Content
- What is the proboscis reflex in newborns
- Norms for newborns and babies
- How to check the proboscis reflex
- When the reflex fades
- Can the reflex persist as the child grows up?
- Reasons for the preservation of the proboscis reflex
- What if the reflex does not disappear?
- Differential diagnosis
- Electroneuromyography (ENMG)
- Electroencephalography (EEG)
- Ultrasonic encephaloscopy (UES)
- Cranial nerve ultrasound
- MRI
- Treatment methods
- Medications
- A nicotinic acid
- Cerebrolysin
- Piracetam
- Surgery
- Proboscis reflex video
Proboscis reflex in newborns is included in the list of vital innate skills necessary for survival and rapid physical development. This physiological ability of the infant is oral automatism, which is activated in response to external stimulation of the surface of the upper or lower lip.
What is the proboscis reflex in newborns
The proboscis reflex in a newborn baby is an automatic reaction of the facial muscles and peripheral nerve endings in response to touching the surface of his lips. This skill is innate, and is also present in all healthy children without intrauterine developmental abnormalities, signs of local lesions of the central nervous system. The main task of the proboscis reflex in newborns is to prepare the mouth apparatus to capture the mother's nipple.

At the moment of contact of the surface of the baby's lips with the mammary glands, a reflex contraction of his circular muscle of the mouth occurs. The baby's upper and lower lips are folded together and then pulled forward in a "tube" or "proboscis" shape.
If, after completing these steps, continue the direction of the nipple towards the oral cavity of the newborn, then he will tightly capture his halo to receive breast milk. The proboscis reflex is necessary for an infant only in the early stages of physical development. This skill belongs to the category of transient oral automatisms that fade away as the child grows up.
Norms for newborns and babies
A sign of normal development of the facial muscles, central and peripheral nervous system of the child is his immediate response to an external stimulus in the skin of the upper or lower lip.
Too slow twisting of the lips into the "proboscis" indicates dysfunction on the part of certain centers of the brain, the consequences of cerebral palsy, birth trauma, asphyxia as a result of entanglement with the umbilical cord. The faster the proboscis reflex manifests itself in a newborn child, the better the interaction of the brain with peripheral nerve receptors and the circular muscle of the mouth.
How to check the proboscis reflex
The proboscis reflex in newborns is checked by a pediatrician during a routine examination of the infant to assess the general characteristics of his physical development.
The doctor of this specialization performs the following actions:
- Lays the child with his back on the flat surface of the couch.
- With a special hammer to diagnose reflex reactions, or touch the baby's upper lip with a finger.
- Visually observes the reactions of the oral apparatus of the newborn and the motor activity of his facial muscles.
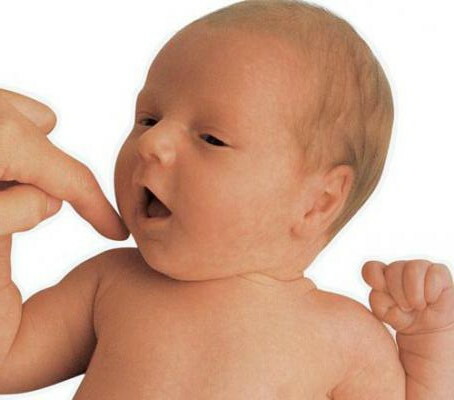
In a child with full development of the central nervous system, muscle tissue and peripheral nerves, the lips curl into a "tube" immediately after the doctor has performed the above manipulations. In children who have undergone difficult childbirth, cerebral hemorrhage, skull trauma, a violation of the speed of reproduction of the proboscis reflex, or its complete absence, is possible.
When the reflex fades
According to physiological norms, the independent extinction of the proboscis reflex should occur after the child reaches the age of 3 months.
Can the reflex persist as the child grows up?
In pediatrics, there are periodically clinical cases when the proboscis reflex persists in children after they have reached the age of 3 months. Such symptoms indicate the possible presence of severe neurological disorders, damage to the cerebral cortex or pathways of the spinal cord.
Child over 3 months with a preserved proboscis reflex should be examined by a pediatric neurologist. If necessary, an additional examination of the baby's body is carried out using hardware and laboratory tests.
Reasons for the preservation of the proboscis reflex
The proboscis reflex in newborns, which lasts longer than 3 months, indicates the presence of pyramidal signs.
These are pathological manifestations that arise under the influence of factors:
- insufficient development of the cerebral cortex;
- the consequences of spinal cord injuries;
- damage to certain areas of the central nervous system;
- dysfunction of the central motor neuron;
- cerebral palsy;
- epilepsy (violation of reflex automatisms is one of the harbingers of epileptic seizures);
- extraneous neoplasms in the brain or spinal cord (benign and oncological tumors can equally cause a similar symptom);
- local damage to the cerebral cortex caused by an infectious process, previously suffered skull injuries, the consequences of hypoxia.
Pathological reasons for the preservation of the proboscis reflex are determined by the results of a more detailed examination using differential diagnosis methods. Special attention is paid to the functional state of the cerebral cortex, peripheral nerves and spinal cord.
What if the reflex does not disappear?
The proboscis reflex in newborns, which does not disappear for more than 3 months, requires a study of the child's central nervous system. Parents of an infant should immediately seek medical attention from a neurologist.
Differential diagnosis
The purpose of the differential diagnosis of children with a preserved proboscis reflex is to detect pathological causes of dysfunction of the central nervous system, peripheral nerves or diseases of the spinal cord. The examination method is selected by a pediatric neurologist depending on the clinical case and the possible presence of additional symptoms of a neurological disorder.
The examination method is selected by a pediatric neurologist depending on the clinical case and the possible presence of additional symptoms of a neurological disorder.
Electroneuromyography (ENMG)
ENMG is aimed at determining the functional state of the nerve endings of the peripheral type, which are responsible for the mobility of the circular muscle of the child's oral cavity.
The examination allows for the differential diagnosis of pathologies:
- lesion of the anterior horns in the spinal cord;
- dysfunction of peripheral nerve endings;
- damage to the roots of the spinal cord.
The object of electroneuromyography is the peripheral nerves and muscular apparatus of the body. With the help of ENMG, the electrical impulses of the nerves are fixed, the degree of sensitivity of the muscle fibers that they innervate is determined.
Registration of the functional activity of peripheral nerves and muscles is carried out using electronic sensors attached to the surface of the skin. Before diagnostics, the child's epithelial tissues must be dry and clean. Electroneuromyography is contraindicated in children and adults who have a pacemaker or an electroneurostimulator of the brain. The average cost of ENMG is 3400 rubles.
Electroencephalography (EEG)
With the help of this research method, the electrical activity of all parts of the child's brain is recorded. Electroencephalography can detect neurological disorders that cause involuntary contraction of the circular muscle of the mouth with reproduction of the proboscis reflex. The main object of diagnostics is the cerebral cortex of the child.
The survey is carried out as follows:
- In the office for electroencephalography, special sensors are fixed on the surface of the child's cranium.
- The doctor turns on the diagnostic equipment, after which the process of reading the electrical activity of the patient's cerebral cortex is started.
- Information data is transmitted in digital format to a computer monitor in the form of a graphic bar, and is also recorded on the hard disk of this device.
EEG is a completely safe and painless diagnostic method, the average duration of which is 15-20 minutes.
Electroencephalography allows you to detect pathological conditions of the central nervous system that can cause the preservation of the proboscis reflex:
- encephalopathy of an infectious or metabolic nature of origin;
- focal damage to the cerebral cortex, accompanied by local degenerative changes in the tissues;
- tumor neoplasms in the central nervous system;
- hemorrhages in the brain, which are a consequence of a birth injury.
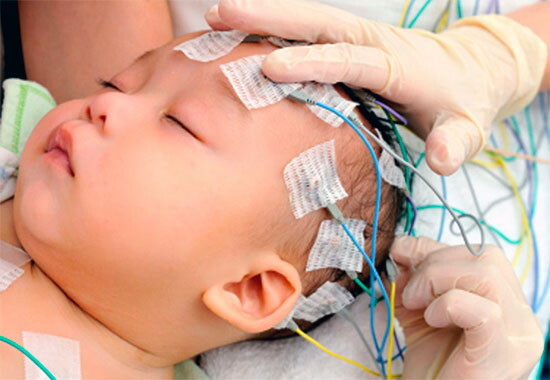 The EEG is carried out during the period when the child is in a state of calm. Then an additional load is created on individual centers of the brain. For example, photo-stimulation of the organ of vision is performed using short flashes of light. Electroencephalographic data are analyzed by a neuropathologist, and the average cost of this differential diagnosis method is 600 rubles.
The EEG is carried out during the period when the child is in a state of calm. Then an additional load is created on individual centers of the brain. For example, photo-stimulation of the organ of vision is performed using short flashes of light. Electroencephalographic data are analyzed by a neuropathologist, and the average cost of this differential diagnosis method is 600 rubles.
Ultrasonic encephaloscopy (UES)
The use of ultrasound encephaloscopy is indicated for children with a preserved proboscis reflex, who need to carry out additional examination of the anatomical structures of the cerebral cortex. With the help of this method of differential diagnosis, the neuropathologist checks the fact of the possible presence of volumetric extraneous neoplasms in the central nervous system of the child.
UES is also indicated for newborns with signs of intracranial hypertension, hemorrhages in the brain tissue, who have undergone hypoxia due to difficult childbirth or intrauterine developmental abnormalities.
For ultrasound encephaloscopy, special preparation rules are not required. This method of differential diagnosis is performed according to exactly the same principle as an electroencephalogram. A distinctive feature of this examination method is that the analytics of the structure of the brain is carried out not by fixing the electrical impulses of the central nervous system, but by scanning it with waves ultrasound. The price of UES in a private clinic is 2900 rubles.
Cranial nerve ultrasound
The proboscis reflex in newborns persists for more than 3 months only in the presence of a concomitant neurological disorder that disrupts the functions of the infant's nervous system. An ultrasound examination of the cranial nerves is indicated for patients who do not have signs of focal brain damage.
Analysis of the functional state of the peripheral nerves responsible for the innervation of the muscles of the triangle zone allows confirm or deny the fact of their defeat by infectious microorganisms, autoimmune or inflammatory process. This method of differential diagnosis is performed after electroneuromyography, when the likelihood of the growth of a brain tumor is excluded.
An ultrasound of the cranial nerves is performed to achieve the following goals:
- detect anatomical changes in the structure of peripheral nerves;
- determine the possible presence of congenital anomalies of the nervous system;
- assess nerve vascularization;
- diagnose tumors outside the central nervous system that compress nerve endings.
The advantage of the method of differential diagnosis in the form of ultrasound of the cranial nerves is its broader capabilities. With the help of this examination, pathological changes in the autonomic system of the child are determined, or the fact of an extensive neurological disease is confirmed. The average cost of an ultrasound of the cranial nerves is 1100 rubles.
MRI
This method of differential diagnosis allows you to simultaneously conduct a comprehensive examination of all parts of the child's body, as well as study the structure of the brain.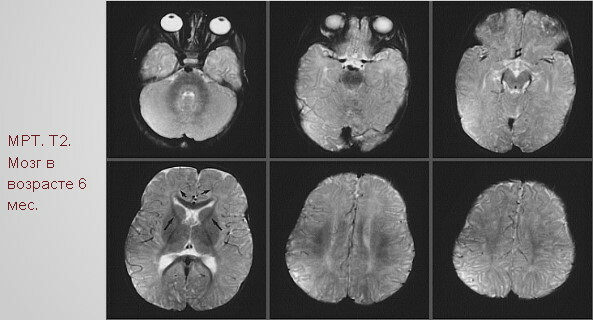
With the help of MRI, diseases and pathological conditions of the body are detected that can cause the persistence of the proboscis reflex:
- hemorrhage in the brain with the formation of a dense intracranial hematoma;
- benign and oncological tumors in the central nervous system or spinal cord;
- encephalopathy;
- consequences of traumatic brain injury;
- focal lesions of certain areas of the brain, which developed due to fetal hypoxia during difficult labor;
- bulbar syndrome;
- epilepsy;
- congenital or acquired vascular diseases that impair cerebral circulation;
- inflammatory lesion of peripheral nerves, which are responsible for the innervation of the muscles of the nasolabial triangle zone.
The interpretation of the results of MRI diagnostics is carried out by a neuropathologist, neurologist or surgeon. The advantage of this examination is that it is absolutely painless, it takes about 15-20 minutes, and during one session allows you to explore the peripheral and central nervous system. The price of this diagnostic method is about 3300 rubles.
Treatment methods
The treatment regimen for the proboscis reflex, which persisted for more than 3 months, is developed individually by a pediatric neuropathologist, depending on the diagnosed disease. Automated lip folding in response to external stimuli is just one symptom of a neurological disorder.
Medications
The use of drug therapy is aimed at treating acute, chronic diseases of the central nervous system and peripheral nerves, causing the persistence of the proboscis reflex. The table below lists drugs that are prescribed for patients with pathological proboscis reflex caused by focal brain lesions and epilepsy.
| Name of the medication | Pharmacological properties |
| Lamotrigine |
 Lamotrigine is a drug that belongs to the therapeutic group of sodium channel blockers. This tool prevents the release of excess amounts of the substance glutamate, and also prevents the emergence of an intracellular electrical signal, which causes dysfunction of certain areas Central nervous system. Lamotrigine is a drug that belongs to the therapeutic group of sodium channel blockers. This tool prevents the release of excess amounts of the substance glutamate, and also prevents the emergence of an intracellular electrical signal, which causes dysfunction of certain areas Central nervous system. |
| Carbamazepine | Carbamazepine is a drug that blocks the conductance of sodium channels located on the surface of a neuron. This medication prevents the propagation of an electrical signal that causes the central and peripheral nervous systems to malfunction. |
| Ethosuximide | Ethosuximide is a drug that prevents the spread of pathological impulses in the structure of the brain by blocking calcium channels. |
The above drugs are prescribed by a neurologist or neuropathologist, depending on the clinical manifestations of the neurological disorder. The dosage regimen and the timing of therapy are selected individually.
A nicotinic acid
Nicotinic acid is a vitamin preparation that comes in the form of an injection solution with a dosage of 10 mg per 1 ml of medicine. This medication prevents the progression of degenerative changes in the structure of the brain, has vasodilator and antispasmodic effect, has a beneficial effect on the functions of the central nervous system and peripheral nervous systems. Nicotinic acid is administered intramuscularly, subcutaneously or intravenously, 1 ml 2 to 3 times a day. The average cost of the drug is from 36 to 72 rubles.
Cerebrolysin
Cerebrolysin is a nootropic agent that helps restore normal brain function. This medication is available in the form of a liquid concentrate for injection.
The dosage of Cerebrolysin is determined individually, depending on the general condition of the patient, but on average is in the range from 5 to 50 ml. In the process of treating children of the younger age group, a nootropic agent of this type is prescribed in an amount of 0.1-0.2 ml per 1 kg of the child's body weight. The price of 5 ampoules of Cerebrolysin is from 860 to 1048 rubles.
Piracetam
Piracetam is a nootropic drug that comes in the form of yellow capsules. This tool allows you to get rid of neurological disorders caused by vascular diseases of the central nervous system, circulatory disorders in the tissues of the brain, traumatic brain injury and severe intoxication organism.
The dosage regimen for this medication is 1 capsule up to 3 times a day. The duration of the therapeutic course is 2 weeks. The average cost of the drug Piracetam is from 131 rubles. for 60 capsules.
Surgery
Surgery is a radical therapy that is used only in extreme cases. For example, if the persistence or sudden appearance of the proboscis reflex is caused by extraneous neoplasms in the structure of the brain. In such a situation, it is possible to remove the tumor, which disrupts the stable functioning of the central nervous system.
Surgical operation is performed for benign and oncological neoplasms, but only in the absence of medical contraindications. Clinical cases are common when brain tumors are inoperable, and potential surgical intervention will only cause an exacerbation of neurological symptoms.
Surgical operation to remove a tumor in the central nervous system is carried out under the influence of general anesthesia in compliance with the algorithm of actions:
- The patient is transported on a gurney to the sterile conditions of the operating room.
- The patient receives general anesthesia.
- The surgeon treats the skin surface of the patient's head, dissects the epithelial tissue with a scalpel, and then opens the cranial vault to provide access to an extraneous neoplasm.
- With the help of surgical instruments, a benign or cancerous tumor causing the proboscis reflex is removed.
- Medical manipulations are carried out to restore the integrity of the cranium.
Upon completion of the surgical operation, the patient is transferred to the intensive care unit for 3 days, where 24-hour monitoring of his vital signs is carried out. Average terms of rehabilitation after removal of a brain tumor are 1-2 months, depending on the type of extraneous neoplasm, its size and localization in the structure of the central nervous system.
The proboscis reflex in newborns is one of the innate automatisms required to quickly find and capture the mother's breast. This skill is retained in a child for the first 3 months after birth. After a specified period of time, there is a gradual extinction of the proboscis reflex with complete disappearance.
The persistence of this innate automatism indicates a number of severe neurological pathologies. Birth trauma to the skull, tumor neoplasms, encephalopathy, focal lesions of the cerebral cortex can cause similar symptoms. Treatment of diseases of the central nervous system and peripheral nerves is carried out with the use of nootropic drugs, blockers of sodium and calcium channels.
Proboscis reflex video
Reflexes of newborns:



