Many do not even realize that they suffer from dyslalia. These are quite common in speech therapy. pronunciation defects in people who do not suffer from hearing or articulation problems. The main manifestation of dyslalia is the replacement, distortion or absence of certain sounds in speech.
If the degree of development of such a defect is not strong, then this does not affect the quality of human life. But there are more complex forms of dyslalia that are very noticeable when talking to others.
Record content:
- 1 What happens to the sounds in dyslalia?
-
2 Dyslalia classification
- 2.1 Mechanical
-
2.2 Functional
- 2.2.1 Motor type
- 2.2.2 Touch type
- 2.3 Acoustic-phonemic
- 2.4 Articulatory-phonemic
- 2.5 Monomorphic type
- 2.6 Polymorphic
-
3 Simple dislalia
- 3.1 Sigmatism
- 3.2 Rotacism
- 3.3 Pararotacism
- 3.4 Lambdacism
- 3.5 Parasigmatism
- 3.6 Jotacism
- 3.7 Gamacism
- 3.8 Kappacism
- 3.9 Chitism
- 4 Defects of opposition of consonants for deafness-voicedness
- 5 Complex dislalia
- 6 Causes of mechanical dyslalia
-
7 Causes of functional dyslalia
- 7.1 Biological prerequisites
- 7.2 Social prerequisites
- 8 Diagnostics
-
9 Dyslalia correction
- 9.1 Preparatory stage
- 9.2 Staging
- 9.3 Exercises for Automation
- 9.4 Differentiation
- 10 The prognosis of what will happen without treatment
- 11 Dislalia video
What happens to the sounds in dyslalia?
It becomes difficult for a person to pronounce certain sounds correctly. This leads to the fact that he either completely misses them or unconsciously distorts them. For example, a vivid example of dyslalia is the situation when a person says [v] instead of [l]. Often, children suffer from the fact that they cannot pronounce growling sounds. Often this defect goes away on its own, but sometimes it remains and requires correction.
Most often, abnormalities are diagnosed before the age of 6 years.
Dyslalia classification
There are 6 main types of dyslalia, which can be caused by different reasons.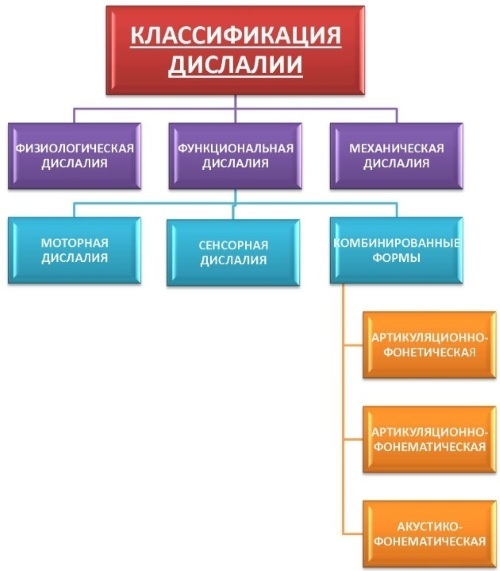
Mechanical
Dislalia of this type is most often associated with the peculiarities of the anatomical structure of the articulatory apparatus. That is, the problem may be in the improper formation of the palate and even the lips. Some of these features can be eliminated. At the same time, mechanical dyslalia does not have any effect on a person's spelling or vocabulary.
Functional
This type of defect can develop against the background of social factors or due to neurodynamic pathologies of the brain.  Vocabulary and writing are subject to change. In turn, functional dyslalia can be motor or sensory.
Vocabulary and writing are subject to change. In turn, functional dyslalia can be motor or sensory.
Motor type
Such a deviation is caused by neurodynamic shifts that occur in the central section of the so-called motor speech analyzer. During speech, a person moves his lips and tongue incorrectly, which is why he pronounces sounds incorrectly. This type of defect is also called phonetic.
Touch type
In this case, changes occur in the speech-auditory analyzer. A person cannot distinguish acoustically similar phonemes (for example, soft, hissing or voiced). In this case, sounds are replaced or greatly distorted during oral speech. That is, this deviation is phonemic. Also, with the development of such a defect, the patient may begin to replace letters while writing.
Acoustic-phonemic
Speech disorders of this type occur against the background of selective inaccurate analysis of phonemes according to their phonetic characteristics. A person suffers from poor sound perception and cannot fully distinguish sounds, therefore, he incorrectly recognizes and reproduces them.
With the development of the acoustic-phonemic form of dyslalia, patients do not suffer from hearing impairment. They can recognize some sounds well, while others cannot.
Articulatory-phonemic
This group of defects includes deviations that are characterized by incorrect selection of phonemes according to articulatory parameters. This type of disorder can manifest itself in different ways. For example, a person may have an incompletely formed articulatory base. In this case, instead of the correct sound, he chooses the one that seems to him the most suitable for the signs of articulation.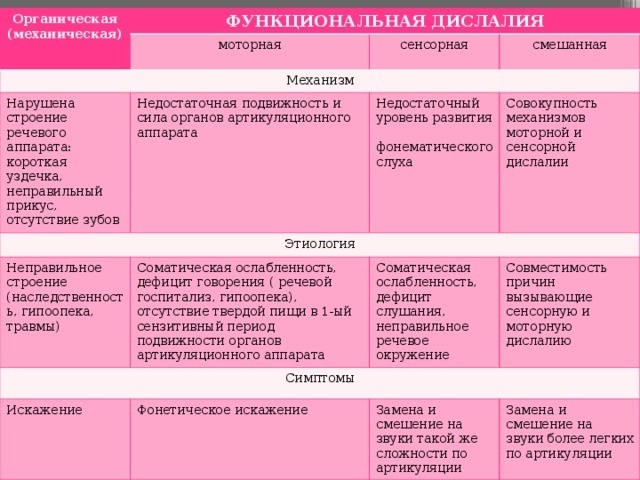
Also, the articulatory base can be fully formed, for example, when the child knows the phonemes well, understands how they sound, but replaces them with others when pronouncing.
Monomorphic type
A person does not pronounce only one group of sounds. For example, he clearly pronounces all phonemes except voiced and hissing.
Polymorphic
The patient has problems with sounds from different groups. Polymorphic dyslalia is a fairly extensive group of simple and complex defects. They can combine. If a doctor diagnoses a phonemic defect, then a "pair" is added to its name. That is, instead of sigmatism, parasigamatism can be diagnosed.
Simple dislalia
Dislalia in speech therapy is a defect that can be simpler when only one group of phonemes changes. Such situations are encountered in medical practice quite often.
Sigmatism
In this case, a person cannot correctly pronounce sibilant [f], [w], [w], [h] and sibilant phonemes [s], [s '], [z], [z'].
Rotacism
This deviation affects only the sounds [р] and [р ’]. This is a very common type of dyslalia. Children can pronounce these phonemes correctly only after 2 years. In most cases, it's all about articulation training. The child does not immediately understand how to correctly place the tongue in order to pronounce these sounds.
There are several types of rotacism:
| Rotacism type | Peculiarities |
| Side | When pronouncing sounds, the lateral edges of the tongue do not touch the upper extreme teeth. |
| Gorlovoy | The root of the tongue is weak. |
| Velar | As soon as the tongue approaches the hard and soft palate, vibration begins. |
| Uvular | The small tongue vibrates. |
| Rolling | The tongue moves too much. |
| Fricatical | The sound [p] is pronounced in English moner. |
Pararotacism
In this case, instead of [p], the person says [l]. Slightly less common is the replacement for [d] or [d]. There are about 30 subtypes of this type of deviation.
Lambdacism
Most often, there is a slight replacement of the sound [л] by [л ’]. In more rare cases, a person pronounces [y] instead of this phoneme.
In more rare cases, a person pronounces [y] instead of this phoneme.
Parasigmatism
It happens interdental, lateral, a little less often denture. The person changes [f] to [w], [w] to [s]. There are other variations as well. This defect is symmetrical. This means that in case of problems with soft sounds, a person also distorts soft sounds.
Jotacism
With such a deviation, the patient cannot pronounce [y] correctly. It replaces this sound or simply "swallows" it.
Gamacism
It is characterized by a lack of pronunciation of the phonemes [г] and [г ']. The patient can also replace them with similar ones when the tongue is in the closest position to the correct position.
Kappacism
The patient cannot pronounce [k] and [k '] correctly.
Chitism
There are problems with the phonemes [x] and [x ’]. When pronouncing, there may be too much vibration of the tongue.
Defects of opposition of consonants for deafness-voicedness
Dislalia in speech therapy is a very extensive topic that includes problems with the pronunciation of consonants with incorrect voicing and deafness. According to the ontogeny of speech, the child begins to distinguish these phonemes rather late because of their acoustic proximity. But later, this feature of the Russian language should be fairly easy to learn.
However, defects of this type occur in 4% of cases in children diagnosed with a violation of sound pronunciation. The reason for this deviation is most often the incorrectly developed phonemic perception or problems with the coordination of the work of the vocal apparatus or articulatory apparatus. Often, the defect appears simultaneously with the development of hearing loss or problems with the vocal cords.
Deviations of this type are fairly easy to spot:
- the person begins to deafen the sonorous phonemes;
- the patient, on the contrary, pronounces voiceless consonants too loudly;
- voiced and dull sounds are mixed.
Complex dislalia
Dislalia in speech therapy can also manifest in more complex forms. These are situations when several defects are combined at once. The most common are rotacism and lambdacism and rotacism and sigmatism.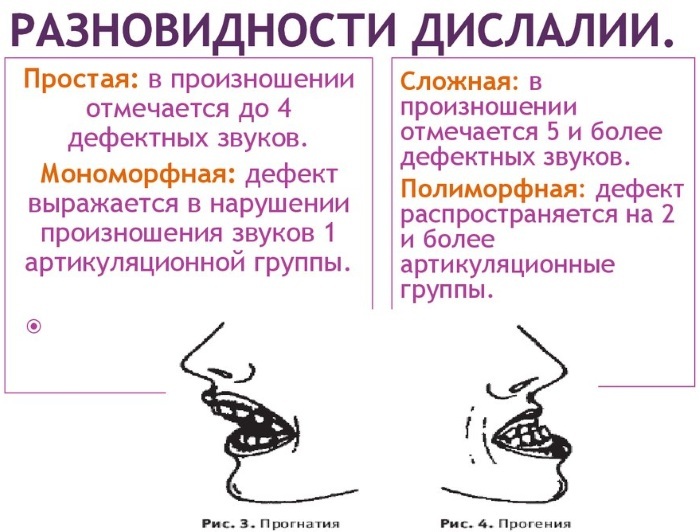
If a person has too short hypoglossal frenulum, then in this case he utters the sound [p] very muffled or replaces it with other phonemes that fall into the category of lower softening hissing.
Also, the patient may suffer from a defect in the opposition of sounds according to their parameters of hardness and softness or voiced and deafness. The most difficult type of deviation is total dyslalia. In this case, the child pronounces almost all consonant sounds incorrectly. At the same time, no problems are most often observed with vowel sounds.
There is also such a thing as Hottentaticism. In this case, of all consonants, the child pronounces only [t].
Causes of mechanical dyslalia
The main reason for the development of this type of dyslalia is an organic defect. That is, a child or an adult had an incorrectly developed articulation apparatus (lips, tongue or jaw).
Of the most common anomalies that provoke such speech problems, one can single out:
- Short frenum of the tongue. There is a shortened sublingual ligament, then in this case problems arise with the upper lingual sounds.
- Macroglossia and microglossia. These are violations in which the language can be too massive or, conversely, small. As a rule, children with physical or mental retardation suffer from such problems.
-
Lips that are too thick or too stiff. In this case, a person cannot correctly pronounce lip or labiodental sounds.
Also, problems can arise against the background of an incorrect bite or with improper construction and growth of teeth.
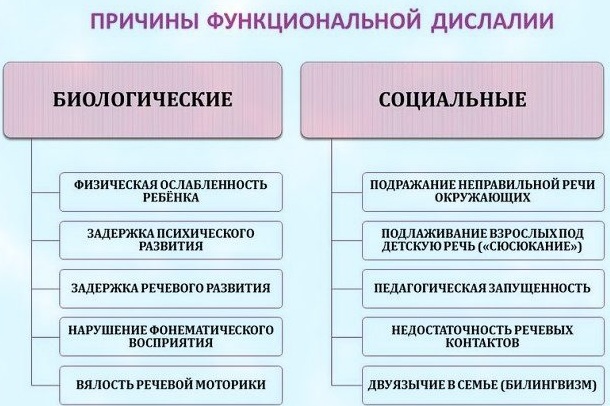
Causes of functional dyslalia
With the development of this deviation, the articulatory apparatus is not disturbed. This means that there is no organic basis responsible for disturbances in the process of sound production. Functional dyslalia predominantly develops against the background of one of the factors.
Biological prerequisites
This group of factors, against the background of which functional dyslalia develops, includes:
- mental retardation;
- chronic diseases;
- somatic pathologies;
- infectious diseases that the patient suffered at the time of the active formation of speech;
- hypovitaminosis;
- nutritional problems, against the background of which conditions such as dystrophy develop.
Disorders of this type negatively affect neurodynamics. She, in turn, is responsible for differentiation, which is carried out through the hearing aid, as well as the speech motor analyzer.
Social prerequisites
Dislalia in speech therapy is a deviation that can develop due to incorrect education of speech on the part of parents. Adults often lisp with small children. They memorize this pronunciation and begin to imitate it.
This also happens if the parents themselves suffer from lisp, burr of other speech defects. If, at the time of the active formation of speech, the child finds himself in a bilingual environment (for example, when the family moves to another country), then this can also cause dyslalia.
Diagnostics
Diagnostic measures begin with the fact that the doctor asks the mother of the child how her pregnancy took place, whether she had serious illnesses during this period.
You also need to take into account what the child himself was ill with at an early age. It is necessary to determine if there are problems in psychomotor development. To simplify the initial collection of anamnesis, it is recommended to provide the doctor with a medical record and other documents detailing all deviations.
In addition to the standard survey, the doctor checks the condition of hearing, vision and musculoskeletal system. During the examination, the doctor determines the mobility of the articulatory apparatus. To do this, the child is invited to perform a few simple exercises.
Also, the diagnosis includes an assessment of sound pronunciation. The doctor must understand how complex the defects are. Particular attention must be paid to phonetic hearing, that is, how well the patient is able to divide sounds into standard groups.
In his conclusion, the speech therapist must indicate the form and type of dyslalia, as well as the features of sound pronunciation. If the doctor has revealed that the child suffers from a deviation of the mechanical type, then it is additionally necessary to undergo an examination by a dentist, as well as an orthodontist.
With functional dyslalia, consultation with a neurologist is required. He will conduct appropriate analyzes and give his opinion. In addition, a speech therapist can issue a referral to an otolaryngologist who will assess the condition of the hearing aid. Only with a complete diagnosis can one begin to work on correction.
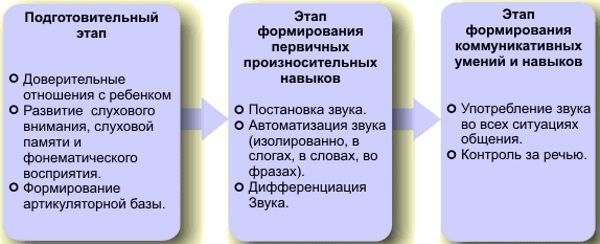
Dyslalia correction
Dyslalia correction is carried out in three stages. Only with a comprehensive approach can the deviation be corrected as quickly as possible.
Preparatory stage
If a child suffers from a mechanical type of dyslalia, then the first step is to eliminate the defects that caused it. For example, a doctor may perform tongue repair or prescribe orthodontic treatment.
In the case of motor dyslalia, it is required to undergo a course of exercises aimed at the correct development of the motor skills of the vocal apparatus. For this, logomassage or articulatory gymnastics can be prescribed.
If a child is diagnosed with functional dyslalia, then the main task is to develop phonemic processes. To form the correct sound pronunciation, it is necessary to perform exercises for fine motor skills and work out the so-called reference sounds.
Staging
At this stage, it is necessary to form primary pronunciation skills. The doctor should give the child an isolated sound. This can be done with mechanical aids or by doing mimic exercises. It is also important to establish the automation of sounds in individual syllables, then in words and sentences.
Exercises for Automation
An important part of this stage is not only the final correction of the pronunciation of sounds, but also the formation of correct communication skills. That is, the child must learn to accurately use the necessary sounds in the process of communication, without thinking about it.
It is important that speech therapy activities are regular, at least 2-3 times a week. Also, the doctor will give homework. At home, the child should also do articulatory gymnastics independently or with parents.
If simple dyslalia is diagnosed, then usually there are serious improvements in 1-3 months. In the case of a complex defect, correction may take up to six months.
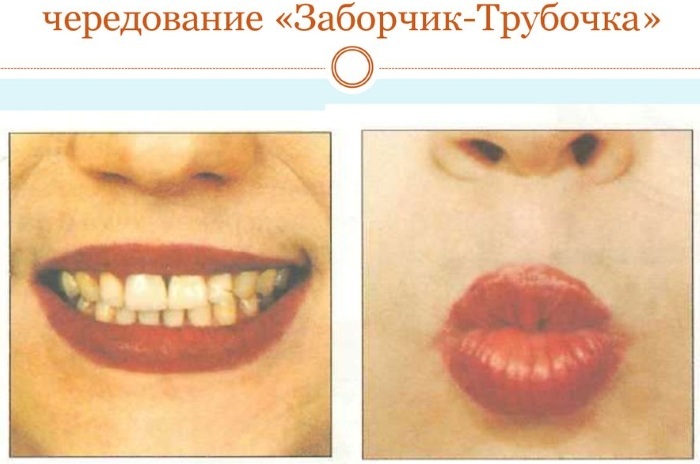
There are a number of basic exercises that doctors recommend for many types of dyslalia:
- Smile. You need to smile so that your front teeth are visible. This position of the lips must be fixed for 10 seconds.
- The tube. It is necessary to clench the teeth and pull the lips forward, creating a tube shape with them. They should also be in this position for 10 seconds.
- After that you need alternate "smile" and "tube" 10 times or more. Each time you need to hold the position of the lips for 10 seconds.
- Funnel. In the next exercise, you need to open your teeth and stretch your lips. After that, you need to sharply pull them in and tuck them under the teeth. Perform 10 times.
- Timpani. The lips are under the teeth. In this position, they need to be patted, as it were, creating sounds.
- Horse. The lips are relaxed. You need to start snorting like horses usually do.
- Bolt. In the next exercise, you need to clench your teeth and start moving your lower lip to the right and left.
- Hide and seek. The lower lip is hidden under the upper teeth. In this position, you need to stand for 5 seconds. After that, the same manipulation is performed with the lower lip. You need to do 10 repetitions.
Differentiation
Dislalia in speech therapy is a deviation that may require differentiation in the event that the delivered sound begins to mix with others. This requires additional corrective measures. It is necessary to develop auditory differentiation, to consolidate the pronunciation. The child should be able to perform phonemic analysis and synthesis.
To do this, the patient is offered to listen to paired words in which there is a new sound and the phoneme that he previously used as a substitute. As soon as the child recognizes the word, he must correctly pronounce the sound that he heard in it.
In the initial stages of differentiation, the doctor pays attention to each of the mixed sounds. At the same time, he consistently pronounces them together with the child and tries to form in him an auditory image of the reproduced phoneme. The speech therapist adheres to a certain plan.
First, he must clarify the articulation of sound and create a kind of support for tactile or visual perception. After that, he highlights a separate sound in the syllable. Then the task becomes more complicated and you need to clarify the sound in the word, and then in a long sentence.
The second stage of differentiation consists in mixing similar sounds. The child must learn to quickly identify each of them. It is also important to pay attention to the development of synthesis as well as phonemic analysis.
The prognosis of what will happen without treatment
If you do not begin to correct the dislalia in a timely manner, then in the future this can lead to problems in writing. If a child hears sounds incorrectly, then he will not be able to write dictations well and fully study at school. In rare cases, this even leads to a developmental disability, since it is more difficult for children with such disabilities to learn to read and count.
It depends on how successful the child will be at school. Therefore, it is recommended that such defects be corrected before visiting an educational institution.
With such a deviation, it will be more difficult for a child to interact with other children. Dislalia can be the subject of jokes from classmates. This can lead to depression and withdrawal. The child ceases to feel confident, is afraid to answer at the blackboard. This negatively affects learning and social networking.
It is easier to make adjustments at a younger age. An adult with dyslalia also has to deal with difficulties at work, especially if it involves communication with people. If we are talking about a mechanical defect against the background of an incorrect position of the teeth, then every year the situation may worsen. Problems do not appear only in speech.
A person may begin to develop concomitant pathologies of other organs and systems. Therefore, the sooner the adjustment is made and, if necessary, treatment, the faster the child will be able to live a full life and develop without any deviations.
Thus, dyslalia in speech therapy is a defect that can develop for numerous reasons. This is a deviation that lends itself well to correction, even when it comes to a complex form of dyslalia. But a complete correction of the pronunciation is possible only with the correct diagnosis.
Dislalia video
Diagnosis - dyslalia:



