Craniostenosis is a serious disease characterized by deformation changes in the bones of the skull in children of newborn age. This pathology occurs on average in 1 child per 2000 babies.
The disease is characterized by premature fusion of the cranial sutures, which prevents the full development of the brain, the formation of nerve endings and blood vessels. According to statistics, craniostenosis most often affects boys, and this pathology is extremely rare in newborn girls.
Deformational changes in the skull of this type are detected in the first days after the birth of a child, or they are established by a pediatrician at a later stage in the development of the baby. The severity of the symptoms of the disease depends on the type of craniostenosis and its severity.
Early diagnosis of the disease makes it possible to develop an effective treatment regimen to restore the natural shape of the child's skull and eliminate premature sutures.
The maximum therapeutic effect is achieved if the sick infant received qualified medical care no later than 2-3 months. own life.
At a later stage in the development of a newborn, the risk of complications and negative consequences provoked by surgical intervention, as well as compression squeezing of the centers of the brain, optic nerve and great vessels that provide blood supply fabrics.
Record content:
- 1 Views
-
2 Stages and degrees
- 2.1 Mild degree
- 2.2 Average degree
- 2.3 Severe degree
- 3 Symptoms
- 4 Reasons for the appearance
-
5 Diagnostics
- 5.1 Craniometry
- 5.2 Abdominal ultrasound
- 5.3 Clinical examination of blood and urine
- 5.4 ECG of the heart
- 5.5 Venography of blood vessels
- 5.6 Spiral CT
- 6 When to see a doctor
- 7 Prophylaxis
-
8 Treatment methods
- 8.1 Medications
- 8.2 Traditional methods
- 8.3 Other methods
- 9 Possible complications
- 10 Video about craniostenosis
Views
Craniostenosis in newborns is classified into separate types, based on the nature of deformation changes in the infant's cranium, as well as the nature of the origin of the disease. The table below lists the main types of this disease, and also describes in detail the characteristics of the pathological process.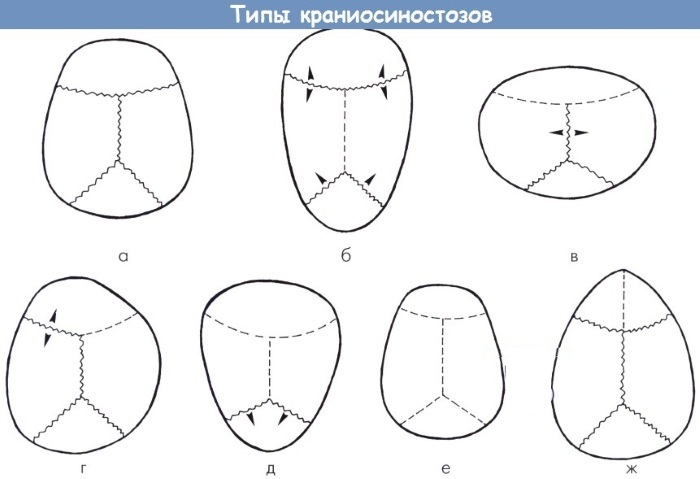
| Types of craniostenosis | Distinctive features of the disease |
| Congenital | Congenital craniostenosis is characterized by deformation of the skull and fusion of its sutures even at the stage of intrauterine development of the fetus. This pathology occurs during the first 12 weeks of pregnancy. The nature of the origin of the disease is not fully understood, but most scientists from all over the world are inclined to the factor of genetic failure. In this case, the child is already born with a deformed cranium, which is diagnosed by doctors in the first 1-2 hours after childbirth. At the same time, most pathologies do not have a hereditary relationship, since in the families of parents of newborn children with craniostenosis, there were no cases of such a disease earlier. |
| Acquired | Acquired type craniostenosis is a disease that occurs after a child is born. This pathology is a complication of a surgical operation on the bones of the skull, it can be caused by difficult childbirth or traumatic brain injury. The main danger of acquired craniostenosis is that it is difficult to diagnose it in the early stages of pathological fusion of the cranial sutures. In most cases, negative changes in the cranium are manifested by concomitant symptoms associated with impaired functions of the brain, the organ of vision and hearing. Pathology of this type is successfully treated if therapy is carried out in relation to a child whose age is not older than 5-6 years. |
| Syndromial | Syndrome-type craniostenosis is a more severe disease of the bones of the skull that characterized not only by deformational changes in the shape of the head, but also by the appearance of concomitant developmental anomalies. In most cases, this type of disease has a congenital etiology. Babies with syndromic craniostenosis have an inadequate number of toes and toes and are born with cleft in the upper lip or palate, suffer from heart disease or other abnormalities of internal organs and musculoskeletal apparatus. Treatment of syndromic type craniostenosis requires restoration of the physiologically correct shape of the head, as well as elimination of concomitant injuries. |
| Trigonocephaly | Trigonocephalic craniostenosis is a disease characterized by the early fusion of exclusively metapic sutures of the skull. As a result of this pathological process, the child's head is characterized by a triangular bulge in the frontal lobe. At the same time, the occipital segment of the skull retains its natural shape without signs of negative changes. Children with trigonocephaly suffer from visual impairment and intraocular pressure. |
| Brachycephaly | Craniostenosis of the brachycephalic type occurs due to early overgrowth of the lambdoid and coronal sutures of the cranium. As a result of this pathological process, an increase in the transverse diameter of the head of a newborn child occurs. A visual examination gives the impression that the infant's skull is 2-3 times larger than its physiologically natural size. |
| Scaphocephaly | Craniostenosis of the scaphocephalic type is one of the most severe pathologies in this category. This disease occurs due to the fact that there is a premature fusion of the sagittal suture of the skull. In this regard, a narrowing of the head occurs on the sides, but at the same moment a volumetric bulge forms in its front and back. Scaphocephalic craniostenosis can be complicated by functional disorders of the brain, tissue which are experiencing the strongest compression compression, and also do not receive sufficient blood volume nutrition. |
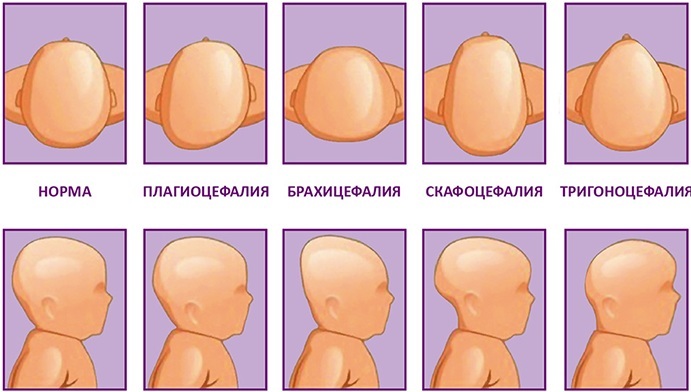
Craniostenosis in children is a pathological condition of the bones of the skull, the type of which is determined by the results of a diagnostic examination of the infant. The disease can be established in the first hours after the birth of a child, or it manifests itself at a later stage of its development.
Early detection of the disease and correct diagnosis allow for effective surgical treatment with minimal risk of complications.
Stages and degrees
Craniostenosis in children is a disease that is divided according to the severity of deformation changes in the skull, as well as the possible presence of symptoms of various complications.
Mild degree
Children with a mild degree of craniostenosis show signs of deformity of the cranium, but with impaired development of only a separate segment of the bones. For example, the presence of an abnormal bulge exclusively in the frontal or occipital part of the head, without signs of severe compression of the brain.
At the same time, there are no symptoms of complications associated with dysfunction of other organs and elements of the musculoskeletal system. Mild craniostenosis responds well to surgical treatment with minimal risk of complications.
Average degree
Craniostenosis of moderate severity is a pathological condition of the bones of the head, when several seams of the cranium grow together at once. The child has a simultaneous deformation of the forehead and the back of the head.
A more detailed examination reveals the first signs of dysfunction of the organ of vision, hearing, cerebral circulation. The lack of qualified treatment leads to further progression of the disease and the development of irreversible complications.
Severe degree
Severe craniostenosis is characterized by total deformation of the skull bones with impaired brain function. Children with a similar diagnosis suffer from cramps of the lower extremities, sudden loss of consciousness, occurs a rapid decrease in visual acuity and hearing, disturbances in the work of the central and peripheral nervous systems.
A child with severe craniostenosis needs urgent surgery to restore the anatomically correct position of the skull bones. Otherwise, such children will face lifelong disability or death.
Symptoms
Craniostenosis in children has the main diagnostic feature, which is detected based on the results of a preliminary examination of the child. This is a deformed head that has an unnatural and bizarre shape.
Also, this disease is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- increased intracranial pressure, which progresses as the compression of the brain tissue increases;
- the child is worried about nausea with periodic release of vomit;
- there is a severe headache;
- there is a sudden appearance of cramps of the lower extremities, and the occurrence of epileptic seizures is not excluded;
- visual acuity worsens, and a more detailed examination reveals atrophic changes in the optic nerve;
- individual parts of the lining of the brain become inflamed, which resembles meningeal symptoms;
- the child has poor hearing, which is due to the compression of the nerve endings responsible for the processing and transmission of environmental sounds;
- cerebral circulation and coordination of movements are disturbed;
- signs of dizziness appear (this symptom can be reported by children over 3 years old who have received an acquired form of craniostenosis, but have not yet undergone a course of surgical treatment).

The most severe types of deformational changes in the bones of the skull can cause the development of mental disorders. A child may significantly lag behind in mental and physical development, the consequences of which cannot be eliminated even after a successful surgical operation.
Reasons for the appearance
Craniostenosis in children appears under the negative influence of external and internal factors. Pathology can manifest itself at the stage of embryonic development, or at a certain stage of the child's independent life.
In this regard, the following reasons for the appearance of this disease are distinguished:
- damage to the fetus with dangerous bacterial and viral infections that cause malformations of embryonic development (in medical practice, this pathology is most often provoked by rubella, toxiplasmosis, pale spirochete, gonococcus);
- hereditary predisposition to premature fusion of the cranial sutures, when such a disease is transmitted to the child along with genetic information from one of the parents;
- the use of alcoholic beverages, drugs, tobacco smoking, which is carried out during pregnancy;
- difficult childbirth, which led to damage to the bones of the skull (similar situations occur if women have a physiologically too narrow pelvis and birth canal, and the obstetrician refused to use the caesarean method section);
- unsatisfactory environmental situation caused by the presence in food and water of chemically hazardous or radioactive substances that negatively affect the intrauterine development of the fetus;
- traumatic brain injury that a child received as a result of falling or hitting a hard surface;
- negative consequences and complications caused by surgery on the brain.
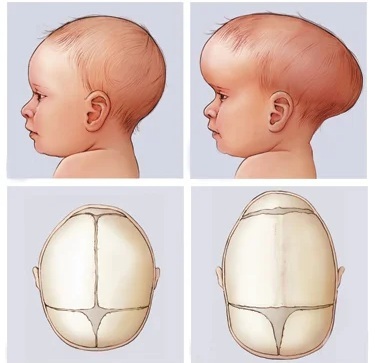
In the event that the overgrowth of the sutures occurred at the stage of intrauterine development, then the deformational changes in the cranium are more pronounced. Pathology acquired after birth does not cause critical changes in the shape of the head.
The cause of the craniostenosis is determined at the stage of the child's diagnostic examination. The nature of the origin of the disease does not affect the specifics of the organization of the therapeutic course.
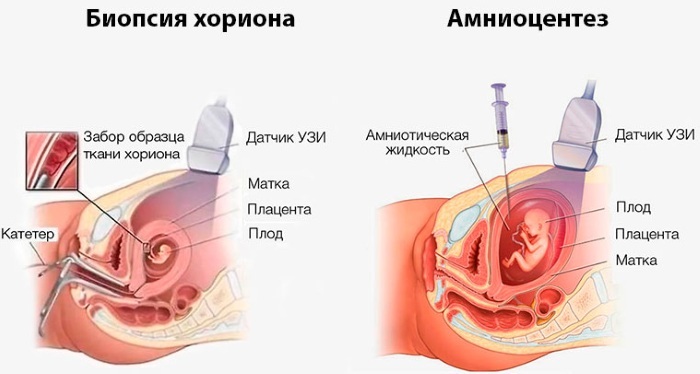
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of craniostenosis begins with a preliminary examination of the child's head. The doctor establishes physiological changes in the shape of individual segments of the skull.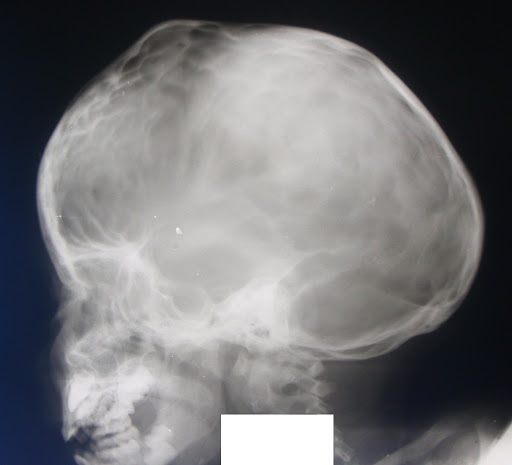
Then the patient is assigned to undergo instrumental examination methods, the results of which make it possible to determine the severity of the disease, functional disorders of the centers of the brain and assess the performance of other internal organs.
Craniometry
Craniometry is a diagnostic technique that includes measuring the anthropometric parameters of the child's skull. The data obtained are compared with standard indicators, which are the norm for children of the corresponding age.
During this diagnostic procedure, a centimeter tape, a cephalometer, and a special computer program based on Sp-CT examination are used.
Abdominal ultrasound
Ultrasound of the liver, kidneys and other internal organs, if craniostenosis of the syndromic type is found in a sick child. This method of examination allows you to timely establish the pathology of the development of vital systems of the body. Especially if the child has signs of a dysfunctional disorder on the part of one or another internal organ.
Clinical examination of blood and urine
To obtain general information about the patient's state of health, the attending physician prescribes the donation of capillary blood from the ring finger bunches, as well as morning urine. Then the obtained biological materials are amenable to clinical research.
ECG of the heart
Compression of the brain, increased intracranial pressure, impaired blood circulation, can provoke a painful condition of the heart. An ECG can detect a decrease in heart rate, as well as signs of arrhythmia.
Venography of blood vessels
This method of diagnostic examination makes it possible to determine the functional state of the great vessels that provide blood delivery to the cranial cavity. 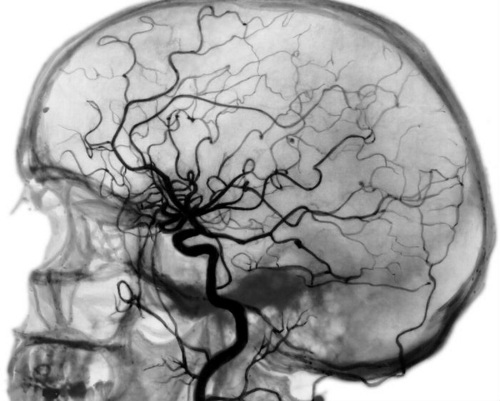 Venography displays in detail the intensity of the outflow of venous blood, makes it possible to confirm or refute suspicions of the presence of intracranial hypertension.
Venography displays in detail the intensity of the outflow of venous blood, makes it possible to confirm or refute suspicions of the presence of intracranial hypertension.
Spiral CT
This method of diagnostic examination of children with signs of craniostenosis detects prematurely closed the seam of the skull, and also determines the severity of the pathology with the possible presence of intracranial pressure. The informational data obtained from the results of the Sp-CT scan are used in the planning of the surgical operation.
The total cost of comprehensive diagnostics of a child suffering from craniostenosis, which is carried out in a private clinic, averages from 7,000 to 8,500 rubles. In a public hospital, these services are provided free of charge.
When to see a doctor
A visit to the doctor should take place immediately, as soon as the parents notice the physiological changes in the shape of their child's head. It is almost impossible to independently determine the premature fusion of the cranial sutures. Therefore, children should only be examined by a specialized specialist.
A child with signs of craniostenosis should be examined by the following specialists:
- a neuropathologist to exclude dysfunctions of the central and peripheral nervous system;
- an ophthalmologist who examines the condition of the optic nerve;
- a cardiologist in order to timely detect a decrease in the rhythmic activity of the heart.
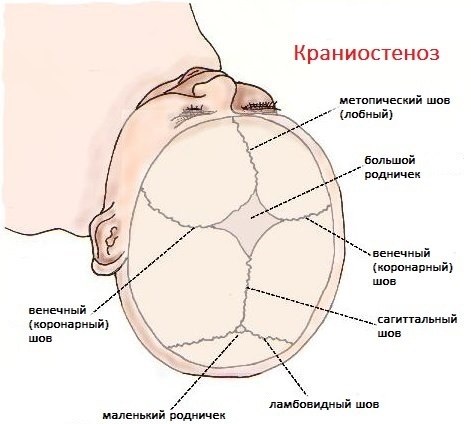
The first doctor who examines the child should be the local pediatrician. After performing a preliminary examination, he decides on the possible involvement of doctors of other profiles.
Prophylaxis
In order to minimize the likelihood of developing intrauterine or acquired craniostenosis, it is recommended to observe the following prevention rules:
- parents planning to conceive a baby donate blood for genetic research for a predisposition to deformational changes in the bones of the skull;
- women who are in a state of pregnancy should not use drugs, alcoholic beverages, tobacco products and hormone-based medications;

- before pregnancy, eliminate all foci of chronic infection that are present in the body;
- during the period of intrauterine development of the fetus, regularly undergo routine medical examinations.
A pregnant woman should monitor the quality of her diet, consume enough dairy products, meat, chicken eggs, fresh vegetables and fruits.
Treatment methods
The only effective treatment for craniostenosis in children of all ages is surgery.
Medications
Deformational changes in the bones of the skull caused by premature fusion of its sutures cannot be eliminated with the help of drug therapy.
Traditional methods
Previously, one of the most common methods of alternative treatment of craniostenosis in newborns was tying the skull with dense tissue, which did not lead to disability and irreversible changes in the tissues of the head brain. Currently, therapy for this disease is carried out only in health care institutions.
Other methods
Treatment of craniostenosis is possible only with the help of a surgical operation performed by a neurosurgeon. The main task of this method of therapy is to expand the internal volume of the cranium, as well as to give the bones an anatomically correct shape.
The scheme of the surgical intervention is developed individually, taking into account the external symptoms of each patient. If necessary, severely deformed parts of the skull are removed, and modern plates made of polymer materials are installed instead.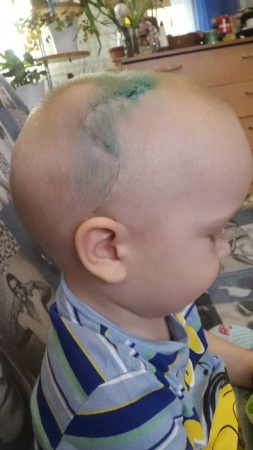
Throughout the entire period of the surgical operation, the child is under the influence of general anesthesia. The average duration of surgery is 3 hours.
Upon completion of medical manipulations, the patient is transferred to the intensive care unit for 24 hours, where he is under the round-the-clock supervision of doctors.
In the absence of complications, the child is placed in the general hospital of the neurosurgical department. After 8-10 days, the patient is discharged home.
The first examination after surgery should take place after 3 months. The child is required to undergo a spiral CT scan.
Possible complications
Lack of timely access to a doctor for the treatment of a newborn, suffering from craniostenosis, can lead to the development of the following complications:
- cerebral stroke;
- lag in physical and mental development;
- dysfunctional disorders in the work of internal organs;
- inflammation of the cerebral cortex;
- complete or partial deafness;
- a significant decrease in visual acuity, or the onset of complete blindness;
- violation of coordination of movements;
- epileptic seizures and cramps of the lower extremities;
- severe dizziness, excluding the possibility of independent movement;
- adherence to bed;
- the onset of a lethal outcome.
Congenital or acquired craniostenosis is a serious disease that is diagnosed in infants. Pathology is characterized by premature fusion of the cranial sutures, which leads to deformational changes in the shape of the head.
The disease can occur in a mild, moderate or severe form, disrupt cerebral circulation and the functions of the central nervous system, or be limited only by a visual defect in the structure of the skull. Treatment of this disease is possible only by performing an operation under sterile conditions in the neurosurgical department.
Video about craniostenosis
Malysheva about the deformity of the skull in a child: