A child who goes to grade 1 must be able to read and write. If there are any developmental deviations, then it will be difficult for him to assimilate the material in the classroom, his academic performance will fall. To avoid this, it is necessary to deal with the baby from birth.
There is a certain sequence of staging sounds. If this is neglected, then there will be various violations in the pronunciation of sounds, which are considered in speech therapy from the point of view of the disease (sometimes they can be corrected).
Record content:
-
1 Types of violations of the pronunciation side of speech in speech therapy
- 1.1 Alalia
- 1.2 Dislalia
- 1.3 Dysarthria
- 2 Causes of speech disorders in children
- 3 Negative impact on the development of the child
- 4 When does a child need sound correction?
- 5 Characteristics of OHP levels
- 6 What sounds does a speech therapist start with?
- 7 Reference sounds in speech
- 8 Stages and sequence of sound production
- 9 Conditions for fixing sounds in speech
- 10 Sound warm-up
-
11 Speech therapy correction techniques for pronunciation difficulties
- 11.1 Sounds [L], [L ']
-
11.2 Zuki [R], [R ’]
- 11.2.1 Harmonic
- 11.2.2 Komarik
- 11.3 Sound [W]
- 11.4 Sound [W]
- 11.5 Sound [H]
- 11.6 Sound [K]
- 11.7 Sound [H]
- 11.8 Sound [X]
- 11.9 Sound [Y]
- 11.10 Sound [D]
- 11.11 Sound [S]
- 11.12 Sound [Z]
- 12 General recommendations
- 13 Video about setting sounds in children
Types of violations of the pronunciation side of speech in speech therapy
Even a temporary delay in speech development can adversely affect the entire development of the child. Learning correct speech is a prerequisite for mastering literacy and schooling. In speech therapy, certain types of disorders are distinguished, which include alalia, dyslalia and dazarthria.
Alalia
Alalia is a complex speech development disorder. It denotes the lack of formation of all parts of speech as a result of the fact that the speech zones in the cerebral cortex were affected before birth and from 0 to 3 years.
In turn, alalia is subdivided into:
- motor;
- sensory.
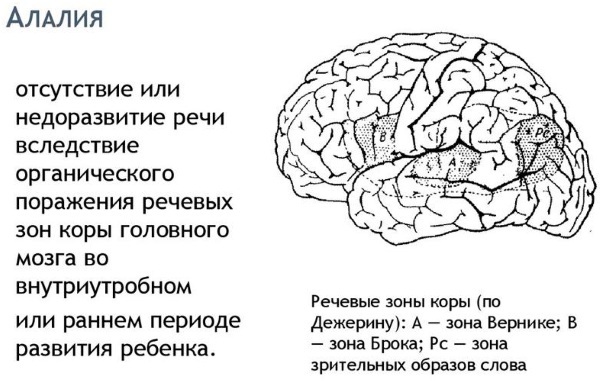
It happens that a child has a mixed form of the disease, but some type is predominant. Motor (expressive) alalia can be corrected, while a child with sensory (impression) alalia has physical hearing but does not understand what others are saying.
Dislalia
Dyslalia is understood as a violation of the pronunciation of sounds, but the child has good hearing and a normally developed articulatory apparatus. A child with this diagnosis skips, replaces, mixes up or distorts sounds when he utters them. In speech therapy, dyslalia is considered a common disease.
Approximately 25-30% (sometimes 50%) of preschool children and 18-20% of primary school children are diagnosed with this speech impairment. If it is not corrected in time, in the future the child will not be able to fully master the writing, the development of such disorders as dysgraphia and dyslexia is possible.
Dysarthria
With dysarthria, the central part of the analyzer (speech motor) is affected and the work of the muscles of the speech apparatus is disrupted. The child suffers from speech motor skills, sound pronunciation, speech breathing, so speech is slurred, indistinct. If dysarthria is diagnosed, then a speech therapist, neurologist, psychiatrist works with the baby.
Causes of speech disorders in children
A child's speech can be delayed at any stage of its development for a variety of reasons. These children very often have a poor vocabulary that does not correspond to their age group. The development of phrasal speech is somewhat delayed, and defects in the pronunciation of sounds persist for a long time.
One of the reasons for such a temporary delay in speech development can be various diseases suffered by a child at an early age. The development of speech is greatly influenced by gastrointestinal diseases, as a result of which the nutrition of the whole organism and the cerebral cortex is disrupted.
Speech disorders can also be caused by:
- infection of the fetus;
- lack of fetal oxygen;
- rhesus conflict;
- risk of miscarriage;
- toxicosis;
- chronic high or low blood pressure in a pregnant woman or other diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- the fall of the expectant mother, as a result of which the fetus was injured;
- bad habits of a pregnant woman (smoking, alcohol, drugs);
- difficult childbirth (including fleeting, protracted) or childbirth that began earlier than the due date;
- if obstetric instruments were used during childbirth;
- intracranial birth injury in a newborn;
- traumatic brain injury from birth in early childhood;
- jaundice in a newborn (nuclear);
- genetic predisposition (a history of one of the parents of a disease associated with speech impairment);
- a child under 3 years old often suffered from ARVI, pneumonia, rickets and other diseases;
- the baby underwent surgery using general anesthesia;
- a preschooler grows up in unfavorable social conditions;
- the child has been diagnosed with cerebral palsy;
- the tongue or upper lip has a short frenulum;
- malocclusion, abnormal structure of the dentition or palate;
- the child has not developed phonemic hearing.
Among the etiological factors, social causes can also be distinguished. If adults speak hastily, tongue-tied, dialectically, then the child will imitate them.
When the child is not engaged, then the preschooler is left to himself: he does not hear the correct speech, they do not communicate with him, as a result of which he withdraws into himself, speaks little and badly. If the family alternately speaks 2 languages, then this can lead to speech impairment (dyslalia).
Negative impact on the development of the child
A negative impact on the development of a preschooler is exerted by:
- television;
- gadgets (tablets, smartphones, etc.);
- unfavorable conditions (lack of educational toys, books, places for games and for drawing, modeling);
- the child does not walk on the street, has poor physical skills, does not have household chores, does not know how to take care of himself according to his age;
- from the point of view of psychology, a comfortable atmosphere is not recognized in the family (there is no trust, constant screaming, insults, punishment, as a result of which the baby is stressed, lack of attention from adults, minimal or no bodily contact, especially with mother).
Pregnancy planning is a warning factor in the normal development of a child.
When does a child need sound correction?
Moms often have a better understanding of what her child is saying. However, speech defects, which many parents do not notice for a long time, can bring developmental and communication problems to the baby in the future. Before you start to panic that the child does not speak somehow a sound and take action, you need to find out what sounds should be formed at a certain age:
- Up to 3 years old, the baby correctly pronounces the sounds - B-Bb, M-Mb, B-Bb, P-Pb, T-T, D-Db, K-Kb, G-Gb, X-Xb, F-Fb, H-Hb, J. Possible softening of sounds is considered normal.
- From 3 to 4 years old, the child learns to pronounce C-C, Z-Z;
- At the age of 4-5 years, the preschooler masters Sh, Zh, Ch, Sh, Ts.
- At about 5-6 years old, the child already knows how to correctly speak P-Pb, L-L.
Now that the age norms are known, an assessment can be made: how the child pronounces the sound, whether it distorts it, replaces it with a simpler one. If the sound is pronounced incorrectly, then it is necessary to correct the sound pronunciation. It is necessary to deal with the child (parents, speech therapist), without classes the pronunciation will be even worse.
The work of a speech therapist is divided into 3 stages:
- Sound production.

- Sound automation.
- Difference of sounds.
It is not recommended to put sounds on your own by the parent; this should be done by a professional speech therapist. But from the 2nd stage, parents can continue the learning process at home.
If there are other disorders of the speech apparatus, then the child must be shown to a neurologist. Individual complex treatment will be prescribed.
Characteristics of OHP levels
General speech underdevelopment in speech therapy is indicated by the abbreviation OHP. This term is understood as various kinds of speech disorders, when the components of speech are violated (grammar, vocabulary, syllable and sound pronunciation).
At the same time, the child has good hearing and intelligence. If you do not deal with the correction of speech disorders with a preschooler under 5 years of age, then a diagnosis of OHP of a certain level can be made. There are 4 levels depending on the degree of OHP violation.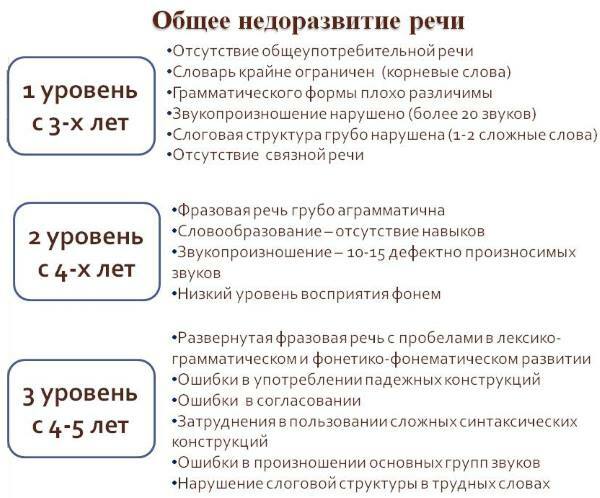
| Levels of general speech underdevelopment | Views | Symptoms |
| Level I | Motor Alalia | Non-verbal manifestations: underdevelopment and poor development of gross and fine motor skills, lack of self-care skills. Psychological manifestations: memory and attention are insufficiently developed, a feature of behavior - hyperactivity, disinhibition, inactivity or lethargy, low performance, increased fatigue. Speech manifestations: speech skills are formed with a delay, some sounds are replaced by others, the child cannot repeat a syllable or word correctly, articulatory movements are performed with labor, poor vocabulary, the child speaks in short phrases, mainly uses nouns in the initial form, the speech is incoherent, the events are not presented consistently. |
| Sensory alalia | Increased susceptibility to different sounds. The child pronounces meaningless sound combinations, scraps of words, unconsciously repeats other people's words, replaces some sounds with others, or skips them, combines parts of different words with each other into one word, does not distinguish between words-paronyms, cannot relate a word to an object, or phenomenon. Attention, auditory perception, memory - difficulties arise with all of this. The child behaves impulsively, chaotic or inert, withdrawn. During speech, they actively gesticulate and work with facial muscles. Speech is incoherent, it makes no sense, others do not understand it. The child uses the lip-reading technique to understand the speech of others. |
|
| Aphasia | The child rearranges sounds and syllables, repeats phrases, activities, emotions, replaces sounds, combines elements of two expressions into one, cannot perform sound-letter analysis of a word, all this is accompanied by problems with reading and letter. In speech, there are mainly nouns, the infinitive form of the verb, long pauses, the strength and sonority of the voice is reduced, the rhythmic and melodic aspects of speech are disturbed. | |
| Dysarthria | Indistinctness, indistinctness, poor intelligibility of speech. Weak articulatory motor skills, including respiratory muscles (rapid and intermittent breathing during speech activity). The child distorts, replaces or skips sounds, speech is slurred, slow, expressionless. Disturbed articulation of most sounds, including vowels. Reduced strength, changed the timbre of speech. Predominantly hissing and sibilant sounds are pronounced interdentally or sideways, some sounds softened where not required. In severe cases, the motor muscles can be completely immobilized (paralysis). The child cannot differentiate sounds by ear, and is also unable to analyze and synthesize the sound structure of a word. Difficulties in communication and its insufficiency lead to a low vocabulary, inconsistency of words. |
|
| Rhinolalia | Respiratory function is impaired, congenital malocclusion. The development of intelligence can be different (normally, with mental retardation or mental retardation of varying degrees). A baby under 1 year old does not babble. The articulation of sounds is characterized by quietness or soundlessness. The development of speech occurs with a delay - the child pronounces the first words only at the age of 2-3 years. Indistinctness, inexpressiveness, incomprehensibility of speech. For some sounds, posterior or nasal pronunciation is characteristic. The child is unable to differentiate sounds. The voice is deaf and quiet. In order for the sound pronunciation to be more intelligible, the preschooler strains the articulatory apparatus, as a result of which a grimace appears, the general impression of what has been said decreases. In addition to inaccurate articulation and distorted sound pronunciation, the auditory difference in sounds is disturbed, there is inability to perform phonemic analysis, as a result of which writing disorders (dysgraphia and dyslexia). The vocabulary is insufficiently formed, the words are not consistent with each other. |
|
| II level | Delay in speech development (the child pronounces phrases only at 3-4 years of age or later), sentences are mostly short, consisting of 2-3 words. In speech, the official parts of speech and the adjective are little used. Speech is accompanied by gestures, words without morphological characteristics. Vocabulary is quite varied, but significantly lower for the norm according to age. Children cannot name body parts, flowers, objects and their details that summarize concepts. The child is not able to change the word, form a new one, use the word in the necessary case form, does not distinguish words by numbers. The members of the proposal are not coordinated among themselves. The preschooler rearranges or abbreviates syllables, does not pronounce one consonant if they are nearby ("table-tol"). The child is not in a position to select a sound and name its position in a word, name examples for a given sound. During pronunciation, sounds are mixed, distorted. Soft consonants are replaced by hard ones, voiceless ones - voiced, hissing - whistling ones. Movement is not coordinated, clumsy, digital praxis is not formed. Decreased auditory-speech memory, poor attention, insufficient development of verbal-logical thinking, therefore, rapid fatigability is observed, the child is often distracted, makes many mistakes. |
|
| III level | Expanded phrases, consisting of 3-4 words, complex sentences are practically absent in speech. It is found that the structure of phrases is broken, the main members of the sentence dominate in speech, difficulties arise in the perception and structure of sentences. A child cannot form the plural correctly, inflect a word by gender, person and case, does not agree on a noun with an adjective and numeral. When a preschooler retells the text, he skips important points or expresses them in the wrong sequence. The child understands speech almost close to the norm in age. Problems with the perception of logical and grammatical structures with additional members of the sentence, with understanding the meanings of complex prepositions, prefixes or suffixes. The vocabulary seems to be normal, but when constructing a phrase, the child does not know the name of this or that part of the subject, does not distinguish the lexical meaning of words, difficulties arise with the formation of new words. Phonetic defects: complex sounds are replaced by simple ones, voiced ones - deaf, hard ones soften, incorrectly pronounced whistling, hissing, sounds L and Lb, P and Pb, words consisting of several syllables (the child rearranges or skips them). The preschooler cannot determine the 1 and the last sound in a word, cannot pick up words for a given sound. |
|
| IV level | Speech is a little blurry, inexpressive, as articulation is indistinct. The child cannot differentiate hissing, affricates. There are no gross violations in sound pronunciation. Difficulties arise with the pronunciation of words consisting of several syllables (the preschooler skips, rearranges, reduces the number of sounds and syllables). There are problems with understanding the lexical meaning of the word, separate concepts are often confused ("picture" - "Coloring"), the child cannot explain the meaning of proverbs, phraseological units, choose a synonym and antonym, form new word. The preschooler incorrectly agrees on nouns, numbers, adjectives, forms the plural form of the word with errors, does not use prepositions accurately. When choosing the right and wrong words, the child chooses the correct option. During the story or retelling of a given text, the baby disrupts the sequence of actions and events, experiences Difficulty in identifying what was the main thing and what was secondary, can repeat some points several once. |
What sounds does a speech therapist start with?
The sequence of setting sounds in speech therapy begins with those sounds that the child already utters at the age of 3 years. Sounds are predominantly simple for the articulatory apparatus, they are also reference ones (more complex sounds are put on their basis). These sounds include vowels and consonants: B-Bb, M-Mb, B-Bb, P-Pb, T-Tb, D-Db, K-Kb, G-Gb, X-Xb, F-Fb, N -N, J.
The sequence of staging sounds is performed gradually. In speech therapy, it is recommended to start working on sounds that are familiar to the baby and he pronounces them well.
Reference sounds in speech
In speech therapy, reference sounds are understood as sounds that are similar to those that are problematic in articulation, but they are pronounced correctly by children.
Based on the reference sounds, it will be easier to teach the preschooler to pronounce correctly or put complex sounds (hissing, whistling and sonorous). The reference sounds for C are I, F, for Zh - V, Z, for C - T, C.
Stages and sequence of sound production
The sequence of setting sounds in speech therapy is mainly determined over a long period of time. During the work, parents, speech therapists and of course the child himself are involved. There is a certain system according to which the process of producing sounds is more effective.
The sequence of setting sounds in speech therapy is divided into the following stages:
- Training.
- Actually, work on the setting of sounds.
- Securing the correct pronunciation in a syllable, word, phrase, sentence (principle - from simple to more complex).
- Difference between sounds, highlighting a specific sound, designating its place in a word.
You can proceed to the next stage if the preschooler has no difficulties at this stage. If we neglect even small mistakes, then in the future it will be much more difficult to correct them.
You can put the sound in different ways:
- thanks to articulatory gymnastics and massage;
- imitating;
- mechanically (with the help of speech therapy instruments - probes);
- from other sounds (many sounds are similar in articulation).
Conditions for fixing sounds in speech
The success of the production of sounds depends on many factors: on the frequency of classes, the degree of problems with sound pronunciation.
Performance can be divided into the following conditions, which must be met:
- development of phonemic hearing;
- control of speech therapist, parent and self-control;
- awareness of why these classes are needed (motivation). Parents are encouraged to praise their baby for even minor successes.
Each of these conditions is complementary.
Sound warm-up
The simplest sound workouts: how a mosquito rings, how a beetle buzzes, what sound a trumpet makes, how a snake hisses, how a bell rings, how a frog croaks, how a sheep bleats, how a goat a steamboat / steam locomotive hums, how a wolf howls, how a hammer knocks, how a hedgehog snorts, how a baby babbles, how a goose cries, how a cow hums, how a clock ticks, as he says duck / chicken / kitten / foal / tiger cub.
Speech therapy correction techniques for pronunciation difficulties
Pronunciation disorders are of varying degrees. We consider the most common ones that do not apply to OHP.
Sounds [L], [L ']
Articulation exercises:
- smile (stretching the lips well), lowering and raising the lower lip;
- open your mouth and make a “watch” with your tongue in a narrow position, run your tongue over your teeth, lower and raise your tongue first on the lower lip, then on the upper;
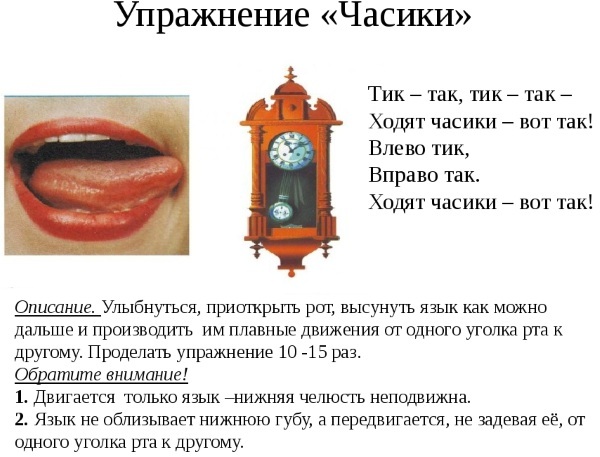
- close your mouth and press on your cheeks with a narrow tongue.
Breathing exercises:
- pull in your cheeks;
- take air into your mouth (as if inflating a balloon).
Zuki [R], [R ’]
These sounds are considered difficult, and their production is time consuming. Articulation exercises consist in the development of mobility and vibration: raising the tongue (its tip) to the upper lips or teeth and lowering it to the lower ones, "attach" the tongue to the upper palate, a small piece of thin paper or cotton wool is placed on the tip of the tongue, which must be blown away.
The exercises "accordion" ("balalaika") and "komarik" ("motor") are also used.
Harmonic
When the sound D or F is pronounced with a finger, previously washed, or with a nipple (a spatula or finger is pulled), movements are made in horizontal directions under the edge of the tongue. As a result of such mechanical action, the tongue vibrates.
Komarik
Sounds T, D or Z are pronounced often.
Sound [W]
Exercises:
- "Bowl" ("ladle");
- "shovel";
- "Rocked";
- "clock";
- holding a wide tongue near the upper teeth, then on the lower lip;
- blow on cotton balls;
- inflate soap bubbles and blow on them too.
Sound [W]
The same exercises are used as for Sh. At the beginning, the sound is worked out in syllables, then at the beginning of a word, in the middle and at the end. The most difficult exercises are with words with this sound in each word of a phrase, sentence.
Sound [H]
The H sound is corrected in the same way as the previous sibilants.
Sound [K]
Most often, the sound is corrected by imitation (exercises are performed in front of a mirror). If this fails, then the sound K is corrected on the basis of the sound T using a mechanical device (spatula).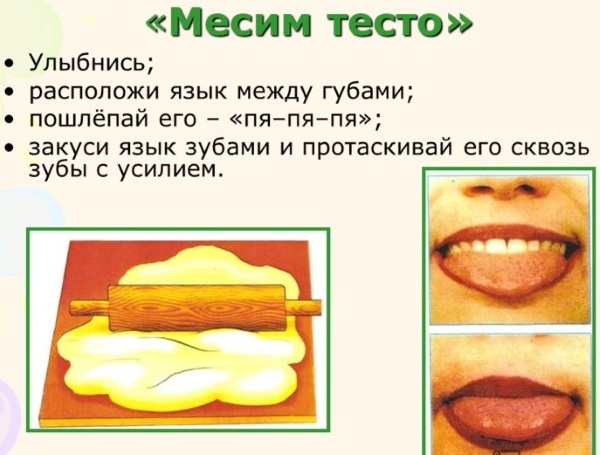
The kid says "TA" several times, after the speech therapist presses the device on the back of the tongue (front part) and holds it in this position behind the lower front teeth. The child says "TA", but "TYa" is heard. Further, the pressure is increased and "KYa" is obtained, after which the device moves a little further and the sound "K" is obtained.
Sound [H]
When a preschooler correctly pronounces the sound K, he is asked to put his hand slightly above the larynx and pronounce K and G. At the same time, the speech therapist explains what is the difference between a dull sound and a voiced one. Then the child repeats syllables with paired sounds. If it was not possible to fix the sound, then they put the sound G from D using a spatula.
Sound [X]
The sound X is obtained if you pronounce K with aspiration, in the end you get "KX". Then only the sound "X" is pronounced.
If it was not possible to fix the sound, then they put the sound X from C using a spatula.
Sound [Y]
At the beginning, words are pronounced, in the place of which there should be the sound Y, but I is consciously said (hedgehog - Iozh, I play - I play, I sew - shiu). Then the duration of the vowel I decreases, the syllabic sound becomes non-syllable.
If it didn't work out to correct the sound, then they put the sound Y from Z with a spatula.
Sound [D]
Work on the correction of the C sound begins after the child correctly pronounces the C sound. The kid is given tasks for the pronunciation of the vehicle, while there should not be any breaks and extraneous sounds (if there are any, then you need to correct this immediately).

Then the child will repeat the words in which the sound is at the end of the word. After this, the exercises become more complicated - words are selected in which C is at the beginning of the word. The most difficult tasks: phrases and sentences, in all words of which the sound C is present.
Sound [S]
Articulation exercises are the same as for correcting hissing sounds. Sound C is worked out independently at the beginning. Then he is brought to automatism, pronouncing words (at the beginning, middle and end), phrases, sentences, poems.
Sound [Z]
Work on correcting the sound Z should be only after the child has learned to pronounce S correctly (automatically). To understand the difference between the paired sounds C and Z, it is necessary to attach the back of the palm of the larynx. These sounds are pronounced for a long time and alternately. When the sound Z is pronounced correctly, automation exercises are given.
General recommendations
The sequence of setting sounds in speech therapy is regulated by certain stages.
When setting and correcting sounds, the following is important:
- work on the development of auditory perception, attention and memory; phonemic perception; articulation;
- personal example (an adult and a speech therapist must pronounce sounds correctly);
- timeliness of corrective work (for most sounds, the age limit is 4-5 years, only the P sound is corrected at 6 years old).
Examples of tasks for children to automate the pronunciation of problem sounds
Possible tasks to automate problematic sounds:
- name what is shown in the paintings;
- story based on the picture;
- memorizing sayings, phrases, small verses;
- repetition or retelling of short phrases, sentences, texts.
The sequence of setting sounds can be carried out independently, but it is better to seek professional help. In speech therapy, there are several methods for correcting sound pronunciation, which should be carried out by a speech therapist, and at home, parents can continue the lesson.
Author: Inna Krylova
Article design: Vladimir the Great
Video about setting sounds in children
Setting the sounds T and D:



