AV block 1, 2, 3, 4 degrees are characterized by a violation of the process of transmission of electrical impulses from the atria to the ventricles. Deviations will be visible on the ECG tape. Pathology requires drug treatment: drugs are prescribed depending on the symptom complex and the stage of the blockade.
Record content:
- 1 What is AV block, causes of the disease
-
2 AV block symptoms
- 2.1 Intra atrial block
- 2.2 Intraventricular block
- 3 Pathogenesis of AV block
-
4 Classification and stages of development of AV block
- 4.1 1st degree AV block
- 4.2 2nd degree AV block
- 4.3 III degree AV block (complete AV block)
- 4.4 IV degree AV block (terminal)
- 4.5 Frederick's syndrome
- 4.6 Morgagni-Adams-Stokes syndrome
- 5 Complications of AV block
-
6 Diagnosis of AV block
- 6.1 ECG
- 6.2 Laboratory research
- 7 Differential diagnosis
- 8 AV block treatment
- 9 Forecast
- 10 Video: AV block
What is AV block, causes of the disease
Atrioventricular blocks are accompanied by complete cessation or slowing down of the passage of electrical impulses
. The defeat affects the bundles of His (legs) and AV nodes. The manifestation of symptoms directly depends on the type of violation. Pathology occurs in 15-18% of patients with cardiac diseases.The atrioventricular node, as part of the conduction system, ensures correct and consistent contraction of the ventricles and atria. Impulses travel from the sinus node to the AV node, which allows the atria to contract in an optimal manner and ensure blood flow to the ventricles. When the interval is lengthened, the rhythm of myocardial contraction is disrupted.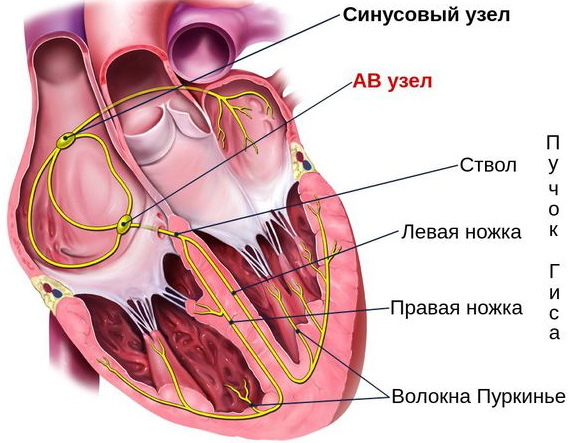
Conventionally, AV blockade is divided into organic and functional. The latter type is found in physically strong girls and men who do not abuse alcohol and tobacco. Most often, blockade II and I degree can develop during sleep. Isolated cases are caused by a short-term increase in the activity of the vagus nerve.
Pathology of the cardiac (organic) type occurs due to the progression of a number of diseases:
- tumors;
- hemochromatosis;
- sarcoidosis;
- amyloidosis;
- myocarditis of diphtheria, thyrotoxic, autoimmune genesis;
- connective tissue pathology;
- myxedema;
- cardiomyopathy;
- heart disease;
- heart attack;
- syphilitic organ damage;
- cardiosclerosis;
- rheumatic processes in the myocardium.
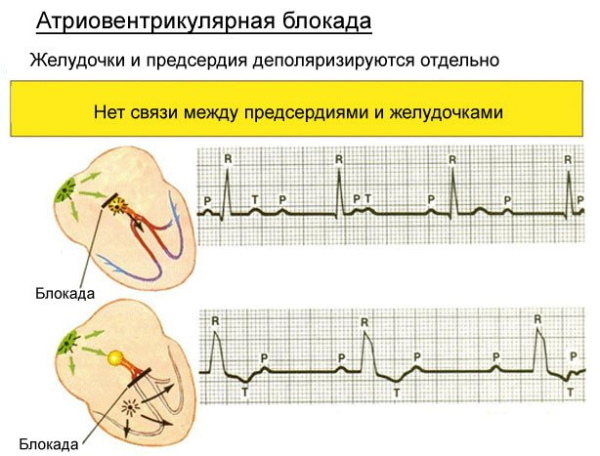
Atrioventricular block can occur after surgery:
- catheterization of the departments (most often the right) of the heart;
- RFA of the heart;
- surgical intervention for congenital heart defects;
- aortic valve replacement.
In cardiological practice, atrioventricular block of the congenital type occurs in 0.2% of patients. Some parts of the conducting system are absent in humans.
The main reasons for the development of pathology can be considered intoxication of the body caused by prolonged use of calcium channel blockers, beta-blockers and glycosides. Lithium salt preparations can provoke a lengthening of the interval.
AV block symptoms
Symptom complex of atrioventricular blockade directly depends on the presence and severity of diseases, concomitant pathology, etiology, degree and level of damage. Sometimes a blockade that develops in the AV node is asymptomatic.
Patients may experience:
- angina pectoris;
- dyspnea;
- weakness.
The pathology is accompanied by a decrease in the speed of cerebral blood flow, so the patient complains of fainting, confusion and severe dizziness. Blockade 3 degrees can be accompanied by an attack of Morgagni-Adams-Stokes.
Intra atrial block
Grade 1 atrial block is usually asymptomatic. As the pathology develops, patients complain of fainting, weakness, dizziness and fatigue. The condition is extremely dangerous for the patient - a severe course of the disease can end in the death of the patient.
Intraventricular block
With intraventricular blockade, the branches and legs of the PSS are affected.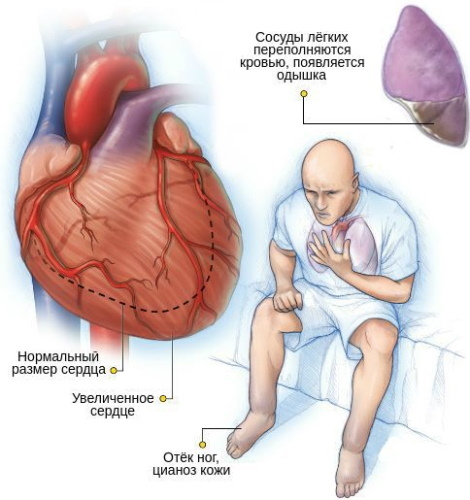
There are several main forms of the disease, the symptoms of which may vary:
- His bundle block. The wave of excitement is interrupted in one of the legs. The patient feels weak, complains of pain in the region of the heart and confusion.
- Blockade of peripheral branches. Against the background of pathology, blood circulation is disturbed. Typical symptoms of a blockage include increased heart rate, discomfort in the left side of the chest, dizziness, and weakness.
- WPW syndrome. Most often, an attack occurs during a night's sleep. Heart rate may increase while maintaining rhythm.
The disease can be manifested by headache, chest pain and shortness of breath.
Pathogenesis of AV block
The first wave impulse is generated by the sinus node. It is located in the right atrium. The node operates autonomously. The pulse frequency varies between 65-80 beats / min. The conducting system, as the main coordinator, transfers the first impulse to the AV node. In it, the impulse is briefly delayed and goes to the bundle of His.
The conductive system is responsible for coordinating the process of transmitting an electrical impulse. If the sinus node loses its ability to independently generate impulses, then the AV node begins to generate.
With blockade, the heart rate is significantly reduced. Dizziness and weakness occur when your heart rate drops and your blood circulation slows down. Most often, AB blockade is functional.
Full or partial loss of impulses can be considered a complication after myocardial diseases. AV blockade of the hereditary type is caused by the penetration of polysaccharide, protein and lipid complexes into the cells of the myocardium.
Classification and stages of development of AV block
Pathology is classified according to the type of course:
- Chronic. The form is quite common, the disease is usually asymptomatic. The risk of death with adequate treatment is minimal. The patient should regularly visit a doctor who is obliged to monitor the patient's condition. Depending on the severity of the pathology, drug therapy or surgery is prescribed.
- Sharp. The most severe form of pathology that arose under the influence of external factors (trauma, cardiac diseases). Symptomokoplex can vary depending on the age and gender of the patient. The attack occurs suddenly, if care is not provided, the risk of death of the patient is high. Treatment is carried out in a hospital setting.

Classification by the degree of damage:
- Partial blockade. The condition, with adequate treatment, does not pose a threat to the patient's life. The attack may be intermittent.
- Complete blockade. In this case, the impulse is not transmitted from the atrium to the ventricle. The risk of developing a coma is high. The condition is urgent, the patient must be immediately taken to the intensive care unit. Death occurs with cardiac arrest.
Classification by seizure duration:
- Paroxysmal blockade. The attack lasts several hours and is intermittent.
- Transient (transient) blockade. An episode can last for days or weeks.
- Permanent (regular) blockade. The attack does not go away on its own, the intervention of specialists is required.
Pathology is also classified by severity. There are 4 stages.
1st degree AV block
AV block I degree on the ECG is characterized by a slight lengthening of the interval. The reasons for the development of a mild form of pathology are considered diseases of the heart and blood vessels. In children, the disease can occur at the stage of formation in the womb if a woman has had systemic lupus erythematosus. Signs of manifestation are subjective, pathology may be asymptomatic.
The disease can only be diagnosed during a detailed examination of the patient. Mild AV block is characterized by an increase in the interval by 0.1-0.2 sec. The patient must regularly visit the doctor, the observation is carried out dynamically. Recovery lasts up to 12 months. The patient should systematically take medications prescribed by the cardiologist.
2nd degree AV block
AV block II degree on the ECG occurs in people with heart disease.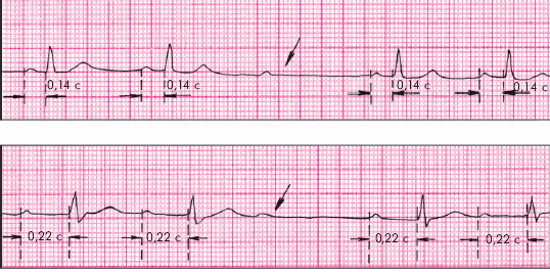
Pathology can be divided into 2 types (depending on the results of the cardiogram):
- Mobitz 1 (blockade 2 degree). The PQ interval lengthens gradually. The process is cyclical. Elongation occurs before the QRS complex collapses. The symptom complex is poorly expressed, signs of manifestation occur when the body is overloaded. The disease can only be detected by diagnostic means. Mobitz 1 is observed in people with ischemic heart disease and vegetative dystonia. Patients recover quickly with adequate treatment. Taking medication is required.
- Mobitz 2. Ventricular complexes fall out, the 2nd, 3rd, 4th impulses reach the node. Pathology in this case is classified as "AV block 2: 1, 3: 1 and 4: 1". P waves are visible on the ECG tape, the QPS complex is visible after 2-3 waves. Rhythm disturbance occurs in people with organic heart disease. The symptom complex is pronounced, patients periodically complain of confusion, dizziness, headache (irradiation to the back of the head).
Mobitz 2 is characterized by spontaneous prolapse of the ventricular complex.
III degree AV block (complete AV block)
Grade III AV block on the ECG may indicate myocarditis. The severe form of the disease is characterized by a complete cessation of the transmission of impulses from the atrium to the ventricles. The heart rate drops to 40 beats / min. The ventricles generate impulses on their own. Deviations from the norm are expressed.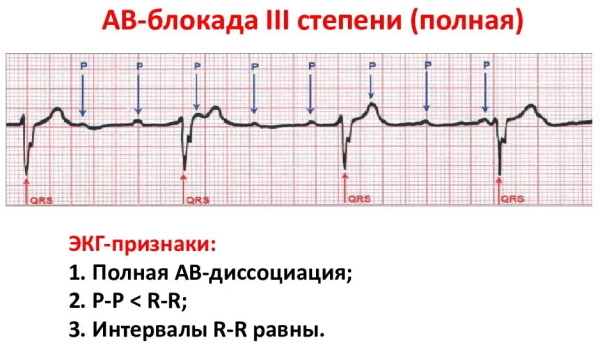
The characteristic symptoms of pathology are considered:
- severe dizziness;
- loss of consciousness;
- rapid fatigue;
- pain in the left side of the chest;
- shortness of breath.
With AV block, the heart rate may drop to 20-25 bpm. Oxygen ceases to flow to the brain, the patient loses consciousness.
IV degree AV block (terminal)
IV degree AV block on the ECG is quite rare. The patient has characteristic signs of heart failure, the pulse decreases to 30-35 beats / min. Against the background of an increase in the contractile activity of the ventricles, the formation of separate foci of excitation occurs.
With terminal blockade, the risk of developing ventricular extrasystole is high. There are several types of the disease. Pathology is characterized by cardiac arrhythmias: the ventricles begin to contract chaotically.
The main signs of the development of extrasystole are considered:
- frequent fainting;
- angular pain;
- asthma attacks;
- weakness;
- prolonged migraine;
- dizziness;
- chest pain.
In the absence of adequate treatment, the risk of death is high. The patient is monitored regularly. Most often, patients are prescribed an operation, during which a pacemaker is sewn in.
Frederick's syndrome
Frederick's syndrome is a life-threatening condition characterized by blockage of the AV node and atrial fibrillation. The disease is accompanied by disturbances in rhythm and conduction. Pathology is caused by a number of cardiac diseases.
These include:
-
Ischemic heart disease. The disease occurs against the background of rest angina and unstable angina. The processes occurring in the myocardium disrupt the transmission of impulses from the atrium to the ventricles.
- Myocardial infarction. Frederick's syndrome can occur against the background of necrosis and fibrosis. In the subacute and acute preinfarction period, the vagal influence increases.
- Non-coronary diseases. Frederick's syndrome occurs due to cardiomyopathy, autoimmune, thyrotoxic myocarditis. If a large volume of the heart muscle is damaged, there is a high risk of developing inflammatory processes, which leads to sclerosis and fibrosis.
- Medicinal intoxication. With a systematic self-increase in the daily dose of medications that can reduce the heart rate, the risk of arrhythmias and conduction disturbances is high. Glycosides, calcium channel blockers, lithium salt preparations and beta-blockers can contribute to the development of Frederick's syndrome.
The characteristic symptoms of pathology include:
- dizziness;
- shortness of breath;
- pain in the left side of the chest;
- nausea.
The patient loses consciousness for 1-2 minutes. After paroxysm, chills, drowsiness and great weakness are observed.
Morgagni-Adams-Stokes syndrome
The Morgagni-Adams-Stokes syndrome is understood as a complex of signs that have arisen against the background of cerebral ischemia and a sharp decrease in the functional activity of the heart.
Predisposing factors include:
- organic congenital changes in the conducting system;
- intoxication with carbon tetrachloride, vinyl chloride, amiodarone, novocainamide;
- changes in the myocardium of a pathological type caused by dystrophy of the atrioventricular and sinoatrial node.
An attack can occur for the following reasons:
- Uncoordinated myocardial contractions. Attacks occur against the background of ventricular fibrillation. Muscles contract with high cleanliness and individually. The release of blood is impossible. The condition leads to clinical death against the background of circulatory arrest. Loss of contractile function occurs with electrolyte imbalance and is often idiopathic in nature.
- Undulating rhythm. An attack can develop with a decrease or increase in heart rate (more than 200 beats / min. or less than 40 beats / min.). Against the background of diffuse vascular lesions, the patient loses consciousness if the pulse drops to 40-50 beats / min. Arrhythmia cannot be considered the cause of an attack.
- Blockades. The most common reason. The blockade occurs against the background of the transition of an atrioventricular incomplete blockade to a complete one. Dissociation occurs between the ventricles and the atria. The latter, under the influence of impulses, are intensely reduced.

There are several main types of the syndrome:
| Syndrome type | Description |
| Mixed | Ventricular and atrial tachycardia alternate with asystole. The attack occurs against the background of a sharp decrease in heart rate. |
| Tachyarrhythmic | Its development is due to an increase in heart rate up to 200-210 beats / min. It occurs against the background of Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome, atrial fibrillation, ventricular fibrillation and sinus tachycardia. |
| Adynamic | The reason for the occurrence is considered to be a decrease in heart rate to 20-30 beats / min. In this case, the patient's sinoatrial node fails and a blockade of 2-3 degrees is observed. With a complete and severe violation of conduction, the risk of cardiac arrest is quite high. |
The seizure takes place in several stages, the patient develops an arrhythmia, he is in a fainting state, which is characterized by:
- pallor;
- disorientation;
- discoordination;
- severe dizziness.
Palpation reveals bradycardia or tachycardia.
The second stage lasts 25-30 seconds. At this time, the blood pressure decreases, the patient loses consciousness. Development of clinical minor seizures is possible. If the patient was not helped on time, then after 3-5 minutes. pulse and respiration disappear, clinical death occurs.
Complications of AV block
Atrioventricular blockade 2-3 degrees pose a danger to human life. In the absence of adequate treatment, there is a high risk of developing complications due to a slowdown in the rhythm.
These include ventricular tachycardia, ectopic arrhythmias, and heart failure. With complete circular blockade, Morgagni-Adams-Stokes attacks may occur, caused by bradycardia and cerebral hypoxia.
Shortly before the seizure, the patient begins to complain of dizziness, weakness, fever in the head. The attack is accompanied by loss of consciousness and cyanosis. First aid consists in performing chest compressions. In the hospital, the patient is connected to mechanical ventilation. With atrioventricular block, cardiogenic shock can develop in people who have had myocardial infarction.
AB blockade is characterized by impaired blood flow. There is a high risk of developing kidney disease, liver disease and cardiovascular failure, accompanied by fainting and collapse.
Diagnosis of AV block
AV block 1, 2, 3, 4 degrees is diagnosed in several ways. The ECG will show the lengthening of the interval of the electrical impulse. A specialist before scheduling an examination should carefully examine and interview the patient.
When collecting anamnesis, the cardiologist asks the patient about hereditary factors, bad habits and tries to determine his lifestyle.
Before the examination, you need to measure the blood pressure: if the process is started and the patient develops a 2 or 3 degree of blockade, then there are jumps in blood pressure.
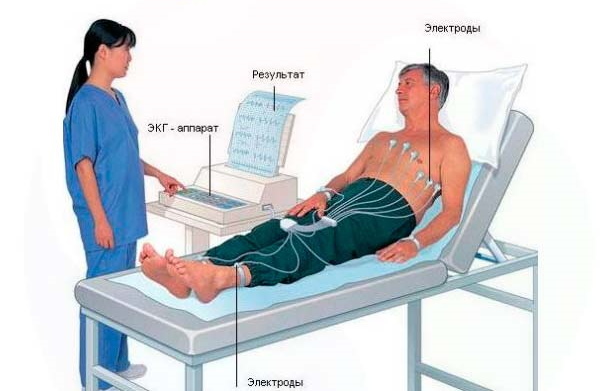
ECG
Before carrying out the procedure, the specialist must fill out the journal and enter all the patient's data into it. The patient exposes the chest, shins and wrists and lies down on the couch. Before installing the electrodes, the skin must be degreased with an alcohol wipe. A gel is applied to the sensors to improve contact.
After receiving the ECG tape, the terminals are removed, the skin is wiped from the gel. During the procedure, experts do not recommend the patient to talk and be nervous. The patient does not feel any discomfort, the examination lasts up to 15 minutes.
With atrioventricular block, the following deviations from the norm are possible:
- Decreased heart rate. Bradycardia can have different severity (depending on the stage of the formation of the pathological process).
- Symmetrical, alternating or complete loss of heart contractions. In this case, the lower chambers of the organ cease to function.
- Elongation PQ (Mobitz 1). Ventricular complexes change their frequency.
- Increase in the QT interval by 0.2-0.21 sec. This indicates the development of a mild form of atrioventricular block.
The blockade on the ECG tape is displayed specifically, so it is quite easy to diagnose the problem.
Laboratory research
In addition to the ECG, the patient can be assigned the following examinations:
- Holter monitoring. The method is considered quite effective and informative. Blood pressure and heart rate are assessed every 30-35 minutes. To obtain a more accurate result, the procedure can be carried out several times.
-
EFI. The procedure is considered analogous to electrocardiography. The modified version is invasive. A puncture is made in the femoral artery and a probe is inserted into it, which makes it possible to assess the activity of most cardiac structures. The examination is quite difficult, but informative, especially with blockages of the 3rd degree.
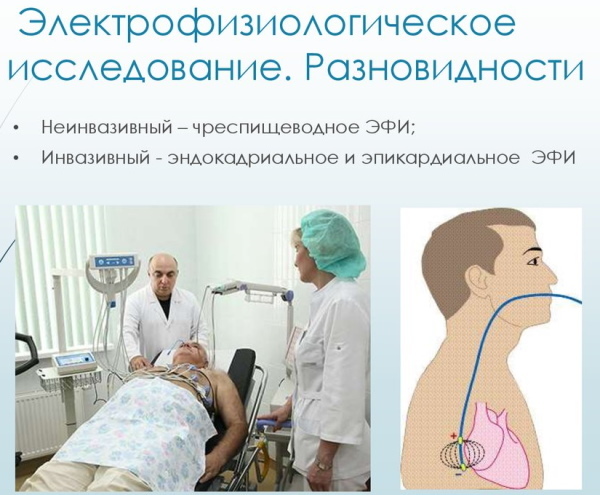
The patient is obliged to pass a blood test (biochemical, general and hormone). This allows you to comprehensively assess the state of the endocrine, nervous and cardiovascular systems. If necessary, a cardiologist can prescribe a radioisotope study, coronary angiography, MRI and computed tomography.
Differential diagnosis
Differential forecast:
- Atrioventricular dissociation. The rhythm of ventricular contraction increases in comparison with the frequency of atrial contraction.
- Atrial blocked extrasystole. Unlike blockade of the 2nd degree, there is no regularity between the loss of the QRS complex and the shortening of the P-P interval. P-waves change shape. Subsequently, there is a prolapse of the ventricular complex.
- Slip rhythm. There are teeth on the ECG, their frequency is increased. Complete blockade differs from the escape rhythm in the greater frequency of QRS complexes.
The blockade of the 2nd degree is also characterized by the loss of the QRS complex.
AV block treatment
1st degree atrioventricular block does not require specific treatment. Specialists must monitor the patient dynamically. If conduction disturbances were caused by prolonged use of antiarrhythmic drugs or glycosides, it is necessary to adjust their dose or completely cancel the intake.
With atrioventricular blockade of cardiac origin, which has arisen against the background of cardiosclerosis, myocarditis or myocardial infarction, the patient is prescribed beta-adrenostimulants (Orciprenaline, Isoprenaline).
First aid medications that can stop a Morgagni-Adams-Stokes attack include Isoprenaline (sublingual administration is indicated) and Atropine (subcutaneous or intravenous administration). With congestive heart failure, the patient should take glycosides, vasodilators, and diuretics.
To radical methods of eliminating atrioventricular blockade include the installation of a pacemaker. The device allows you to restore the rhythm and heart rate.
The main indications for surgical intervention include:
- Morgagni-Adams-Stokes attack;
- atrioventricular block of 2-3 degrees;
- congestive heart failure.
The decision to install a pacemaker is made by a cardiac surgeon.
Forecast
With atrioventricular block 2 3 degrees, the prognosis is poor. If the patient does not have a pacemaker inserted, the risk of developing heart failure is quite high. Most often, patients in this category are disabled.
It is necessary during the examination to identify concomitant diseases and to prescribe the patient adequate treatment.. In most cases (up to 90%), with blockages of 4 degrees during an attack, the patient dies.
AV block 1, 2, 3, 4 degrees is accompanied by a violation of the heart rhythm and conduction. On the ECG tape, vibrations of the ventricular complexes are clearly visible. Preventive measures aimed at preventing pathology require the identification and elimination of various etiological factors.
Video: AV block
Heart block - atrioventricular block:



