Cervical dystocia of the uterus - This is a congenital or acquired pathology of the tissues of the genital organ, which is characterized by its functional disorders. In most cases, this disease remains undetected until the onset of the active phase of labor.
During contractions, sufficient stimulation of the smooth muscles of the uterus does not occur, which leads to a too slow opening of its cervix, or the complete absence of a lumen in the cervical canal.
At the same time, there is a spasm of the muscles that are responsible for opening the birth canal. Dystocia of the cervix can be caused by pathologies of the tissues of the genital organ or severe diseases of the peripheral nervous system.
In the first case, dysfunctional disorders are caused by structural changes within the cervical canal. With a painful condition of the peripheral nervous system, an inadequate innervation of the muscles responsible for the opening of the uterus occurs at the time of the onset of active labor.
This pathology in gynecological practice is much less common, but in most cases it has an innate nature of origin. The main danger of this disease is that it is detected in the last days of pregnancy, when the time for the birth of the child is already approaching.
Record content:
-
1 Views
- 1.1 Congenital
- 1.2 Acquired
-
2 Degrees
- 2.1 Easy
- 2.2 Average
- 2.3 Heavy
- 3 Symptoms and Signs
- 4 Causes
- 5 Diagnostics
-
6 Treatment methods
- 6.1 Aprofen
- 6.2 No-shpa
- 6.3 Galidor
- 6.4 Cesarean section
- 7 Possible consequences and complications
- 8 Dystocia Videos
Views
Cervical dystocia of the uterus is a gynecological disease of the female reproductive system, which poses a threat to the health of the woman in labor and the child herself. There are 2 main types of this pathology.
Congenital
Dystocia of the cervix of the uterus of congenital etiology is characterized by a violation of the process of development and formation of tissues of the genital organ. In this case, negative changes in the structure of this part of the reproductive system occur even at the stage of the girl's puberty. This type of pathological condition of the musculature of the cervix may have a genetic nature of origin.
In a special risk group are women whose blood relatives had similar health problems, and the resolution of their labor activity was carried out by caesarean section.
Congenital dystocia of the cervix can be detected during the diagnostic examination of the patient, if initially there are signs of significant changes in the structure of the epithelial tissues of the reproductive organ. Women who have cervical dystocia of the uterus caused by a congenital disorder of innervation may not be aware of the presence of this disease.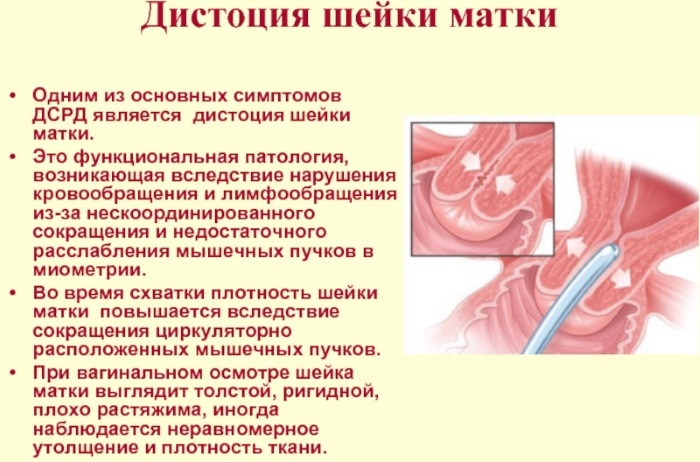
In this case, a gynecological examination does not reveal any signs of pathology. Problems begin directly during labor, when the cervix does not open.
Acquired
Dystocia of the cervix is a disease that also has an acquired nature of origin. This type of pathology is much more common, as it is caused by the negative impact of one or several factors at once. In most cases, acquired cervical dystocia develops against the background of existing diseases of the female reproductive system.
This type of disease can be diagnosed in the early stages of pregnancy or even at the stage of planning the conception of a child. A gynecologist, who detects structural changes in the tissues of the cervix, warns a woman in advance about possible complications during childbirth.
Degrees
Dystocia of the cervix is a pathological condition of the female reproductive system, which is detected with the onset of active labor. Depending on the clinical symptoms that are observed in a pregnant woman, several degrees of severity of this ailment are distinguished.
Easy
Mild cervical dystocia is characterized by the manifestation of not pronounced spasm of the muscles responsible for the opening of the genital organ. During a gynecological examination of a woman in labor, it is established that the increase in the lumen of the walls of the cervical canal is too slow. In this case, there are signs of good labor.
Mild cervical dystocia does not cause significant complications, since ultimately there is a slower, but still full disclosure of the genital organ. At the initial stage of labor, a woman feels a pulling pain in the lower abdomen, which is caused by a spasm of the muscles of the cervix.
Average
Dystocia of the cervix of moderate severity is characterized by a pronounced spasm of the muscle fibers of the cervical canal. A pregnant woman begins to experience intense contractions, pain from which covers the entire lower abdomen, and also spreads to the lumbosacral spine.
A vaginal examination reveals a spasm of the cervix with preservation of slight dynamics to its disclosure. The prognosis for self-resolution of labor becomes unfavorable.
In case of moderate cervical dystocia, the obstetrician-gynecologist decides to use the caesarean section method. In some cases, when labor pains are unstable or not too intense, the doctor may use medication.
Medicines used for moderate cervical dystocia have antispasmodic properties. At this stage of the pathological state of the genital organ, caesarean section can be avoided, but only if medication is used in a timely manner.
Heavy
Severe cervical dystocia is a dangerous pathology of the reproductive system of the female body, which is manifested by the complete absence of signs of disclosure of the genital organ. In this case, labor pains are characterized by increased intensity.

There is a real threat to the preservation of the life of a child who is not able to be born in a physiologically natural way. A pregnant woman experiences severe and sharp pain in the lower abdomen and lumbar spine, which leads to a rapid loss of physical strength.
In this case, an immediate cesarean section is shown, which prevents hypoxia, fetal freezing, and the occurrence of birth trauma.
Symptoms and Signs
Dystocia of the cervix is a painful condition of the female reproductive system, the signs of which are found in its clinical manifestations, as well as the general well-being of the woman in labor.
This pathology is characterized by the following symptoms:
- there are intense contractions that differ in the strength of their manifestation;
- the woman experiences severe spasmodic and pulling pain in the lower abdomen, which spreads to the lumbosacral spine;
- a vaginal examination reveals a spasm of the smooth muscles of the cervix, which is responsible for the expansion of the walls of the cervical canal;
- there is a too slow dilatation of the cervix, the dynamics of which lags far behind the overall intensity of the birth activity (in this regard, the child has been in the womb for too long, which negatively affects the state of his health);
- a decrease in the contractile activity of the muscles of the uterus, which complicates the process of giving birth to a child naturally through the birth canal.
After the obstetrician-gynecologist establishes the clinical symptoms of cervical dystocia, a decision is made on further stimulation of the organs of the reproductive system, or the performance of a cesarean section. Surgery to remove the baby from the uterus as quickly as possible increases the chances of fetal survival.
Causes
There are a large number of factors, the influence of which causes the development of cervical dystocia. Moreover, this pathology can occur in women of various age groups who have not previously suffered from diseases of the internal genital organs.

There are the following main causes of cervical dystocia of the uterus:
- hereditary predisposition to the development of a pathological state of the tissues of the genital organ, when this disease is transmitted through the female line along with genetic information;
- dysfunctional disorders of the nerve endings of the autonomic system, manifested by the lack of full innervation of the smooth muscles of the cervix;
- previously transferred infectious diseases of the internal genital organs, as a result of which degenerative changes occurred in the structure of the tissues of the reproductive system;
- the consequences of severe injuries to the pelvic organs, as a result of which the uterus was damaged;
- postoperative complications that developed as a result of a previous surgical intervention (adhesions, infection of the operated tissue site);
- anatomical disturbances in the development of the uterus, which led to the growth of an excess amount of connective tissue directly inside the cervix of the genital organ;
- too frequent use of abortions, the use of which has led to negative changes in the structure of the tissues of the uterus;
- complications arising after previous diathermoelectrocoagulation of the cervix;
- benign and oncological neoplasms that have developed in the tissues of the genital organ during the intrauterine development of the fetus;
- cicatricial changes on the surface of the cervix arising from the results of previous childbirth, which were difficult and with a large number of complications.
All of the above factors can cause cervical dystocia of the uterus. At the same time, the severity of the pathological state of the genital organ directly depends on how much the structure of the tissues of the cervical canal is changed.
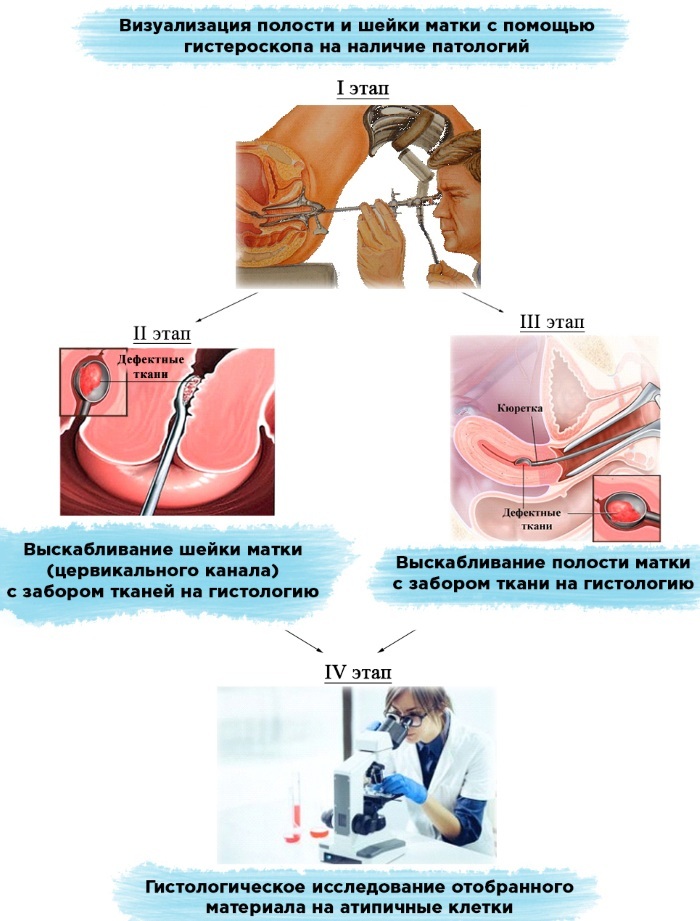
Diagnostics
The potential tendency of a woman to develop cervical dystocia can be detected before pregnancy, or immediately at the beginning of active labor.
The table below shows modern diagnostic methods that are used to determine pathological condition of the tissues of the genital organ before the conception of the child, as well as in the early stages fetal development.
| Examination type | Purpose of diagnostics of a particular type |
| Ultrasound | Ultrasound examination of the organs of the female reproductive system allows you to determine the condition of the tissues of the cervix, as well as detect possible changes in their physiological size. For example, the appearance of scars, overgrowth of fibrous or connective tissue. This type of examination is carried out at the planning stage of the child, as well as in the early stages of his intrauterine development.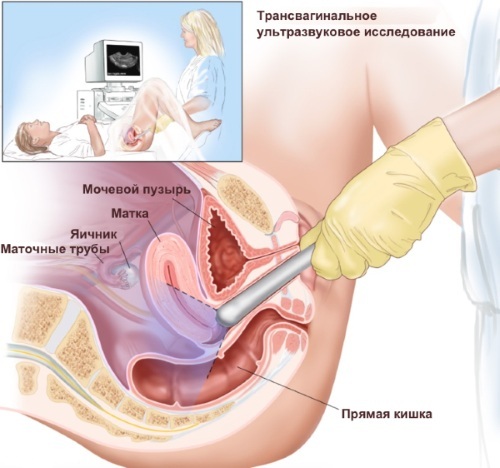
|
| Endoscopy of the cervix | Endoscopic examination of the cervical cavity makes it possible to obtain comprehensive information about the state of the female genital organ. An endoscopic device equipped with a video camera is inserted into the vagina towards the cervical canal. The resulting image is transferred to a computer monitor screen, which is subsequently studied by a doctor. |
| Examination by a gynecologist | The initial examination of the condition of the walls of the cervix begins with an appointment with a gynecologist. This specialist visually determines the possible presence of structural changes in the tissues of this organ of the reproductive system. Based on the results of the examination, a decision is made to conduct a more detailed diagnosis using instrumental and hardware methods, or the doctor does not find any pathologies requiring increased attention. |
| MRI | MRI diagnostics are indicated for women who are planning a pregnancy, but during their initial examination were detected degenerative changes in the structure of the tissues of the cervix, there are suspicions of the presence of tumor neoplasms. This survey method is one of the most informative. |
| Smears of the mucous membrane of the cervix | The selection of smears from the mucous membrane of the cervical canal is used in order to timely detect the possible presence of an inflammatory process of an infectious nature of origin. If the source of bacterial microorganisms is identified, the woman is prescribed a course of therapy with antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs. |
Diagnosis of cervical dystocia in the last stages of pregnancy occurs immediately at the time of onset the birth of a child, when the doctor detects a spasm of the cervix with too slow or incomplete opening of it lumen. In such circumstances, a visual examination by a gynecologist is sufficient.
The average cost of a comprehensive diagnosis of cervical dystocia, which is carried out at the planning stage of a child or in the early stages of fetal development, ranges from 9500 to 12000 rubles.
Treatment methods
Dystocia of the cervix can be eliminated urgently during the onset of the active phase of labor. To ensure the birth of a healthy child without signs of hypoxia, means of drug therapy or a method of surgical intervention can be used.
Aprofen
Aprofen is an effective vasodilator and antispasmodic agent that comes in the form of a white powder. This medication is prescribed to pregnant women with signs of cervical dystocia in order to relax the spasmodic muscles of the genital organ.
The dry powder is added to drinking water, and the resulting solution is taken orally. The dosage is determined individually by the gynecologist based on the severity of the pathology.
No-shpa
No-shpa is a broad-spectrum antispasmodic, the active component of which is drotaverine hydrochloride with a concentration of 20 mg in 1 ml.  For pregnant women with signs of cervical dystocia, this medication is prescribed in a dosage of 40 to 80 mg of the active substance, which is administered intramuscularly. No-shpa is considered a symptomatic therapy drug that does not have a toxic effect on the infant's body.
For pregnant women with signs of cervical dystocia, this medication is prescribed in a dosage of 40 to 80 mg of the active substance, which is administered intramuscularly. No-shpa is considered a symptomatic therapy drug that does not have a toxic effect on the infant's body.
Galidor
Halidor is a myotropic antispasmodic that comes in the form of white tablets with a grayish tinge. Table 1 This medication contains 100 mg of the active substance in the form of bencyclane fumarate. To eliminate the spasm of the smooth muscles of the cervix during the onset of the active phase of labor, a pregnant woman is prescribed a single dose of 1-2 tablets of this drug.
Cesarean section
Surgical operation to remove the child from the uterine cavity by performing a cesarean section is the only one a way to successfully complete labor when cervical dystocia cannot be eliminated with medication therapy. Surgery is performed under the influence of anesthesia.
Possible consequences and complications
The main complication of cervical dystocia is that a woman loses the opportunity to give birth to a child on her own.
Due to the spasm of the walls of the cervix, the lack of sufficient opening of the cervical canal, the baby cannot leave the cavity of the genital organ in order to further move along the birth canal. Therefore, there is a risk of oxygen starvation of the fetus, as well as the onset of death of the child inside the uterus.
Cervical dystocia is a pathological condition of the cervix, which is characterized by a spasm of smooth muscles responsible for the expansion of the lumen of the cervical canal at the beginning of the active phase of labor activities.
This disease of the female reproductive system can be caused by dysfunction of the peripheral nerves, degenerative changes in the structure of uterine tissues, inflammatory processes with a chronic form currents.
To eliminate this pathology, antispasmodic and vasodilating medications are used. In the absence of a positive therapeutic effect, the caesarean section is used.
Dystocia Videos
Doctor about cervical dystocia: