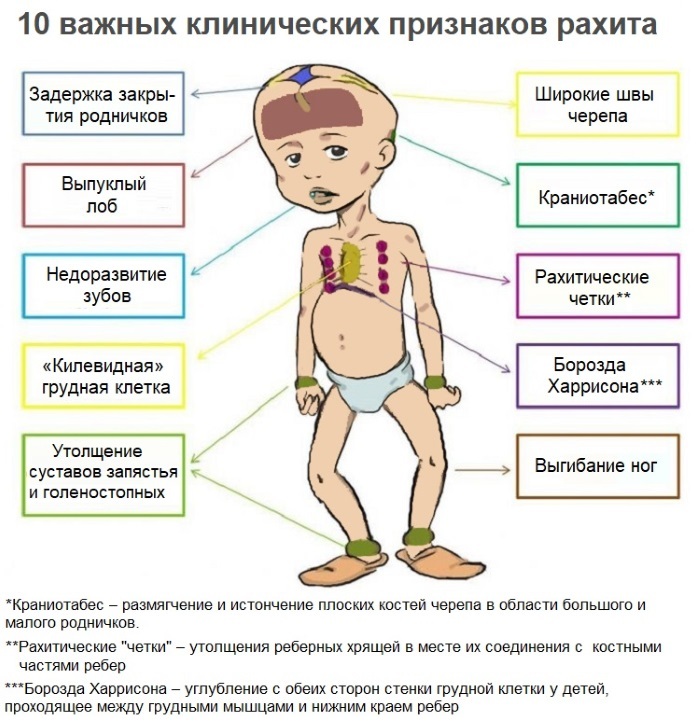
Abnormal head reshaping with the subsequent violation of the correct shape and possible destruction of the bone in medicine is called deformation of the skull. In newborns, this phenomenon is often associated with the presence of serious hereditary pathologies or received birth trauma.
For this reason, deformity can be acquired or congenital, due to which the clinical symptoms have significant differences. The most dangerous complications include violations in the work of internal organs, mental retardation.
After the birth of a child, parents should monitor the size of the newborn's head circumference in order to timely identify possible deformities of the cranium. Only in this case it is possible to identify a dangerous pathology at an early stage in order to timely start complex treatment and avoid possible complications.
Record content:
- 1 Views
- 2 Stages and degrees
- 3 Symptoms
- 4 Causes
- 5 Diagnostics
- 6 When to see a doctor
-
7 Treatment methods
- 7.1 Cranial orthoses
- 7.2 Seeing an osteopath
- 7.3 Surgical intervention
- 8 Possible complications
- 9 Skull deformities video
Views
Deformation of the skull in newborns should be determined in a timely manner by a specialist, as this allows establish the exact reasons for the development of pathology, choose the right effective treatment and correct the condition child. Otherwise, the occurrence of complications and concomitant diseases is possible.
Pediatricians distinguish the following types of skull deformities:
-
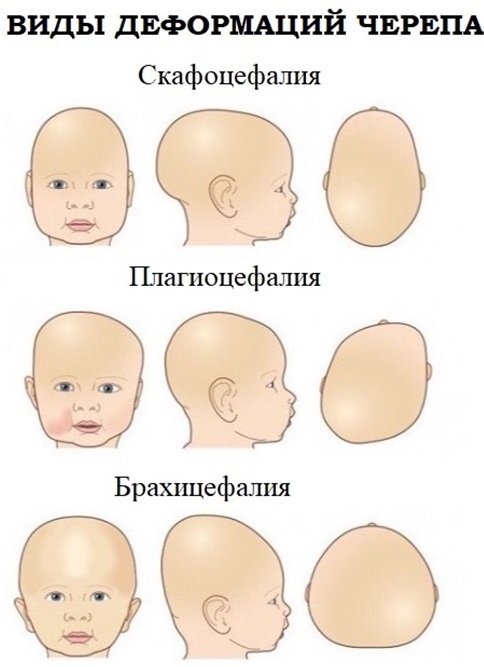
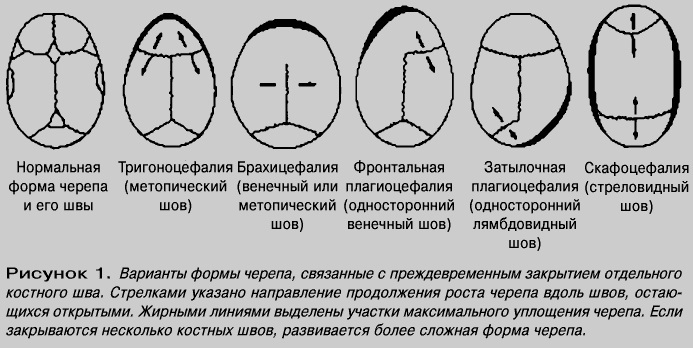
Brachycephaly. This type of deformity is characterized by the development of a cut flat forehead, expansion of the parietal bones with a simultaneous protrusion of the occipital bone forward. Pathology can occur against the background of intrauterine infections transferred or injuries received during childbirth.
- Acromegaly. The child is diagnosed with a symmetrical increase in the size of the skull compared to the trunk. The reason may be endocrine diseases, provoked by the rapid development of oncological neoplasms in the pituitary gland. At the same time, the growth of the nose and limbs occurs.
- Scaphocephaly. This type of skull deformity is characterized by the protrusion of the occipital or frontal bone forward. Additionally, the child may be diagnosed with impaired growth and development of the brain. There are no symptoms of mental retardation.
- Plagiocephaly Against the background of deformation, flat, flattened lateral surfaces appear on the head. This pathology is most often diagnosed with a rather large head size with a relatively large fetal body weight during a woman's pregnancy.
- Dolichocephaly. The child has a narrow, elongated head with a high forehead. This type of deformity does not cause disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system.
- Trigonocephalus. The pathology is characterized by the presence of a narrow, pointed forehead with a simultaneous increase and significant protrusion of the lower jaw. Pathology develops against the background of premature fusion of the cartilaginous septa of the skull.
-
Microcephaly. As a result of the development of pathology, the child is diagnosed with a disproportionately small size of the head in comparison with the body. This type of deformity occurs against the background of impaired formation of the brain and premature fusion of the skull bones. Pathology is fraught with developmental delays.
The shape of a newborn's head largely depends on labor and the way the baby is born. For example, if the obstetrician-gynecologist was forced to resort to caesarean section, then the skull will have a brachycephalic shape. As a result of passing through the birth canal, the newborn will have a dolichocephalic head shape.
Stages and degrees
Deformation of the skull in newborns does not always indicate the presence of pathology. When the child can sit up and spend more time in an upright position, then the situation will change. Pediatricians say that by 2-3 months of life, the skull becomes more symmetrical, deformities disappear.
Too rapid overgrowth of the non-ossified part of the cranial vault can provoke the development of various deviations. In this case, the cranium becomes stiff ahead of time, which is why the child can be diagnosed with intracranial pressure.
Intrauterine pathology of the anlage and subsequent development of bone tissues at the stage of embryogenesis can affect the deformation of the head shape.
Deviations from the norm in 98% of all cases occur for the following reasons:
- Dysplasia.
- Infectious diseases.
- Genetic pathologies.
- Incorrect position of the fetus in the womb.
Even in the process of difficult childbirth, the child's brain is damaged in isolated cases, since it is well protected from possible compression. But subsequently, parents, together with a qualified pediatrician, will have to make a lot of efforts to eliminate the existing deformation of the skull.
Deviations from the norm should be detected at an early stage, before the final closure of the fontanelle occurs. In this case, craniosacral therapy will be effective. The doctor can correct the asymmetry of the skull using special manual techniques.
A deviation in the size of the child's skull from the norm may indicate the presence of a serious pathology.
Pediatricians distinguish the following forms of deformation of the bones of the head:
-
Hydrocephalus. This is a congenital condition when the child has a too big head. Against the background of this pathology, dropsy of the brain can develop, which provokes a significant swelling of the fontanelle, an increase in the size of the cranium. The danger of the disease is that the child can develop serious neurological disorders that can lead to death.
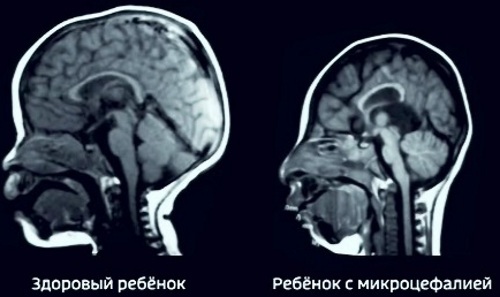
- Microcephaly. The baby's head is too small. The fontanelle closes ahead of time, which is why the cranium cannot enlarge. This pathology is fraught with the development of numerous complications.
Only a qualified doctor can determine deviations from the norm, since often in the process of the development of a newborn, the asymmetry of the skull and the existing irregularities are smoothed out. The head of the child acquires the correct shape only by 1 year. The final cranial circumference in 98% of children is formed closer to 7 years.
Symptoms
Deformation of the skull in newborns is characterized by the appearance of various painful symptoms and cosmetic defect. Most often, the child is worried about attacks of acute headache, which practically do not go away even with the use of various medications.
But in most cases, the deformation of the skull occurs in children on its own, without causing disturbances in the work of the central nervous system.
Only under the condition of strong compression of a certain area of the brain, the following symptoms occur:
-
Displacement in the nape of the bone plates: frequent and profuse regurgitation, violation of the sucking process, blurred vision, scoliosis, speech defects, curvature of the cervical vertebrae.
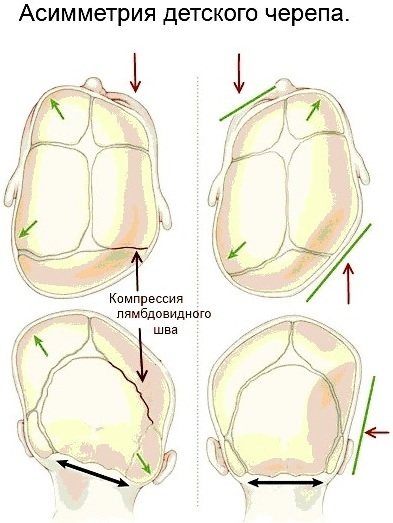
- Asymmetry of the sphenoid bone: strabismus, impaired articulation, increased intracranial pressure.
- Depressed forehead: increased fatigue, muscle weakness, significant lag in psychomotor development.
- Asymmetry in the temporal region: decreased hearing acuity, impaired coordination of movements.
In the absence of comprehensive treatment, a severe form of pathology can lead to the fact that in the future the child will not be able to serve himself on his own.
Only timely seeking medical attention will help reduce the risk of complications.
Parents should be alerted to the following deviations in the appearance of the newborn's skull:
- The presence of soft or hard bumps on the child's head.
- Crimson, bluish spots on the skull.
- Asymmetry of facial expressions.
- Development of infant jaundice.
- Asymmetry of the jaw and part of the facial skeleton.
- Constant lacrimation.
- Bulging fontanelle at rest.
If at least 1 of these symptoms occurs, the child's parents should seek the advice of a pediatrician. To correctly determine the diagnosis, the newborn will be prescribed an ultrasound scan, MRI.
Causes
Pediatricians distinguish several reasons at once that can provoke the onset of deformity of the skull in a newborn. Pathology can be congenital or acquired. Most often, the deformity of the skull is formed in a child in the womb.
Symptoms of pathology appear immediately after birth. Even during pregnancy, it is possible to identify possible deviations using an ultrasound examination of the fetus.
Most often, bones change their shape due to the rapid development of various diseases that negatively affect the child's body even at the stage of laying the bone tissue during the first 3 months pregnancy.
The reason may be infectious diseases that the expectant mother had previously had. The greatest danger is posed by pathologies of a bacterial and viral nature. Pediatricians also do not exclude the presence of genetic disorders that were caused by various chromosomal abnormalities.
After the conception of a child, the quality of the laying of bone tissue largely depends on the presence of meningococcus, influenza virus or sexually transmitted infections in the expectant mother. Among the hereditary causes, it is also possible to single out the long-term use of medications by a pregnant woman, which have a negative effect on the development of the internal organs of the fetus.
In 35% of all cases of deformities of the skull in newborns occur against the background of rickets. This pathological condition develops against the background of insufficient vitamin D content in the body, due to which there is a gradual softening of bone tissue. Negative changes in the body occur in a short time.
In newborns, deformity of the skull can also be associated with difficult childbirth, when the woman had rapid contractions or the eruption of the head took too long.
Pathology can develop due to the presence of bone diseases in the child. For example, osteoporosis, when the skeleton softens with a subsequent decrease in cell density. In 5% of cases, while still in the womb, the child develops osteomalacia, osteodystrophy or osteodysplasia. The condition may worsen against the background of circulatory disorders with insufficient tissue nutrition.
Diagnostics
To correctly determine the diagnosis, the pediatrician must collect a detailed history. Increased attention is paid to the fact of heredity, the course of pregnancy. The information about the diseases, injuries suffered by the woman and the effect on the body of various toxic substances is being studied.
The doctor should collect as much information as possible about the method of delivery (the child was born through the birth canal or the obstetrician-gynecologist had to perform a caesarean section). The presence of hematomas in the head area of the newborn and the duration of attempts are taken into account.
The pediatrician examines the child and gently probes the main bony protrusions. The need for prescribing treatment largely depends on the condition of the fontanelle and the time of its overgrowth. A measuring tape is used to determine the size of the head. The specialist pays attention to the ratio of different parts of the skull.
| Diagnostic method | Description |
| X-ray | This method is relevant if the pathology is detected at an early stage, and the doctor has no doubts about the diagnosis. With the help of radiography, you can get an overview of the child's head and identify the existing deformities.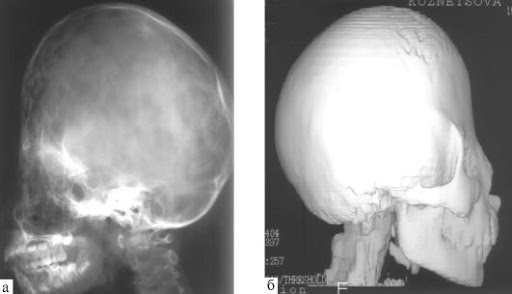
|
| Magnetic resonance imaging or computed tomography | This diagnostic method is relevant in severe cases, when the doctor cannot accurately determine the type of deformity using X-ray. MRI and CT allow you to get the most reliable research results. |
| Doppler blood vessels of the brain | This diagnostic method is used if the doctor suspects a violation of the intracranial circulation. |
| Ultrasound procedure | Ultrasound is highly accurate in detecting deformities of the skull in an unborn child at any stage of pregnancy. |
In clinics in Moscow and St. Petersburg, the ultrasound procedure costs from 1600 to 2300 rubles. For MRI and CT you will have to pay 840-3200 rubles. Doppler examination costs from 500 to 13450 rubles.
When to see a doctor
Initially, parents or a pediatrician may notice deformities of the newborn's cranium during a routine examination. In 99% of all cases, it is the pediatrician who prescribes a referral to a physiotherapist, maxillofacial surgeon and neurologist.
In special cases, the help of a neurosurgeon may be needed. The most accurate clinical picture will be drawn up only if the child is examined by all of the above specialists.
At the first suspicion of a curvature of the skull of a newborn, parents should consult a qualified pediatrician as soon as possible. If the doctor does not notice any deviations from the norm, then you can contact specialists from other clinics. It is forbidden to self-medicate. Only timely started therapy can achieve positive results.
In severe cases, surgical treatment may be required, the expediency of which is determined by the neurosurgeon. To combat deformities of the skull, a special cranial orthosis can be used, but this is only in that situation if the child is not yet 1.5 years old.
Treatment methods
Deformity of the skull in newborns can be eliminated only with timely referral to the pediatrician. The doctor must determine the cause of the development of the pathology and send the parents together with the child for a consultation with a neurologist, traumatologist and endocrinologist.
Therapy should be prescribed at an early stage of the disease. Only in this case it will be possible to correct cosmetic defects and exclude the likelihood of the development of concomitant pathologies.
Among the main methods of therapy are:
- The use of medications. The use of drugs is indicated in the case when the child's pituitary gland is disrupted and concomitant diseases have arisen against the background of complications of the existing pathology.
- Surgery. The duration of treatment depends on the type of deformity. For example, removal of bone fragments for the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid and decrease in intracranial pressure, excision of cartilage tissue.
Only complex treatment can reduce the likelihood of deterioration in the functioning of the central nervous system after changes in the structure of the bones of the skull.
If the deformity of the skull is insignificant and not a pathology, then parents of a newborn can adhere to the following recommendations:
- It is necessary to periodically change the position of the child during sleep and rest.
- It is necessary to properly equip the sleeping place.
- To effectively combat skull deformities, the muscles of the child's neck and back should be strengthened.
- It is forbidden to use soft pillows and mattresses.
- During wakefulness, the child should be in an upright position for more time.
Every mother should remember the importance of breastfeeding. Those children who feed on breast milk are least susceptible to various infant pathologies, and also have stronger bones and immunity. Often, minor deformities of the skull in newborns go away on their own thanks to regular breastfeeding.
Cranial orthoses
Deformation of the skull at an early stage can be corrected by regularly changing the position of the child's body. If the newborn has already developed asymmetry, then experts recommend using a cranial orthosis.
This medical device helps the baby's skull to form symmetrically. The effectiveness of a cranial orthosis is that it exerts slight but constant pressure on a specific part of the head, which helps to get rid of deformities in a specific area.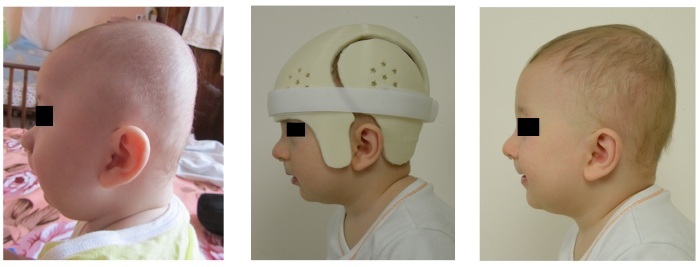
The use of this device is most relevant only from 4 to 6 months of a child's life. During this period, the bones of the skull are quite soft and grow slowly, but the size of the brain increases rather quickly. For 4 months, the medical bandage is worn constantly.
The cranial brace may only be removed for a short period of time to allow the baby's skin to breathe. The bandage should be adjusted about once a week.
In addition, there are cranial orthoses to deal with deformities of the skull in an older age, but in this case, the treatment will take much longer. In 95% of all cases, treatment lasts from 7 to 11 months. Re-fabrication of the cranial orthosis may be necessary to correct severe deformities.
Seeing an osteopath
Numerous reviews of parents confirm the fact that timely access to an osteopath is a guarantee of a quick and complete recovery of a newborn. The first year of a child's life is optimal. Most of all, the child's body lends itself to correction from 5 to 7 months of life, since during this period of time there is an active development of the cervical vertebrae.
An osteopath helps relieve tension and spasm from tissues and muscles, improve lymph flow, normalize blood supply to internal organs, and activate metabolic processes.
The complex effect on the child's body allows you to restore the stable work of the whole body. For treatment, the doctor uses soft, painless techniques that do not cause complications and are absolutely safe. The likelihood of developing adverse reactions is excluded.
Timely referral to an osteopath allows you to get rid of the asymmetry of the skull, thereby avoiding the development of brain hypoxia, which develops against the background of circulatory disorders.
A qualified doctor helps prevent the likelihood of complications from the work of the central nervous system. Timely elimination of deformities of the bones of the skull reduces the risk of developmental delay and deterioration in visual acuity.
Surgical intervention
In 7% of all cases, the bones of the newborn's skull grow together prematurely. The result is inelastic, hard fragments that press against other bones in the skull as the brain grows in size.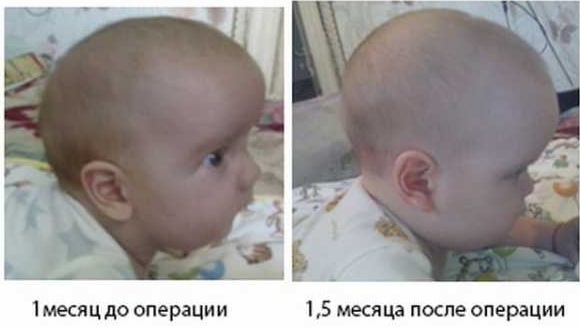
This pathological condition is called craniosynostosis (premature skull formation and suture obliteration). To reduce the likelihood of complications and deterioration of the child's condition, specialists use surgical intervention, during which the prematurely fused bones of the skull are severed.
Possible complications
The development of a deformity of the skull can be extremely dangerous for the health and life of the child. In the absence of medical care or ineffectiveness of the therapy, a violation may occur blood circulation in the brain with the subsequent formation of discirculatory encephalopathy, microangiopathy.
The presence of abnormalities in the growth of various parts of the nervous system can lead to the development of convulsive syndrome, mental retardation, and epilepsy.
From the first days of life, the child should be regularly examined by a pediatrician. It is necessary to monitor the nutrition of the newborn and provide him with daily walks with sufficient sunbathing. At the first manifestation of signs of deviation from normal development, you need to seek qualified medical help.
The presence of deformities of the skull requires urgent diagnostic procedures with subsequent determination of the diagnosis. Only a timely started complex treatment allows you to keep your child healthy. Long-term lack of medical care is fraught with disability.
Skull deformities video
Malysheva on the deformity of the skull in a child:



