The prolapse of the uterus is a pathology of the female body, in which the organ itself, vaginal wall, bladder, other organs of the small pelvis are displaced relative to their normal (physiological) position.
Symptoms of this condition in the early stages of the process are not clearly expressed. Doctors often deal with the consequences in the form of gaping and prolapse (prolapse) of organs beyond the boundaries of the genital crevice.
The content of the article:
- 1 Disease types
- 2 Stages and degrees
- 3 Symptoms
- 4 Reasons for the appearance
- 5 Diagnostics
- 6 When to see a doctor
- 7 Prophylaxis
- 8 Lifestyle
-
9 Treatment methods
- 9.1 Exercises
- 9.2 Conservative therapy
- 9.3 Surgical methods
- 10 Possible complications
- 11 Video about prolapse of the uterus
Disease types
The uterus, in its physiological position, is located in the upper part of the small pelvis, holding the dome of the vagina. The organ is securely fixed by a ligamentous apparatus, multiple fasciae and muscles, which create a flexible but strong frame for the entire peritoneum.
Normally, the uterus can move and deviate within small limits. The weakening of any group of tissues supporting it causes displacement of the organ in the vagina and gradual sliding (prolapse) towards the exit from the perineum.
Depending on which muscles or ligaments have ceased to perform their supporting function, prolapse can develop in the anterior (about 30% of cases), middle or posterior regions. The condition is complicated by the fact that the displacement of the uterus changes the position of the surrounding organs, and also leads to deformation of the walls of the vagina.
Types of pathology:
- partial omission - the body of the uterus changes position without leaving the vagina, or no more than 1 cm protrudes beyond the boundaries of the genital slit;
- complete omission (apical prolapse) - loss of the entire organ;
-
cystocele - the condition accompanying the displacement of the uterus and the anterior vaginal wall, with bladder prolapse;
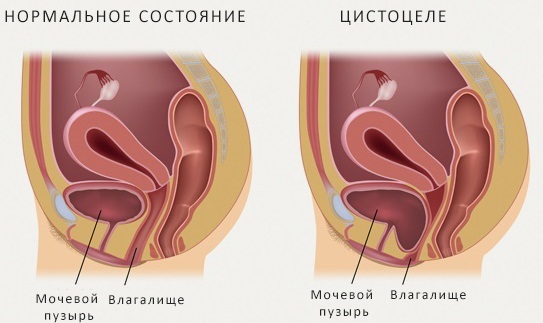
- rectocele - pathology arising from the pressure of the displaced uterus and the posterior wall of the vagina, leading to protrusion of the rectal area.
There is a complex classification of different types of prolapse of the pelvic organs in women. Even a slight displacement of the uterus can cause complications from previously suffered injuries, sprains, which provokes not only cystocele or rectocele, but sometimes prolapse of intestinal loops (enterocele), urethral prolapse, as well as various combined pathology.
Stages and degrees
At an early stage of the process, the displacement of the uterus is insignificant and has no specific symptoms. Pathology develops slowly, starting at any age, it can only reveal itself in premenopause or after the attenuation of hormonal functions. Although sometimes, with accompanying aggravating factors, prolapse can grow rapidly.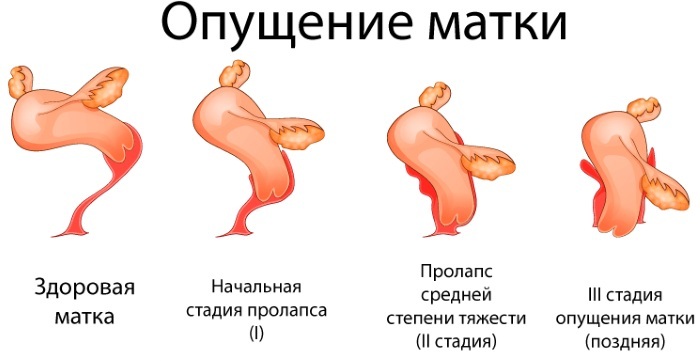
According to the degree of prolapse of the body of the uterus in the vagina, 4 stages of pathology are distinguished:
| Stage | Description | Symptoms |
| I | A slight displacement of the cervix down the vagina, the walls are somewhat weakened, it is possible that the genital gap does not close | Menstrual irregularities, possible discomfort during intercourse |
| II | The body of the uterus is displaced downward, but is located inside the vagina, when straining the neck of the organ protrudes from the genital slit | Feeling of a foreign object in the vagina, frequent urge, impossibility (difficulty) of intercourse, severe pulling pains, incomplete emptying of the bladder |
| III | The cervix and part of the uterus gape out of the vagina even at rest, the organ is prone to infringement and trauma | Discomfort (pain) when walking and sitting, bleeding, often infection of the uterus and surrounding tissues |
| IV | Prolapsus uteri. The organ and the walls of the vagina are completely outside the boundaries of the genital slit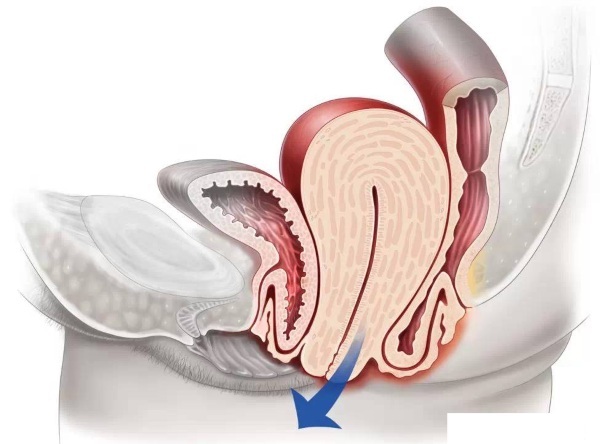
|
Severe pain, inability to sit, bedsores, abscesses, inflammation in places of friction of organs |
The prolapse of the uterus reveals symptoms and consequences as the pathology progresses. In addition to mechanical displacement of organs, violations in the functions of urination, defecation, infection of the bladder, kidneys, and other concomitant diseases are naturally noted.
Symptoms
Clinical signs of prolapse of the uterus are nonspecific and may initially be mistaken for a common malaise. Symptoms that make it possible to independently suspect uterine prolapse appear at stages when it is no longer possible to do without surgery.
You should be especially careful about any unusual sensations during intercourse. Accumulation of air, fluid, pain or poor closure of the vagina require an urgent visit to the gynecologist to assess the condition of the vagina and the height of the cervix.
Classic signs that the uterus has deviated from its normal position or is shifting downward:
- sensation in the vagina of a foreign body;
- discomfort when walking, sitting;
- feeling of pressure and heaviness in the lower abdomen;
- drawing pain in the sacrum, behind the pubic bone;
- swelling of the labia or "eversion" of the vagina at the border of the genital slit;
- frequent cases of cystitis, incontinence when sneezing, coughing, or vice versa, congestion in the bladder.
- frequent cases of cystitis, infections of unknown origin, pyelonephritis;
- pain during (after) intercourse, bleeding after sex;
- difficulty with bowel movements.
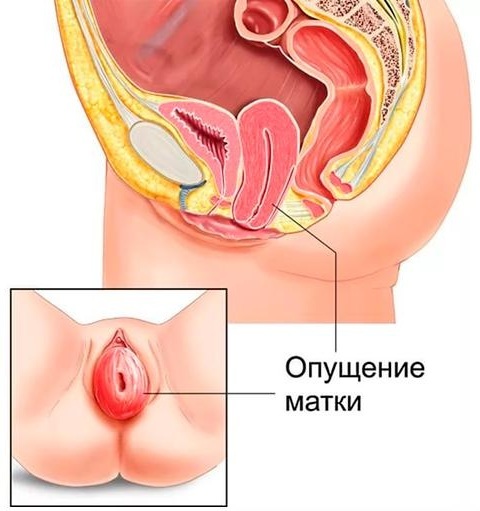
In the last stage of prolapse, the uterus exits from the vagina
One of the most striking symptoms of prolapse of the uterus and surrounding organs - non-closure of the genital gap, can appear in the early stages, but is not perceived as a serious signal of trouble.
The gaping entrance to the vagina provokes drying out of the mucous membrane, facilitates the penetration of infections. So secondary diseases lead women to a doctor who can detect prolapse of the uterus during a standard gynecological examination.
In women of reproductive age, a displacement of the uterus can be suspected by a change in the nature of menstruation. They become profuse, long lasting, and painful. Pain from the swelling may persist after the bleeding is over.
Reasons for the appearance
The prolapse of the uterus, the symptoms and consequences are manifested according to the factors that caused the pathology. The process is associated with any weakening of the system of ligaments, muscles, their fascia, which control the position of the uterus. The muscle tone of the perineum and peritoneum can change for many reasons.
Factors provoking displacement and prolapse of the uterus:
- Difficult childbirth with ruptures, episiotomy (dissection of the perineal tissue), improper obstetrics. Overstretching and mechanical damage to the vagina, muscles, ligaments can lead to vacuum extraction or the application of forceps.
- Insufficient attention to the recovery of the body after childbirth, multiple pregnancies.
- The consequences of surgical interventions in the small pelvis: scars and adhesions inside the vagina, on the body of the uterus, reproductive organs.
- Congenital pathologies in the structure of the uterus or a change in its shape and position as a result of past diseases.
- High physical activity, regular hypothermia, heavy lifting.

- Estrogen deficiency caused by illness, stress or natural aging.
The risk of developing pathology increases in the presence of excess weight, frequent constipation, and persistent coughing. A combination of several factors significantly increases the likelihood of prolapse of the uterus. The ligamentous and muscular corset is weakened due to a sedentary, especially sedentary lifestyle.
Diagnostics
It is impossible to independently determine the displacement of the uterus in the early stages. At the same time, a routine gynecological examination is able to reveal pathology at the very beginning of development. Early or progressive forms of the disease are detected by a gynecologist by palpation. The condition of the pelvic floor, the tone of the vagina, the muscles responsible for supporting the organs, are assessed during the vaginal-abdominal examination.
The stage of prolapse or prolapse is determined by the gynecologist by palpation at rest and when the patient is straining.
If a displacement of the uterus, vaginal walls, and other peritoneal organs is detected, additional studies will be required:
- urine analysis, for the timely diagnosis of concomitant infections;
- urography, prescribed when there is a danger of blockage of the urinary ducts;
- ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs, to detect possible complications;
- bladder catheterization is required in the presence of concomitant cystocele;
- rectal examination is prescribed when rectocele, weakness of the sphincter, concomitant hemorrhoids are detected;
- colposcopy, scraping or biopsy are required to examine ulcerations and erosions on the cervix with varying degrees of oncological alertness.
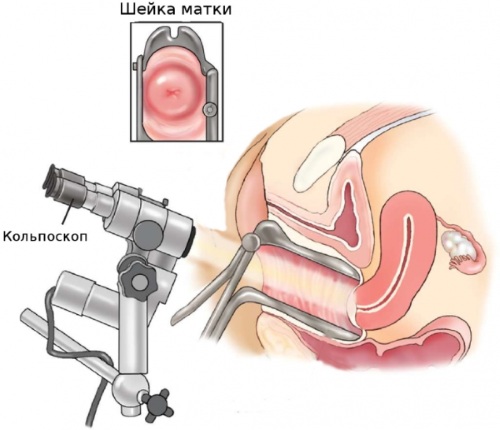
All procedures can be done at a public clinic or at a private center.
Average prices for the most necessary studies for prolapse of the uterus:
- a gynecologist's appointment - from 1000 to 3000 rubles;
- Pelvic ultrasound (complex) - 1300 rubles;
- Gynecological ultrasound - 500 rubles;
- Ultrasound of the bladder - from 300 rubles;
- Ultrasonic scanning of veins - starting from 300 rubles;
- colposcopy - 300 rubles;
- biopsy of the uterus - from 600 rubles
- cystoscopy - 900 rubles.
Some studies are prescribed only when necessary to differentiate uterine prolapse from cysts, fibroids, or cervical cancer. The required set of studies is determined by the doctor.
When to see a doctor
Any unusual manifestations in the genital area, atypical pains, changes in the course of menstruation should force a woman to consult a gynecologist. Even if there are no unusual manifestations, regular visits to a specialist (at least once a year) able to detect the first deviations in the position of the uterus or detect muscle weakness, sprain fascia.
Particular attention should be paid to any signs of displacement of the uterus immediately after childbirth, in the first year after any operation on the pelvic organs, with the approach of menopause. Women who become pregnant with a diagnosis of prolapse of the uterus should be constantly monitored by a gynecologist.
Pain that accompanies prolapse of the uterus is difficult to distinguish from symptoms of other conditions. Pulling pains in the sacrum, behind the pubis, in the lower back can be caused by other gynecological problems, kidney diseases, and pathologies of the spine.
In any case, unusual sensations in the vagina, pulling pain, sexual dysfunction require medical attention. The gynecologist conducts an initial examination and prescribes the necessary studies.
Based on the results of the examination, consultation of narrow specialists may be required: a proctologist, urologist, oncologist, surgeon. With varicose veins of the lower extremities and external genitalia caused by pressure on the vessels of the pelvic floor, it is necessary to visit a phlebologist.
Prophylaxis
Prolapse of the uterus, the symptoms and consequences of which are difficult to treat, can be prevented or treated at an early stage.
The following medical measures help to avoid organ prolapse:
- High-quality obstetric care and obstetric support during childbirth, including the correct suturing of ruptures of the birth canal, perineum.
- After childbirth, the support functions of the pelvic floor are restored with the help of therapeutic exercises, electrical muscle stimulation, and laser therapy.

- Treatment of any diseases accompanied by cough is imperative. The therapy is carried out until the symptom disappears completely, avoiding chronic conditions.
- Regular constipation or hemorrhoids require examination and timely treatment at any age. All conditions that increase intra-abdominal pressure are dangerous.
- At the first signs of menopause, it is advisable to consult a gynecologist for the appointment of hormone replacement therapy. This will prevent a sharp weakening of muscles and ligaments due to a lack of estrogen.
Special exercises to strengthen the muscles of the vagina, abdominal wall and pelvic floor should be done regularly all women who have given birth, after reaching the age of 40, as well as in the presence of any risk factors for prolapse uterus.
Lifestyle
Changes in some habits, working and living conditions, leading to a weakening of the ligamentous-muscular apparatus or provoking stretching and tearing of internal tissues, are also of preventive importance.
Methods for self-prophylaxis of prolapse of the uterus:
- Maintaining optimal weight and high physical activity significantly reduces the risk of excessive pressure on internal organs. The general tone, the tightened state of the abdominal muscles and the pelvic floor is ensured by regular sports, fitness, and swimming.
- Despite the indications for sports, excessive exercise, heavy lifting, overstrain of the peritoneum and lower back should be excluded.
- A balanced diet not only helps to control weight, but also eliminates constipation, which is dangerous for the internal organs due to excessive straining during bowel movements.
- When early stages of pathology are detected, sex life is temporarily limited due to the danger of aggravating the condition. Starting from stage II, reliable contraception should be provided, because the onset of pregnancy contributes to the rapid progress of prolapse.
With a sedentary lifestyle, it is difficult to maintain the ligamentous apparatus and muscles in good shape. Stagnation of blood in the small pelvis due to sedentary work is an additional risk factor for any intra-abdominal pathology. Without regular breaks and special training, there is a danger of sudden organ prolapse with little exertion.
Treatment methods
The prolapse of the uterus has several methods of treatment only in the very early stages, while the symptoms are moderately expressed, and the consequences have not yet passed into a chronic form. At the first stage, it is possible to stop the process with the help of remedial gymnastics, a set of exercises for the abdominal muscles, sphincters, muscles of the vagina and pelvic floor.
Exercises
Kegel Exercise Rules:
- You can identify the muscle group that needs training while urinating. Squeezing the sphincters, they try to stop the stream. When it is possible to do this for longer than 5 seconds, you can repeat the exercise alternately with slight straining.
- You can use such an inconspicuous workout, drawing in the sphincters of the perineum and anus, and then relaxing them for 5 seconds, anywhere: at the workplace, in transport, while driving a car. The exercise is repeated 10 times, the muscles are relaxed for a few minutes, then the complex can be repeated.
- A simple Kegel intake during physical exertion is especially effective. Performing exercises for the press, while cycling, with static stretches, the cycle of compression and relaxation of the perineum is repeated without stopping the workout.
- Gradually complicate the exercise by increasing tension, maximally "pulling" the perineum into itself, straining the anus and abdominal muscles. The technique is called "lock", it simulates the fastening of the fastener from the navel through the crotch to the tailbone.
An important condition for the effectiveness of training is the gradual increase in the load. In the first weeks of training, they try not to overstrain the weakened areas, otherwise you can harm the muscles of the pelvic floor and get pain instead of alleviating the condition.
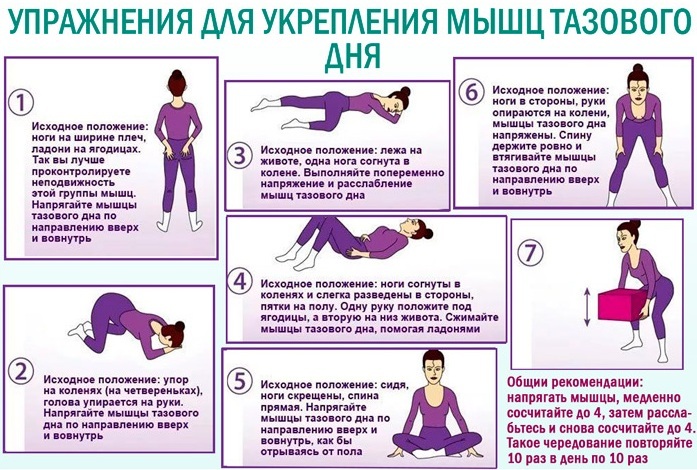
Therapeutic gymnastics for the prolapse of the uterus in the early stages:
- Walking in a circle with a rubber ball (about 15 cm in diameter) clamped between the thighs. The duration is about 3 minutes.
- Standing with your hands locked behind your back, raise your arms up, at the same time lifting on your toes and bringing the pelvis forward. The head is thrown back and the head is pulled to the hands, and the pubis is up. At the same time, Kegel techniques are performed, straining the muscles of the perineum. Repeat up to 6 times.
- Lying on your back, perform alternating swings with straightened, bent legs, circular movements, bicycle, flattening and spreading straight legs, "scissors". At the same time, frequent, rapid contractions of the perineal muscles (blinking) are performed.
- Perform a bell crawl on the stomach, moving forward and backward for 2 minutes.
- Lying on your stomach, arms outstretched in front of you, alternately raise your right arm and left leg and vice versa. Hold each position for several seconds, pulling in the vagina as much as possible.
- Sitting on the floor, putting on a tourniquet on the shins, the legs are extended to the sides and the legs are alternately lifted, overcoming the resistance of the elastic band. Each technique is performed up to 10 times.
There are many simple exercises that can be combined with Kegel techniques to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles. Results do not appear earlier than after a month of daily training.
You can check the effectiveness of the exercises after 60 days by going through a gynecological examination. Any complex of medical gymnastics must be selected taking into account the stage of prolapse of the uterus, the characteristics of the disease and must be approved by a doctor.
Conservative therapy
With the prolapse of the vagina and uterus, exercises are combined with the following methods of symptomatic therapy:
- the use of pessaries (uterine rings);
- wearing a hysterophore bandage, reinforced around the waist;
- the use of tampons for the vagina of a large size.
These measures only temporarily relieve the condition and can have many side effects. Among the undesirable consequences, there is an overstretching of the walls of the vagina, infringement of the cervix, the formation of abrasions, bedsores, erosive foci with prolonged use.
When using such devices, the vagina should be irrigated daily with antiseptics and visit a gynecologist for control at least 2 times a month.
Surgical methods
The only way to eliminate the pathology after stage II is surgery. Depending on the degree of prolapse and associated disorders, different types of surgical interventions are prescribed.
Such radical methods are most often used:
- Colpoperineography - a minimally invasive intervention, which involves fixing the organ in a normal position using special mesh implants with suturing of the stretched anterior or posterior wall of the vagina. The method completely preserves the uterus and its functions. After full recovery, conception and gestation are possible.
-
Colporrhaphy - type of plastic surgery for excision of the vagina with suturing of the muscles. The intervention involves layer-by-layer stitching of the tissues of the deformed posterior or anterior wall, which is also shown to eliminate postoperative scars. With a strong prolapse or prolapse of the organ, several sequential operations are required
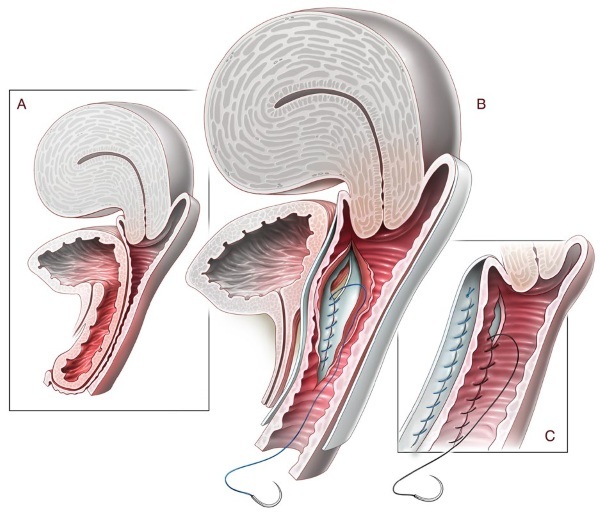
- In the case of incomplete prolapse of the uterus in patients with a history of childbirth, the so-called "Manchester" procedure. The operation involves the necessary suturing of the walls, partial removal of the body of the uterus with rigid fixation of the remaining part. Reproductive function is not preserved.
- Operation Emmett - plastic surgery of the cervix, performed with incomplete prolapse of the organ. It can be carried out by several methods: surgical, laser, radio wave. During the procedure, a part of the uterus is removed, a neck of the desired size is formed and it is fixed in its normal position.
- Extirpation of the uterus belongs to the most radical methods. It is resorted to in case of complete, complicated organ prolapse or in women in menopause, if the preservation of reproductive function is irrelevant. During the operation, the uterus is removed entirely with the obligatory fixation of the vaginal dome.
In each case of prolapse of the uterus, the method is chosen individually, if possible using a low-traumatic access - laparoscopy. Many methods of fixation have been developed, each of which is used depending on the indication. The individual selection of the method is made by the surgeon according to the recommendations of the attending gynecologist.
Even minimally invasive methods of surgical treatment of organ prolapse require long-term recovery in compliance with all the doctor's recommendations. Otherwise, there is a great chance of repeated prolapse or prolapse of the uterus, the dome of the vagina, intestines, and other organs.
Possible complications
The prolapse of the uterus, the symptoms and consequences of which tend to constantly progress, cannot simply stop on its own. The incipient displacement inevitably develops from stage to stage in the absence of treatment and the preservation of traumatic environmental factors.
Possible consequences of untreated prolapse of the uterus:
- infections of the urinary tract, kidneys, vagina;
- physical impossibility of sexual intercourse and conception;
- functional and secondary infertility;
- erosive lesions of the cervix, wounds, fistulas, mechanical damage to the organ;
- violation of the blood supply to the pelvic organs, concomitant varicose veins, hemorrhoids;
- long-term use of pessaries in case of refusal of surgical treatment causes bedsores, abrasions and, as a result, infection of the vaginal walls.
Prolapse of the uterus with timely diagnosis and treatment does not pose a threat to the life and health of a woman. Ignoring the symptoms or recommendations of the gynecologist leads to serious consequences, long-term therapy and even the loss of several organs.
The prognosis for surgical treatment at any stage of the disease is favorable. Timely correction at stages I - II allows you to preserve the possibility of pregnancy and a normal sex life.
Article design: Vladimir the Great
Video about prolapse of the uterus
About uterine prolapse:
