disorders in the structure of the cardiovascular system. |
Reasons for the appearance
Cicatricial changes on the ECG, characteristic of cardiosclerosis, can appear in people of different ages, but in most cases are considered a sign previously transferred cardiovascular pathologies, such as:
- Rheumatism. Despite the fact that earlier the term was used only to diagnose pathologies of the musculoskeletal system, the most dangerous form is considered to be cardiac rheumatism, in which the localization of inflammation is located in the very myocardium.
- Thrombosis and embolism of blood vessels, provoking blockage and overlap of blood vessels, leading to impaired blood circulation.
- Myocarditis. Pathology of an infectious nature, often affecting people who have had mumps, measles or chickenpox.
- Coronary artery disease (CHD). It is accompanied by impaired cellular metabolism, oxygen metabolism and blood supply caused by numerous concomitant diseases. The large number of scars appearing on the heart leads to poor circulation and possible death.
-
Heart attack. One of the main causes of a scar on the heart is caused by the death of one of the areas of connective tissue. In some cases, a heart attack ends in death, and with survival, there is a lifelong danger of the development of repeated cardiac pathology.
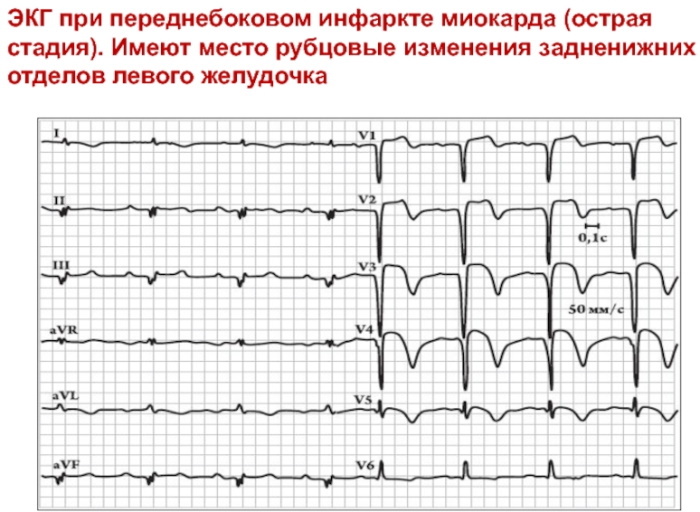
Myocardial dystrophy is distinguished into a special group, as a cause provoking scarring of the myocardium, accompanied by pathological changes in metabolic processes leading to dystrophy and dysfunction of the heart muscle.
Among the causes of the disease:
- lack of vitamins in the body;
- deficiency of magnesium, calcium and potassium;
- excess weight;
- frequent and high-intensity physical activity.
The risk of scarring also increases significantly for genetic reasons, so doctors strongly recommend that all relatives of a patient with a scar on the heart visit a cardiologist at least once a year.
The most dangerous cause of a scar on the heart, which can lead to the development of coronary artery disease and fatal the outcome is postinfarction cardiosclerosis, accompanied by severe coarsening of the connective tissue myocardium.
Such a pathology can occur in patients of any age and is accompanied by:
- rupture of an atherosclerotic plaque, accompanied by a sharp jump in blood pressure, tachycardia and acceleration of venous blood flow;
- blockage of blood vessels associated with blood thickening;
- spasm of the coronary artery.
Symptoms
Cicatricial changes on the ECG are the most common and main cause of coronary heart disease. Due to vasoconstriction caused by the formation of cholesterol plaques, blood flow is disturbed, accompanied by the appearance of severe pain and discomfort in the chest.
Scarring caused by inflammation or myocardial infarction is manifested by:
- unpleasant pressing pain in the chest;
- heart palpitations;
- hypertension with an excess of the norm of blood pressure indicators by 20 mm Hg. Art. and higher;
- shortness of breath, which occurs, including at rest or during sleep;
- hypoxia with pronounced blue discoloration of skin, lips, limbs;
- malfunctioning of the heart;
- fatigue, fading of vitality;
- exhaustion, sharp weight loss (up to the development of anorexia);
- swelling of the limbs and internal organs;
- an increase in the size of the liver.
The appearance of any of these symptoms requires an immediate appeal to a cardiologist, due to fear of the rapid development of coronary artery disease, which can lead to death.
The scar that has arisen after a heart attack gradually thinns the walls of blood vessels, preventing them from fully pumping blood. The expanding connective tissue leads to an increase in the size of the myocardium, but does not improve its work. A thinned heart is not able to completely expel the blood entering the heart, as a result of which some of the blood goes to the lungs. If the situation is not corrected, a recurrence of the heart attack follows.
Diagnostics
Cicatricial changes that appear on the ECG are considered a good reason for a thorough examination. It is recommended to visit a cardiologist not only after a cardiogram, but also if the patient has been disturbed for a long time by strong and sharp pains in the left sternum.
Having studied the patient's condition, the doctor will have to collect information about the extent of the foci of cardiosclerosis, about the state of blood vessels, about the presence of blood clots and plaques in the main arteries, determined after conducting:
- ECG in dynamics;

- Echocardiography;
- MRI of the heart;
- general blood test and coagulogram studies;
- studies of the main vessels.
Of particular importance is the patient's own story about the family history, which may contain information about the presence of coronary artery disease.
Treatment
Cicatricial changes on the ECG allow you to notice a dangerous condition and prevent a second heart attack or the development of coronary artery disease. Treatment of pathology is carried out in a comprehensive manner.
Drug therapy
Based on the selection and prescription of drugs to normalize cardiac activity (Allapinin, Amiodarone, Asparkam), restore blood circulation (Nicotinic acid) and reduce the amount of cholesterol in the blood (Statins). The dosage and course of treatment is selected individually by the doctor for each specific case separately, but it is especially important to start treatment as early as possible in order to prevent scarring that can begin in any moment.
Surgery
In severe cases, it is necessary to apply surgical treatment, which consists in the installation of pacemakers.
Depending on the situation, the following can be assigned:
- Living heart transplant. The most expensive and time-consuming operation, used for patients under 65 years of age, and consists in a donor heart transplant.
- Bypass surgery. It is indicated for atherosclerosis and requires the installation of shunts to expand the cardiac arteries.
- Removal of an aneurysm, performed for excision of the damaged area in the left ventricle.
After surgical treatment, a rather impressive scar remains, but unlike a scar, it does not pose a danger to the further life of a person.
Stem cells
An innovative method for the treatment of healed tissue, which is the use of cardimioblasts (stem cells) designed to replace the gradually growing area of connective tissue, with a more elastic and lightweight muscle.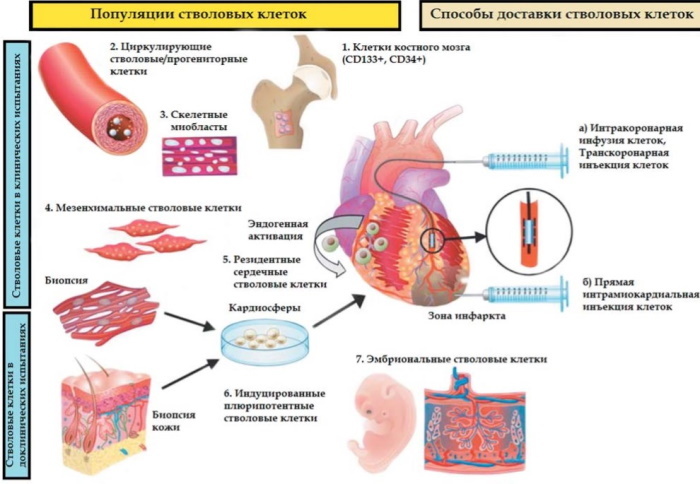
Stem cell injections prevent dangerous post-infarction scarring of tissue, as well as:
- restores vascular tissue in a natural way;
- cleans the ducts from deposits and expands their lumen;
- increases vascular elasticity;
- improves blood flow to all organs and tissues.
In addition to preventing scarring, stem cells also develop a network of collateral vessels, increase filling the heart with blood and eliminate the signs of a previous heart attack, while preventing it from recurring appearance.
Diet and physical activity
Since the main cause of ischemia and heart attack is considered to be blockage of blood vessels due to the formed cholesterol plaques, of no small importance is the normalization of the patient's nutrition, which requires completely excluding the ingestion of a rich cholesterol food.
The daily diet of a patient with such a pathology should consist of:
- lean types of meat, poultry and fish;
- a large number of various vegetables and fruits;
- fermented milk products;
- cereals and legumes.
Completely excluded from the diet:
- dishes prepared by frying with an abundance of fats;
- industrial confectionery;
- butter;
- smoked products and sausages;
- carbonated drinks.
You should also stop drinking alcoholic beverages and smoking.
Moderate physical activity is also necessary for such patients, which helps, if necessary, to lose weight and improve blood circulation. Swimming, dancing, yoga, and cardiovascular equipment can tone your muscles and heart rate and improve your well-being. Undesirable for such people are considered increased strength training associated with lifting a lot of weight and can lead to a worsening of the condition.
In addition to sports, patients with a tendency to scarring need long walks in the fresh air, which improve the oxygen metabolism of the body.
Possible complications and prevention
The danger of cicatricial changes in the myocardium lies in their rapid progression, leading to the gradual replacement of elastic muscle tissue denser and tighter scar tissue, which is the main reason for the inability of the heart muscle to perform its main functions. Expanding in size, the heart ceases to fully perform pumping functions, leading first to a violation, and then to a complete cessation of blood circulation. The lack of full gas exchange leads to oxygen starvation, forming heart failure, which, if untreated, leads to death.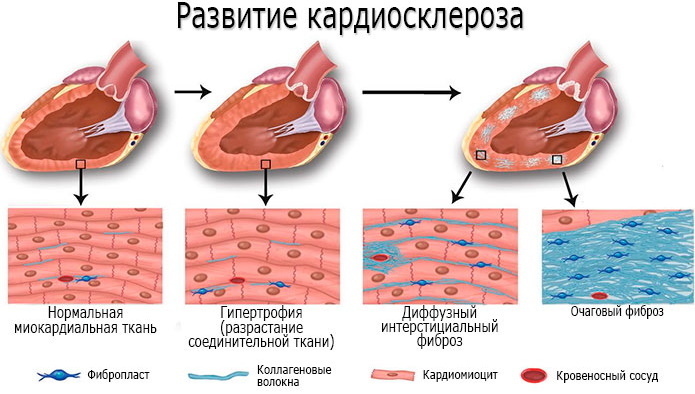
The main prevention of scarring is taking care of the state of the heart system, which is impossible without proper nutrition and optimal physical activity. The limitation of toxic effects and timely treatment of infectious pathologies are also of particular importance.
In addition, you must also monitor the state of your blood pressure, vascular patency, and prevent excess weight and high cholesterol levels.
Cicatricial changes in the myocardium that appear on the ECG are one of the common pathologies that indicate previously transferred dangerous diseases and leading to impaired blood circulation. Having changed its structure due to myocardial scarring over time, it becomes unable to fully fulfill its functions, leading to disruption of cellular metabolism and the release of blood into the lungs, causing ischemia and heart attack.
Occurring in people at any age and caused by cardiovascular or infectious and inflammatory pathologies overgrowth fibro-connective tissue, in the absence of timely treatment, provokes the development of dangerous pathologies leading to sudden death of a person.
Video about cicatricial changes in the myocardium
ECG signs of myocardial infarction:



