Content
- Stages and degrees of overabundance
- Easy stage
- Moderate stage
- Severe stage of hypercalcemia
- Symptoms and Signs
- Causes
- Hyperparathyroidism
- Crayfish
- Medications
- Vitamin D overdose
- Vitamin A overdose
- Severe dehydration
- High level of protein in the blood
- Hyperthyroidism
- Prolonged immobilization
- Sarcoidosis
- Excess calcium intake
- Genetic diseases
- Magnesium regulation
- Diagnostics
- Treatment methods
- Treatment by type of hypercalcemia
- Oral phosphates
- Calcitonin
- Diuretics
- Bisphosphonates
- Corticosteroids
- Hemodialysis
- Possible consequences and complications
- Hypercalcemia video
Hypercalcemia is a condition, in which the concentration of calcium in the blood is higher than normal. Excess manifests itself in many symptoms and can affect various body systems: destroy bone mass, affect the functioning of the heart and brain, promote the formation of stones in kidneys.
Stages and degrees of overabundance
Calcium is the most abundant mineral in the body, accounting for up to 2% of body weight. About 99% of the calcium in the human body is found in teeth and bones, and only 1% is found in soft tissues, blood and body fluids. Calcium concentration is maintained thanks to the hormonal regulation system.
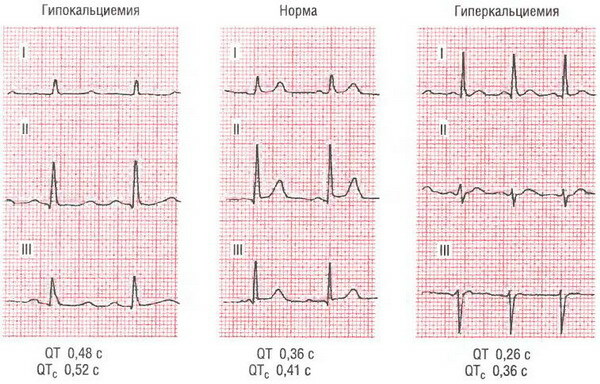
The level of ionized calcium in the blood usually rises at a lower pH due to the weakening of the bond between albumin and calcium. Chronic hypercalcemia carries health risks including impaired kidney function, heart disease, and even death.
The following are the maximum daily mineral levels that must not be exceeded. This includes calcium from foods as well as dietary supplements. Exceeding this level for a short time is unlikely to cause any problems, but it is not safe to do so in the long run.
| Age | Men | Women | Pregnancy | Lactation |
| 0-6 months | 1000 mg | 1000 mg | — | — |
| 7-12 months | 1500 mg | 1500 mg | — | — |
| 1-8 years old | 2500 mg | 2500 mg | — | — |
| 9-18 years old | 3000 mg | 3000 mg | 3000 mg | 3000 mg |
| 19-50 years old | 2500 mg | 2500 mg | 2500 mg | 2500 mg |
| 51+ | 2000 mg | 2000 mg | — | — |
Consuming more of the mineral with food and supplements is unlikely to significantly increase blood calcium levels. but can cause other problems, such as constipation, or reduce absorption of other minerals, including iron and zinc.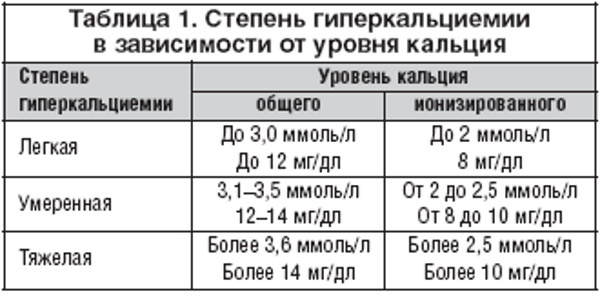
The normal range for blood calcium is 8.5 to 10.5 mg / dL. These values may vary slightly from laboratory to laboratory.
An excess of calcium in the body (the symptoms are the same for both men and women) contributes to the deposition of calcium sediment on blood vessels and tissues. The increase in concentration takes place in several stages. They vary in severity and duration of the course.
Easy stage
Mild hypercalcemia is characterized by no or mild symptoms. Treatment is prescribed after the final diagnosis has been established and the cause of the disease has been identified. The calcium concentration does not exceed 10.51 - 12 mg / dl.
Moderate stage
The moderate stage is accompanied by an increase in the mineral in the range of 11.5-18 mg / dl. The process leads to the development of bone resorption. At this stage, there is a change in the functioning of the kidneys and the appearance of negative symptoms.
Severe stage of hypercalcemia
The form is fixed with an increase in calcium ≥ 18 mg / dL and the appearance of severe symptoms. Hemodialysis is prescribed to correct renal failure.
Symptoms and Signs
An excess of calcium in the body (symptoms occur at 12 mg / dL serum mineral levels) leads to muscle weakness and arrhythmias. This occurs in the case of a severe stage, when excess calcium suppresses neuromuscular and myocardial depolarization. Neurological features include impaired concentration, a change in mental state from irritability to confusion.
Levels above 14 mg / dL can cause encephalopathy, and levels above 15 mg / dL are a medical emergency. Severe, sharp abdominal pain can be a sign of pancreatitis. Bone changes lead to bone pain, gait abnormalities, and fractures.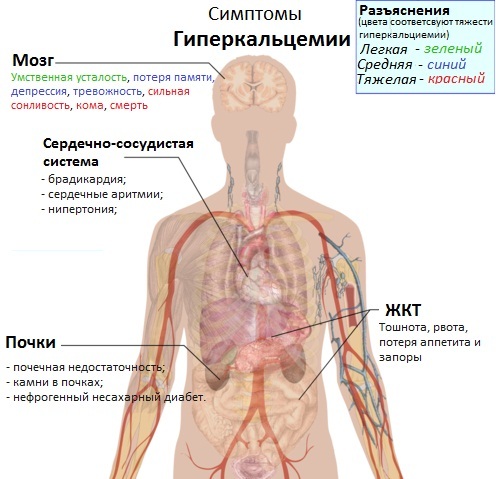
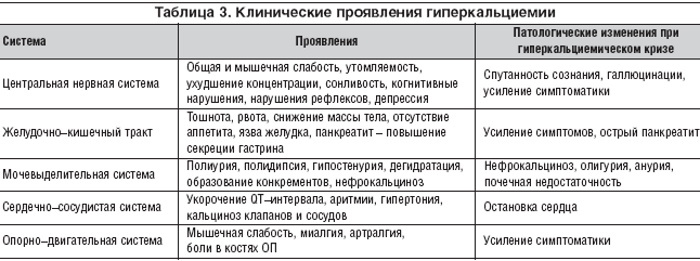
Common signs common to all stages of hypercalcemia include:
- nausea and vomiting;
- frequent urination;
- excessive thirst;
- abdominal pain;
- muscle pain;
- confusion of consciousness.
Causes
An increase in calcium does not always mean that there is a disease that requires treatment. The doctor interprets the diagnosis based on the medical history, causes and test results.
The two most common causes of elevated plasma concentrations of the mineral are overactive parathyroid gland and cancer.
Hyperparathyroidism
Overactive endocrine glands located at the back of the thyroid gland are the most common cause of hypercalcemia. This can happen when one or more of the parathyroid glands is enlarged benignly or due to cancer. Blood calcium levels are controlled by parathyroid hormone (PTH). Parathyroid cells release PTH when they sense a drop in levels.
The hormone increases the amount of the mineral in the blood by increasing the absorption of calcium from the intestines and kidneys. PTH also mobilizes calcium and phosphate from bones: it breaks down and releases bone minerals to compensate for low calcium levels. This process is known as bone resorption.
PTH increases the amount of vitamin D, which is converted to its active form, calcitriol, and accordingly increases intestinal absorption of calcium. If the PTH level gets too high, the calcium concentration rises sharply.
Crayfish
Besides parathyroid cancer, other types of carcinomas can cause hypercalcemia by secreting a protein that mimics PTH. These include cancers of the lungs, ovaries, and kidneys. Carcinoma that spreads to the bone and damages bone cells contributes to the excessive concentration of calcium in the blood.
Medications
Some medications cause or contribute to an increase in the level of the mineral in the blood plasma.
These include:
- lithium;
- antacids for heartburn;
- water tablets used to treat high blood pressure.
Vitamin D overdose
Vitamin D is able to increase the level of the mineral as it increases the amount of calcium absorbed in the intestines. This usually happens in the case of taking excessively high doses of the vitamin (20 - 100 thousand. IU per day) for a long time.
It's important to note that sun exposure does not cause dangerously high levels of vitamin D or calcium. The only risk of overdose comes from the large amount of vitamin D supplements.
Vitamin A overdose
Excess vitamin A can lead to hypercalcemia. This usually only happens if high-dose vitamin A supplements are taken for a long time.
Severe dehydration
An excess of total calcium in the body is observed in the case of a symptom of dehydration. But the ionized or free mineral in this case remains normal and metabolically active.
High level of protein in the blood
For control, the level of albumin and protein is checked. When they are elevated, more calcium binding occurs, and therefore total calcium may be "falsely" high while free calcium metabolism is normal. The doctor can rule out this in the diagnosis by checking the level of ionized (free) calcium.
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperfunction of the thyroid gland contributes to the development of hypercalcemia.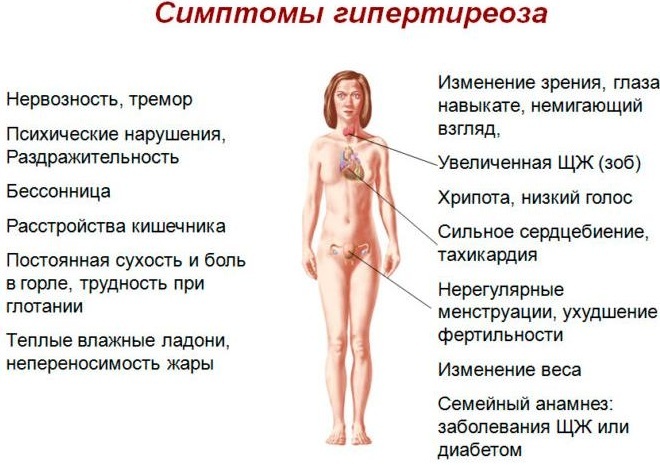
The mechanism is poorly understood, but some evidence suggests that the following changes occur with hyperthyroidism:
- increased sensitivity of bones to PTH;
- the level and sensitivity of interleukin-6 changes upward;
- the regulation of adrenal hormones is disrupted.
The result of these changes is an increased mobilization of calcium and phosphate from the bones (resorption).
Prolonged immobilization
Prolonged immobility with diseases often contributes to an increase in the concentration of the mineral and the development of osteoporosis. Serum calcium levels rise during the first days of immobilization. After returning to the usual way of life, the balance is quickly restored. Especially often, calcium rises rapidly in multiple fractures.
Sarcoidosis
Hypercalcemia is a complication of sarcoidosis, an inflammatory disease that affects several organs in the body. In sarcoidosis, production of active vitamin D gets out of control while parathyroid hormone levels rise. This causes a spike in calcium levels.
Excess calcium intake
Consuming too much of the mineral is rare. This has been seen in people taking increased doses of calcium carbonate (40-60 grams per day) along with alkaline foods such as milk, bicarbonate, or antacids.  The system becomes overloaded and cannot clear calcium quickly enough. The phenomenon is known as lactic acid syndrome or Burnett's disease.
The system becomes overloaded and cannot clear calcium quickly enough. The phenomenon is known as lactic acid syndrome or Burnett's disease.
Genetic diseases
Genetics (certain mutations in genes) in some people is a factor in increasing blood calcium levels. This happens when you have a rare condition called familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia.
Magnesium regulation
Magnesium is essential for controlling blood calcium levels. It is a co-factor in the production and activation of vitamin D. The calcium to magnesium ratio is important and most people do not get enough magnesium when compared to calcium.
The data suggest that the optimal ratio is 2/1. Meanwhile, getting more calcium, for example, 4 times than magnesium, is associated with numerous chronic diseases.
The modern lifestyle has shifted the balance in favor of calcium, so it is extremely important to formulate a conscious, balanced diet with the right amount of both minerals.
Diagnostics
If you have alarming symptoms, you should contact a medical institution to see an endocrinologist. After collecting the history, the doctor will prescribe a series of studies.
Diagnostics begins with a blood and urine test. The diagnosis is established after obtaining the results of changes in the concentration of the ionized form of calcium and parathyroid hormone.
- A blood test for serum calcium is in the range of 200-250 rubles. without blood sampling.
- Determination of calcium in urine - 200-220 rubles.
- Measurement of the level of electrolytes, urea, phosphates, PTH, alkaline phosphatase. A biochemical blood test is estimated at 300-500 rubles.
- Determination of serum urea concentration costs 150-200 rubles.
- An analysis for the content of PTH together with blood sampling costs 800-1 thousand rubles. RUB 200
- Immunoelectrophoresis of serum proteins reveals the presence of abnormal immunoglobulins. Their accumulation in the blood or urine indicates the presence of malignant neoplasms. The cost of the research is 3-5 thousand. rub.
- To assess daily urinary calcium excretion, a 24-hour urine study is required. It is necessary to assess the risk of stone formation. The cost of the analysis is within 200-300 rubles.
Treatment methods
An excess of calcium in the body, the symptoms of which in a chronic or severe form are pronounced, should always be treated by a doctor. After instrumental and laboratory diagnostics, the specialist will find out what causes the increased calcium level and will prescribe the appropriate therapy for the underlying disease.
Treatment of hypercalcemia is required if symptoms are present or if calcium levels exceed 15 mg / dL, even in asymptomatic patients.
Treatment is based on hydration, taking drugs that lower calcium levels, and stopping drugs that cause hypercalcemia (thiazides, diuretics, vitamin A and vitamin D).
Treatment by type of hypercalcemia
- Patients with asymptomatic or moderately symptomatic hypercalcemia (total albumin-corrected calcium <12 mg / dL) do not need immediate treatment, but they are advised to avoid aggravating factors hypercalcemia. Adequate hydration (at least 6-8 glasses of water per day) is recommended to minimize the risk of nephrolithiasis. Additional therapy depends on the cause of the increase in mineral.
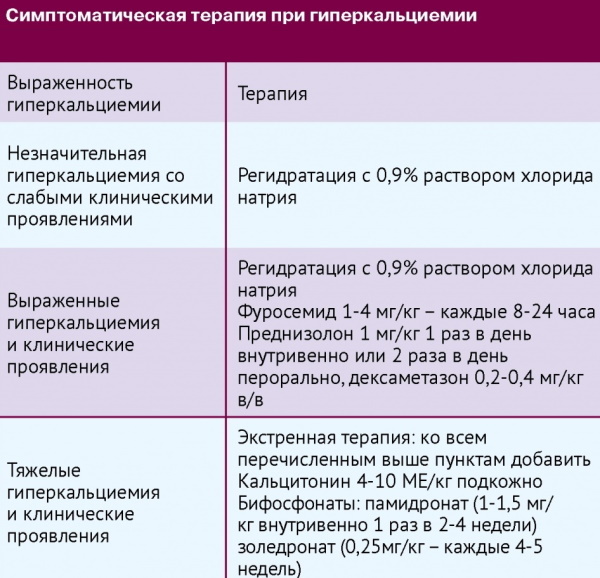
- Moderate hypercalcemia, asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic (total albumin-corrected calcium between 12 and 14 mg / dL) in some cases does not require immediate therapy. However, the same precautions should be followed as for a mild form. Patients are usually treated with saline and bisphosphonates.
- Severe concentration stage. Patients with total albumin-corrected calcium> 14 mg / dL require more aggressive therapy.
Oral phosphates
When severe symptoms appear, oral phosphates are prescribed, which bind calcium, preventing its absorption in the intestine. The starting dosage is 250 mg of sodium or potassium salts 4 times a day. If necessary, the dosage can be increased to 500 mg.
Calcitonin
A fast-acting peptide hormone produced when calcium levels rise. It has a depressing effect on the activity of osteoclasts. It is injected subcutaneously every 12 hours at 4-8 units / kg.
Diuretics
An excess of calcium in the body (symptoms can vary from frequent urination, thirst to cardiac dysfunction) is normalized by the administration of an isotonic solution of salts and loop diuretics. The drugs stimulate the excretion of calcium in the urine. In the absence of heart failure, 1–2 L of saline is administered over a 2–4 hour period.
To ensure diuresis, 20-40 mg of furosemide is administered intravenously every 2-4 hours. Salt therapy requires careful monitoring as it can lead to fluid overload in patients who cannot clear the injected salt due to impaired renal function. In such patients, the concentration of potassium and magnesium in serum is determined every 4 hours.
Bisphosphonates
The drugs inhibit bone resorption, which is primarily responsible for hypercalcemia:
- Zoledronic acid is administered intravenously in a single dose of 4-8 mg.
- Pamidronate is used at a dosage of 30-90 mg once a day. Re-introduction is required after 7 days.
- Ibandronate remains effective for 14 days when given 4–6 mg IV.
- The use of etidronate at 7.5 mg / kg for 3-5 days.
Although IV bisphosphonates are usually well tolerated, side effects can include flu symptoms.
Corticosteroids
Steroid hormones are used for the toxic effects of vitamin D. The appointment of prednisolone 20-40 mg in tablets increases the productivity of calcitriol and reduces the absorption of calcium in the intestinal lumen.
Hemodialysis
The method consists in purifying the patient's blood with a dialyzer. It contains 2 liquid dialysates, which ensure the exchange of concentrations of substances between blood and fluid.
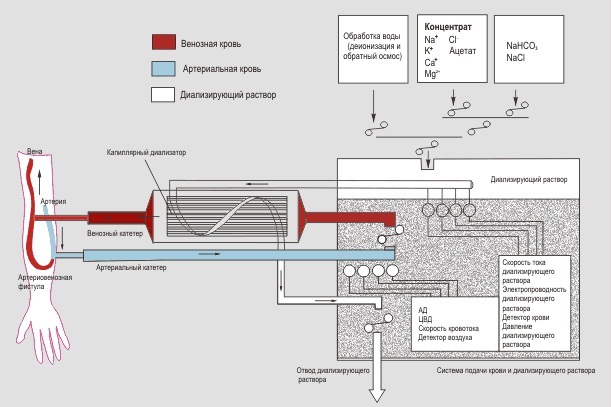
The optimal dosage for hemodialysis is unknown. Most patients need at least 3 sessions a week for several hours. Dialysis is usually prescribed for patients with severe hypercalcemia.
Possible consequences and complications
The outlook is good for people with mild hypercalcemia who have a treatable cause. In most cases, there are no complications.
People with high calcium levels due to conditions such as cancer or sarcoidosis may feel unwell. More often than not, this is due to the disease itself, and not to the high levels of the mineral.
Complications in the gastrointestinal tract with elevated calcium levels are expressed by the development of pancreatitis, peptic ulcer disease.
An excess of the mineral puts you at risk of calcium crystal formation in the kidneys, which contributes to:
- calcium deposition in the kidneys (nephrocalcinosis);
- dehydration;
- increase in AD;
- kidney failure;
- the development of kidney stones.
Psychological problems may also arise:
- depression;
- trouble concentrating;
- violation of the thinking process.
Hypercalcemia leads to:
- bone cysts;
- fractures;
- osteoporosis.
Too much calcium can lead to an irregular heartbeat.
An excess of calcium contributes to the deposition of salts in the tissues of organs, which disrupts their normal functioning. Renal tissue is primarily attacked. The development of renal failure worsens the ineffectiveness of drug treatment and requires surgical intervention, after which patients need to regularly purify and restore the electrolyte balance of the blood by hemodialysis.
Timely contact with a medical institution minimizes complications caused by the disease.
Treatment of an excess of calcium should be aimed both at reducing its concentration in serum and, if possible, at treating the underlying disease. Effective therapies reduce the amount of mineral in the body by inhibiting bone resorption, increasing urinary excretion of calcium, or decreasing intestinal absorption of calcium. The best choice depends on the cause and severity of the symptoms.
Hypercalcemia video
Hypercalcemia Syndrome: