Speech is necessary for full-fledged communication of people with each other. As a result of the influence of internal or external factors, speech underdevelopment is sometimes noted in completely healthy children.
The defect can be expressed by stuttering, difficulty in pronouncing certain sounds, or a small vocabulary. Pathology is treatable, while it is important to examine the child in a timely manner and identify OHP (general speech underdevelopment).
Record content:
- 1 The norms of the development of the child's speech
-
2 General speech underdevelopment in children
- 2.1 OHR level 1
- 2.2 OHR level 2
- 2.3 OHR 3 levels
- 2.4 OHR level 4
- 3 Classification of speech disorders
- 4 OHR reasons
- 5 Symptoms
- 6 Diagnostics
- 7 Treatment and system of correction of general speech underdevelopment
- 8 What should parents do?
- 9 Forecast and prevention of speech disorders
- 10 Video about OHP in a child
The norms of the development of the child's speech
The general underdevelopment of speech can be noted in a child, starting from birth.
Depending on age, a child should normally have the following speech skills:
| Age parameter | Child's speech skills |
| Up to 2 months | The newborn reacts to speech: he smiles to a quiet one with a pleasant intonation, to a cry he begins to cry. |
| From 2 to 3 months | The child begins to pronounce individual sounds. For example, the sounds of letters are "a", "m" or "o". |
| From 3 to 6 months | Children begin to pronounce combinations of sounds. The most common ones are agu, ba, pa, and so on. |
| After 6 to 9 months | The child can pronounce words from simple syllables. For example, "pa-pa", "ma-ma", "ba-ba". It can also repeat simple sounds for animals ("meow", "woof", "moo"). From this age, it is necessary to begin to develop the child's speech. |
| From 9 to 12 months | The vocabulary of children includes from 5 to 20 simple words. The child can build simple sentences - "mommy give", "daddy on". |
| From 1 to 3 years old | During this period, the vocabulary of children can increase to 500 words. At the same time, they can express a whole sentence with one word and facial expressions. For example, the word "bibi" can mean that a car has passed or honked. Closer to the age of 3, a child can pronounce sentences of 3-5 words, but some sounds may be distorted. The most common are hissing sounds, as well as the sound from the letters "L" and "R". |
| From 3 to 7 years old | The child's vocabulary includes about 3000 words. He can think logically and construct sentences practically correctly. Difficulties may arise with the declension of words ("mom is sleeping", instead of "mom is sleeping") and the generic affiliation of the subject ("dad fell asleep"). Problems with the pronunciation of difficult-to-pronounce sounds disappear by the age of 7. |
| After 7 years | The child's vocabulary is quite extensive, he must be able to pronounce all the sounds and combinations of syllables. |

Small deviations in the development of speech are permissible, but in order to accurately determine whether this is not a pathology, you need to be examined by a specialist.
General speech underdevelopment in children
OHP is not uncommon, pathology is recorded in about 40% of children from 3 to 7 years old. At the same time, speech underdevelopment is divided into 4 degrees of severity, which are discussed below.
OHR level 1
Speech in children with the first level is practically absent. A child can make a maximum of a sentence of 1-2 words, while some of the sounds are pronounced incorrectly and what is said is accompanied by facial expressions. The meaning of most of the words is incomprehensible to the child. For example, the syllable "on" can mean not only "must", but also "give." Speech development corresponds to the age of 3-9 months.
OHR level 2
Children with the second level can build sentences of 2-4 words. But at the same time, there is a poor pronunciation of some sounds or their complete non-pronunciation. For example, "wampa" is a lamp, "yba" is a fish, or "syay" is tea.
The child remembers new words with difficulty, often declines incorrectly in cases, and also does not understand the difference between letters and numbers. Speech development is similar to that of children from one to three years of age.
OHR 3 levels
Children with the third level can build short but coherent sentences, and it becomes difficult to combine different parts of speech. For example, "I am" - I ate or "I ride the bus" - I was riding the bus.
Pronunciation of sounds with errors is rare, but it is possible to change the letters in places ("kobala" instead of "sausage"). The vocabulary can be about 1500 words, while the word "chair" can mean - chair, stool and chair.
OHR level 4
In children with a fourth level of pathology, vocabulary may be age appropriate. But when constructing long sentences, difficulties arise in the sequence of laying out thoughts. The pronunciation and word formation of long words is also problematic for the child. At the same time, almost all sounds are pronounced correctly.
When testing a child for OHP, it is important to take into account his age, and you can also compare speech development with peers (but not be equal to them).
Classification of speech disorders
The general underdevelopment of speech is divided not only by levels, but also by classification, both for oral and written.
To divide into the classification of oral speech, the following deviations were taken into account:
- improper voice formation;
- failures in the fluency of speech and speed of pronunciation;
- violations in the pronunciation of sounds;
- non-observance of intonation.
The table below shows the main classifications for speaking and writing:
| Oral speech | Written speech | |
| External speech underdevelopment | Internal speech underdevelopment | |
| Dysphonia. Speech impairment is caused by the development of a deviation in the vocal apparatus. Pathology can occur at any age and is expressed by a complete lack of speech, hoarseness or distortion of the pronunciation of sounds. | Alalia. Complete or almost complete absence of speech due to damage to the brain cells (during intrauterine development) responsible for speech. | Disgraphia. It is manifested by changing the places of letters when writing words. |
| Bradilalia. Violation of speech is manifested by stretching of vowels and a slowdown in the pronunciation of words. | ||
| Tahilalia. Pathology is characterized by fast pronunciation of words. | ||
| Stuttering. Violation of speech is expressed by intermittent pronunciation of words, pathology arises from muscle cramps in the speech apparatus. Stuttering is often worse with excitement. | Aphasia. It is also expressed by a complete or almost complete absence of speech due to a violation of the activity of brain cells. In this case, the pathology is caused by injuries or complications from serious diseases. | Dyslexia. Pathology is expressed by the lack of recognition of letters or the combination of syllables due to a violation of the activity of the nervous system. As a result, reading is impossible. |
| Dislalia. Pathology is manifested by incorrect pronunciation of sounds, in the absence of deviations in the development of the speech and hearing apparatus. The violation can occur, for example, due to incorrect language setting or if the child does not know how to pronounce this sound correctly. | ||
| Rinolalia. Speech impairment is characterized by nasalness, which occurs due to the improper development of the speech apparatus (air when pronouncing words does not come out through the mouth, but through the nasal cavity). | ||
| Dysarthria. Pathology is caused by a disruption in the activity of the nerve cells responsible for speech. |
At the same time, 11 classifications of oral speech and 2 classifications of writing also have a further division by degrees of severity.
OHR reasons
Underdevelopment of speech is more common in childhood. With timely diagnosis and exclusion of the cause, general speech underdevelopment can be cured.
The most common causes of the development of pathology include the following factors:
| Internal. Violations of the development of the speech apparatus, cells of the nervous system or the brain (responsible for speech) caused during pregnancy | External. The development of pathology is provoked by the influence of external factors |
| Diseases of the mother during this period. For example, rubella, flu, allergies. | Deficiency of vitamins and minerals in the child's food during the period of active maturation. |
| Transfusion of infected blood. | The presence of pathologies of the central nervous system. |
| Long and severe toxicosis. Pathology causes a deficiency of essential vitamins and minerals for the normal development of all organs and systems in the fetus. | Unfavorable conditions in the family. Parents do not take care of the child, and also frequent scandals and fights cause fear in the child, with possible subsequent dumbness. |
Rhesus conflict between mother and child.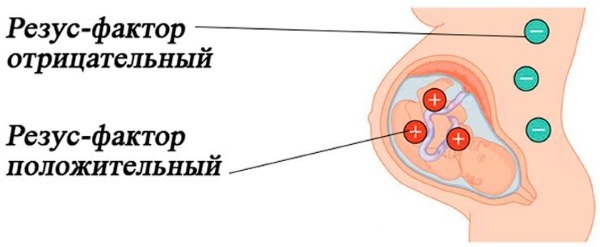
| |
| Pregnant woman smoking, alcohol or drug use. | Frequent stress and nervous exhaustion. For example, the cause of the development of pathology may be stress from visiting the kindergarten. |
| The age of the pregnant woman is up to 18 and after 45 years. | Injuries with damage to the speech apparatus or brain cells. |
| Frequent abortions. | |
| Previous severe labor. | Improper teaching of sounds and words to the child using the "lisp" method. |
| Regular stress or depression in a pregnant woman. | The presence in the family of a deaf person who mispronounces sounds and sets intonation. |
| Taking dangerous medications, especially antibiotics or hormones. | Weak immunity, as a result of this, diseases are often accompanied by the development of complications. |
| Hypoxia. Violation of oxygen supply to the fetus through the placenta, as a result, the development of tissues (especially the brain) occurs in violation. | Parents speak 2 or more languages, as a result, the child memorizes incorrectly and is confused in pronunciation. |
| Birth injury. If the child is stuck in the birth canal, then there may be a disruption in the activity of brain cells. | Imitation of immediate family members with OHP (for example, stuttering, slow speech, or incorrect pronunciation of sounds. |
| Prematurity or prematurity of the child. | Complication after severe illness. |
Hereditary predisposition, if close relatives had or have OHP, then the probability of development in a child is higher than 50%.
Symptoms
General speech underdevelopment in children (as well as in adults) is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- the child begins to pronounce the first words and sentences after 3 years;
- the child understands the speech of adults, but cannot formulate a sentence himself;
- difficult to pronounce even simple sounds;
- after 7 years, the child does not pronounce the sounds "L" and "R";
- rearrangement of letters in places in words;
General speech underdevelopment. Symptoms - the child speaks in short sentences (2-4 words) or shortens words. For example, "obaka" - a dog or "I drink" - I want to drink tea;
- wrong declension in cases and time;
- too fast or slow pronunciation of sentences, as a result, it is difficult to make out what the child said;
- when talking, the child pays more attention to gestures than words;
- there are no prepositions in the sentences;
- poor memory, as a result it is expressed by a small vocabulary and incorrect pronunciation of words.
Stuttering is the most striking sign of OHP, while the child can pronounce a word by syllables with a length of a minute. The general underdevelopment of speech not only interferes with the normal communication of children with peers and adults, but also causes severe psychological stress.
It is important that parents spend a lot of time with their children and often may not notice the beginning of the development of OHP, so it is necessary to undergo annual examinations by specialists.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of OHP is performed by a speech therapist, and further treatment can be complex (speech therapist, psychologist, surgeon and other specialists), depending on the cause of the development of the pathology.
To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor takes the following measures:
1. Data collection from the words of parents:
- the presence of a hereditary predisposition;
- when the first deviations are noticed;
- clarifies the approximate vocabulary of the child;
- how the pregnancy proceeded, what diseases the mother had during this period;
- in what time the child was born, how was the birth;
- the age of the mother at the time of childbirth;
- whether the child has had head injuries or recent illnesses.
2. Examination of the child:
- the doctor asks you to pronounce certain words. This allows you to determine the correct pronunciation of sounds;
- after that, the speech therapist asks to make a proposal (this item depends on the child's age) according to the picture. According to the length of the sentence, the correctness of the use of cases, verbs and prepositions, speech is also assessed;
- checks the memory. To do this, the child is shown 5-7 objects, after that they are removed, and the child must list which objects he remembered;
- asks the child to recite a verse or retell a short story;
- also in children under 7 years of age, the doctor asks the age, first name and last name. The child should be able to answer independently.
3. Hardware inspection:
- at the ENT, it is mandatory to check the state of the speech apparatus, especially the state of the tonsils and adenoids. With the pathology of the development of these organs, nasalness, hoarseness and impaired pronunciation of sounds that are difficult for a child are possible.
- if the child has had head injuries, an x-ray may be required. To test the nutrition of brain cells.
With severe stuttering and constriction of the child, an examination by a psychologist may be required.
Treatment and system of correction of general speech underdevelopment
OHP in most cases is treatable with the goal of:
- elimination of incorrect pronunciation of sounds;
- development of correct perception of words by sounds;
- enrichment of vocabulary;
- the correctness of the construction of long sentences;
- the ability to parse words by sound.
The most important thing is the ability to communicate and maintain a conversation with the interlocutor.
To eliminate OHR, the following techniques are used:
| Speech correction methods | Method essence | Examples of |
| Speech therapy exercises | The method is aimed at developing memory and thinking, the ability to control the muscles of the face and tongue, as well as the correct breathing when pronouncing sounds. |
|
| Speech therapy massage | The massage is aimed at strengthening the muscles of the speech apparatus, the formation of the correct bite, and also restores the blood supply to the tissues that are responsible for the development of speech. It is important that massage has contraindications. | For a massage, a specialist can use a special brush, vibrating massager or probe massage. It is recommended to carry out the procedures only with a specialist with experience and with the presence of certificates. |
| Medication method | A specialist prescribes medicines to improve blood circulation in the brain. When choosing drugs, it is important to take into account the presence of contraindications in the patient. |
|
| Visit to a psychologist | The doctor conducts a conversation with the child and teaches not to be ashamed of a defect, not to withdraw into oneself. And also reveals whether OHP is a consequence of a psychological disorder. A psychologist, for effectiveness, can prescribe baby sedatives. |
|
For a quick and successful result, it is recommended to use these methods in an integrated manner.
What should parents do?
Parents can diagnose general speech underdevelopment on their own, and can also prevent its further development.
This requires:
- show the child to a speech therapist to determine the exact diagnosis and the cause of the pathology;
- not distort words and their pronunciation in the presence of children;
- conduct speech therapy classes with the child at home (they are appointed by a specialist);
- to exclude not only scandals at home, but also loud conversations;
- do not put pressure on the child's psyche to achieve quick results;
- conduct classes, if possible, in the form of a game;
- communicate with the child on an equal footing, even if he is only 3 years old. "Shushukanye" is prohibited, as it is one of the main reasons for the beginning of the development of the ONR;
- contact a speech therapist, even if there are doubts about the OHP (for this it is necessary to compare the norms of speech by age with the capabilities of the child);
- read fairy tales or stories to the child before bedtime, they enrich the vocabulary, and the child, on a subconscious level, learns to pronounce words and build sentences correctly;
- limit the time the child spends in front of the TV and computer. It can be replaced by looking at picture books, sculpting from plasticine and walking in the fresh air.
It is also imperative to show the child to a psychologist, since children with OHP are often notorious, as they differ from their peers.
Forecast and prevention of speech disorders
With the right approach, OHP can be completely eliminated, even if there is a general underdevelopment of the first level of speech. The result is influenced by the child's age, adherence to the treatment course (both with a specialist and at home) and the atmosphere in the family. If the pathology is detected late (after 6 years) or the classes were not conducted regularly, then the child may not restore the level of speech development or remain completely dumb.
For prevention, parents should:
- avoid quarrels in the presence of children;
- devote enough time to the child (even if there is a shortage of it);
- do not "lisp" with children;
- read more books with your child (in childhood, only illustrated editions are enough);
- if the child does not pronounce any sound well, you need to independently pronounce it with him;
- provide the child with a nutritious and varied diet;
- timely treat infectious pathologies;
- if a child for some reason does not attend kindergarten, then he must communicate with peers at least on the playground;
- during the period of bearing a child, exclude bad habits and take vitamin preparations.

It is important not to miss the annual examinations of the child by specialists.
Speech begins to form in children almost from birth, so it is necessary to monitor its formation from the first days of a child's life. If you suspect the presence of speech underdevelopment, an urgent examination by a speech therapist is necessary. If the pathology is confirmed, then the treatment must be started immediately, then a complete cure from the general underdevelopment of speech is possible.
Author: Kotlyachkova Svetlana
Article design: Vladimir the Great
Video about OHP in a child
Evaluation of children with OHP:



