The most effective way of transporting drugs into the human body is parenteral administration. In this case, the funds used go directly into the bloodstream, bypassing gastrointestinal tract. This method allows you to achieve a quick and lasting result, which is especially important in the provision of urgent medical care.
Record content:
- 1 Definition
- 2 Advantages and Disadvantages of Medicines
- 3 How are absorbed and distributed
-
4 Methods of administration
- 4.1 Intravenous administration
- 4.2 Subcutaneous administration
- 4.3 Intra-arterial administration
- 4.4 Intrathecal administration
- 4.5 Intramuscular injection
- 5 Preparation and Precautions
- 6 Video about parenteral routes of drug administration
Definition
The parenteral route of drug administration is a technique for transporting drugs, vaccines, as well as other immunobiological agents, which allows the substance to bypass the gastrointestinal tract person.
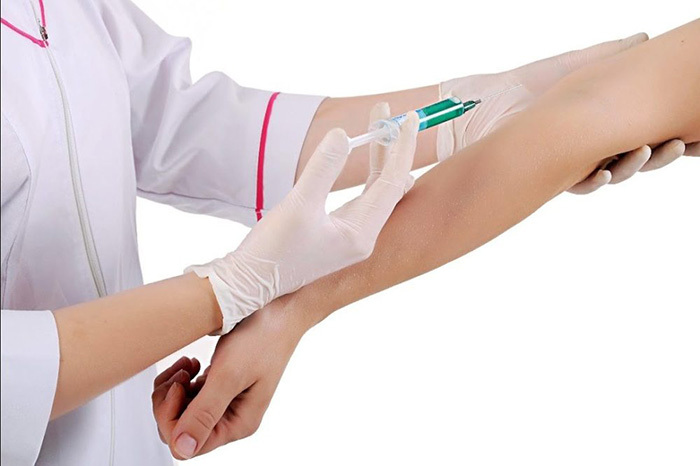
This type of administration always takes place with a violation of the general integrity of the skin, venous or vascular integuments. In some cases, the term can be used as an injection of a filtered substance to diagnose basic pathological processes in the body.
The parenteral route of administration is used much less often than the enteral route, which is explained by a significant reduction in side effects and complications during its implementation. It is often used when the patient requires urgent medical attention, as well as in the presence of individual characteristics of the body.
This route of drug administration provides the most stable biological filtration. medicinal substance, which is possible due to its passage through the capillary walls and cell membranes. It is the only way to deliver oil solutions to the human body.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Medicines
The parenteral route of drug administration has a number of advantages that prevail over the oral route.
The main advantages taken into account in medical practice:
- Treatment of unconscious patients. It becomes possible to administer the drug using special techniques, while the function of the method does not require any reactions or movements from the patient. It is the main advantage that makes it possible to save a person's life.
- Provision of timely medical care to patients whose symptoms include severe vomiting and other pathological manifestations in the digestive system. In this case, the parenteral administration method allows the use of drugs without the risk of rejection.
- Improving the bioavailability of the main components of the drug type of treatment, that is, increasing the digestibility of the drug with a low physiological ability in humans. It makes it possible to increase the absorption of the active substance, due to which the desired effect occurs much faster. At the same time, there are no characteristic side symptoms, because in this case the human gastrointestinal tract is not affected.
- An increase in the rate of onset of the therapeutic effect due to the biochemical characteristics of parenteral administration. It is especially important in the presence of a critical condition of the patient or those pathological processes that require rapid removal of symptoms.
- The possibility of using those types of drugs that are poorly absorbed when the active substance is in the stomach or intestines. In addition, the parenteral route is well suited for reducing the effects of stomach acids and enzymes that adversely affect the effectiveness of treatment.
- The lack of dependence of the diffusion rate due to large porous structures in human membrane tissues, including endothelial cells. Allows to reduce the time for a course of treatment without reducing the cumulative effect.
- The possibility of assimilation of the main substance of the drug to the full extent, without the harmful effects of such factors such as the time of the last meal and exposure to various fermented structures or bile in the gastrointestinal tract person.
- Refers to an integral part of the therapeutic effect in the case of severe inflammatory processes in the kidneys or liver. This makes it possible to avoid various complications when taking the drug orally.

Also, one of the most important indicators, which refers to the advantages of parenteral administration, is the possibility of using an active substance of peptide or protein structure.
The parenteral route of administration of drugs is characterized by frequent use in the provision of urgent medical care, which increases the chances of a quick recovery and the absence of negative symptoms in further.
In addition to the above advantages, the parenteral method has various disadvantages, the main of which is the presence physiological complications after the procedure: abscesses, necrosis or allergic reactions to an individual stimulus.
The use of substandard or non-sterile instruments during the procedure increases risks of contracting various infectious or autoimmune diseases, in particular hepatitis and HIV.
Often, the parenteral route of administration can lead to endophlibitis, a special form of inflammation that occurs in the veins.
Based on statistical data, persistent allergic reactions with the parenteral method develop much more often than with the standard method of taking medications. Therefore, the most severe contraindication to the use of technology is the presence of tolerance to a certain substance.
A secondary complication is oil or air embolism, in which a certain amount of air can enter the walls of the blood vessels. This process can contribute to the development of thrombosis or strokes. Frequent insulin injections in diabetes mellitus can lead to atrophy.
A relative disadvantage of this method of application is that the patient is not able to independently inject the desired drug, therefore, he must contact a specialized medical institution. This can become the main factor in the development of complications in the case when an urgent intake of a certain substance is required.

Also, the use of parenteral administration is impossible if the patient has a state of shock due to disturbances in the blood circulation. In addition, this procedure is quite painful.
How are absorbed and distributed
The distribution of medicinal substances is the transition of a drug from the bloodstream to the organs and tissues of the body. Most of the drugs used can be unevenly distributed, which significantly reduces the effectiveness of treatment.
The distribution process is influenced by numerous factors, the most important of which are:
| Cause | Description |
| Solubility in lipids and water | Medicines of the hydrophilic type have a low molecular weight, therefore, although they are able to pass in the area of extracellular barriers, they cannot penetrate through the membrane structure. At the same time, lipophilic drugs spread relatively easily through the tissues of the body. Substances that do not dissolve in water and fats penetrate into the cellular structure based on the function of the transmembrane system. |
| Indicator of binding to protein structures | When it enters the bloodstream, the drug is in it based on 2 fractions: bound and free. Since proteins cannot interact with receptors or enzymes, this in some cases makes it difficult to transport. A decrease in the binding function leads to an increase in the quantitative indicator of the free fraction, by 15-20% of the total level. |
| Features of blood flow | After the drug enters the circulatory system, it first reaches the tissues and organs that are best supplied with blood - the kidneys, lungs, liver and heart. |
| Presence of a biological barrier | It can be encountered in the distribution of certain types of drugs. In this case, the introduction of the substance is interfered with by the walls of the capillaries, plasma-type membranes, as well as the blood-brain barrier or BBB. |
The absorption of the substance used, first of all, depends on the technique of its administration and physicochemical characteristics. The dosage form can also affect the indicator.
Carrying out parenteral transport by injection allows you to achieve the greatest absorption, in contrast to tablets or drops.
Methods of administration
The parenteral route of administration of drugs is characterized by the presence of varieties that differ based on the localization and the injection site through which the active substance enters blood flow.
The drug is administered subcutaneously, intradermally, and intramuscularly. The latter option involves the ingress of the active substance into the blood and lymphatic vessels. In addition, the drug can be administered intraosseously, which is carried out if it is impossible to use other methods.
A separate type of administration involves the use of intravenous injections, - directly into the vascular tissue of a person. This use is indicated in patients who need to avoid the passage of a substance through the kidneys and liver.
In some cases, it is possible to inject the drug into the pleural, articular or abdominal cavity.
Specific routes of administration using the parenteral route:
- Intranasal. Through the human nasal cavity.
- Intrathecal or epidural. Directly into the cerebrospinal fluid.
- Intratracheal or inhalation. A rare technique in which a substance is introduced into the body by inhaling medicinal components using an inhaler.
- Subconjunctive. In the case of local therapy of pathological processes of the eye, with the help of the conjunctiva itself.
- Transdermal. The introduction of the components of the substance through the skin.
The above specific varieties are used relatively rarely, in the presence of any contraindications or possible complications associated with the administration of the drug. Separate techniques allow the body to receive the required substance in a specific area of the body, which will speed up the absorption process.
Intravenous administration
Preparatory measures for intravenous administration of a substance are characterized by actions that typical of sanitary recommendations - disinfection and washing of the doctor's hands, including sterilization of the syringe needle and gloves. The prepared instrument is preliminarily placed in a sterile vessel.
After that, the injection itself is performed, which implies the following actions:
- Placing the patient's hand on a fixed and solid surface.
- Finding the correct vein for injection through a medical examination.
- A tourniquet is applied to one third of the shoulders, after which the patient clenches and unclenches his fist for better visibility of the vein walls. It should also be felt well.
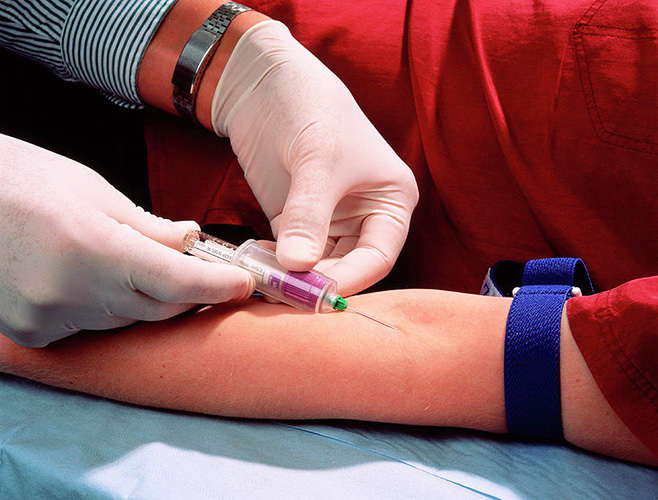
Intravenous injection is done on the basis of a clear sequence of actions. Taking into account the method of application and the main indications, the rate of introduction of the substance may change.
The main algorithm includes:
- Treatment of the intended injection site and nearby skin with a previously moistened cotton swab with alcohol or any other disinfectant.
- Removing the protective cap from the needle. The syringe itself is located in the right hand, while the cannula is fixed with the index finger. Using the left hand, the doctor grasps the patient's forearm, and the thumb stretches the skin layer while simultaneously fixing the vein. Before the direct injection of the substance, the patient clenches his fist tightly.
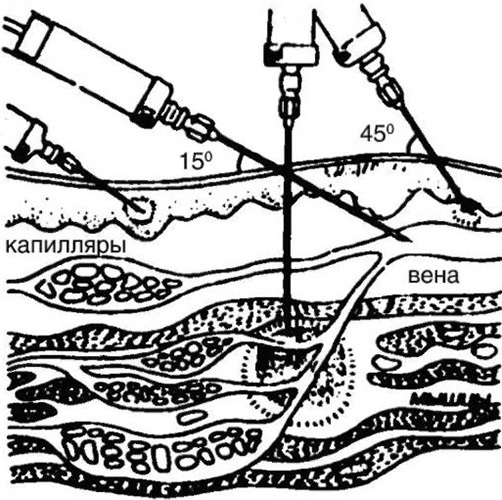
- The entry of the needle under the vein and skin at a designated angle of 15 °, after which it moves 15-18 mm. With the help of the left hand, the syringe piston is pulled, which is characterized by the appearance of blood in the vessel.
- Compression of the left hand with simultaneous removal of the tourniquet. In this case, the patient can hold the palm of his hand, after which the doctor slowly injects the drug into the vein.
The intravenous injection process involves careful monitoring of various indicators of the patient's condition, such as: pale skin, nausea, dizziness, or fever.

After the injection of the substance, the needle should be quickly removed from the vein, while the injection site itself is pressed with a cotton pad moistened with alcohol. The patient should sit quietly for about 5-10 minutes. with a slightly bent arm at the elbow. A correctly administered injection assumes no blood or swelling.
Subcutaneous administration
The preparatory stage for subcutaneous injections does not differ in any way from intravenous ones. First, you need to sterilize your hands and additional instruments.
The ampoule is also examined for the presence of external manifestations, the substance is drawn into a syringe. The doctor treats the skin and the injection site with alcohol.
After that:
- The skin is collected in a fold with the left hand.
- The needle is placed at a 45 ° angle in the middle of the fold. The insertion depth is 15 mm.
- Using his fingers, the doctor fixes the skin fold, while simultaneously pressing the plunger.
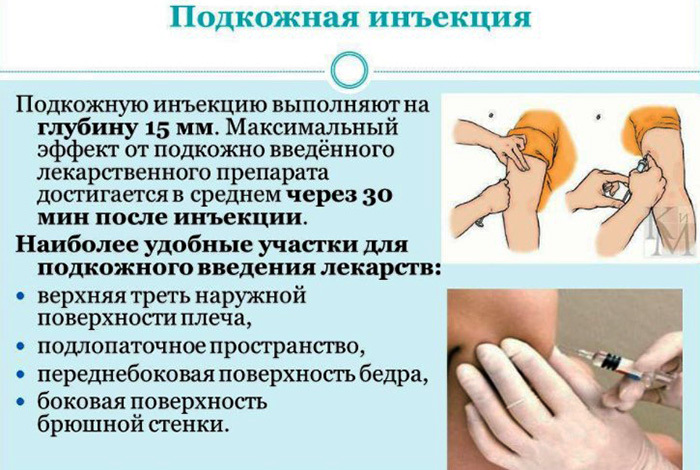
As in the case of the intravenous method, after the administration of the drug, the doctor applies alcohol-based cotton wool to the injection site. The patient also needs to rest for 5 to 10 minutes. External manifestations should not be characterized by a blue skin tone and swelling.
Intra-arterial administration
In order to perform intra-arterial injection of the drug, the doctor chooses the arteries that are located in proximity to the outer layer of the skin - the elbows, cervical, femoral or axillary sections.
The preparatory process for the introduction is carried out in accordance with the general recommendations. The area for the injection is determined by the healthcare professional based on where the most pulsating is observed.
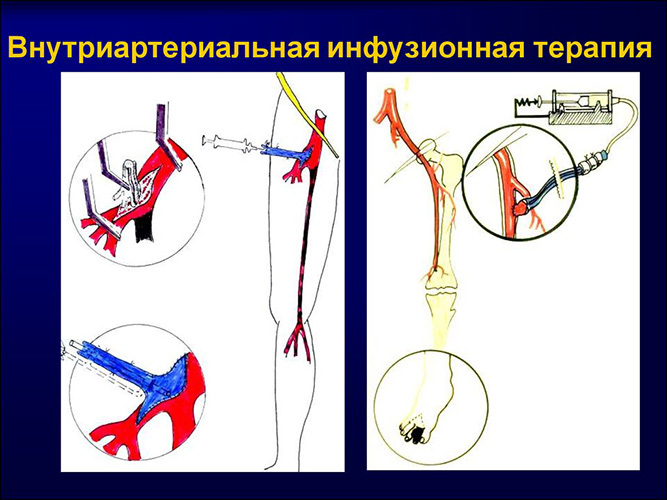
The arterial zone and skin are pierced according to the rules typical for intravenous administration, taking into account the movement of blood through the arteries. At the end of the procedure, a bandage is applied to the injection area, which applies additional pressure.
Intrathecal administration
Intrathecal medication is the most painful and difficult method and should only be performed by an experienced technician. The injection allows the required substance to be introduced into the cerebrospinal fluid.
In this case, the patient is placed on the left side while pressing the head to the chest and legs to the abdomen. The location of the injection is taken into account based on where the vertebrae of the upper lumbar spine are located. In addition to antiseptics, the site is treated with local anesthetics.
The needle itself is inserted into the spinal canal, while the dosage of the injected substance is strictly adjusted based on the depth of the inner walls. This technique allows the drug to be administered in a minimal amount, which is characterized by a significant decrease in side effects and the development of complications in the future.
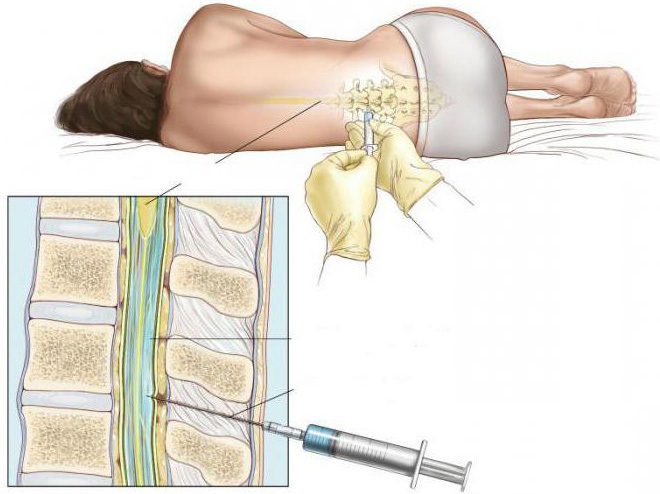
After the injection, the patient must lie immobilized for 25-30 minutes.
Intrathecal administration of the drug is used in the treatment of pain of various localization, in particular with painful manifestations in the neck, back or chronic discomfort in the abdomen. Allows to eliminate complications in case of incorrectly performed operations on the neck and back.
Intramuscular injection
Intramuscular drug administration is the most popular drug delivery method in medical practice. The preparatory stage is similar to the intravenous type.
In order to deliver the injection, the patient lies on the couch in a face down position, while the place itself is selected in the upper area of the gluteus muscle, which is pretreated with an antiseptic solution.
The injection includes the following steps:
- Stretching the skin with the fingers of the left hand, while holding the syringe with the right.
- The entry of the needle into the upper region of the gluteus muscle with a sharp movement, approximately 2/3 of its length. The insertion angle should be straight - 90 °.
- Checking the penetration of the needle into the muscle tissue by pulling the piston with the left hand. There should be no blood.
- The introduction of the drug, after which - sterilization of the injection site.
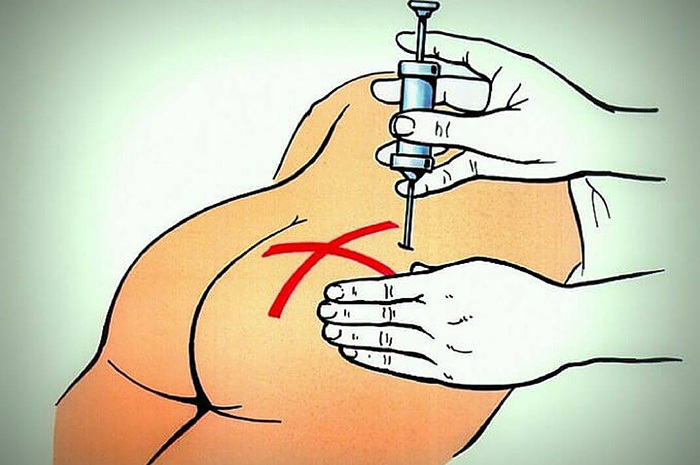
Also, intramuscular delivery of the substance involves the use of the deltoid and trapezius muscles. Improper execution of the technique can lead to complications such as abscess, paralysis and muscle fibrosis. In addition, the patient may develop gangrene or urticaria, and in rare cases, anaphylactic shock.
Preparation and Precautions
The parenteral method of delivery of the substance requires strict adherence to recommendations and antiseptic rules, because the introduction of drugs without the use of sterilization can develop various diseases of an infectious and pathogenic type.
Particular attention should be paid to the fact that the tools used, as well as the hands of medical workers, must be carefully treated with antiseptic agents. Immediately before the injection, the doctor should wash his hands with soap and water, and then treat with a cotton pad dipped in alcohol.
The injection is often carried out in the treatment room of a polyclinic or hospital, in urgent cases, it is possible to administer it at home, only with the help of an experienced health worker.
In addition to the tools themselves, there should be tweezers with disinfectant solution, alcohol, iodine on the desktop, as well as special devices for non-contact opening of ampoules with a substance. The site is covered with a sterile tissue to avoid the risk of infection. The table should be opened only with the pins.
The medicinal product is available in the form of vials or ampoules. Before putting a substance into a syringe, you should carefully read its name, expiration date, and dosage. After that, it is necessary to check the solution for transparency.
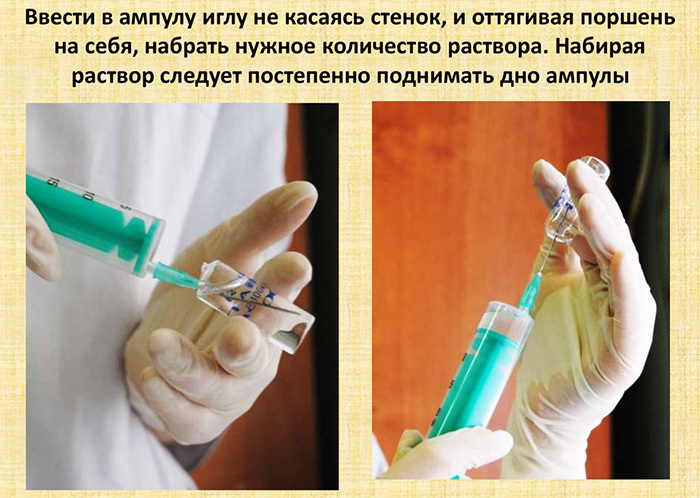
Each injection requires 2 needles from the doctor, where one is used for the purpose of collecting the substance (it is recommended to use a wide lumen), and the other for direct injection of the drug. Changing instruments allows you to provide additional sterility, while the treatment with antiseptics should also take place for the necks of the ampoules.
When the oil solution is introduced into the human body, the bottle with the substance is heated to 38 ℃ using a water bath. In order to deliver the drug ready for use, sterile trays are used, at the bottom of which there are cotton pads moistened with alcohol.
In medical practice, there are often cases in which a health worker is cut by shards of glass from a vial or ampoules. If this happens, it is necessary to rinse the wound using hydrogen peroxide, then lubricate its edges with iodine and apply a dry bandage soaked in an antiseptic.
It is strictly forbidden to use cotton wool as a protective cap for a needle. Neglect of this rule often entails the development of subcutaneous infiltration due to the presence of small hairy fibers. This can be especially dangerous for the patient's health. In this case, it is best to use disposable caps without leaving the syringe needle unprotected.
If the medicinal product is supplied in the form of a powder substance, it must be dilute with a solvent - isotonic solution, liquid for injection or novocaine. Otherwise, the doctor will not be able to produce the parenteral route of administration of the substance into the human body.
Video about parenteral routes of drug administration
Parenteral route of drug administration: video instruction:


