Hypertensive crisis - This is a serious condition in which there is a sharp increase in blood pressure to critical levels (180/120 and above). The condition requires urgent care, as it leads to serious consequences.
Record content:
-
1 Symptoms
- 1.1 1st type
- 1.2 2nd type
-
2 Algorithm of actions step by step
- 2.1 Sit down or lay down the patient
- 2.2 Provide fresh air
- 2.3 Measure blood pressure and pulse
- 2.4 Call an ambulance
- 2.5 Calm the sick person
- 2.6 Remove external stimuli
- 2.7 Give medicines
- 2.8 Traditional methods (in the absence of drugs)
- 2.9 Breath
- 2.10 Provide warmth in the legs
- 2.11 Provide warmth in the body
- 2.12 Provide cold when hot
- 2.13 Observation
- 3 Consequences of failure to provide emergency care
- 4 Hypertensive crisis video
Symptoms
Hypertensive crisis is of 2 types, differing in symptoms, features and severity of manifestations.
1st type
Type 1 hypertensive crisis most often occurs in the early stages of hypertension, manifests itself sharply (for the onset of an attack, several minutes and any stressful situation for the body: physical exertion, emotional stress) and lasts up to 6 hours, it is quickly stopped with the help of medicines.
You can find out 1 type of hypertensive crisis by the following symptoms:
- a sharp headache (mainly in the temples and the back of the head) and dizziness;
- blurred vision, "fog" before the eyes;
- stabbing pain in the sternum;
- trembling in the body;
- feeling of heat and increased sweating;
- feeling anxious;
- the presence of red spots on the face, neck and chest.
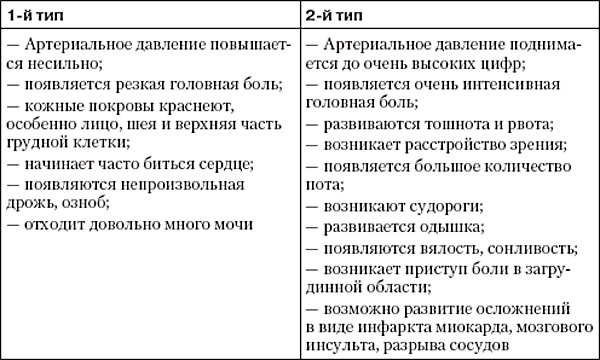
Type 1 hypertensive crisis is also characterized by an increase in heart rate by 30-40 units. and an increase in systolic (upper) pressure by 60-100 units, less often - diastolic (lower) pressure by 30-70 units. This type predominantly occurs in young or middle-aged people.
2nd type
The second type of hypertensive crisis most often occurs in the elderly or patients with prolonged hypertension in severe stages. Development is gradual (from several hours to several days), over a long period (up to 4-5 days). In the second type of crisis, an increase in diastolic pressure is predominantly observed.
The following symptoms also occur:
- headache and dizziness;
- visual and hearing impairment (noise and ringing in the ears);
- pain in the heart of a constricting character;
- tremor, trembling;
- trembling in the body;
- nausea and vomiting;
- feeling of muscle weakness;
- loss of limb sensitivity;
- violation of cardiac conduction;
- state of stunnedness, stupor.
At the beginning of the onset of a crisis, the patient feels a headache, weakness due to a slight increase in pressure. Over the course of several hours or days, the condition worsens due to the continued increase in pressure.
Algorithm of actions step by step
An emergency in a hypertensive crisis should be carried out as quickly as possible and in accordance with the algorithm described below. First aid consists in stopping an acute condition and eliminating some of the symptoms of an attack before the arrival of doctors.
Sit down or lay down the patient
The first thing to do is to provide the patient with complete rest. It is advisable to lay it on a bed or sofa (carefully and without sudden movements) and put it under your head and shoulders pillow (to ensure a half-sitting position), arms and legs should be extended along body.
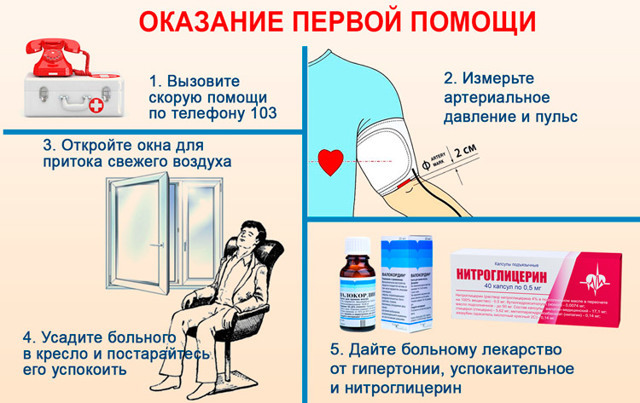
If the attack has developed in the workplace, on the street or in transport, the person should be seated or, if possible, given him a half-recumbent position. In no case should the patient's legs be lifted above the head, as this increases the pressure - the head should be higher than the level of the body and legs.
Also, the patient should not be allowed to move, since changes in body position can provoke changes in the hemodynamics of the body, tachycardia and fainting. In severe cases, a heart attack or stroke is possible.
If the patient has vomiting or nausea, then the patient's head must be turned to the side so that he does not choke on the vomit. To eliminate nausea, you can give the patient water - you should drink it in very small and slow sips.
If a person is alone at home (or indoors) during an attack, then it is necessary immediately after the appearance symptoms of hypertensive crisis open the front door, then sit down or lie down and immediately call an ambulance help.
Provide fresh air
The patient must undo the collar, remove the tie (women should unbutton and remove the bra) so that nothing squeezes the neck and chest. You also need to unfasten the belt and any crushing parts, and remove your shoes and socks. Next, you need to open the window and ensure the flow of fresh air into the room. If possible, you need to lay the patient near the window or as close to it as possible.
Measure blood pressure and pulse
An emergency for a hypertensive crisis is carried out only after measuring the pressure - before that, you should not start first aid, even if there are symptoms of an attack. The measurement algorithms are different, depending on the device.
Algorithm for measuring with an electronic (automatic) tonometer:
- It is necessary to put the cuff on the shoulder (preferably naked), 2 cm above the elbow bend.
- Next, the cuff must be tightened tightly, but not overtightened. The fabric should not hang on or fall off your hand.
- After that, you need to make sure that the patient relaxes and turn on the device.
- The electronic tonometer works in automatic mode, so no additional action is required. After a few seconds, the device will display data on the pressure level (systolic and diastolic), as well as the pulse level.
Algorithm for measuring pressure with a hand-held tonometer:
- It is necessary to put the cuff on the arm in accordance with the requirements described above.
- The head of the phonendoscope should be installed on the area in the ulnar fossa and held with the left hand, and the earplugs of the device should be installed in the ears.
- Next, you need to take the bulb of the device in your right hand, close its valve and begin to quickly squeeze it, pumping air into the cuff and following the movement of the arrow on the tonometer.
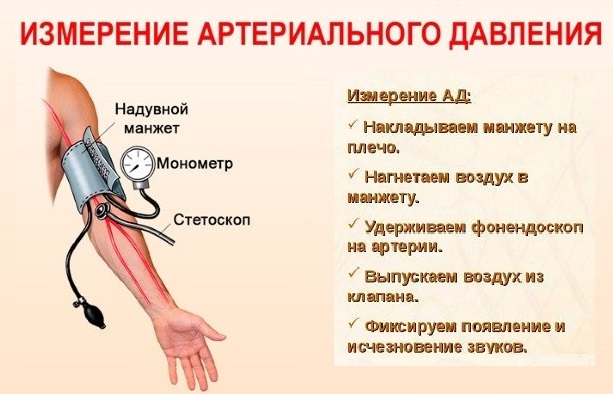
- When the pointer reaches 200 mm. rt. Art. gradually open the valve of the bulb so that the air slowly escapes from it.
- After that, you need to carefully monitor the movement of the arrow on the device, while listening to the pulsation tones in the earplugs. The upper pressure level is the moment the tones appear, the lower pressure level is the moment the tones completely disappear (the last “knock”).
Since it is impossible to count the pulse using a hand-held tonometer, it must be counted in the following way: put 2 fingers (index and medium) to the carotid artery, or on the wrist (bending it slightly) and count the number of strokes in 30 seconds, then multiply the result by 2. You can also count the number of heartbeats at the temples, in the popliteal fossa, in the bend of the elbow.
Algorithm for measuring pressure with a semi-automatic device:
- It is necessary to put on a cuff on the shoulder according to all the rules.
- Next, you need to take a pear in your hand and start squeezing it to pump air.
- When the number on the screen of the device lights up, you need to open the valve of the pear and begin to slowly release air from it.
- The device will automatically calculate both the upper and lower pressure, as well as the pulse and display the results on the screen.
Call an ambulance
After measuring the pressure, you should immediately call an ambulance, even if the patient feels a little better. Doctors will be able to provide the necessary therapy upon arrival and, if necessary (if the patient's condition is unsatisfactory), hospitalize him for further observation and treatment. In uncomplicated type 1 crisis, hospitalization is usually not required.
Calm the sick person
In a hypertensive crisis, the patient is in a state of stress and excitement, and the body begins to produce more adrenaline, which causes vasoconstriction and an additional increase in pressure. Therefore, it is important to calm the patient down in order to reduce the level of stress, as well as eliminate the high tone of the muscles and blood vessels (due to which the pressure also increases).
It is necessary to clearly explain to the person that the attack will go away faster if you calm down and relax. If the patient is unable to calm down on his own, you can give him a diluted tincture of valerian or motherwort.
Additionally, as a first aid, you can do a light massage of the head, earlobes and neck with the collar zone. Massage movements should be very light - this will help eliminate muscle and vascular spasm.
Remove external stimuli
If possible, you need to turn down the lighting (natural and artificial) in the room as much as possible, to ensure silence. External factors indirectly affect the patient's condition and can aggravate the course of the crisis and cause an increase in symptoms. There should not be a lot of people in the room - only the patient and the person providing first aid (there can be 2 of them, but no more).
Give medicines
An emergency in a hypertensive crisis does not provide for the intake of drugs to reduce pressure, which the patient takes on an ongoing basis (course). They exert their effect only when their active substances accumulate in the body, therefore it is pointless to give them.
In case of a hypertensive crisis, it is required to give the patient one of the following drugs, which have an emergency effect and reduce pressure within a few minutes:
| Drug name | Dosage |
| "Captopril" | 1 tablet once |
| "Kapoten" | 1 tablet once |
| "Captopres" | 1 tablet once |
| "Cordaflex" | 1 tablet once |
| "Nifedipine" | 1 tablet once |
| "Corinfar" | 1 tablet once |
After taking the pill, patients need to note the time - 30 minutes. If during this time the doctors do not come and the pressure does not drop by 20-30 units, then you need to give the person 1 more pill. However, it is contraindicated to give more than 2 tablets, as this can cause collapse - a sharp drop in pressure, dangerous by a deterioration in blood circulation in the organs.
It is important to ensure a smooth process of pressure reduction - in the first hour it should decrease by no more than 25%. A decrease to normal values should occur within 2-6 hours. (with the 1st type of hypertensive crisis). With the 2nd type of attack, a decrease in pressure occurs within several days and is monitored by a doctor in a hospital.
If pain in the heart area appears (they can be transmitted to the shoulder and scapula), it is required to give the patient nitroglycerin. It improves blood circulation in the heart muscle, relieves pain and prevents the development of a heart attack. The drugs "Carvedilol" and "Anaprilin" will also help - they have a complex effect, reducing blood pressure and relieving heart pain.
If a hypertensive crisis is accompanied by edema on the face (most often this is typical for type 2), the patient should be given pill "Furosemide" is a diuretic that removes excess fluid from the body, eliminates edema and reduces pressure. If the patient is already using "Furosemide" in the form of injections, then the usual dosage can be administered to him.
Traditional methods (in the absence of drugs)
If it is not possible to give the patient pills to reduce blood pressure, then you can use some alternative methods. Recipe number 1: you need 1 tsp. l. dried mint and 200 ml of hot water.
Cooking process:
- Mint leaves need to be poured with water.
- Next, the product should be infused for 3-5 minutes, then strain and dilute until warm.
- Give the infusion to the patient to drink in slow sips.
Mint infusion will help reduce blood pressure by 15-20 units. Warm drink promotes vasodilation, calming.
Recipe number 2: it is necessary to dissolve 1 tbsp in 1 glass of mineral water (without gas). l. honey and ½ tbsp. l. lemon juice, give the patient a drink in slow small sips.
Breath
It is necessary to ensure that the patient breathes evenly and deeply (if possible), but slowly, in order to normalize the pulse and prevent pressure surges. Breathing should not be fast, intermittent and shallow - this causes tachycardia, pressure surges, heart pains.
Provide warmth in the legs
A warm foot bath stimulates blood flow to the lower extremities and reduces the high pressure load on the organs. If the patient is sitting, then his legs should be dipped in a container (basin, saucepan, bucket) with slightly hot water.
If the patient is lying down and unable to stand up, a towel or napkins soaked in mildly hot water can be used. (needs to be re-wetted every 2-3 minutes)., or a warm (but not hot) heating pad (it should be applied to the back surface shins).
Provide warmth in the body
If the patient has chills, then you need to provide him with warmth by any means - wrap him in a blanket, give a heating pad, put a heater next to him. But the heat should not be too strong, as otherwise it will increase the pressure even more.
Chills in a patient must be eliminated, since in this state a person has a spasm of muscles and blood vessels and an increase in pressure.
Provide cold when hot
If the patient is hot, there is increased sweating, then a towel soaked in cold (but not too much) water should be applied to his forehead. You should also moisten your chest and ankles with cool water and wipe them periodically.
Observation
Immediately after completing all the actions, you need to monitor the patient's condition, every 3-5 minutes. taking a pressure measurement. Measurement data should be recorded with a time stamp, so that they can then be presented to the emergency doctor to assess the severity and dynamics of the attack.
An ambulance for a hypertensive crisis will help save a person from the consequences of an attack and even death. Therefore, it is important to constantly be near the patient and monitor his condition, as well as the manifestation of symptoms.
Consequences of failure to provide emergency care
If you do not provide assistance to the patient in time, the following consequences are possible:
-
Brain disorders. Due to high blood pressure, blood circulation in the brain is impaired, the risk of hemorrhage, stroke, cerebral edema and serious disorders of the central nervous system increases. Paralysis, decreased cognitive abilities (attention and memory), impairment of hearing and vision are also possible.
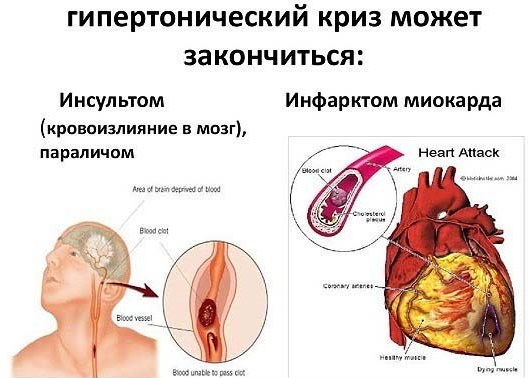
- Cardiopulmonary disorders. As a result of a strong increase in pressure, a violation of the heart rhythm occurs, arrhythmias or tachycardia develop, and pain in the heart appears. The risk of heart attack increases. In severe cases, cardiac asthma develops due to weakening of the work of the heart muscle and stagnation of blood in the pulmonary circulation. Against the background of cardiac asthma, pulmonary edema develops.
- Vascular disorders. High intravascular pressure increases the risk of rupture of blood vessels. The elasticity of blood vessels decreases, they become less strong, which increases the likelihood of atherosclerosis and thrombosis. Also, a decrease in the elasticity of blood vessels is fraught with internal hemorrhages.
- Disorders of the kidneys. A hypertensive crisis also affects the kidneys - it causes acute renal failure, which can later develop into chronic or fatal.
A hypertensive crisis is a very dangerous condition, the consequences of which can be avoided with timely first aid. It is important to strictly follow the algorithm of actions and not leave the patient.
Hypertensive crisis video
Malysheva on how to help yourself with a hypertensive crisis:



