Content
- What is MID, what analyzes determine the indicator
- Norms of monocytes in the analysis of blood in children, women, men
- When is the analysis prescribed?
- The reasons for the increase in monocytes, what symptoms accompany monocytosis
- Reconvalescence
- Viral infections
- Bacterial infections
- Systemic granulomatous processes
- Diffuse connective tissue diseases
- Malignant blood diseases
- Neutropenia
- Rare causes
- What to do with an elevated monocyte count
- Blood MID video
MID is a collection of 3-shaped blood elements. An increase in their number in the analysis indicates the presence of various violations. To determine the level and establish the reason for its increase, laboratory diagnostics are required.
What is MID, what analyzes determine the indicator
MID - a number of blood corpuscles that are part of the lymph. Diagnostics allows you to determine the level of monocytes, eosinophils and basophils.
Other indicators are also taken into account:
- Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR). This element is responsible for the quantitative content of protein in the body. With an increase in speed, inflammatory processes may develop or malignant neoplasms may occur.
- The quantitative content of red blood cells (RBC). The components are involved in oxygen metabolism and are responsible for the transport of various enzymes and amino acids. They also activate immune processes. With a rare increase in erythrocytes, the risks of thrombosis are significantly increased. With a sharp decrease in them, anemic conditions occur.
- Hemoglobin (Hb) level. The component is part of erythrocytes and is responsible for oxygen metabolism. With an increase in the concentration of hemoglobin, the patient experiences severe dehydration. A component deficiency may indicate trauma, anemic conditions, or other disorders caused by a lack of iron in the body.
- Hematocrit (volume of red blood cells). It is also a constituent component of red blood cells. On its basis, the number of erythrocytes is calculated in relation to the total volume of circulating blood.
- Platelet concentration. Their function is normal blood clotting. With a change in the concentration of components in the blood, the presence of congenital diseases is observed. An increase in the level of the formed element occurs as a result of profuse blood loss caused by injuries, surgical interventions, and labor.
-
Granulocyte level. These components are a collection of eosinophils, basophils and neutrophils. Their increase in the body occurs against the background of inflammatory processes. A decrease in the level of granulocytes can indicate various disorders of the hematopoietic system.
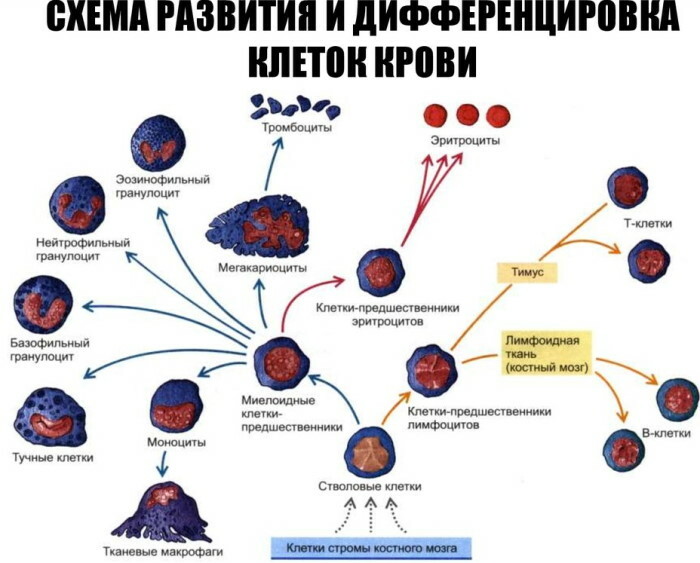
The leukocyte formula is also being studied, which, in addition to the main 3 blood components, includes lymphocytes and neutrophils.
To study the characteristics, a blood sample is taken from a finger. In more rare cases, lymph may be drawn from a vein.
Norms of monocytes in the analysis of blood in children, women, men
MID in the blood test can be increased in children, women and men for various reasons (internal and external). At the same time, the norms of blood parameters may differ depending on the age and gender of the patient.
The quantitative content of formed elements (monocytes) in an adult ranges from 2-9% or 0.08-0.6x109 / l. According to other sources, the indicator can vary from 3 to 11%.
Erythrocyte rates:
- For men - 3.8-5.5x1012/л.
- For women - 4.3-6.2x1012 /л.
Normal values (for hemoglobin):
- Men and women - from 120 to 140 g / l.
- children - 110-120 g / l.
In terms of the width of the distribution of erythrocytes, the norm for children and adults is from 11.5 to 14.5%.
Indicators for hematocrit:
- women - from 35 to 45%.
- Men - 39-49%.
- Children - 32-62%.
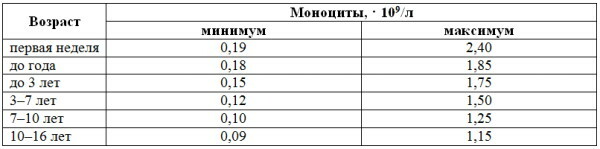
| Child's age | Monocytes | Eosinophils | Basophils |
| Newborns and children under 12 years of age | 5-11% | 1-5% | 0-0,5% |
| 12 to 18 years old | 3-12% | 1-5% | 0,7% |
When is the analysis prescribed?
https://www.youtube.com/watch? v = iMcScN4zKeI
The study is prescribed during preventive examinations, as well as during the period of treatment of the disease to track the dynamics.
Indications for the procedure:
- inflammatory diseases;
- diseases of the hematopoietic system;
- allergy;
- infectious and viral damage to the body;
- anemic conditions, especially during pregnancy tracking and in childhood.
Also, the study is mandatory during pregnancy. With the development of any negative signs, diagnostics are assigned to patients during menstruation.
It should be borne in mind that the accuracy of the results depends on preliminary preparation, which includes the following:
- Food intake should be no later than 12 hours before the analysis. In this case, you should refuse to eat fried, spicy and flour foods.
- The day before the procedure, you must stop drinking alcohol and coffee. During this period, it is recommended to consume more pure water.
- Smoking should also be completely stopped 12 hours before the study.
- Before diagnosing a day, it is necessary to avoid stressful situations and give up physical exertion.
- For 1-3 days before the analysis, you should stop taking medications, in particular those affecting the function of the blood.
- The study should not be carried out during menstruation (only as directed by a doctor).
- The procedure is not performed after some other examinations carried out earlier - ECG, X-ray, fluorography.
If these rules are observed, the risks of incorrect data display are almost completely absent.
The reasons for the increase in monocytes, what symptoms accompany monocytosis
MID in the blood test can be increased with various internal diseases. In this case, the level of formed elements increases to 1 thousand. per 1 μl of blood and depends on the severity of the disorder and other physiological factors.
There is practically no symptomatology for violations. The diagnosis is made based on the manifestations characteristic of a particular disease.
The development of a violation can be suspected by the following indirect signs:
- weight loss (in the absence of changes in lifestyle;
- complete or partial loss of appetite;
- general weakness and fatigue;
- psycho-emotional disorders - anxiety, panic attacks;
- dislike for meat food;
- disorders of the nervous system - insomnia, irritation, apathy;
- changes in stool - the presence of impurities, irregularity, the presence of foamy discharge;
- pain syndrome developing in the epigastric region;
- cough (especially dry and with a viscous secretion or blood);
- pain in the area of muscles and joints;
- a rash on the skin or mucous membranes, which has a specific character (in some cases, rashes can form in the genital area);
- discomfort and the development of pain during sexual intercourse.
These symptoms can develop both individually and in a complex manner, depending on the pathology that provoked a decrease in the number of blood corpuscles.
Reconvalescence
The condition is otherwise called recovery - the period after the transferred and cured disease. In most cases, the process develops in children after an infection. In this case, the condition indicates the complete removal of the pathogen that provoked the development of the disease.
There are no manifestations, the flow form is insignificant. The process lasts up to 2 weeks and does not require any therapy.
Viral infections
MID in the blood test is slightly elevated in viral infections and does not require special therapeutic measures. When infected with a virus, monocytes act as the first defense reaction of the body. Heading to the lesions, they are converted into macrophages and absorb microorganisms. In this case, the elements produce antigens on their surface to a specific infectious agent.
Macrophages are also responsible for the production of various mediators and cytokines and guide the neutrophil to the affected area.
In some cases, infectious and viral diseases can additionally lead to enlargement of the lymph nodes.
Classification of violations:
- Acute viral infections. The most common illnesses are flu or ARVI. The increase in the number of monocytes is insignificant and gradually returns to normal in 2 weeks after improvement of the condition.
- Infectious mononucleosis. Pathology develops in children when infected with the Epstein-Barr virus. The condition is accompanied by characteristic symptoms and can persist from several months to several years. In this case, a large number of lymphocytes are formed, which have properties similar to monocytes.
It is possible to establish the exact form of the disease only after carrying out complex diagnostic procedures.
Bacterial infections
An increase in the level of monocytes can be observed with a chronic course of bacterial infections. Most often, the condition develops against the background of tuberculosis, brucellosis, or syphilis. Also, pathology can be observed with endocarditis and rickettsioses. At the same time, the level of blood corpuscles differs insignificantly from the number of monocytes during the development of viral infections.
The main reason for the violation is the failure in the processes of phagocytosis. When capturing pathogenic cells, macrophages are not able to completely destroy them, as a result of which microorganisms remain on the surface of monocytes and are protected from the effects of other immune cells.
Against the background of the process, a chronic course of the disease arises, which can persist for several months or years. The condition stabilizes only after appropriate therapy is carried out, aimed at eliminating the underlying cause of the disease. The concentration of monocytes is moderate. The main and only disorder in children, leading to the onset of pathology, is scarlet fever.
Systemic granulomatous processes
Pathology is a chronic non-infectious systemic disease that develops against the background of the formation of granulomas from macrophages, lymphocytes and mast cells. These formations accumulate in the tissues.
The disorder occurs in children as a result of the development of ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease.
In adult patients, the following diseases are the main causes of pathology:
- sarcoidosis;
- histiocytosis;
- Wegener's granulomatosis.
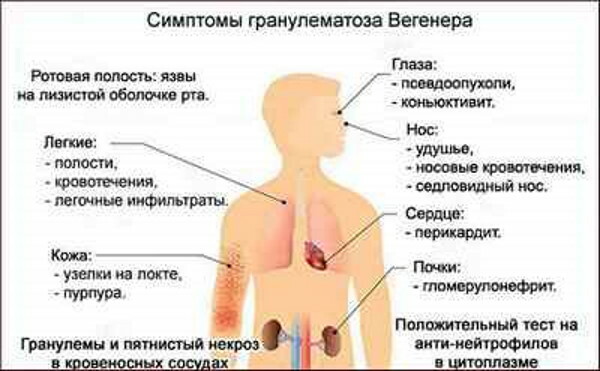
Monocyte counts are slightly elevated compared to bacterial or viral infections.
Diffuse connective tissue diseases
An increase in MID in the blood can also occur when diffuse connective tissue diseases occur. Moreover, the disease is rare and requires additional tests to accurately determine its presence, stage of development and form.
At the moment, the exact reasons for the development of pathology have not been established. According to one of the most popular theories, against the background of the production of autoantibodies, monocytes are formed in the bone marrow tissue. The inflammatory process is directly related to the production of monocytes.
The main causes of the disease are the following disorders:
- systemic lupus erythematosus;
- systemic scleroderma;
- dermatomyositis;
- polymyositis.
The number of formed elements is associated with the stage of the disease. During remission, their level remains within normal limits.
Malignant blood diseases
Oncological pathologies of the circulatory system can also lead to an increase in the level of monocytes. The process is associated with the transformation of bone marrow stem cells. At the same time, the concentration of formed elements is high and can reach half the level of the total number of leukocytes. The increased number of monocytes persists for a long time and decreases only after the use of chemotherapy or surgical interventions associated with bone marrow transplantation.
Possible causes (pathologies):
- chronic myeloid leukemia (observed in adults);
- Hodgkin's lymphoma (a disorder typical for children);
- acute course of monocytic leukemia (in children).

With exacerbated forms of the disease, a so-called leukemic failure can occur.
Neutropenia
A group of diseases characterized by a decreased production of neutrophils, which are produced by the bone marrow. Most often, pathology develops in children and is due to an innate (genetic) predisposition.
Causes:
- pediatric agranulocytosis (TVN);
- neutropenia (a cyclic form of the disorder);
- chronic course of neutropenia (myelocachexia).
In most cases, this form of monocytosis is accompanied by an increase in the level of eosinophils in the blood.
Rare causes
MID in the blood test can also be increased for other more rare reasons that arise in some cases and are most often observed in young children.
Thus, the violation develops against the background of the following factors:
- Parasitic invasions. These pathologies include malaria, Borovsky's disease (including the visceral form of the disorder).
- Intoxication (poisoning). In most cases, it occurs against the background of poisoning with tetrachloroethane or phosphorus.
- The use of medications. Monocytosis can develop as a result of prolonged use of glucocorticosteroid drugs (injection).
Also, the condition may be due to the use of chemotherapy drugs (treatment of myelosuppression).
What to do with an elevated monocyte count
First of all, diagnostics are assigned, which will allow to establish the exact cause of the pathology.
Research types:
- Blood analysis. The leukocyte formula is studied, the presence of autoantibodies and oncological markers is determined.
- Microbiological research (PCR test, ELISA). Diagnostics is aimed at studying the composition of sputum and allows you to determine a specific pathogen.
- X-ray. The study reveals pathologies in the lung tissue.
- Sonographic research. Diagnosis is an ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs and helps to determine the presence of brucellosis or mononucleosis.
- Histology. The procedure involves the collection (puncture) of biological material and its subsequent laboratory study. It is most often used for suspected parasitic infestations.
After all examinations and diagnosis, treatment is prescribed. In this case, the therapy regimen is developed individually and depends on the form and severity of the disease.
All actions are aimed at eliminating the underlying pathology, which provoked an increase in the concentration of formed elements. With previous infectious diseases, treatment is not carried out.
MID in the blood test is increased and requires mandatory conservative therapy. In this case, one or another method is selected depending on the form of the disorder and the age of the patient, since childhood and adult diseases require different therapeutic approaches.
Conservative methods:
- Anti-infective therapy. In most cases, treatment is aimed at adherence to bed rest, drinking plenty of fluids, and taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). In addition, drugs are prescribed that eliminate concomitant symptoms - analgesics, antiseptics, nasal drops. In case of development of a bacterial lesion, antibacterial drugs are used. If you have tuberculosis, anti-tuberculosis drugs are used (for example, Isoniazid, Rifampicin, Ethambutol).
- Treatment of inflammatory processes. When inflammation occurs, glucocorticosteroids are used. The most commonly prescribed remedy is Prednisolone. In more complex and severe cases, immunosuppressants (eg, methotrexate) are prescribed.
- Chemotherapy. Similar means are used in the presence of malignant tumors. In this case, all drugs are injected into a specific body cavity (depending on the location of the tumor).
In addition to the main therapy, dietary food is prescribed, which must be adhered to until complete recovery.
In severe conditions, surgical intervention is performed. This method of treating monocytosis is used in the presence of tumor-like processes, as well as in the case of congenital forms of neutropenia. The technique allows you to completely get rid of the disease, but at the same time has a high risk of death.
The prognosis for a complete clinical cure directly depends on the pathology that led to an increase in monocytes in the blood. Thus, some childhood diseases caused by natural physiological causes do not require therapy and go away on their own. At the same time, there is no threat to the child's life.
However, in other cases (with congenital forms of neutropenia or cancer of the blood), the risks mortality rates are high enough, therefore, mandatory therapy and medical supervision are required.
An increase in the concentration of formed elements in the blood may be asymptomatic, therefore, it is necessary to periodically undergo such studies as a prophylaxis. The MID analysis will allow you to detect pathology in time and select the appropriate and timely treatment.
Blood MID video
Why are monocytes elevated in adults and children: