Content
- Types of disease
- Acute herpetic
- Aphthous
- Catarrhal
- Ulcerative
- Bacterial
- Candidal
- Traumatic
- Symptoms and Signs
- Acute herpetic
- Aphthous
- Ulcerative
- Candidal
- Causes
- Diagnostics
- Treatment methods
- Medications
- Folk remedies
- Possible consequences and complications
- Video about stomatitis
Stomatitis - inflammation of the oral mucosaaffecting the soft tissues of the lips, cheeks, gums. The cause of the development of the disease can be local or systemic factors. Pathology is manifested by the appearance of aft, spots, papules or plaques, as well as accompanying symptoms - fever, general malaise and swollen lymph nodes. The nature of the stomatitis treatment will depend on its type and the severity of the course.
Types of disease
Depending on the reasons that caused the inflammatory process, stomatitis is distinguished from an infectious and non-infectious nature.
Acute herpetic
An infectious disease caused by the herpes simplex virus. Pathology is manifested by inflammation of the oral mucosa with the appearance of rashes in the form of bubbles, as well as an increase in temperature. Infection occurs by airborne droplets or contact-household. The incubation period lasts from 2 to 17 days. According to statistics, pathology occurs in children aged 1-4 years, less often in adults.
Aphthous
An inflammatory disease of the oral mucosa, characterized by the formation of ulcers - oval or round, with clear boundaries in the form of a narrow red border. Pathology proceeds with frequent exacerbations and periodic remissions.
Catarrhal
Damage to the oral mucosa, manifested by swelling, soreness, redness of areas of soft tissues, which are covered with a white or yellow coating. Pathology is accompanied by hypersalivation and the appearance of an unpleasant odor from the oral cavity. The most common cause of the disease is non-compliance with the rules of oral hygiene.
Ulcerative
It occurs as a consequence of the advanced stage of catarrhal stomatitis. It often develops in people suffering from gastric ulcer or enteritis.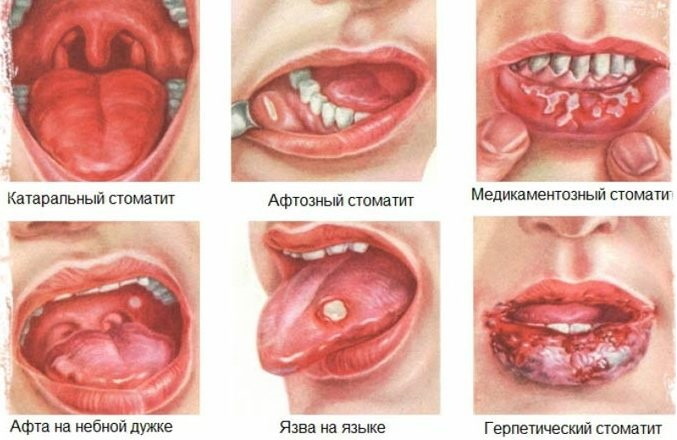 With the ulcerative form of pathology, the deeper layers of the oral mucosa are affected.
With the ulcerative form of pathology, the deeper layers of the oral mucosa are affected.
Bacterial
One of the forms of manifestation of stomatitis, provoked by streptococci and staphylococci. In the affected area, single ulcers appear, covered with a white film. The affected mucous membrane swells, acquires a bright red hue.
Candidal
The most common type of stomatitis among children under 3 years of age. The pathology is provoked by a fungus of the genus Candida. An increase in the activity of the fungus is associated with a decrease in the Ph of the oral cavity, as well as a weakening of the body's defenses. Candidal lesions in the mouth of a child are referred to as superficial diseases. There are 3 forms of pathology: mild, moderate and severe.
Traumatic
Stomatitis occurs after mechanical injury to the gums, tongue, lips or cheeks, resulting from the consumption of solid food or hot drinks. Most often, traumatic stomatitis is characteristic of preschool children and does not require treatment.
Symptoms and Signs
Stomatitis can manifest itself in different ways depending on the species.
Acute herpetic
Depending on the severity, there are 3 forms of the disease, each of which is manifested by signs: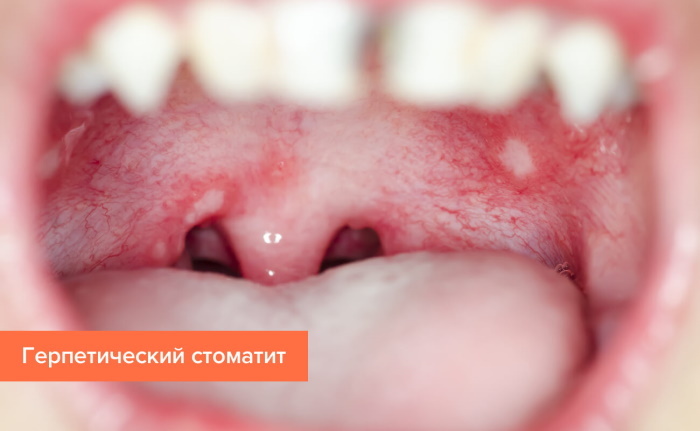
| Light form |
|
| Medium |
|
| Heavy |
|
Aphthous
There are 3 stages of pathology, each of which is characterized by symptoms: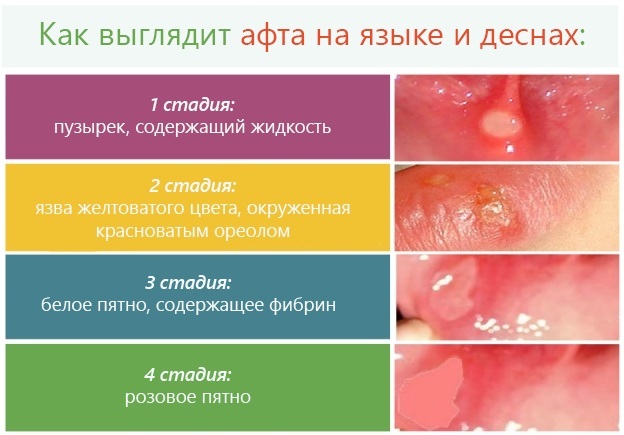
| Easy |
|
| Average |
|
| Heavy |
|
Ulcerative
Of the symptoms of the disease are observed:
- temperature rise to 37.5;
- headache;
- weakness;
- swollen lymph nodes;
- severe pain syndrome.
Candidal
Each of the 3 forms of stomatitis is manifested by a different intensity of symptoms: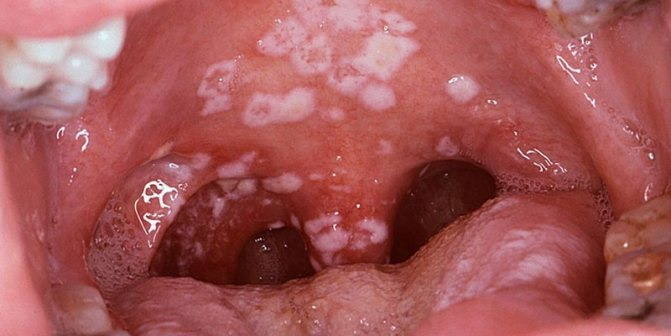
| Light form |
|
| Medium form |
|
| Severe form |
|
Causes
Stomatitis on the gums (treatment must be started immediately) occurs due to many reasons, which can be conditionally divided into 2 groups:
- external;
- internal.
External causes of stomatitis include:
- inadequate oral care;
- mechanical injury to the mucous membrane;
- chemical burn;
- an allergic reaction in response to medication.
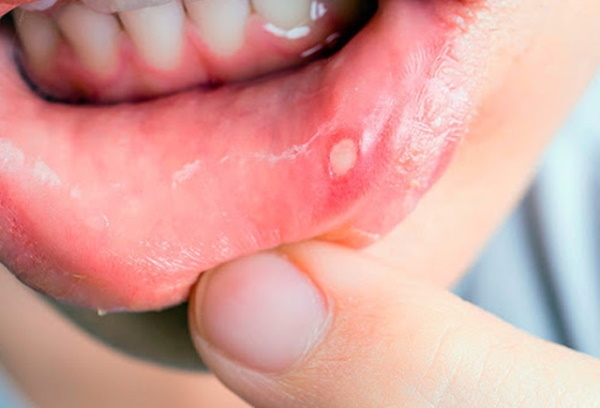
Stomatitis on the gum
Internal causes of the disease include:
- damage by viruses, bacteria or fungi;
- the presence of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- weakening of the immune system due to stress;
- deficiency of vitamins and minerals;
- violation of metabolic processes.
Diagnostics
Stomatitis on the gums (treatment is carried out with drugs of local and systemic action) is easily diagnosed at a doctor's appointment. To diagnose aphthous, catarrhal or traumatic stomatitis, a visual examination of the dentist is sufficient.
In the case when a viral or bacterial infection has become the cause of the disease and the patient's condition is accompanied by an increase in temperature and general malaise, laboratory diagnostics are prescribed:
- Clinical blood test. It is a detailed study of the qualitative and quantitative composition of blood, which allows to characterize such indicators: erythrocytes, leukocytes, platelets, as well as ESR and leukocyte formula. The delivery of the analysis is shown in cases where stomatitis is accompanied by an increase in body temperature, a state of general intoxication. For research, venous or capillary blood is used. Collection of biological material is carried out on an empty stomach. Research cost - from 600 rubles.
-
Microscopic examination of a smear from the oral mucosa is prescribed for candidal stomatitis. The research material collected on an empty stomach from the affected areas using a spatula is spread over the glass and dried in a natural way. The smears are stained using various methods: according to Gram, Ziehl-Nielsen, Romanovsky-Giemsa, as well as using a mono dye. Depending on the method chosen, the mushrooms are colored in different shades, which indicate the development of candidal stomatitis. Research cost - from 800 rubles.

- Microbiological smear examination from the oral mucosa is also required for candidal stomatitis. A method for diagnosing infections of the oral cavity, the essence of which is the quantitative inoculation of pathological material on nutrient media and tracking their incubation under aerobic and anaerobic conditions. The biomaterial is taken shortly after waking up before the start of hygiene procedures and food intake using a cotton swab. Under laboratory conditions, the swab is washed off and the biomaterial is inoculated onto Sabouraud's medium. Research cost - from 1100 rubles.
- PCR diagnostics indicated for symptoms of acute herpetic stomatitis. The polymer chain reaction is the most sensitive and fastest way to diagnose herpetic stomatitis. PCR is a process that consists of repeating cycles of copying viral DNA molecules in order to obtain multiple copies. Scrap taken from the mucous membrane with the affected areas is used as a biomaterial. Analysis cost - from 1800 rubles.
Treatment methods
Stomatitis on the gums (treatment is carried out under the supervision of a dentist, pediatrician or therapist) is eliminated with the help of various drugs, the use of which will depend on the type of pathology and age the patient. In infectious and inflammatory processes of the mucous membrane, therapy consists of drugs with anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, analgesic effects. With aphthous and catarrhal stomatitis, it is enough to use local preparations in the form of rinsing or applications.
Medications
The use of medications in the treatment of stomatitis allows:
- eliminate the causes of the disease;
- prevent further development of the pathological process;
- eliminate the focus of inflammation;
- increase overall resistance;
- relieve painful symptoms.
For the treatment of children and adults, depending on the type of stomatitis, the following groups of drugs are used:
- antiseptics;
- antiviral;
- immunomodulatory;
- antihistamines;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
Antiseptics can suppress or prevent the growth of bacteria in the mouth by disinfecting the mucous membrane of the affected area.
For the treatment of stomatitis in children and adults, the following are used:
-
Chlorhexidine - solution for topical application, exhibiting bactericidal and fungicidal action. The drug remains active on the surface of the mucous membrane, showing activity against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Treatment of the oral cavity in children under 3 years of age is carried out with a cotton swab 2-3 times a day. Older children rinse the mouth on their own up to 3-4 times a day.

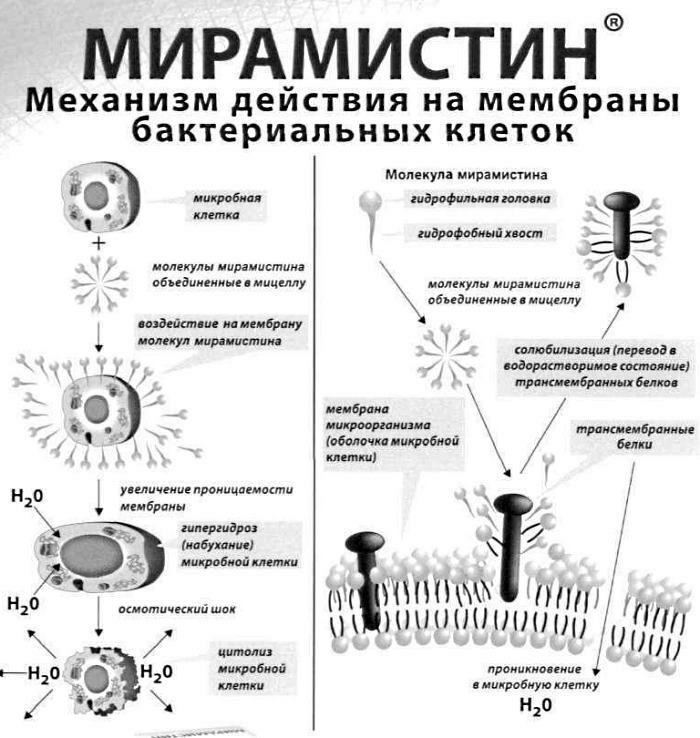
- Miramistin - a solution for topical application with a wide spectrum of antimicrobial action. The drug is used as a mouthwash. A single dose is 10-15 ml. Frequency rate - 3-4 times a day.
- Hexoral - preparation in the form of an aerosol for topical use. It has antimicrobial, antiviral and anesthetic effects. The product is suitable for children from 3 years of age. For the treatment of stomatitis, the drug is sprayed onto the affected area for 1-2 seconds, 2 times a day.
Antiviral agents are used in the treatment of herpetic stomatitis. For the treatment of adult patients use:
- Amiksin - antiviral drug in pill form. In the treatment of herpes infection on the first day, the dose of the drug is 125 mg. After 48 hours, the patient takes another 125 mg of amixin. The course of treatment requires 1.25-2.5 g of the drug (10-20 tablets).
- Valacyclovir - an antiviral drug in the form of pills, used in the treatment of herpes infection. A single dose for adults is 0.25-2 g. The frequency and duration of treatment depends on the severity of the disease.
For the treatment of children are used:
- Acyclovir - antiviral drug in the form of tablets for children from 3 years old. The dosage regimen is 20 mg of the drug per 1 kg of the child's weight, but not more than 800 mg per day. The resulting dosage is divided into 4 doses. The duration of treatment is 5 days.
- Viferon - a preparation in the form of rectal suppositories, which is suitable for the treatment of children from birth. The dosage is calculated individually, depending on the age of the child.
Immunomodulators are a group of drugs that eliminate the imbalance of various parts of the immune system. The funds are used for recurrent and herpetic stomatitis.
For the treatment of adult patients use:
-
Tiloram - antiviral immunostimulating agent in the form of tablets. The drug helps to stimulate interferons in the body. The tablets are taken orally after meals. In the first 2 days, the dosage is 124 mg, then after 48 hours, another 125 mg. The course of treatment will require 1.25-2.5 g.
- Immunal - a herbal remedy containing the juice of the herb echinacea. The drug has immunostimulating and anti-inflammatory effects. The agent is taken orally after meals. The dosage regimen is determined individually, depending on the dosage form.
In pediatric therapy, the following are used:
- Polyoxidonium - an immunomodulatory agent in the form of tablets for children from 3 years of age. The drug is taken 20-30 minutes before meals, 2 times a day. Children aged 3-10 years are prescribed ½ tablet. Children over 10 years old - 1 tablet. The duration of treatment is 7 days.
NSAIDs help relieve pain and fever. Children are shown the use of paracetamol and ibuprofen. Any drug from the NVPS group is suitable for adults: Nimesil, Ketoprofen, Meloxicam.
There are also topical preparations in the form of ointments and gels that are suitable for both children and adults:
- Holisal - a dental gel that has a local anesthetic and anti-inflammatory effect. The drug is used 2-3 times a day before or after meals. A strip 1 cm long for adults and 0.5 cm for children is applied to the affected area and rubbed lightly.
- Kamistad - a combined preparation that relieves pain and inflammation in case of damage to the oral mucosa, approved for use in children over 12 years old. A strip of the drug 0.5 cm long is applied to the inflamed area 3 times a day, rubbing lightly.
Folk remedies
Stomatitis on the gums (treatment takes 3 to 10 days, depending on the severity of the case) is eliminated not only with the help of drugs, but also with traditional medicine.
For quick healing and disinfection of the affected mucous membrane, homemade solutions and decoctions are used:
-
Chamomile infusion. The plant has antiseptic and wound healing properties. To prepare the infusion, you need 1 tsp. l. dry inflorescences pour 1 cup boiling water and let the mixture brew for 30 minutes. The infusion is used as a mouthwash 3-4 times a day after meals.

- Infusion of yarrow. 1 hour l. the dried plant should be poured with a glass of boiling water and allowed to brew for a quarter of an hour. The prepared infusion is used for rinsing the mouth 3-4 times a day.
- Hydrogen peroxide solution. Dissolve 1 tsp in a glass of warm water. l. hydrogen peroxide and rinse the mouth 3-5 times a day.
- A solution of soda and salt. Dissolve 1 tsp in a glass of warm water. l. salt and soda. The prepared solution is rinsed in the mouth every 2-3 hours during the day.
Possible consequences and complications
In the absence of timely treatment, stomatitis can turn into a chronic recurrent form. In addition, there is a risk of transition of the catarrhal form of stomatitis to the ulcerative necrotic form with damage to the deep layers of tissues and even bone.
Other complications of stomatitis include:
- bleeding gums;
- the development of secondary infections - damage to the tonsils, chronic laryngitis;
- in severe cases, tooth loss.
Stomatitis unites a group of diseases that have different origins and symptoms. Ulcers and aphthae occur on the oral mucosa - gums, cheeks, lips. The process of damage to soft tissues is accompanied by severe pain and inflammation. So that stomatitis does not become chronic and does not cause the development of secondary infections, it is important to visit the dentist on time and determine the tactics of treatment.
Video about stomatitis
Malysheva about stomatitis: