17 OH-Progesterone Is a steroid hormone that is synthesized in women by the tissues of the gonads, the adrenal cortex and the placenta during the period of gestation. The rates of this substance vary depending on the day of the menstrual cycle, age and the possible presence of diseases of the reproductive system.
Record content:
- 1 Functions in the body
- 2 How and under what conditions is it produced
- 3 Indicator table is normal
- 4 Symptoms of the rise and fall
- 5 Reasons for promotion and demotion
- 6 Indications for research
- 7 How is it determined
- 8 Preparation and analysis
- 9 Decoding the results
-
10 How to bounce back
- 10.1 Medications
- 10.2 Traditional methods
- 10.3 Other methods
- 11 Video about progesterone
Functions in the body
17 OH-Progesterone is a sex hormone that affects the functioning of the internal genital organs.
If a woman's indicators of this steroid are within normal limits, then it fully performs the following physiological functions:
- regulates the phases of the menstrual cycle (on different days, a different concentration of the sex hormone is recorded, which can increase sharply, and then again decrease to the minimum);
- takes part in the process of puberty (increasing the level of steroid hormone in girls adolescence, ensures the full development of internal genital organs and the formation reproductive function);
- in combination with the biochemical activity of other sex hormones contributes to the maturation of the egg and the release it into the uterine cavity (this is an important function of the steroid hormone, without which it is impossible to conceive child);
- acts as a regulator of the process of bearing a fetus, its stable development in the womb and birth after 9 months.
- participates in processes that are aimed at biochemical reactions of 17 OH-Progesterone with other steroid hormones necessary to maintain the stable function of the female reproductive system.
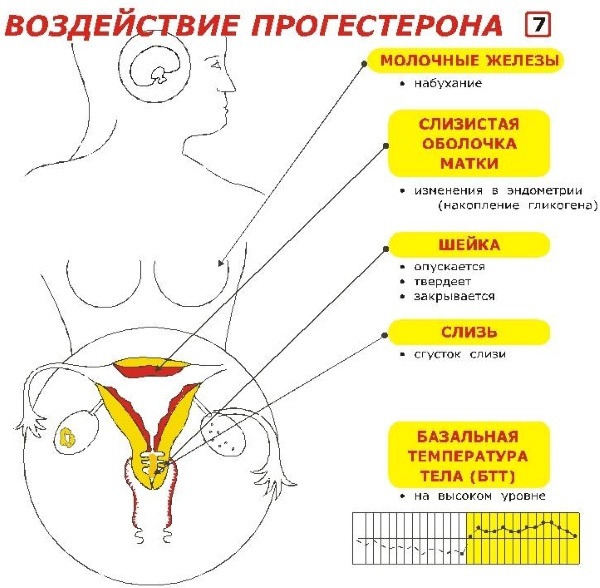
In the event that the body did not have the hormonal activity of 17 OH-Progesterone, women would not have stable menstrual cycle, it would be impossible to conceive, carry and give birth to a healthy child at the appointed term.
How and under what conditions is it produced
17 OH-Progesterone (the norm in women is determined by a biochemical study of venous blood) is a female sex hormone, which is a product of the metabolic synthesis of steroids progesterone and 17-hydroxypregenolone.
The largest quantities of 17 OH-Progesterone are produced by the adrenal glands and together with the blood flow spreads through the tissues of internal organs, and also provides regulation of the functions of organs reproductive system.
Under the influence of metabolic processes, the residual part of 17 OH-Progesterone, which was preserved in adrenal tissues, enters into chemical interaction with the substance 21-hydroxylase and 11-b-hydroxylase. Then the steroid is converted into cortisol, which is also used by the female body for the stable functioning of the genital organs.
Depending on the state of the female body, the phase of the menstrual cycle, 17 OH-Progesterone can also turn into another hormonal substance - androstenedione, which is a precursor of estradiol and testosterone.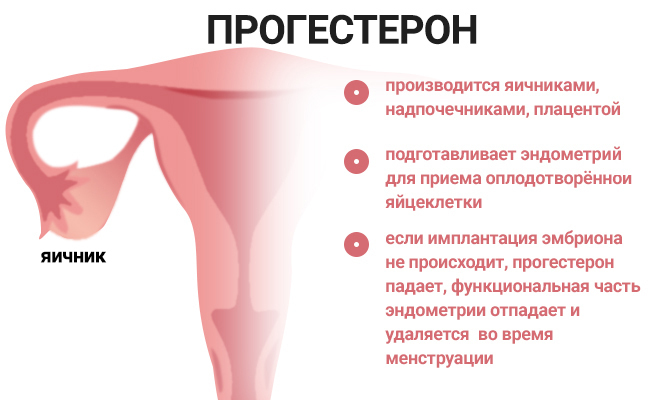
In addition to adrenal tissue, 17 OH-Progesterone is produced by the ovaries. The secretory activity of these endocrine glands occurs in the first 1-2 days of the menstrual cycle. Then the appendages practically stop the production of this steroid, and its main synthesis is carried out by the tissues of the adrenal glands.
In the morning, the concentration of the hormone is highest. Throughout the day, the steroid level decreases, but remains stable. At night, the concentration of 17 OH-Progesterone is the lowest due to a decrease in the activity of the adrenal glands and organs of the female reproductive system.
After the conception of the child occurred, the active development of the fetus began, then the placenta also begins to synthesize the steroid hormone. The concentration of 17 OH-Progesterone varies depending on the trimester of pregnancy. At different periods of fetal development, the level of this hormone is monitored by doctors in the process of routine examinations of a woman.
A decrease in the concentration of a steroid during pregnancy may indicate a pathological condition of the placenta.
In girls who were born prematurely, a high level of 17 OH-Progesterone in the blood serum is recorded. During the first 7 days of independent life, the concentration of the steroid returns to normal, and the use of special medications is not required. In children born on time, such reactions of the body practically do not occur.
Before puberty, 17 OH-Progesterone is produced in small quantities. Its concentration increases sharply when the girl reaches the age of 11-12 years.
This is a period of active formation of internal genital organs, as well as the acquisition of reproductive function. The maximum steroid level is recorded in adulthood, when a woman begins to have a sex life, has a stable menstrual cycle.
Indicator table is normal
17 OH-Progesterone (the norm in women is established by a comprehensive examination in a biochemical laboratory) is a sex hormone, concentration which varies depending on the age of the patient, the phase of the menstrual cycle, the presence of concomitant diseases of the reproductive system, trimester pregnancy.
The table below shows the indicators of the rate of steroid hormone for the female body:
| Age, phase of the menstrual cycle, term of fetal development during pregnancy | Indicators of the norm (unit of measurement ng / ml) |
| A child up to 2 months of age. | 0.96 to 10.46 |
| Children from the age of 2 months. up to 1 year | 0.66 to 2.81 |
| Indicators for a child aged 1 to 10 years | 0.2 to 0.8 |
| Indicators for girls aged 11 to 17 years, taking into account the period of puberty according to the Tanner scale | 1 stage of sexual development - from 0.03 to 0.9 2nd stage of sexual development - from 0.05 to 1.15 Stage 3 of sexual development - from 0.1 to 1.38 4 stage of sexual development - from 0.29 to 1.8 5 stage of sexual development - from 0.24 to 1.75 |
| Adult women aged 18 to 59 years, taking into account the phase of the menstrual cycle | Follicular phase - from 0.4 to 1.51 Luteal phase 1.00 to 4.51 |
| Indicators of the norm for women aged 60 years and older who are in the postmenopausal period | 0.13 to 0.51 |
| From 1 to 6 weeks of pregnancy | 1.32 to 3.30 |
| From 7 to 14 weeks of pregnancy | 1.1 to 2.8 |
| From 15 to 24 weeks of pregnancy | 1.65 to 4.62 |
| From 25 to 33 weeks of pregnancy | 1.98 to 10.2 |
| From 34 to 40 weeks of pregnancy | 2.64 to 13.20 |
The above indicators of the norm of the level of 17 OH-Progesterone are characteristic for women of a particular age group, the phase of the menstrual cycle and the period of pregnancy. They are taken into account by doctors during a comprehensive diagnosis of the body, determining the performance of adrenal tissues and the level of female sex hormones.
Symptoms of the rise and fall
17 OH-Progesterone (the norm in women is determined by a biochemical blood test) - it is a steroid hormone, an increase in the concentration of which is manifested by the following symptoms:
- various violations of the menstrual cycle, which can be expressed in too abundant discharge, prolonged menstruation;
- a feeling of aching or pulling pain that is localized in the lower abdomen;
- inflammation of the uterine appendages, the development of which is accompanied by pain from the lumbar spine;

- the inability to conceive a child (in medical practice, there are clinical cases when too high a concentration of steroid hormone was manifested exclusively by this symptom);
- dysfunction of the adrenal cortex, which entail the development of other diseases associated with disruption of the work of this organ;
- decreased sex drive, which can occur in women of different age groups.
A decrease in the level of 17 OH-Progesterone is accompanied by symptoms that outwardly resemble those of Addison's disease.
A woman experiences the following pathological conditions of the body:
- feeling of chronic fatigue, which over time is aggravated in its manifestation;
- nausea and severe vomiting;
- increased irritability, unreasonable outbursts of rage and anger;
- hyperpigmentation of the skin with the greatest formation of spots in places that are exposed to sunlight;
- prolonged bouts of depression;
- a persistent feeling of thirst with abundant fluid intake (this symptom is mistakenly confused with the manifestation of the first signs of diabetes mellitus);
- growing weakness in muscle fibers, which increases after an attempt to perform any energy-intensive actions;
- rapid weight loss;
- lack of appetite, which periodically changes to a strong feeling of hunger with a craving for sour and salty foods;
- the development of orthostatic hypotension, when a woman suffers from too low blood pressure, which falls even lower after trying to get out of bed and take a standing position;
- an increase in the concentration of potassium in the blood;
- decreased sensitivity of the lower extremities, which is a complication of hormonal imbalance;
- violation of the digestive function of the digestive tract and diarrhea;
- recurrent tremor of the upper limbs and head, which intensifies at the moment of excitement;
- an unexplained feeling of anxiety and anxiety, which occurs suddenly, and then just the same goes away without taking sedatives;
- violation of the rhythmic activity of the heart, which most often manifests itself in the form of tachycardia;
- an increase in the level of eosinophils in the blood;
- an increase in the amount of urine excreted;
- a decrease in the concentration of glucose in the blood and the appearance of signs of hypoglycemia;
- irregular periods, or the complete disappearance of menstruation;
- violation of the reproductive function of the body and the impossibility of conceiving a child;
- dehydration of the body against the background of abundant fluid intake, which is almost immediately excreted by the kidneys in the form of urine.
All of the above symptoms of a decrease in the level of 17 OH-Progesterone have a different severity of manifestation depending on how low the concentration of the steroid hormone is. It is believed that a decrease in the level of steroid hormone carries many more dangers than an increase in the concentration of 17 OH-Progesterone.
Reasons for promotion and demotion
17 OH-Progesterone (the norm in women is established according to the results of diagnostics of the female hormonal background) - a steroid hormone, a decrease in the level of which can be caused by the presence of the following diseases or pathological conditions of the body:
- congenital adrenal insufficiency (this pathology is associated with abnormalities in the intrauterine formation of the fetus, when the tissues of the organ are not receive full development, and after the birth of a child, they do not fulfill their physiological functions for the synthesis of the hormone 17 OH-Progesterone);
- diagnosing Addison's disease in a woman, which proceeds in a chronic or acute form;
- benign and oncological neoplasms, which are localized in the tissues of the adrenal glands, violate organ work, lead to a complete absence or a significant decrease in the production of steroid hormone;
- intoxication of the body with salts of heavy metals or chemical compounds, the active substances of which lead to the destruction of adrenal tissues;
- a hereditary feature of the body, when the endocrine glands do not provide the body with sufficient the amount of the hormone 17 OH-Progesterone (this reason for a reduced steroid level is one of the most common).
An increase in the concentration of the hormone is also a pathology that requires elimination by taking medications, surgical treatment or lifestyle correction.
Too high a level of 17 OH-Progesterone can be caused by the following reasons:
- primary or secondary infertility acquired as a result of previously transferred diseases of the organs of the reproductive system, which caused their dysfunction;
- benign and cancerous tumors of the ovaries, as well as other uterine appendages;
- temporary violation of the menstrual cycle due to the influence of various factors (if this reason is present the increase in the level of steroid hormone is short-term, and the problem itself is eliminated immediately after stabilization cycle);
- hyperplasia of the adrenal cortex, which was acquired during the period of intrauterine development of the fetus.
An increased level of 17 OH-Progesterone is most dangerous because the hormonal substance is capable of cause early sexual development in girls, lead to disturbances in the work of the reproductive organs systems. Determining the causes of hormonal imbalance is the main task in the period of organizing quality treatment.
Indications for research
The analysis for the level of 17 OH-Progesterone is indicated for women who have the following health problems:
- violation of the menstrual cycle;
- all types of adrenal tumors;
- hirsutism;
- impossibility of conceiving a child;

- deficiency of substances 11-hydroxylase and 21-hydroxylase;
- manifestations of an imbalance in female sex hormones;
- decreased sex drive.
Indications for testing the level of steroid hormone are determined by a gynecologist or endocrinologist who examines and treats the patient.
How is it determined
Determination of the level of 17 OH-Progesterone is carried out in a laboratory, which is equipped with all the necessary material and technical base for this type of research. Venous blood is used as a biological material, which is subject to biochemical analysis.
The average duration of the diagnostic procedure is 3 to 8 hours. this type of research is carried out in private and public health care institutions. The average cost of the analysis is 1500-2000 rubles.
Preparation and analysis
The study of venous blood for the level of 17 OH-Progesterone does not require complex preparation procedures. The main rule for collecting biological material and obtaining the most reliable data is the selection of venous blood on the 3-5th day of the menstrual cycle.
During this time period, the concentration of the steroid hormone is optimal, and any changes in its level towards a decrease or increase will be determined using a laboratory study.
Venous blood is donated in the morning between 8 and 11 a.m. The last meal should take place no later than 8 hours before visiting the laboratory.
On the eve of the analysis, it is forbidden to consume alcoholic beverages, drugs and drugs on a hormonal basis. If a woman takes any other medications, then she must notify her attending physician and the specialist who selects the blood.
Decoding the results
In order to independently decipher the results of the biochemical analysis of venous blood at level 17 OH-Progesterone, you need to get your hands on the results of laboratory research and compare its content with indicators norms.
In this case, one should take into account the phase of the menstrual cycle during which blood was taken, the woman's age, the presence or absence of pregnancy. A decrease or increase in the concentration of steroid hormone is a reason for visiting an endocrinologist, gynecologist, comprehensive examination of the adrenal glands, ovaries and other organs of the female reproductive systems.
How to bounce back
Restoration of the normal level of 17 OH-Progesterone involves the use of symptomatic therapy. It consists in eliminating the causes that provoke hormonal imbalance.
Medications
The use of drug therapy is indicated only in the case of a decrease in the level of steroid hormone.
For this, the following means are used that compensate for the dysfunction of the adrenal glands:
-
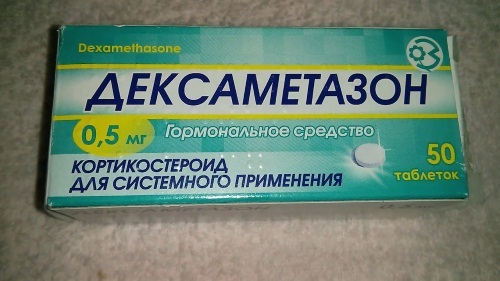
Dexamethasone - it is administered once a day intravenously using a dropper, adding 0.5-9 mg of the drug to a sodium chloride solution with 0.9% concentration (the cost of the drug is 45 rubles. for 1 ampoule);
- Raft - solution for injection, which is injected intravenously at 8-10 mg per day, but at the discretion of the doctor, the dosage can be increased (the price of the drug is 380 rubles. per pack of 10 ampoules);
- Betaspan depot - an injectable drug that is injected deep into the gluteus muscle, 1-2 ml per day (the cost of the medication is 350 rubles);
- Depos - the drug is intended for injection, it is prescribed in the form of intramuscular injections of 1-2 ml per day (the average cost of the medication is 850 rubles).
The duration of the use of the above drugs and the dosage is determined by the attending physician, depending on the severity of adrenal dysfunction, as well as the level of 17 OH-Progesterone in the woman's blood.
Traditional methods
Alternative therapies are not used to treat adrenal disease, which can decrease or increase steroid hormone synthesis. The use of decoctions and tinctures based on medicinal plants may not bring a positive effect, as well as provoke a deterioration in well-being.
Other methods
In cases where drug therapy does not bring a positive result, or diagnosed with diseases that exclude the use of drugs, surgical intervention.
The operation is indicated for tumor neoplasms in the adrenal glands and ovarian tissues. Removal of benign or oncological neoplasms is carried out under local anesthesia in the hospital of the surgical department. Indications for surgery are determined individually by the attending physician based on the results of a diagnostic examination.
17 OH-Progesterone is a steroid hormone that regulates the functioning of the female reproductive system, takes part in maintaining the stability of the menstrual cycle.
If the concentration of this substance in a woman's body is normal, then the optimal balance of sex hormones is maintained. A decrease or increase in the concentration of the steroid leads to infertility, the appearance of a feeling of chronic fatigue, and disruption of metabolic processes in the body.
Article design: Vladimir the Great
Video about progesterone
Progesterone in the female body:



