The endocrine system controls most of the processes that occur in the human body. It is the most important regulatory system. Any failure in the performance of glands of internal secretion will inevitably affect the functioning of the whole organism. Part of the endocrine system is the thyroid gland, which participates in the processes of regulation of metabolism and growth of both individual cells and the whole organism.
This gland is located on the neck in the Adam's apple region. It affects the performance of almost all human organs. Therefore, any pathological changes in the thyroid gland inevitably lead to a number of diseases. To identify them, there are different methods of research. However, the most accurate diagnosis of the working capacity of the thyroid gland allows the analysis of blood on hormones - TTG, T3 and T4.
Thyroid hormones
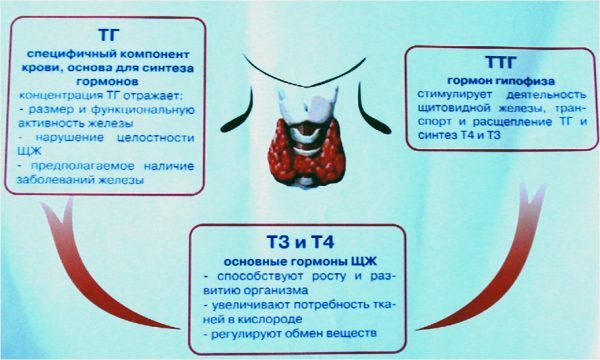
Thyroid stimulating hormone is produced by the pituitary gland, a cerebral appendage, which is a small endocrine gland. Located in the lower part of the brain, the pituitary gland controls not only the thyroid gland, but the rest of the endocrine organs.
Pituitary cells produce TSH with a decrease in the content of hormones T3 and T4.When taking the analysis, the indicator of the amount of antibodies to thyreperoxidase( TPO) is also considered. TTG together with blood circulating through the veins is delivered from the pituitary gland to the thyroid gland, where its interaction with surface receptor cells occurs. When they come into contact, the hormone T3 or T4 is accelerated, and the growth of the tissues of the thyroid gland can also increase. With any endocrine disease, it is necessary to take an analysis for thyroid-stimulating hormones. Their normal blood content, the same for both men and women, indicates the proper functioning of the system that regulates the activity of internal organs.
Hormones T3 and T4 perform the function of managing energy metabolism, which occurs in the body constantly, even at rest. Control over the production of these biologically active substances carries out a thyroid-stimulating hormone.
T4 is called thyroxine, the main product of thyroid synthesis. Its amount is 90% of the total supply of the body with hormones. Four points to the number of iodine atoms in its structure. T3 or triiodothyronine for 90% of its total amount is produced in human tissues through a chemical reaction at which the "detachment" of one iodine atom from thyroxine occurs. As a result, T3 becomes 10 times more active than T4.
Disorders of the hormonal background
Thyroid hormone production produces imperceptibly, but this process is very important for the working capacity of the whole organism as a whole. These biologically active substances in the blood test results may be in excess or in insufficient quantity relative to the norm. Signs of hyperthyroidism - an excess of hormones, are as follows:
- An unstable emotional state, in which hands are shaking, irritability and nervousness appear.
- The body temperature rises, which causes sweating, worried about fever.
- Insomnia is increasing.
- The man is losing weight.
- There are violations of the rhythms of cardiac activity.
In this blood test reveals a high content of triiodothyronine and thyroxine, and the presence of TSH is decreased.
Therapy should be performed before the normalization of the hormonal level. Cure can be achieved by the use of tablets, but sometimes there is a need for radical methods of treatment - surgery. In some cases, radioactive iodine is used for treatment.
When the body is inadequately supplied with hormones( hypothyroidism), the following symptoms appear:
- decreases appetite, but at the same time, the total weight gain occurs,
- appears apathy and depression develops,
- decreases efficiency,
- develops edema,
- in women has a menstrual cycle,pregnancy,
- in men there is a decrease in potency,
- there is a deterioration in the condition of both the skin surface, and nails and hair,
- bothers feelingColdness, chilliness.
In hypothyroidism, it is necessary to determine not only hormones, but also antibodies to thyroid peroxidase. Their testing is mandatory when suspicion of a decrease in the activity of the thyroid gland.
In women, problems with hormones are a complicating factor for pregnancy. When planning it, taking the test for the definition of TTG is mandatory. In the course of pregnancy, this indicator should be monitored periodically.
In children, the rate of development of the brain and the entire nervous system is provided by thyroid hormones. In some families, parents have problems with the functioning of the thyroid gland. To exclude the hereditary factor, the norm of TSH and thyroxin should be periodically determined in such children by taking a blood test.
Conducting the

test There are indications in which a blood test for TSH is prescribed:
- diagnosis of infertility of women and control with its therapy,
- for evaluation of gland functionality,
- diagnosis in newborn children of thyroid function,
- confirmation of the diagnosis of hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism andtheir treatment,
- control in the therapy of thyroid pathologies.
In order to conduct a study of the health of the thyroid gland, venous blood is drawn from the ulnar vein. To obtain the most correct and accurate result, it is necessary to fulfill the following rules:
- The use of alcohol, caffeine and tobacco is prohibited the day before the test.
- In the diet, avoid using heavy food - spicy, spicy, fatty, fried.
- In the previous 12 hours, do not do heavy physical work and avoid emotional stress.
- Blood delivery is performed on an empty stomach. You can drink mineral water without gases.
- A month before the study, the attending physician can cancel taking medications that affect the hormonal background. In particular, for women - hormonal contraceptives.
- It is recommended to exclude iodine and products containing it, for example, iodized salt, sea kale, several days before the test.
Norm of hormones during pregnancy
In pregnancy, the TSH may decrease due to the physiological characteristics of the processes in the body. Therefore, the reduced level of this hormone can not be considered a pathology. Against the background of pregnancy, a strong fraction is given to the free fraction of thyroxin. It becomes the main indicator of the norm or pathology when bearing a child. Decoding of the blood test, indicating a decrease in TSH and an increase in thyroxine - a normal option in pregnancy. This is not a pathology. However, the simultaneous increase in T4 and T3 in significant limits requires the endocrinologist to take urgent measures to bring the indicators to normal.

| Age, years | Norm TTG, μIU / mL |
| 1-6 | 0.6-5.95 |
| 7-11 | 0.5-4.83 |
| 12-18 | 0.5-4.2 |
| Over 20 | 0,26-4,1 |
| In pregnancy | 0,20-4,50 |
The table below is for the possibility of determining the norm of thyroxin, both general and free. Most of the T4 is circulating, it is bound by transport proteins for transport throughout the body. The change in the concentration of total thyroxin leads to a change in the level of transport proteins. In this case, the free thyroxine remains at approximately the same level. According to the analysis, a transcript is made, according to which it is possible to determine any deviations from the normal activity of the organ.
| T4( thyroxine) total, norm | ||
| Age, years | nmol / l | μg / dL |
| For children | 1-6 | 5.95 - 14.7 |
| 5-10 | 68 - 139 | 5.99 - 13, |
| 10-18 | 58 - 133 | 5.91 - 13.2 |
| For men | 20-39 years | 5.57 - 9.69 |
| Older than 40 | 5,32-10,00 | |
| For women | 20-39 | 5.92-12.9 |
| Over 40 | 4.93-12.2 | |
| In pregnancy | 7.33-16.1 |

| T4( thyroxine) free, norm | |
| pmol / l | ng / dL |
| For children5 - 14 years | 8-17 |
| For children over 14 years old | 9-22 |
| Adults | |
| For man | 0,8-2,1 |
| For females | 0,8-2,1 |
| In pregnancy | 0,5-2,0 |
The interpretation of the result includes the presence of such indicators:
- of triiodothyronine total and free,
- of total and free thyroxin,
- thyroid stimulating hormone,
- antibodies to thyroxine peroxidase and thyroglobulin,
- calcitonin.
| Name | Normal indices |
| Calcitonin | 13.3-28.3 mg / l |
| Antibodies to thyroperoxidase | & lt;5.6 Units / ml |
| Antibodies to thyroglobulin | 0-40 IU / mL |
In the entire endocrine system of man, the largest organ is the thyroid gland, while its weight is only 15-20 grams. It produces iodinated hormones T4 and T3, which together with TSH, synthesized by the pituitary gland, regulate the metabolic processes in the body.