Combination of clinical endometritis pictures (inflammation of the lining of the inner layer of the uterus) and myometritis (inflammation of the muscle tissue of the uterus) is metroendometritis. The disease manifests itself in two forms: chronic and acute. It is characterized by the development of an inflammatory process that simultaneously encompasses the muscle tissue of the uterus and the mucous membrane of the organ.
In the chronic course, serous discharge from the uterus, menstrual irregularities and bleeding between periods are noted. The acute form has a more pronounced clinical picture: hyperthermia, discharge with impurities of pus, acute pain in the lower abdomen. The disease is diagnosed with a gynecological examination, with the help of echography and bacterial sowing of secretions.
Record content:
- 1 Views
- 2 Stages and degrees
- 3 Symptoms
- 4 Reasons for the appearance
- 5 Diagnostics
- 6 When to see a doctor
- 7 Prophylaxis
-
8 Treatment methods
- 8.1 Medications
- 8.2 Traditional methods
- 8.3 Other methods
- 9 Possible complications
- 10 Chronic endometritis video
Views
The cause of metroendometritis is an infectious lesion of the uterus.
In medicine, two groups of pathogenic microorganisms are distinguished:
- specific - gonococcal bacillus, chlamydia, herpes;
- nonspecific - streptococcal and Escherichia coli, Klebsibela.
Given the etiology of the disease, metroendometritis is divided into two types: specific and nonspecific. The two types are distinguished by clinical manifestations and treatment methods. The effectiveness of antibiotic therapy depends on the accuracy of determining the type of infectious agent.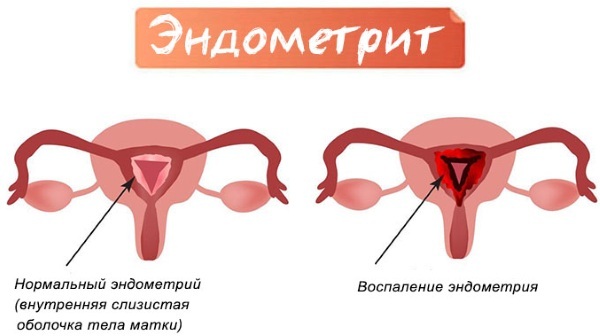
The main sources of the disease are infections and viruses, but metroendometritis can develop against the background of suppressed (or absent) local immunity. This is possible with the "sloughing" of epithelial cells during menstruation, in violation of the microflora of the vagina or damage to the organs of the genitourinary system with specific immunoglobulins.
The ways of penetration of infectious agents into the uterus are different:
- penetration of the infection ascending (through the lower genitals);
- hematogenous pathway of damage (through blood cells);
- lymphogenous pathway (in chronic course).
Stages and degrees
Metroendometritis manifests itself in three forms, each of which is characterized by specific symptoms. In an acute course, a vivid clinical picture is noted, and in a chronic one, it is erased.
Forms of metroendometritis: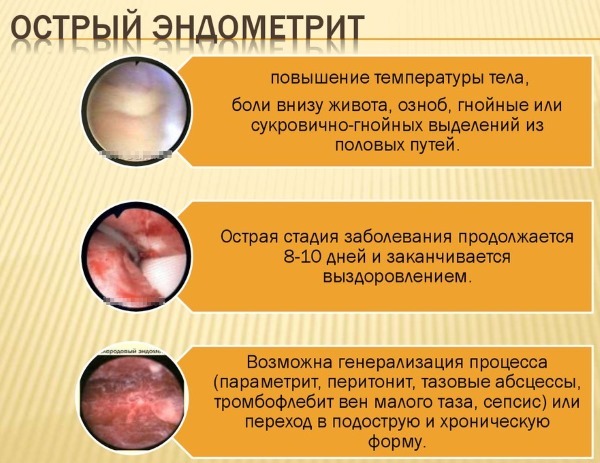
| Form | Description |
| Sharp | The process appears with infection of the endometrium, which provokes the development of endometritis. If during this period, treatment of a problem that affects only the functional layer is started, the spread of the infection can be avoided further. However, if the pathogenic agents have penetrated the blood vessels, the situation is more complicated here - the infection affects the next layers of the endometrium and it becomes more difficult to cure the disease. Symptoms in the acute form are bright and painful. |
| Subacute | It is difficult to diagnose the process due to the lack of visible signs, the inflammatory process develops against the background of an exacerbation of the chronic stage. |
| Chronic | If the acute form of metroendometritis is not treated in a patient, the disease becomes chronic. During the latency period, the woman does not feel any symptoms. |
Any form of metroendometritis requires treatment and monitoring. A woman should carefully monitor her health and listen to all the changes that are happening to her. This allows you to identify the problem at the beginning of its formation and promptly begin therapy for the disease.
Symptoms
Each form of metroendometritis has its own characteristics. The acute one has a pronounced picture, the chronic one is erased, but it can still be determined.
Symptoms of acute metroendometritis usually appear 3-4 days after the cause.
The prerequisites for the development of the disease can be:
- abortion;
- difficult childbirth;
- medical and diagnostic measures on the organs of the genitourinary system.
The patient's condition is rapidly deteriorating.
You can determine the acute form by the following features:
- hyperthermia (38-39 degrees);
- chills;
- general malaise;
- tachycardia attacks;
- symptoms of intoxication;
- acute pain in the lower abdomen and in the sacrum area;
- enlargement and soreness of the uterus, which is determined by palpation;
- discharge is cloudy, serous-purulent, sometimes has a putrid odor.
If there are obstacles to the exit of purulent secretions (fibroids, polyps, scars, etc.), pyometra (an inflammatory process of the inner layer of the uterus, accompanied by the accumulation of purulent secretions) may develop. In such cases, the patient's condition is aggravated and is manifested by acute cramping pains in the lower abdomen.
The initial inflammatory process affects the basal layer of the endometrium, in which there are no clear anatomical boundaries with the myometrium, which leads to the rapid spread of infection to the muscle layers. As a result, an acute phase of metroendometritis appears.
The average duration of the clinical picture in the acute form of pathology is from 5-7 to 8-10 days. In difficult cases, inflammation spreads to the peritoneum, peritonitis or pelvioperitonitis may develop. There is a risk of gangrene and sepsis of the uterus.
Chronic metroendometritis is a continuation of the acute form of pathology. This is possible with poor-quality or untimely treatment. Chronization of the process is also possible as a primary chronic disease.
Chronic symptoms:
- serous, light or pus-filled discharge;
- periodic pulling pains in the pubic, lower back or sacrum;
- on palpation, the uterus is painful, indurated and enlarged.
The chronic process is often accompanied by secondary pathological changes:
- nabotovye cysts;
- chronic adnexitis;
- adhesions of tissues in the small pelvis;
- intrauterine synechiae.
The conditions listed above become provocateurs of reproductive disorders (spontaneous abortions, miscarriages, infertility).
Reasons for the appearance
Chronic metroendometritis is an infection of the inner layer of the uterus. Distinguish between specific and non-specific type of pathology. In the first case, the provocateurs of inflammation are such pathogenic agents as gonococci and Trichomonas, and in the second - streptococci, E. coli, staphylococcus.
The development of a favorable microflora for the reproduction of these microorganisms appears due to such unfavorable factors:
- trauma during diagnostic and treatment measures on the pelvic organs;
- the consequences of artificial termination of pregnancy;
- introduction of a spiral into the uterine cavity;
- promiscuous sex without protection;
- insufficient hygiene of the organs of the genitourinary system;
- operations in the uterine cavity;
- timely not removed polyps;
- protracted, weak and difficult childbirth, as a result of which bleeding opens and placenta remnants are diagnosed;
- bacterial vaginosis, colpitis, endocervicitis, erosion, vaginitis, endometritis;
- stagnation of blood in the vessels that equip the pelvic tissue;
- unreasonably excessive douching of the genital tract with caustic solutions;
- purulent appendicitis.
Diagnostics
Chronic metroendometritis is determined by the results of the diagnostic measures performed. This is primarily a gynecologist's examination, analyzes and instrumental research methods.
The complex of laboratory diagnostic procedures includes:
- a blood test for the concentration of leukocytes and ESR;
- culture of secretions and antibiotic susceptibility testing;
- a smear from the vagina for the severity of inflammation and microbial composition.
Instrumental methods for the diagnosis of metroendometritis:
- Ultrasound. The procedure is carried out twice. The first time on the 5-7 day of the menstrual cycle, the second - on the 17-21 day. Gives high accuracy in the diagnosis of metroendometritis, the following indicators are revealed:
- expansion of the uterine cavity;
- change in the structure of the inner layer;
- the presence of gas bubbles;
- asymmetry of the walls of the uterus.
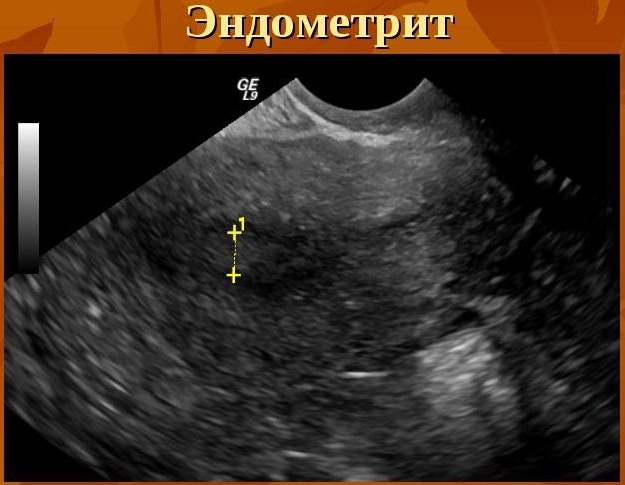
- Hysteroscopy. The study is carried out on the 7-10th day of the cycle. The diagnosis based on the results of this method is made only in 15-30% of cases. This study determines the following with metroendometrics:
- heterogeneity of the thickness of the endometrium;
- the presence of polyps;
- redness of the endometrium;
- the presence of bleeding foci.
- Histology. Research with high accuracy makes it possible to correctly diagnose. It is carried out on the 7-10th day of the monthly cycle. The presence of pathology is indicated by the following indicators:
- lymphocytes;
- plasma cells;
- fibrosis;
- sclerosis of the walls of blood vessels.
- Immunohistochemistry. The method allows to reveal the sensitivity of endometrial receptors to the effects of estrogen and progesterone, which is important for further therapy tactics.
If it is difficult to diagnose metroendometritis and its severity according to these methods, the doctor determines the need for laparoscopy.
An important role in the study of pathology is played by the state of the endometrium, in particular, the thickness indicators. With metroendometritis, there is a thickening of the walls of the endometrium, which appears as a result of a violation of the function of tissue regeneration. Normal tissues of the uterus are replaced by connective tissue.
If concomitant pathological processes are detected, the patient is referred for additional diagnostics and for consultation with other narrow-profile specialists.
When to see a doctor
Chronic metroendometritis is a pathology that does not have pronounced signs, therefore, women often ignore the periodically appearing alarming symptoms. That is why doctors recommend that all women, without exception, visit a gynecologist every six months and take a smear from the vagina for analysis.
Alarms for going to a doctor are:
- discharge of various types (grayish, with impurities of blood or pus, sometimes with a sharp unpleasant odor);
- periodic pulling pains in the lower abdomen;
- irregular menstrual cycle;
- bleeding between periods;
- a feeling of heaviness in the uterus due to its enlarged size.
It is possible to determine the presence of pathological changes in the uterus only after a series of diagnostic procedures.
If there is a suspicion of the presence of concomitant diseases, the patient requires additional diagnostics and consultation of narrow-profile specialists. If appendicitis or intestinal obstruction is diagnosed, the patient is referred to the surgeon.
Prophylaxis
Metroendometritis and pregnancy are incomparable things, the disease does not allow a woman to become a mother, provoking spontaneous abortions, fetal freezing or premature birth. In addition, the disease poses a serious health hazard in general. With the further development of pathology, there is a high risk of the formation of cysts, papillomas and other neoplasms in the uterus.
To prevent the development of metroendometritis, women are recommended:
- be examined regularly by a gynecologist (every six months);
- prevent abortion;
- promptly treat any infectious pathology;
- do not abuse bad habits;
- strengthen immunity, especially during the peak of respiratory infections;
- avoid hypothermia of the genitourinary system;
- avoid promiscuous sexual intercourse;
- monitor the hygiene of the genitals;

- use contraception during intimacy with a new sexual partner;
- do not abuse the use of tampons, it is better to use pads.
Timely detection of the disease makes it possible to stop it only with the help of a conservative treatment method, without resorting to more radical measures.
Treatment methods
Treatment of the chronic form of metroendometritis is carried out at home, but strictly following the recommendations and prescriptions of the gynecologist. First of all, patients need bed rest and rest. The therapy is carried out in a complex manner using dosage forms and traditional medicine.
Medications
Chronic metroendometritis is a disease usually caused by a bacterial infection, therefore it is very important before the purpose of identifying the type of pathogen and determining its sensitivity to drugs of the antimicrobial group. The duration of the course of drug treatment is on average 10 to 14 days.
The therapy is developed individually for each patient, taking into account the diagnostic results. To remove toxic organisms from the uterine cavity, douching with antiseptic solutions is prescribed, and vitamin therapy is performed to increase the immune forces.
Conservative therapy for chronic metroendometritis:

| Group and name of the drug | Description |
| Antimicrobial agents of semi-synthetic penicillins (Ampicillin) | Broad-spectrum antibiotic. It actively affects most of the pathogens, destroying their DNA chain. |
| Cephalosporins in combination with Metronidazole | Systemic drugs and vaginal suppositories may be prescribed. After the course of treatment, a repeated smear analysis is required to determine the effectiveness of the therapy. |
| Hormonal agents (Duphaston) | The drug improves the condition of the endometrium, is an analogue of the hormone progesterone (a hormone produced by the ovaries). Such a tactic allows you to prepare the body for future conception, and with an existing pregnancy, to bear the fetus for the entire gestational period. In addition, with metroendometritis, it restores the thickness of the endometrium. |
| Antispasmodics (No-shpa, Drotaverin) | Easily eliminate pain that appears in the lower abdomen, in the region of the sacrum and lower back. |
| Sorbents (Enterosgel, Activated carbon) | Appointed with pronounced signs of intoxication. Actively remove toxic substances from the body. |
If, after the course of therapy, the patient does not feel relief and, at the same time, signs of septic complications are determined, she needs hospitalization. After carrying out a number of diagnostic procedures, the patient will be prescribed surgical treatment, sometimes the need for resection of the affected areas of the uterus is determined.
Traditional methods
Treatment of metroendometritis is possible with the use of traditional medicine. In the formulation of medicines, herbs and plants are used, which have antiseptic, regenerating and anti-inflammatory properties. They are used to prepare infusions and decoctions for douching and ingestion.
Traditional medicine recipes for the treatment of metroendometritis:
| Means | Recipe | Application |
| Tincture of calendula | 1 hour l. pharmacy tincture of calendula is diluted in 0.5 liters of boiled water. | Douching tincture has an antiseptic and regenerating effect. The procedure is carried out in the morning and in the evening. The course of treatment is 2 weeks. |
| Plantain decoction | 1 tbsp. l. dry leaves of the plant are poured with 250 ml of warm water. All this is put on fire and brought to a boil. It is infused for 30-40 minutes, filtered. | Plantain has anti-inflammatory and hemostatic effects. The medicine is taken orally in 1-2 tbsp. l. three times a day. The course of therapy is from 7 to 14 days. |
| St. John's wort | 2 tbsp. l. dry plants are poured with 0.5 liters of warm water, and sent to the stove. The medicine is brought to a boil and infused for 30-40 minutes, after which it is filtered. | The product has antibacterial properties. Can be used for oral administration, or for douching. Orally the medicine is taken 3 times a day for 3 tbsp. l. The course of admission is 7-10 days. |
| Linden inflorescences and chamomile flowers | Take 2 parts of linden inflorescence and 3 parts of chamomile flowers, combine. 4 tbsp are taken from the received raw materials. l. and pour 1 glass of boiling water. The product is infused for 2 hours, after which it is filtered. | The medicine has an antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effect. It is used for douching. The course of therapy is 7-10 days. |
| Willow bark and linden inflorescences | Take 2 parts of a lime inflorescence and 3 parts of willow bark, combine and mix. Take 4 hours. l. raw materials, pour 1 glass of boiling water and insist for an hour, then filter. | The product has anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties. Used for douching. The course of treatment is 7-10 days. |
Before using any alternative medicine, you should consult with your doctor and test for an allergic reaction.
Other methods
In addition to conservative therapy and folk remedies for the treatment of metroendometritis, other methods are also used. Compresses with ice very well relieves swelling and inflammation. Crushed ice is poured into a heating pad, which is applied to the lower abdomen. A towel must be placed under the heating pad, since without it you can get frostbite of the skin.
The following foods can increase estrogen levels:
- cabbage;
- apples;
- garlic;
- Cherry;
- nuts;
- milk products;
- legumes;
- dates.
Note that the level of the female hormone increases high-quality beer, because it is made on the basis of hops. Modern pharmacists extract useful phytoestrogens from this substance and produce medicines on their basis. One of these drugs is Menomax, which in a short time increases the level of estrogen and normalizes hormones.
The need for surgical treatment is determined if there are remnants of the placenta or ovum in the uterus. Also, with various neoplasms that impede the exit of female secretions from the genital organ.
Possible complications
Metroendometritis poses a serious threat to women who are about to become a mother. The inflammatory process in the uterus often leads to the formation of adhesions, and they, in turn, become an obstacle to the attachment of the fetus.
Also, the disease can lead to such complications:
- miscarriages - prolonged inflammation provokes the development of uterine dystrophy;
- cystitis - the pathogenic microflora present in the inflamed uterus rapidly spreads to neighboring organs;
- hormonal imbalance - inflammation disrupts the general hormonal background, lowers the level of estrogen;
- decrease in the quality of intimate life - with inflammation, pain often occurs during intimate contact;
- psychological disorders - the appearance of periodic pain, the presence of odorless discharge lead to constant discomfort and a violation of the psychological state.
If you start treating the problem in a timely manner, possible complications can be avoided. However, if metroendometritis is not treated, it becomes chronic, and this can already cause female infertility. Infectious inflammation develops rapidly and spreads to neighboring organs, so women it is recommended to regularly (once every six months) undergo a gynecologist's examination and diagnose childbearing organs.
Chronic endometritis video
Doctor about chronic endometritis:



