Down syndrome is usually attributed to one of the most common genetic abnormalities (photos of adults and children diagnosed with this deviation can be seen below). Statistics say that every 800th child on the planet is born with Down syndrome.
A similar disease occurs in the same quantity in all countries and their regions, while neither the climate, nor the color of a person's skin, nor his nationality matter.
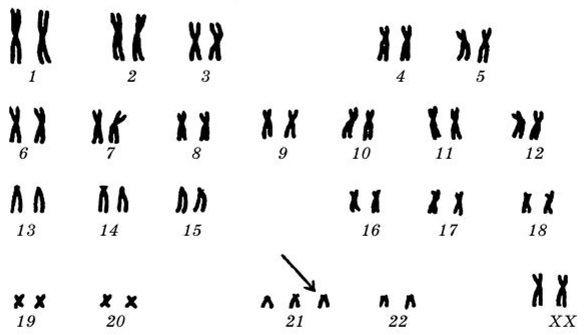
Down syndrome is abnormality in the 21st chromosome, which is accompanied by abnormal formation of mental development, microcephaly (decrease the size of the human brain and skull), slow growth and certain external features.
For the first time this deviation was discovered, studied and described by the British scientist (doctor) John Langdon Down. It was in his honor that the disease was named. Also, in 1959, the Frenchman Jerome Lejeune already described the syndrome in more detail and scientifically explained the genetic origin of this phenomenon.
Revealing this kind of deviation in a person already implies the presence of certain features that you need to get used to, as well as learn to live in society.
Most children with Down syndrome learn easily how to walk, read, perform self-care manipulations, various sports and games. With proper care and education, they can do almost everything that healthy people do.
Record content:
-
1 Varieties of the disease
- 1.1 Trisomy
- 1.2 Translocation
- 1.3 Mosaic
-
2 Down syndrome severity
- 2.1 Deep (heavy)
- 2.2 Moderate (average)
- 2.3 Light (weak)
- 3 Manifesting symptoms
- 4 The reasons for the development of the disease
- 5 Diagnostic measures
- 6 When a specialist consultation is needed
- 7 Treatment
- 8 Medicines
- 9 Other treatments for Down syndrome
- 10 Possible complications
- 11 Down syndrome video
Varieties of the disease
In medical practice today, several types of Down syndrome are distinguished.
Trisomy
It has been proven that 95% of people diagnosed with Down syndrome have an excess chromosome number 47. This type of deviation is not considered genetic. In such situations, cell division begins directly in the egg (in 95% of all cases) or in the sperm (only 5%). As the fetus grows and develops, this extra chromosome gradually penetrates into all cells of the body.
Women over the age of 35 are at greater risk of having a baby with trisomy than young girls. There is a risk that the older a woman is and the later she becomes fertilized, the greater the risk that the cells will start dividing incorrectly.
When a man is 40 years old, such risks also increase, because it is during this age interval that abnormal cell divisions in sperm cells are most often observed.
Translocation
This type of disease is diagnosed in only 4% of children with Down syndrome. In this case, the total amount of chromosomes does not change, there are 46 of them, but some of them can involuntarily begin to disintegrate and over time are added to the rest. As a result of this, signs begin to form that are characteristic only of Down's syndrome.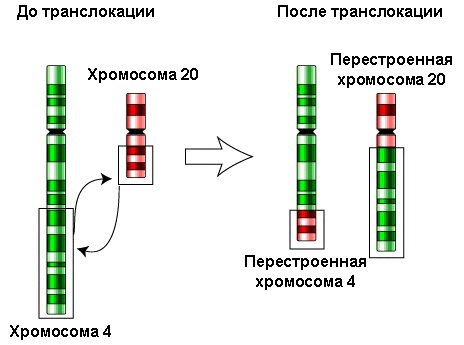
In some situations, special analyzes can be carried out to identify the source that provoked translocation, but most often such a reaction of cell division and attachment is accidental and is considered genetic mutation.
Mosaic
This form of the disease can be diagnosed in 3 out of 100 children who have previously been diagnosed with Down syndrome. Mosaicity is characterized by minimal abnormal cell division after fertilization.
All other cells divide without deviation. As a result of incorrect division, not 46, but 47 chromosomes are formed, and the amount of genetic material significantly exceeds the norm.
At the time of the growth and development of the fetus, all these cells (both those that have divided correctly, and those whose division has passed with deviation) continue to reproduce. A child whose cells, which have divided correctly, significantly exceed animal cells, has every chance that Down's syndrome will proceed more easily with less severe symptoms.
Down syndrome severity
The severity of the course of syndrome D level of mental retardation. Based on this, the degrees of Down syndrome are divided into 3 types.
Deep (heavy)
A deep degree occurs quite often, and significantly aggravate a person's position in society.
In addition to the fact that such people are very closed and do not let anyone near them, their training takes place with great effort, both for themselves and for those who conduct classes with them. Children and adults with a severe degree of the syndrome will need constant care and attention from loved ones.
With a similar degree, timely medical treatment is important, as well as the use of additional techniques that help reduce further complications of the syndrome.
Moderate (average)
The intermediate degree also requires special care and attention. With proper implementation of all recommendations, the disease can be kept "under control." Remedial gymnastics and physical education, speech formation classes are mandatory.
Remedial gymnastics and physical education, speech formation classes are mandatory.
Light (weak)
If a child or an adult has a mild degree of the syndrome, then the chances that such people will practically not differ from healthy people and will be able to achieve success in school and work increase.
With proper development and implementation of all special recommendations, people with mild Down syndrome socialize well and adapt to life. They are more open and make contact with peers and people around them.
Manifesting symptoms
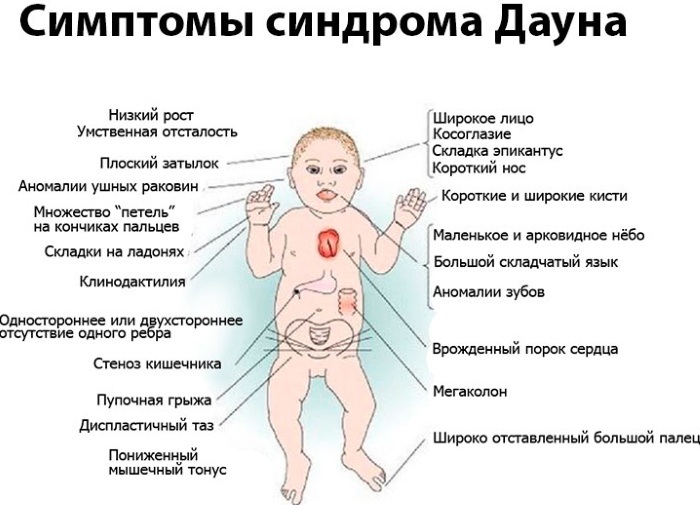
A child, as well as an adult suffering from Down syndrome, has some external signs by which it is easy to recognize the ailment. Over time, the situation can worsen and the number of symptoms increases with age.
Down syndrome (photos of adult patients below in the article) is characterized by the following external signs:
- Short stature. Most often, a person's height does not exceed the mark of 150 centimeters, such a deviation is directly related to the structure of the tubular bone and the improper performance of growth hormone. Children and adults with small stature may also become overweight in the future.
- Abnormal formation of the bones of the skull. The shape of the head of a child or adult seems to be cut off, it is wide and short.
-
Rounded face shapes. A person's face becomes flat due to insufficient development of the facial bones. In this case, there is a pinkness of the cheeks and the absence of any mimic actions.

- Mongoloid type of eyes. It is characterized by the presence of a skin fold that starts from the upper eyelid and ends near the lower one. In this case, the eyes appear slanting.
- Shortened neck. In childhood, folds are clearly visible on all sides of the spine (the skin is not taut). In adulthood, these folds are not so visible.
- The forehead is fairly flat and low. This bone shape is preserved in both the child and the adult.
- Hair grows below normal. But baldness as such is not observed.
- Short nose shape. It is explained by the improper formation of bone tissue. The nostrils are very round and wide, and the base of the nose is also very wide. The nasal septum may be off-center.
- Underdevelopment of the upper jaw. At the same time, it sticks out very much forward and has a narrow shape. The lips are a little thick, their contours are poorly expressed. The lower lip may hang down a bit, causing cracks to form on it.
- In 65% of cases, improper placement of teeth, as a result of which the child's bite is disturbed, the teeth are not even, they can be both blunt and pointed. The teeth are not adjacent to each other, therefore, tooth gaps are formed. In childhood, milk teeth appear late, and some permanent teeth may never appear.
- Large furrowed tongue. Longitudinal cracks may form on it. Due to its large size, the tongue does not always fit in the mouth, for this it must be bent. For this reason, it is not always convenient for the patient to eat and talk. There are cases when a tongue that is too large is excised a little in order to reduce the level of discomfort for a person.
- Small limbs. A similar symptom is observed in both children and adults. The fingers are very short, the little finger is strongly curved towards the inner side of the palm.
- Abnormal formation of the bones of the chest (rib cage). There is a small depression in its lower part. There may be cases when the sternum bulges forward. When diagnosing cardiac pathologies, a heart hump develops.
- Muscle hypotension. It manifests itself in 80% of patients. Due to the weakness of muscle tone, the development of the whole organism is inhibited to a large extent. Such babies can begin to crawl, sit or walk much later.
- The belly sagging down. Due to muscle hypotension, the navel is very low when it is, which leads to the development of an umbilical hernia, as well as a hernia of the white line of the abdomen.
- Joint mobility. As a result of severe weakness, the articular apparatus begins to produce flexion movements of almost 180 degrees. The consequences of this are injuries - dislocations, subluxations (occur in 80% of patients).
- Flat feet. It is diagnosed in conjunction with a small foot size. In childhood, such a violation is practically not noticeable, however, it becomes impossible for an adult to choose shoes for himself, because the size of his foot at 30 years old can be equal to the size of a child's 12 feet.
- Slow development of reproductive structures. This problem is corrected in adolescence, and the size of all organs is normalized. However, in adulthood, infertility can be diagnosed in men, and a woman is at risk of giving birth to an unhealthy baby (in 50% of cases).
- Overdrying of the skin. Very often eczema is formed, due to improper blood circulation. Due to the thin skin, all the veins and blood vessels become visible, which can cause various injuries leading to blood loss.
- Wrong, fuzzy speech. It manifests itself due to improper formation of the pharynx and a lag in mental development in childhood. The person speaks very slowly, his voice is hoarse, the words are not intelligible. A similar violation is manifested in 100% of cases of Down syndrome. Lifelong learning with a speech therapist is required.
Down syndrome (photos of adults and children indicate external differences with healthy people) is also characterized by internal deviations, which indicate the presence of the syndrome:
- Decreased immunity. Children most often get sick with bronchitis, pneumonia and other respiratory diseases.
- Infectious eye diseases.
- Heart disease. It can be diagnosed immediately after birth, or it can manifest itself in adulthood.
- Thyroid disorders (hypothyroidism). Diagnosed in adulthood.
-
Gluten enteropathy. The work of the digestive system is disrupted due to damage to the integrity of the villi located in the small intestine. It occurs in both children and adults.
The life expectancy of people with Down syndrome differs from healthy people. There are cases when children with the syndrome did not live up to 6 years, however, according to statistics, the average life expectancy of a patient becomes 50 years.
The reasons for the development of the disease
Down syndrome is classified as a pathology of genetic origin. It begins its formation directly during conception, in the process of fusion of the egg and sperm.
In 90% of cases, such phenomena occur due to the fact that female germ cells carry sets of chromosomes, the number of which does not exceed 24, although in reality there should be 23 of them. Only 10% of this extra chromosome can be inherited by the baby from her father.
The very process of the development of a chromosomal abnormality is that some of all cells have an extra chromosome (the reason for this is a protein of a special origin).
This function of the protein is to stretch the chromosome itself to the poles of the cell at the time of its division. This happens so that in the future it will be possible for each daughter cell to receive a single chromosome from the existing pair.
In the event that the normal state of this protein is disturbed, two chromosomes from a pair begin to relocate to the opposite pole. Only after this does the process of formation of the shell begin to occur, which indicates the formation of a new full-fledged reproductive cell.
If there is a defect in a protein, the cell contains 24 chromosomes. If such a cell takes part in fertilization, then in 99% of cases the fetus will be diagnosed with Down syndrome.
In addition to a genetic abnormality, the following factors and pathologies can cause the development of Down syndrome:
- The conclusion of marriage between people with family ties. Relatives are considered carriers of the same genetic disorder. And if both have abnormalities in chromosome 21 or protein structure, which are fundamental in the direction of chromosomes, then the probability of having a baby with Down syndrome is more than 90%. The closer the degree of relationship, the greater the chance of developing this genetic disorder.
- Pregnancy before the age of 18. In girls under 18 years of age, the formation processes in the body have not yet been completed. The work of the gonads can malfunction. Oocyte maturation during this period can occur with delay or haste. This is what can cause the development of various abnormal abnormalities in the unborn child.
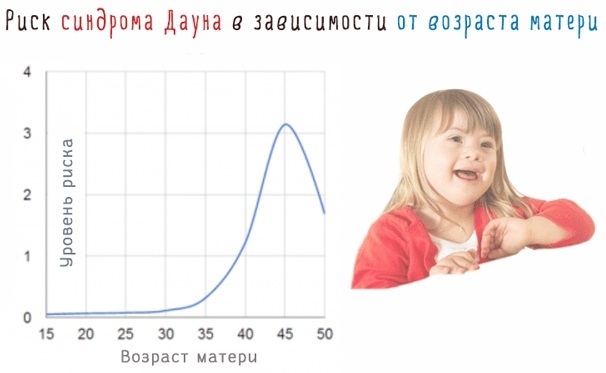
- Pregnancy after 35 years. The older the mother is, the greater the risk of acquiring genetic abnormalities for the fetus. Down syndrome is in the first place in such cases.
- The age of the future father. The older the man, the more changes occur in the process of sperm formation, as well as negative changes in the structure of the genetic material itself.
- The age of the mother of the woman who decided to get pregnant. If a maternal grandmother became pregnant at a later age (after 30-35 years), then her grandchildren in the future are in danger in the form of the development of genetic abnormalities. Indeed, in all women, egg reserves are formed for the rest of their lives, and if the grandmother's age is great, then the risk of fertilization of an egg with an extra chromosome increases significantly.
- Both parents have 21 chromosomes. Often, adults do not know about translocation. After all, such violations do not manifest themselves in any way outwardly. In such situations, part of chromosome 21 is fixed on another chromosome (14th). In medicine, this phenomenon is called "Family Down Syndrome". Such couples, before planning a pregnancy, must undergo medical examinations and pass tests to determine the risk of developing Down syndrome in the fetus. And only on the basis of the results to make a decision about pregnancy.
It is possible to analyze the frequency of birth of a child with Down syndrome in each age interval of a woman based on the data of numerous studies.
| Mother's age | The frequency of birth of children with diabetes |
| 15-19 | 1:2300 (0,043%) |
| 20-24 | 1:1600 (0,062%) |
| 25-29 | 1:1200 (0,083%) |
| 30-34 | 1:870 (0,115%) |
| 35-39 | 1:300 (0,33%) |
| 40-44 | 1:80 (1,25%) |
| 45 | 1:45 (2,2%) |
Since Down syndrome develops at the genetic level, you should not look for its causes in infectious diseases that a woman had previously suffered, heavy robots, or the effect on the body of high levels radio waves.
Diagnostic measures
The diagnosis of Down syndrome is established on the basis of the results of the examination and the current clinical picture. First of all, pregnant women and newborns are checked for pathology. For women who are in a position, special biochemical studies are offered, which make it possible to identify syndrome D in the fetus.
These include:
-
Amniocentesis. It is a study of amniotic fluid that allows you to identify the presence of genetic abnormalities. Held for a period of 22 weeks and 6 days, or a little later. Its cost is 1500-2000 rubles.
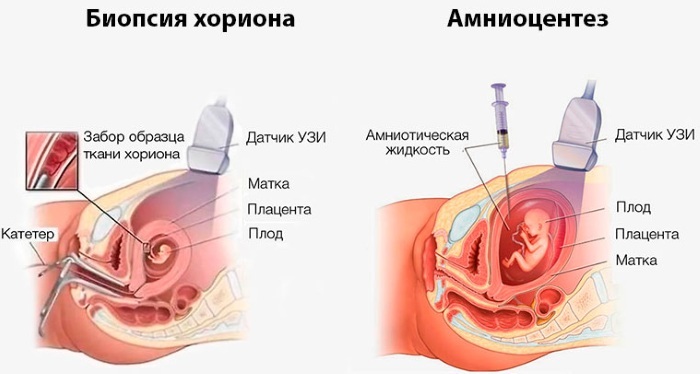
- Chorionic biopsy. It consists in carefully examining the chorion sample for genetic abnormalities. The sample is taken by puncture of the uterus through the front of the abdominal wall. The optimal timing is 9-12 weeks. Cost from 5000 rubles.
- Cordocentesis. A procedure involving puncture of the vessels of the umbilical cord. The blood obtained from the umbilical cord is sent to the laboratory to detect any genetic abnormalities in the development of the fetus. It is carried out after the 20th week of pregnancy. The price ranges from 12,000-13,000 rubles.
Studies aimed at diagnosing the thyroid gland, visual and auditory analyzers, heart disease and leukemia are also important.
Analyze the following indicators:
- thyroid stimulating hormone and thyroxine;
- bone marrow biopsy (diagnosis of leukemia);
- chorionic gonadotropin (hCG).
- plasma protein A (PAPP A).
- alpha-fetoprotein (a low value confirms the presence of Down syndrome);
- beta-hCG.
- free estriol. A low level is a sign of developing fetal Down syndrome.
Based on the indicators of ultrasound, PAPP A, Alpha-FP, hCG and free estriol, a special chart is drawn up, according to which it is easy to determine the level of risk of having a baby with Down syndrome.
For women who have any predisposition to anomalies of this nature, it is mandatory to consult a geneticist. All research is carried out exclusively with the consent of the expectant mother. Material costs also fall on the shoulders of the parents.
When a specialist consultation is needed
Symptoms indicating the presence of Down's syndrome appear already in utero and are visible at the birth of a baby. In most cases, doctors recommend terminating the pregnancy. What decision to make is up to the parents themselves.
However, when deciding to save the fetus, it is important to understand that in the future, help will be needed not only for the mother, but also for the newborn baby. Such a pregnancy until the birth itself will be under the strict supervision of doctors and with regular tests and diagnostic examinations.
After the birth of the child, first of all, there will be a consultation with a neonatologist, neuropathologist, cardiologist, ophthalmologist, surgeon. Such examinations for a child with Down syndrome will need to be carried out regularly.
Treatment
Down syndrome, it is impossible to cure, as well as all the changes in appearance that occur at the same time (photo below from the article). It is important to conduct regular medical supervision by all specialists of a narrow profile. Correctional work with children is also important, which enables them to develop and be more adapted to life.
The sooner you start working with your child, the better you will be able to form in him all the abilities and skills necessary for life.
Down syndrome treatment is as follows:
- bioacoustic correction method;
- physiotherapy;
- physiotherapy exercises and gymnastics;
- transcranial micropolarization;
- regular sessions with a speech therapist and psychologist;
- consultation and work with all family members;
- animal therapy;
- microcurrent reflexology;
- method of ultra-small electrical impulses.
These techniques are aimed solely at improving the mental, psychological, emotional and physiological state of the patient with Down syndrome.
If you have any pathologies of the heart or gastrointestinal tract, surgery may be necessary.
Medicines
Medication therapy for Down syndrome is used to combat diseases that are the result of genetic pathology.
Medicines are prescribed by a doctor based on tests and examinations. Only after receiving all the results is the diagnosis of the concomitant disease established and the tactics of its further treatment determined.
Most often, the following drugs are used in the treatment of adults and children:
- Tsinarizin, Sermion, Cavintol (directed to the treatment of vascular pathologies).
- Actovegin, Solcoseryl, Cortexin (used for neurological diseases).
- Piracetam, Phenibut, Pantogam, Picamilon (nootropics that improve blood flow to the brain).
- Homeopathy (used to treat mental disorders, respiratory diseases).
- Herbal preparations (valerian, motherwort).
The dosage is determined on an individual basis. Therefore, it is strictly forbidden to prescribe these drugs to yourself or your relatives!
Other treatments for Down syndrome
Other popular and equally effective treatments for Down syndrome include:
- Treatment by the method of introducing brain stem cells (the safety and effectiveness of the procedure has long been proven, so more and more patients with a diagnosis of syndrome D are turning to it).
- Dolphin therapy. It arose relatively recently, but has proven itself very well when working with both children and adults who have been diagnosed with a mild degree of mental retardation.
- Massages of different parts of the body.
- Game therapy.
- Sand therapy.
- Paint therapy.

- Gymnastics classes.
- Individual lessons with a speech therapist and psychotherapist.
Using folk remedies is not safe and gives absolutely no results. Most often, these methods are not even discussed.
Possible complications
Down syndrome (photos of adults and children below in the article), is characterized by the fact that with age, the difference from healthy people is more pronounced.
In addition, both in childhood and in adulthood, patients may face the following complications:
- heart disease;
- leukemia;
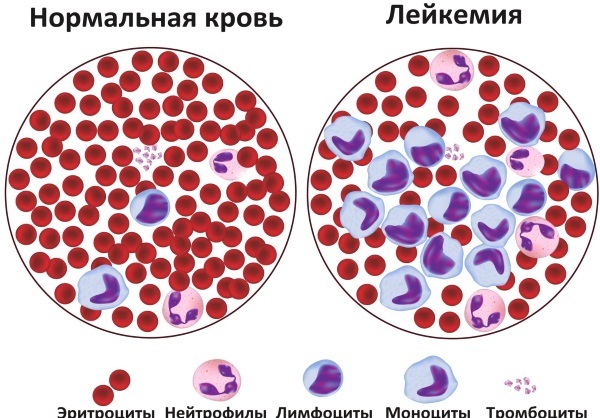
- diseases of infectious origin;
- dementia (develops after 40 years);
- holding your breath during sleep (can be fatal);
- overweight;
- loss of vision;
- impaired renal function;
- ulcers and diseases of the stomach.
Do not ignore the manifestation of other diseases, because they can negatively affect the further life of a person. When the first symptoms of any of the listed diseases appear, it is imperative to seek medical help.
Down syndrome is one of the most unpleasant and dangerous genetic manifestations in the human body.
It has a negative effect not only on a person's health, but also on his appearance (photos of adults with Down syndrome speak for themselves). To somehow help a child and an adult requires daily work and care. After all, the main treatment is love and care from relatives and friends.
Down syndrome video
Down syndrome:



