Problems with the digestive tract cause great discomfort and reduce the quality of life. One of the reasons for such pathologies is the presence in the organs responsible for digestion, Helicobacter pylori. Blood tests for the presence of a microorganism help the gastroenterologist to make an accurate diagnosis, as well as to prescribe an effective treatment.
Record content:
-
1 What is Helicobacter pylori
- 1.1 Pathophysiology
-
2 Features of infection
- 2.1 Children
-
3 Varieties of analysis
- 3.1 Linked immunosorbent assay
- 3.2 Western blot method
- 4 Why is
- 5 Indications
-
6 Preparation and implementation
- 6.1 What affects the result
- 6.2 How to donate biomaterial
- 7 Decoding
- 8 Advantages and disadvantages of the methods
- 9 Where to check in and the cost
- 10 Video about Helicobacter pylori
What is Helicobacter pylori
A blood test for Helicobacter pylori is part of the mandatory procedures for examination by gastroenterologists. The reason for this lies in the fact that Helicobacter pylori is a common microorganism, causing local inflammation of the mucous membranes, ulcerative lesions of this organ, adenocarcinoma, and lymphoma.
Refers to gram-negative microorganisms. Dies upon direct contact with oxygen. The bacterium is spiral-shaped and produces a large amount of toxins that damage the inner surfaces of the intestines and stomach. These organs suffer most from this harmful organism.
A feature of the bacterium is that in 90% of its carriers, it is one of the components of the microflora, without causing an infectious disease. However, with a decrease in immune defense for one reason or another, this particular bacterium is the most dangerous.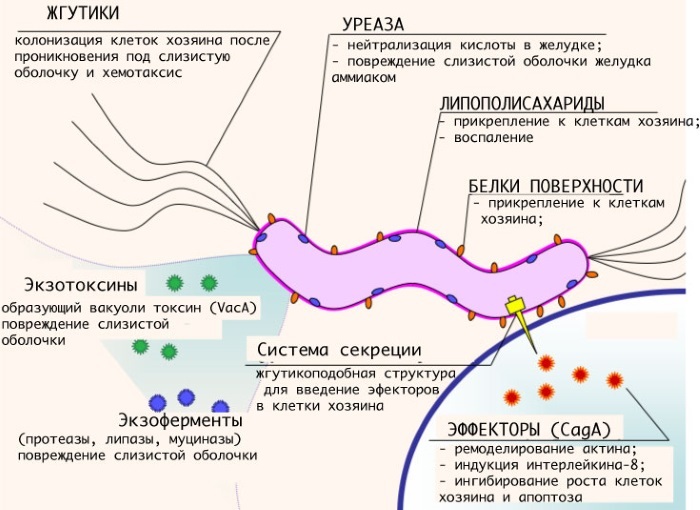
Helicobacter provokes diseases that until recently were considered genetically determined. Poor quality and poor nutrition was considered one of the main reasons for their appearance. However, scientific and clinical studies have proven that gastritis and peptic ulcer disease are provoked by the activity of this particular microorganism.
It is noteworthy that if the majority of pathogenic microbes die in the hydrochloric acid of gastric juice, then it is just for Helicobacter that it is ideal for existence and development. Over the centuries, the bacterium has adapted to the conditions of life in the stomach and has flagella specially adapted for movement.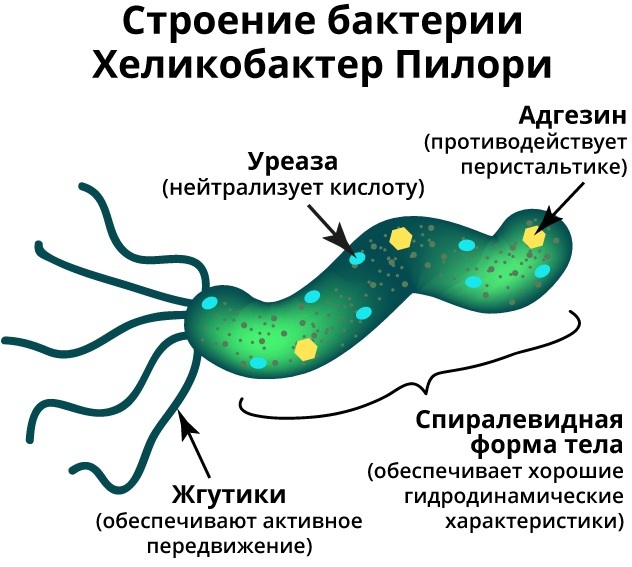
The microorganism is transmitted by the oral or fecal-oral route. It is believed that nurses are at increased risk because the bacteria can be transmitted through poorly sterilized endoscopes. It is assumed that the colonization of humans by this bacterium occurred a very long time ago.
The resistance of Helicobacter to an aggressive gastric environment, the immune system, suggests that it is adapted to life in the stomach for decades. This is why some doctors view the organism as a symbiote.
Changes in the external environment, stress, smoking, alcohol change the internal structures of the microorganism, leading to mutations.
Helicobacter is also a clinically important pathogen that is responsible for a significant proportion of morbidity and mortality worldwide. The prevalence of Helicobacter in our country is extremely wide. In various regions, from 65 to 92% of the population is infected. This fact is due to a low standard of living, bad habits, violation of the simplest hygiene rules.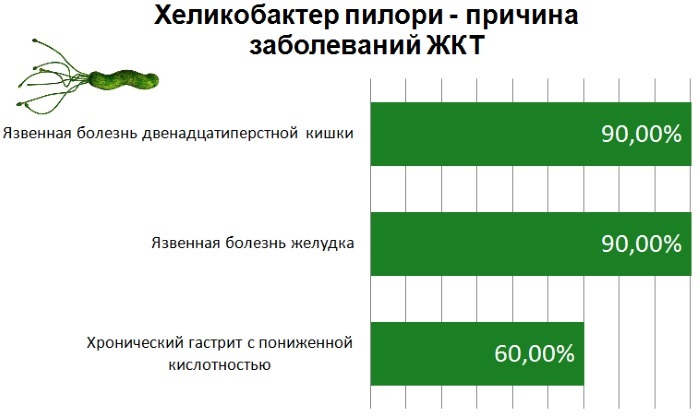
For research, Heliobacter B. Marshal and R. Warren were awarded the Nobel Prize. They also refuted the existing point of view that an ulcer or gastritis is provoked by stress, spicy food and high acidity. Interestingly, to prove the ability of Helicobacter to provoke the development of gastric ulcer, B. Marshall took in her culture.
The scientist developed acute gastritis, which went into remission without therapeutic intervention. This fact finally proved that it is the bacterium in question that is the root cause of the progression of gastritis and peptic ulcer diseases.
In 1994 g. WHO has recognized the link between the presence of Helicobacter and gastric carcinoma. It began to be attributed to carcinogenic organisms of the first hazard class.
Pathophysiology
With infection of the predominantly antrum, the production of gastrin increases. This provokes the development of duodenal ulcers. Inside the stomach, the bacteria synthesize urease. This substance irritates the mucous membranes of the human digestive tract.
In the presence of urease, the gastric mucosa begins to produce a large amount of hydrochloric acid. It begins to eat away at the walls of the stomach and intestines. The organs signal from this painful sensations. If the immune system cannot cope with the activity of Helicobacter, an ulcer or gastritis develops.
When infection is predominantly of the stomach, atrophic gastritis develops. The ammonia produced by Helicobacter pylori disrupts the integrity of the mucous membranes and neutralizes the action of the components of the gastric juice. Cytotoxins, some enzymes contribute to the development of ulcerogenesis.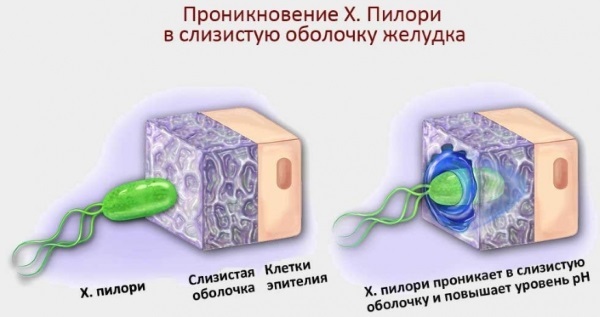
In persons infected with Helicobacter, stomach cancer develops several times more often. The risk of cancer is significantly increased due to the presence of a large number of long-term non-healing ulcers and erosions on the mucous membrane.
The bacterium is capable of releasing strong toxins that cause inflammation of the stomach lining and its rejection. In some cases, the microorganism provokes a decrease in the synthesis of gastric juice. This leads to atrophy of the gastric mucosa.
Features of infection
The bacterium is transmitted through contact with an infected person. Using the same utensil leads to the fact that family members become infected with the same type of bacteria. Dirty hands, saliva, phlegm that is released during coughing become sources of infection.
Children
Helicobacter is excreted in feces and passes into coccal forms. In this form, it can persist for quite a long time. The microorganism enters the body through objects and dirty hands. A child can become infected in cases of eating with unwashed hands or licking surrounding objects.
This method of transmission is often manifested precisely in children, because they often taste the surrounding objects.
Children can contract the bacteria through contact with animals, especially cats.
Sometimes there may be cases of improper handling of the nipple for feeding. Helicobacter also enters the child's body with breast milk. Then the bacterium gets the opportunity for rapid development.
The child can also become infected through kissing. In a small amount, the microbe is found on the oral mucosa. The risk of infection increases significantly if parents themselves do not comply with basic hygiene requirements.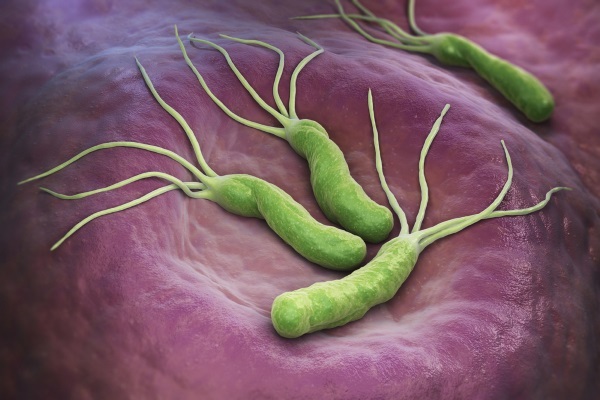
A blood test for babies born to mothers with bacteria in their bodies detects the presence of specific antibodies in the blood. At the same time, there are no symptoms of the disease in the baby. Stool tests also show the absence of bacteria.
A short time after birth, the level of antibodies to Helicobacter decreases. This suggests that immunoglobulins can be passed on to the child from the mother.
Varieties of analysis
A blood test for Helicobacter pylori is carried out in two ways:
Linked immunosorbent assay
An antigen to a bacterium causes a specific immune response. In doing so, it produces antibodies called immunoglobulins. It is a highly accurate and high quality analytical method. For the biomaterial, venous blood is taken.
Such an analysis can be prescribed as a preventive study for all persons who had household contacts with people suffering from pathologies of the digestive tract.
Western blot method
The examination is prescribed in cases of detection of immunoglobulins to the pathogen in the plasma. The test results give detailed information about the presence of antibodies in the blood. 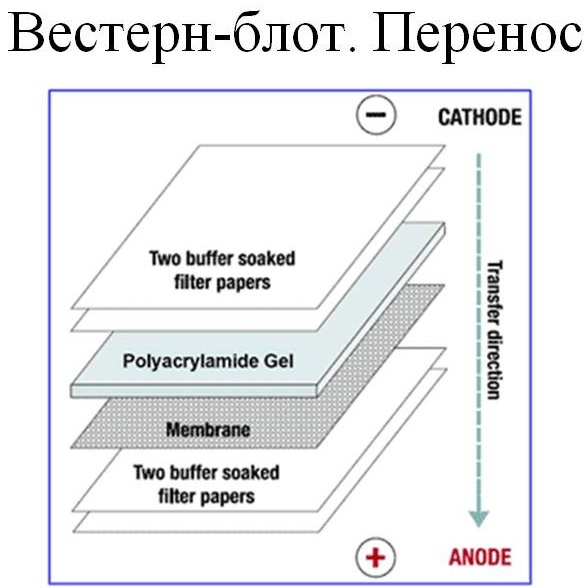 High accuracy of the examination can be achieved by electrophoresis: this separates the proteins of the extract of the microorganism. For biological material, venous blood is taken.
High accuracy of the examination can be achieved by electrophoresis: this separates the proteins of the extract of the microorganism. For biological material, venous blood is taken.
Why is
A blood test must be performed to determine if the patient has antibodies to Helicobacter pylori. In this case, it is not the pathogen itself that is determined, but the presence of immune cells.
They are produced by plasma cells from B-lymphocytes. In laboratory tests, they are found on the surface of lymphocytes and in serum. In the case of Helicobacter, the presence of IgG, IgM, IgA globulins is taken into account.
In analytics, normal readings are not taken into account. The purpose of a laboratory test is to detect the presence of antibodies. The presence of immunoglobulins indicates the presence of Helicobacter. When immunoglobulins are not detected, it is assumed that there is no infection.
Indications
A blood test for Helicobacter pylori is indicated if:
- pain syndrome manifested after the end of meals;
- periodic belching;
- a feeling of heaviness in the epigastric region, even from a snack;
- manifestation of heartburn;
- Difficulty swallowing food when the patient feels the movement of food through the esophagus;
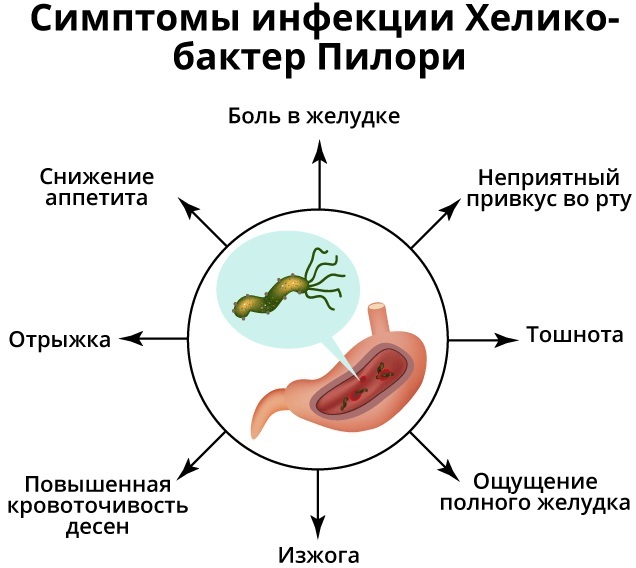
- increased formation of intestinal gas;
- frequent nausea;
- vomit;
- putrid breath;
- alternating diarrhea and constipation;
- violation of appetite;
- unexplained weight loss;
- the appearance of blood, mucus in the vomit and feces;
- the appearance of a small rash on the skin of the face in the form of pink or white pimples;
- the development of dermatitis, eczema, lichen or erythema.
Even mild pains in the stomach area cannot be ignored. In most cases, they signal an onset of the disease.
In children, it is necessary to pay close attention to the characteristic symptoms:
- severe bloating;
- regurgitation;
- crying while pulling up the legs;
- diarrhea or constipation.
In children, the severity of the symptoms of Helicobacter infection is higher than in the adult contingent.
Preparation and implementation
A blood test for Helicobacter pylori provides for the determination of the presence of immunoglobulins in the serum. They are produced as a result of the activity of immune factors that have reacted to the appearance of a pathogenic organism.
Antibodies can be detected by reactions produced. The doctor means that it takes some time (at least a week) for antibodies to form. During this time, an immune response appears to the appearance of pathogens.
To obtain accurate indicators of the analysis, it is necessary to prepare in advance for its delivery.
The patient needs to follow these recommendations:
- 2-3 days before the diagnosis, you must completely abandon alcoholic beverages, including beer;
- the day before the sampling of the biomaterial, it is necessary to limit, or even better, give up heavy physical work and from training in the gym;
- 8 hours before the examination, it is forbidden to eat (you can only drink clean water without gas), and a light dinner is allowed no later than 22 hours;
- on the day of analysis, you must give up cigarettes;
- blood sampling should be carried out in the morning before the first meals;
- before taking the biomaterial, it is forbidden to take all dosage forms (if for any reason it is impossible to refuse medications, then you need to inform the doctor about this).
The analysis shows a false positive result if the listed recommendations are violated. It also happens if not enough time has passed after the infection of the body.
What affects the result
In some patients, the rate of response is markedly reduced. It will take longer to produce immunoglobulins. Certain problems also occur in people with reduced immunity and often sick children.
A false negative result is common in individuals who have been taking immunosuppressive drugs for a long time. They contribute to a decrease in the activity of the immune system, which is why the main titers
How to donate biomaterial
The sampling of biomaterial is carried out in laboratories in a standard way (from a vein). If you have any special reactions to the collection procedure, you should inform the procedural nurse about this.
Decoding
When decoding ELISA, the features of the course of pathological processes are specified and therapeutic methods are selected. Interpretation is carried out by a doctor who knows how to determine the characteristics of immunoglobulins.
Normally, IgG is completely absent, or its titer will be below 1: 5. A titer of 1:20 indicates a positive result. Normally, immunoglobulins of classes A and M should also not be present, or they are observed in insignificant quantities. This factor has no significant diagnostic value.
In cases of positive test results, the pathogen is present. After two weeks after infection, M. proteins are found. If there are suspicions of the development of oncological problems, other examinations are recommended.
If a patient has immunoglobulins in the blood during the initial treatment, this is a symptom of acute inflammation of the gastric wall or the presence of a pathogenic bacterium.
Negative test results appear after successful antibiotic therapy or in the absence of pathogenic bacteria activity. Sometimes this result appears in cases of recent infection.
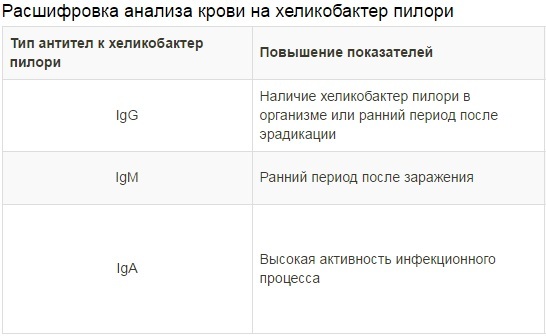
The values of the detected immunoglobulins are as follows:
- It confirms the fact of infection with the bacteria. Immunoglobulins of this type are most often detected 1 to 3 weeks after the entry of pathogenic microbes into the digestive system. IgG persists throughout the disease, as well as a certain period after it.
- IgM are rarely found in the blood, since usually the tests are carried out against the background of severe pain.
- IgA speaks of an early onset of pathology. Infection in humans has occurred, but the disease has a latent course.
Advantages and disadvantages of the methods
Advantages:
- effectiveness (ELISA gives a result accuracy of 95%);
- allows early detection of bacteria;
- makes it possible to assess the pathology in dynamics and monitor the effectiveness of therapy;
- safety (surveys can be carried out repeatedly);
- availability.
There are also disadvantages to this analysis:
- the doctor cannot determine the infection from the initial days of the disease;
- the examination will show only the presence of antibodies, and not the pathogen itself;
- when a microbe enters the body for the first time, the analysis is falsely negative, which significantly complicates the diagnosis;
- a false positive result also occurs after the patient is cured.
Where to check in and the cost
The analysis for Helicobacter pylori is done in state clinics (both in hospitals and in polyclinics), diagnostic centers and private clinics.
The cost of the survey differs slightly depending on the region:
| Region | Research price (rub.) | Note |
| Moscow | 600-1100 | Available in all private clinics. |
| S.-Pb. | 500-890 | In some centers, the cost of collecting biomaterial may be additionally paid. |
| Ekaterinburg | 430-1000 | |
| Chelyabinsk | 520-850 | |
| Ufa | 490-800 | |
| Vladivostok | 480-870 |
It is highly likely to detect Helicobacter only with the help of a blood test. The result is achieved with high reliability and accuracy, and also allows for a differentiated approach to the choice of therapeutic techniques.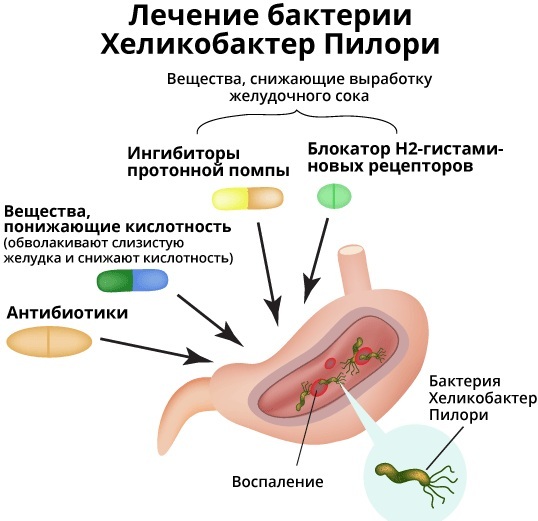
The decision to eradicate the pathogen is made by gastroenterologists based on test data and anamnesis. It can be removed with antibiotic therapy. Eradication is not delayed when a patient is diagnosed with an ulcer of any section or acute inflammation of the mucous membranes of the digestive system.
Blood tests for the presence of a microorganism are an effective way to diagnose diseases of the digestive tract. If Helicobacter pylori does not cause complications to a person, does not cause ulcers or gastritis, you should not take measures for eradication pest, since modern antibiotics can cause more harm than the presence in the microflora of this symbiont.
Video about Helicobacter pylori
What is it and how to treat Helicobacter pylori:



