Content
- The reasons for the development of toxoplasmosis in women
- Sources of infection
- Symptoms of toxoplasmosis
- Forms of toxoplasmosis and features of their course
- Latent form
- Generalized form
- Chronic form
- Cerebral toxoplasmosis
- Ocular toxoplasmosis
- In what cases is toxoplasmosis dangerous for women
- How it proceeds, what can be the consequences during pregnancy and hepatitis B
- Diagnosis of toxoplasmosis
- Taking anamnesis
- External signs
- Laboratory research
- Instrumental diagnostics
- Treatment of toxoplasmosis in women with drugs
- Treatment of the acute form
- Treatment of acute toxoplasmosis in pregnant women
- Treatment of the chronic form
- Specific immunotherapy with toxoplasmin
- Ultraviolet irradiation
- Complications and prognosis
- Video about toxoplasmosis
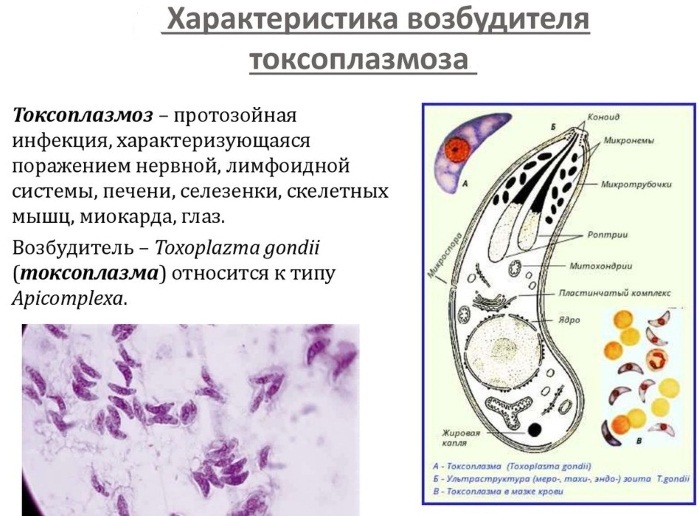
Toxoplasmosis is an infectious diseasecaused by parasites is often asymptomatic. However, it can have serious consequences, especially in pregnant women.
The reasons for the development of toxoplasmosis in women
Toxoplasmosis is an animal disease (zoonosis). For the pathogen, man is just an intermediate host. The parasite multiplies in the intestines of the cat, produces egg-like Toxoplasma oocysts (eggs), which are excreted in large quantities in the feces. After 1-4 days of puberty in the air, eggs become infectious and remain so for several months.
Infection usually occurs as a result of eating undercooked contaminated meat, contact with infected cat feces or mother-to-child transmission during pregnancy.
When a person or a cat has strong immunity, the infection will not cause the development of the disease. The defenses are able to suppress pathogens and prevent them from reproducing. But Toxoplasma in the body can be activated with a decrease in immunity.
Sources of infection
Mammals, birds and humans are infected with the causative agent of toxoplasmosis through contaminated food: the "eggs" of the parasite are colonized in raw meat products, which are quite slimy. This is mainly pork, but sometimes poultry. Even foods that grow in or near the ground can be contaminated with toxoplasmosis eggs (such as cat feces) and become infected.
Toxoplasmosis (symptoms in women are similar to those in men) is carried by pets: cats, dogs. A person may face anthroponosis when cutting meat products. Microtrauma and cuts are the gateway for pathogens to enter the body.
Dangerous parasites can enter the human body not only from a sick cat. In medical practice, the route of infection is most often recorded when eating improperly processed meat. Lovers of raw steak with blood are at risk.
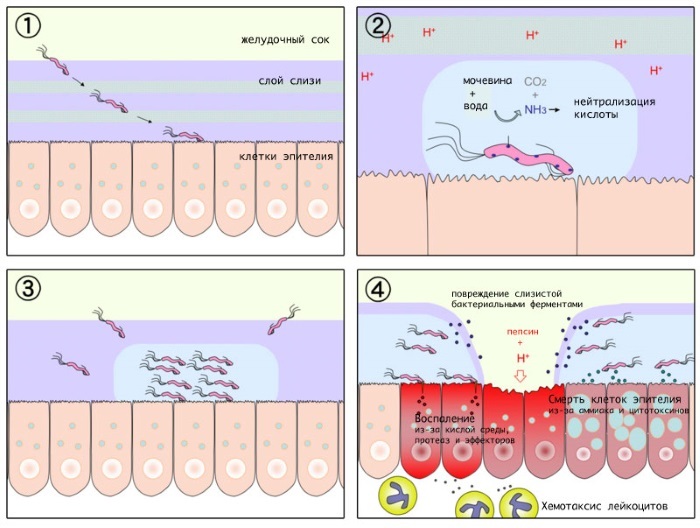
Infection is possible during organ transplantation, blood transfusion. There is also information about the transmission of infection through the bites of blood-sucking insects.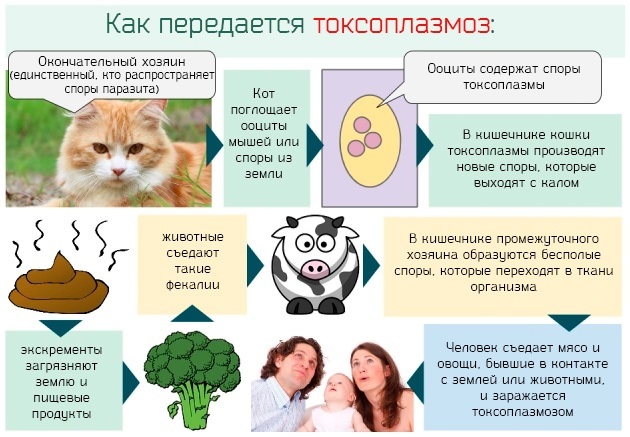
The simplest microorganisms reproduce in 2 ways: by division into sex and by cells, penetrating into the cell membrane of their host. Sexual reproduction of the infection occurs if it is localized in the intestine. The parasites form cysts that are excreted in the faeces of an infected animal or person. Toxoplasma can live outside the body for up to one and a half years.
Symptoms of toxoplasmosis
Toxoplasmosis (symptoms in women are the same as in men) has symptoms similar to the common cold. Acute infection is rare in humans. In most cases, the immune system suppresses the parasitic cells itself, producing antibodies resistant to them.
Signs of infection do not depend on gender and age, these include:
- heat;
- headache;
- convulsions;
- vomit;
- an enlarged liver.
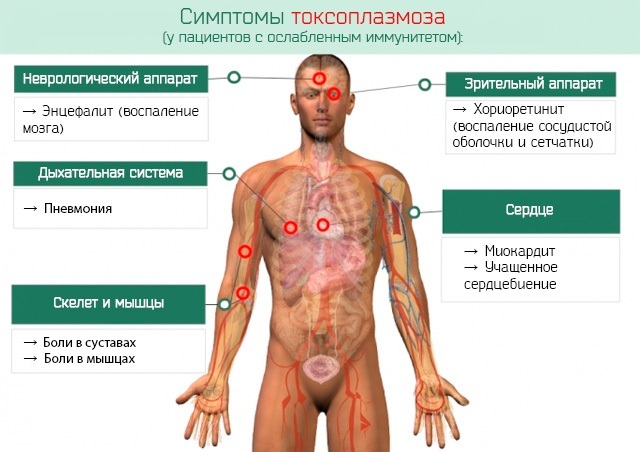
Often, the disease becomes chronic due to exacerbation against the background of unfavorable factors: stress, decreased immunity, pregnancy.
Forms of toxoplasmosis and features of their course
A person is diagnosed with an acute, chronic, latent form of the disease. In the acute form, hyperthermia, enlarged lymph nodes, and joint pain develop. Conjunctivitis, signs of pneumonia, encephalitis are often observed. The variety of clinical signs is associated with the fact that parasites infect almost all human organs.
Latent form
The latent course of the disease is characterized by a complete absence of a clinical picture. Latent forms are commonly seen in people with strong immune systems. With a weakening of immunity, an acute form of the disease is revealed.
Latent toxoplasmosis caused by immunosuppression is characterized by damage to the central nervous system, which leads to:
- headache;
- confusion of consciousness;
- seizures and other neurological signs.
Fever, swollen lymph nodes, and retinal inflammation are often present.
Generalized form
The exanthemic form is indicated by high fever, fever, headache, chills. On the 3rd or 4th day of the development of the disease, you can see a maculopapular rash, which gradually, in 2 weeks, disappears.
- From the first days, symptoms of enteritis develop, an increase in the liver and spleen occurs. Characterized by an increase in lymph nodes, sometimes myocarditis occurs.
- The above symptoms are often combined with lesions of the central nervous system, which can proceed as encephalitis or meningoencephalitis.
Chronic form
Toxoplasmosis in women sometimes takes the form of a chronic course. This type is the most common and can be latent for 3 years.

Symptoms in this case will be:
- migraine;
- attention deficit disorder;
- weakness;
- loss of appetite;
- memory problems.
Some patients experience hallucinations. An important symptom is a lack of interest in everything that happens.
In chronic toxoplasmosis, problems with the cardiovascular system may occur: arrhythmia, tachycardia. When the parasite enters the gastrointestinal tract, the patient develops dry mouth, swelling, and the appetite will completely disappear.
Infection can lead to menstrual irregularities in women. The chronic form of the disease is characterized by an asymptomatic course with rare exacerbations.
In this case, nonspecific signs are observed:
- A slight increase in body temperature.
- Weakness, irritability, memory failure.
- Sleep disturbances
- Constant headaches.
- Swollen lymph nodes.
- Pain and stiffness in joints and muscles.
- Loss of appetite, dry mouth, abdominal pain,
- Sexual dysfunction in women and men.
- Loss of visual acuity.
Cerebral toxoplasmosis
Toxoplasmosis of the central nervous system occurs as a result of reactivation of the disease in patients receiving immunosuppressive or cytotoxic therapy, or in patients with HIV infection. It is rare in immunocompetent people (who are able to develop an immune response).
CNS toxoplasmosis is well documented in HIV-infected patients who are not undergoing prophylaxis. Infection occurs in 30–40% of all patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). The final diagnosis is made with a brain biopsy. The infection usually occurs after the CD4 + count has dropped below 100 cells.
The most common symptoms are headache, confusion and fever.
Ocular toxoplasmosis
Infection of the retina and choroid caused by the intracellular parasite Toxoplasma gondii is the leading cause of posterior uveitis worldwide and a common cause of vision loss due to intraocular infections.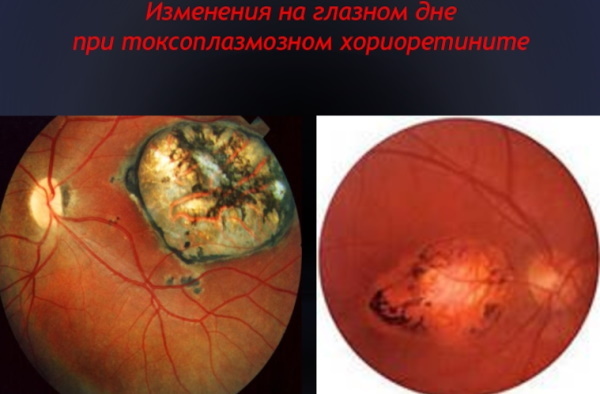
Congenital T. gondii was previously considered the most common cause of ocular toxoplasmosis. But at present, about 1/3 of cases of toxoplasmotic chorioretinitis are caused by congenital infection, and 2/3 - by infection acquired at a later age.
The typical sign is an area of fluffy white focal necrotizing retinitis adjacent to a pigmented chorioretinal scar. Clouding of the vitreous body, leading to the appearance of fog before the eyes, can be seen on examination of the dilated fundus.
Classical therapy for ocular toxoplasmosis consists of antiparasitic and anti-inflammatory drugs, most often oral pyrimethamine and sulfadiazine, as well as systemic corticosteroids.
In what cases is toxoplasmosis dangerous for women
The risk of contracting toxoplasmosis in the expectant mother is small. A particular danger is fraught with a congenital disease, since the fetus is affected even at the stage of formation of vital organs and systems. Therefore, the diagnosis of pregnant women is of great importance.
How it proceeds, what can be the consequences during pregnancy and hepatitis B
Anyone can get infected, but babies born to mothers who contract the infection during or shortly before pregnancy are at risk of developing complications from toxoplasmosis. If a woman is infected for the first time during pregnancy or was infected shortly before conception, then she can transmit toxoplasmosis to her baby.

The risk of fetal infection is about 30%. Early infection carries dangerous risks for the child, including problems with vision, hearing and subsequent learning. In the later stages of pregnancy, the consequences are less severe.
Some babies may have symptoms at birth, such as a buildup of fluid in the brain or an abnormally small head. Others may develop vision or hearing problems as they get older. Toxoplasmosis infections can also lead to miscarriage or stillbirth.
During pregnancy, the question of time of infection of a woman is very important: long before conception or while carrying a child. Treatment is prescribed no earlier than the second trimester. The question of termination of pregnancy is raised only if the woman was infected in the first trimester and there was a serious risk of organic damage to the organs of the central nervous system, vision in the fetus.
Diagnosis of toxoplasmosis
Toxoplasmosis (symptoms in women depend on the degree of infection) is determined on the basis of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay that detects antibodies.
Ocular disease is diagnosed based on the appearance of the eye lesions, symptoms, course of the disease, and often serologic tests.
Taking anamnesis
The doctor will ask about her medical history to find out if the woman has any medical problems that could weaken her immune defenses:
- HIV or AIDS;
- crayfish;
- hereditary immunodeficiency;
- organ transplantation.
The doctor will review the patient's medications to rule out drugs that can suppress immune defenses, allowing the Toxoplasma parasites to become active.
When visiting a doctor, you should talk about contact with cats, especially street cats. To assess the risk of food-related toxoplasmosis, your doctor will ask if raw meat is often consumed in your diet.
External signs
The doctor examines the patient if toxoplasmosis is suspected to check for swollen lymph nodes, liver, spleen, eye damage, and fever.
Laboratory research
To confirm the diagnosis, blood tests are ordered to check for antibodies. Depending on the level of certain antibodies in the blood, the doctor can determine if there is active toxoplasmosis or if there was an episode of infection in the past. Most healthy people do not remember the last episode because 90% of them never show symptoms. In acute infection, the diagnosis can be confirmed by detecting Toxoplasma parasites in blood, body fluids, or infected tissue samples.
A test that measures immunoglobulin G (IgG) is used to determine if a person has been infected. If it is necessary to try to estimate the time of infection, which is especially important for pregnant women, along with other tests, for example, avidity, a test that measures immunoglobulin M (IgM) is also used.
Diagnosis can also be made by direct observation of the parasite in stained tissue sections, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), or other biopsy material. These methods are less commonly used due to the difficulty of obtaining these samples.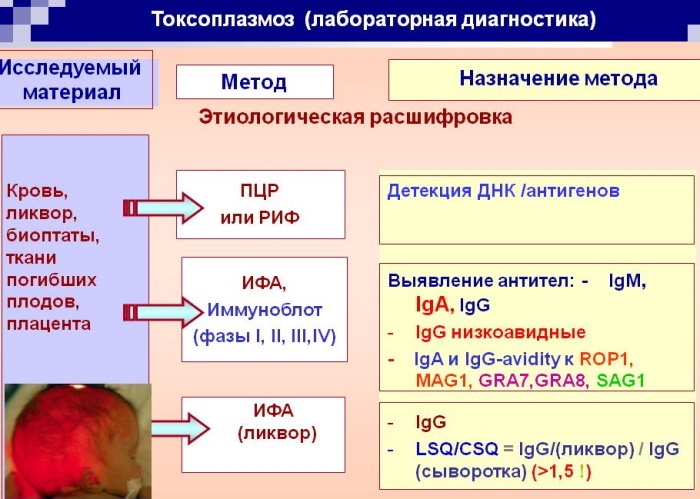
Molecular techniques that can detect parasite DNA in amniotic fluid may be useful in cases of possible mother-to-child transmission
Instrumental diagnostics
If a doctor suspects that toxoplasmosis is affecting the brain, they will order computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the head to check for signs of encephalitis.
In medical practice, it is recommended to conduct research during pregnancy to diagnose congenital toxoplasmosis before birth:
- determination of the state of the barrier function of the placenta in case of possible infection and the presence of infectious agents that have penetrated the fetus;
- Fetal ultrasound;
- dopplerography.
Treatment of toxoplasmosis in women with drugs
Treatment regimens have remained unchanged for 20 years. In most cases, treatment is not required unless the symptoms are severe. If your immune system is weakened, your doctor will prescribe the appropriate combination of drugs. When infected during pregnancy, drugs are prescribed that reduce the risk of developing congenital toxoplasmosis in a child.
Treatment of the acute form
Toxoplasmosis (symptoms in women manifest when parasites are activated) in acute form is treated with Pyrimethamine and Sulfadiazine for up to 3 weeks. Together with the appointment of Pyrimethamine, folic acid should be taken in a prophylactic dosage to prevent dysfunction of the bone marrow. The cycle is repeated after 10 days.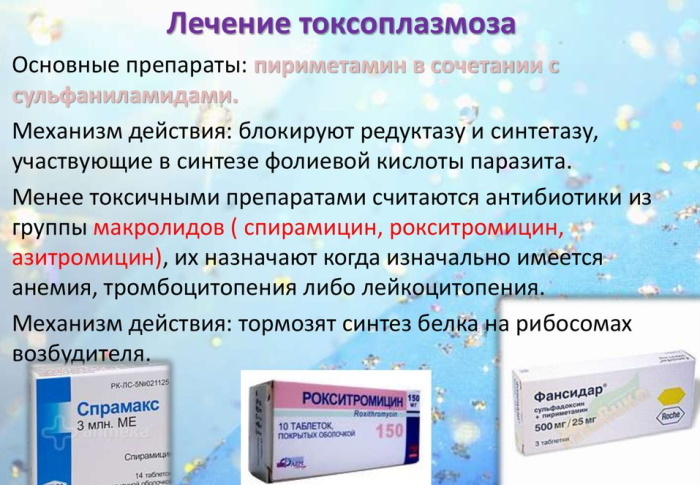
Every 10 days it is necessary to change one of the drugs. Delagil is prescribed 250 mg 3 times a day, Clindamycin 450 mg 3 times a day, Trichopol 250 mg 4 times a day.
In case of intolerance to sulfadiazine, especially in patients with HIV infection, Clindamycin is prescribed together with Pyrimethamine. The scheme is supplemented by the intake of folic acid. Calcium folate is prescribed at 2-10 mg per day throughout the course of treatment.
Eye damage is treated with anti-inflammatory drugs and glucocorticoid drops. The drugs are applied in cycles with breaks of 7-14 days.
Standardized treatment regimens:
| Tindurin. Sulfanilamide |
5 days | The course is repeated after 1-2 months. |
| 7 days for 3 cycles | ||
| Pyrimethamine | 2 days at 2 mcg / kg / day, then 1 mg for 2-6 months. Then 1 mg orally 3 times a week | Duration of treatment is 12 months. |
| Sulfadiazine | 50 mg / kg 2 times a day | |
| Spiramycin | 4 weeks at 100 mg / day, this course alternates with the course of Pyrametacin + Sulfadiazine | Duration of treatment 12 months |
| Spiramycin | 100 mg / day | Within 3 months, while maintaining the manifestations of infectious invasion, the course lasts up to six months. |
| Pyrimethamine | At 1 mg / kg / day for 6 weeks. At the same time, Sulfadiazine is prescribed at 50-100 mg / kg 2 times a day in 4 doses and folic acid 3 mg three times a week. Further, courses alternate with a four-week intake of Spiramycin at 100 mg / kg per day. | The duration of treatment can be up to 12 months. |
The effectiveness of many drugs depends on the individual characteristics of the patient.
With the development of organ pathology, Prednisolone is prescribed at 1.5 mg / kg per day for 2 doses. If necessary, immunocorrective therapy, vitamins and drugs for allergies are prescribed.
Treatment of acute toxoplasmosis in pregnant women
Until the infection is confirmed, if a primary infection is suspected, Spiramycin is prescribed to pregnant women. It is a macrolide antibiotic that prevents microorganisms from crossing the placenta to the fetus.
The drug is injected subcutaneously at 3 million IU at intervals of 8 hours until confirmation of fetal infection. Treatment can be maintained until labor.
If the infection of the fetus is confirmed, Pyrimethamine + Sulfadiazine is prescribed. The treatment regimen is supplemented with a therapeutic dosage of folic acid. The use of Pyrimethamine in the third trimester is not recommended due to the possible impairment of the embryo.
If infection is detected in the 2nd half of pregnancy, Pyrimethamine with Sulfadiazine is prescribed. Treatment is carried out in a hospital.
Treatment of the chronic form
The main drug is antifolate compounds. Pyrimethamine, Tindurin, Daraprim, Chlorichine in combination with sulfonamides are characterized by an eight-fold increase in the effectiveness of active substances compared with an isolated action.
Combined preparations Fansidar, Metakelfin contain both sulfadoxine and pyrimethamine. Spiramycin and Clindamycin are used as alternatives, but they show less effectiveness.
Two treatment regimens are used:
- The use of Chloridine in combination with Sulfanilamide courses of 5-7 days with a break of 7-14 days. The course is repeated three times.
- Use of Pyrimethamine with co-trimoxazole and macrolide antibiotics for 10 days.
Specific immunotherapy with toxoplasmin
Toxoplasmin is a complex of Toxoplasma antigens that acts as an immunomodulator. Has a stimulating effect on the production of interferon gamma, activates the process of differentiation of T cells.
The method of specific desensitization with toxoplasma antigen is based on a gradual increase in dosage. Toxoplasmin is used when diluting 4 ml in 100 ml of isotonic solution, 2-3 drops three times a day for a month. The diluted drug is injected intradermally into 3 points of the forearm.
The advantages of the application are:
- lack of development of allergic reactions;
- convenience and ease of use;
- low cost of treatment.
Ultraviolet irradiation
UV therapy is used as an adjuvant. An isolated appointment has low efficiency. The technique is based on the irradiation of local areas with ultraviolet rays, which is used as an aid. An isolated appointment has low efficiency. The technique is based on irradiating local areas with ultraviolet rays.
The starting dose is ¼ of the biodose and is maintained for the first 2 days. A gradual increase in the dosage regimen ends when 1 biodose is reached in the last days of treatment.
Complications and prognosis
Toxoplasmosis (symptoms in women may be nonspecific) is a parasitic disease, but its course is usually positive. Severe symptoms, such as inflammation of the brain, heart, or retina, develop only in very rare cases (for example, with immunodeficiency).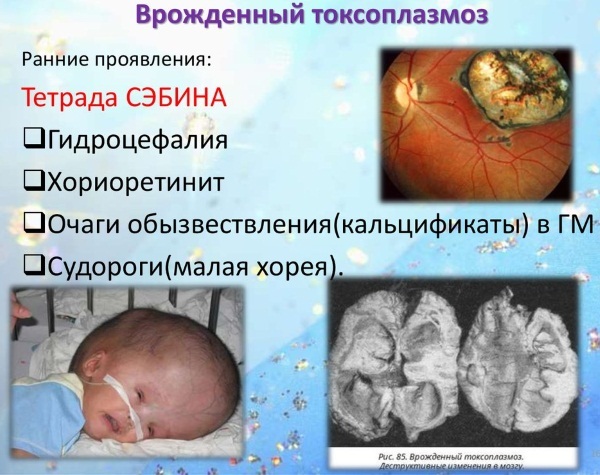
If toxoplasmosis is continually treated during pregnancy, babies are born without any significant symptoms. Children with congenital toxoplasmosis can develop complications including hearing loss, mental retardation, and blindness.
With a normal immune system, a woman is unlikely to experience toxoplasmosis. The body of a healthy person produces protective substances (antibodies) against the pathogen and the symptoms of infection will not be available.
The best way to prevent illness is to practice good personal hygiene. You should avoid contact with unfamiliar animals, especially cats, wash your hands thoroughly after working with the ground, wash vegetables and fruits, eat meat products after sufficient heat treatment.
Video about toxoplasmosis
Komarovsky about toxoplasmosis: